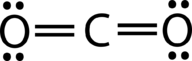分子形状:在中原子上无孤独对等
Section outline
-
How does an electroscope work?
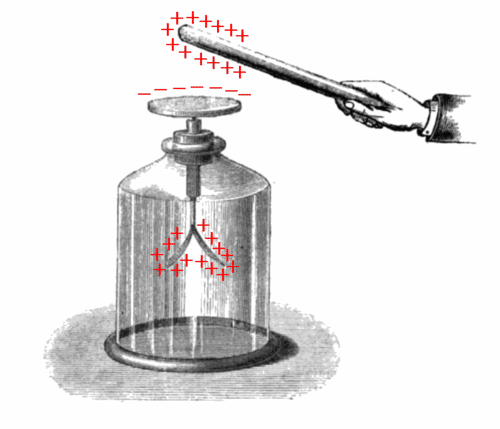
::电子望远镜怎么用?An electroscope is a device used to study charge. When a positively charged object (the rod) nears the upper post, electrons flow to the top of the jar leaving the two gold leaves postivley charged. The leaves repel each other since both hold postive, like charges. The VSEPR theory says that pairs, also a set of like charges, will repel each other such that the shape of the molecule will adjust so that the valence electron-pairs stay as far apart from each other as possible.
::电子望远镜是一种用于研究电荷的装置。 当一个正电荷物体(棒)接近上方柱时, 电子会流到罐子顶部, 离开两颗金色的叶子就会被电荷充电。 叶子会互相反射, 因为两者都有后方, 比如电荷。 VSEPR 理论说, 配对, 也有一些类似电荷, 将会互相反射, 这样分子的形状就会调整, 以便等值电子孔尽可能保持距离 。Central Atom with No Lone Pairs
::中心原子无孤独对等In order to easily understand the types of molecules possible, we will use a simple system to identify the parts of any molecule.
::为了便于理解可能的分子类型,我们将使用一个简单的系统来识别任何分子的部件。A = central in a molecule
::A = 分子中的中枢B = atoms surrounding the central atom
::B = 中心原子周围的原子Subscripts after the B will denote the number of B atoms that are bonded to the central A atom. For example, AB 4 is a molecule with a central atom surrounded by four covalently bonded atoms. Again, it does not matter if those bonds are single, double, or triple bonds.
::B 之后的下标将表示与 A 中原子连接的 B 原子数。 例如, AB4 是一个分子, 其核心原子环绕着四个共价连接的原子。 同样, 这些债券是单一的、双倍的还是三倍的, 也无关紧要 。AB 2 : Beryllium hydride (BeH 2 )
::AB2:氢化(BeH2)Beryllium hydride consists of a central beryllium atom with two single bonds to hydrogen atoms. Recall that it violates the .
::氢化包括一个中央原子,与氢原子有两个单一的链接。H-Be-H
::赫 - 拜 - 赫According to the requirement that electron pairs maximize their distance from one another, the two bonding pairs in the BeH 2 molecules will arrange themselves on directly opposite sides of the central Be atom. The resulting geometry is a linear molecule, shown in the Figure in a “ball and stick” model.
::根据电子对对尽可能扩大彼此距离的要求,BeH2分子中的两对连接对将直接在中Be原子的对面排列。 由此得出的几何学是一个线性分子,在图中以“球棒”模型显示。Beryllium hydride model.
::氢化模型。The bond angle from H-Be-H is 180° because of its linear geometry.
::H-BE-H的联结角为180度,因为其线性几何。Carbon dioxide is another example of a molecule which falls under the AB 2 category. Its Lewis structure consists of double bonds between the central carbon and the oxygen atoms (see Figure ).
::二氧化碳是属于AB2类的一个分子的又一个例子,其刘易斯结构由中央碳与氧原子之间的双重联系组成(见图 )。Carbon dioxide bonding.
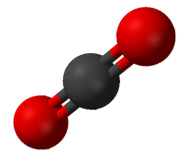
::二氧化碳联结。The repulsion between the two groups of four electrons (two pairs) is no different than the repulsion of the two groups of two electrons (one pair) in the BeH 2 molecule. Carbon dioxide is also linear (see Figure ).
::两组四电子(两对)之间的反射与两组两组双电子(一对)在BeH2分子中的反射无异,二氧化碳也是线性(见图 )。Carbon dioxide.
::二氧化碳。AB 3 : Boron Trifluoride (BF 3 )
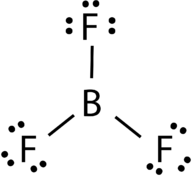
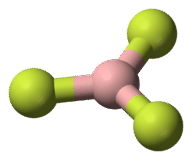
::AB3:三氟化(BF3)Boron trifluoride consists of a central boron atom with three single bonds to fluorine atoms (see Figure ) . The boron atom also has an incomplete octet.
::三氟化物包括一个中子原子,与氟原子有3个单一债券(见图)。Boron trifluoride bonding.
::三氟化物结合。The geometry of the BF 3 molecule is called trigonal planar (see Figure ). The fluorine atoms are positioned at the vertices of an equilateral triangle. The F-B-F angle is 120° and all four atoms lie in the same plane.
::BF3 分子的几何称为三角平面(见图 ) 。 氟原子位于一个等边三角形的顶端。 F- B- F 角度为 120 °, 所有四个原子都位于同一平面上 。Boron trifluoride model.
::三氟化物模型。AB 4 : Methane (CH 4 )
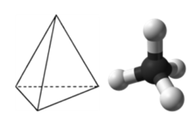
::AB4:甲烷(CH4)Methane is an organic compound that is the primary component of natural . Its structure consists of a central carbon atom with four single bonds to hydrogen atoms (see Figure ). In order to maximize their distance from one another, the four groups of bonding electrons do not lie in the same plane. Instead, each of the hydrogen atoms lies at the corners of a geometrical shape called a tetrahedron. The carbon atom is at the center of the tetrahedron. Each face of a tetrahedron is an equilateral triangle.
::甲烷是一种有机化合物,是自然的主要成分。其结构由中央碳原子组成,与氢原子有四个单一的连接(见图 )。为了最大限度地扩大它们之间的距离,四组连接电子不在同一平面上。相反,每种氢原子都位于称为四面形的几何形状的角。碳原子位于四面体的中心。四面体的每个面部都是一个等边三角形。Tetrahedral structure of methane.
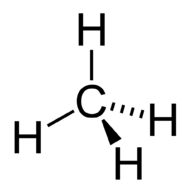
::甲烷的德黑兰结构。The molecular geometry of the methane molecule is tetrahedral (see Figure ). The H-C-H bond angles are 109.5°, which is larger than the 90° that they would be if the molecule was planar. When drawing a structural formula for a molecule such as methane, it is advantageous to be able to indicate the three-dimensional character of its shape. The structural formula below is called a perspective drawing. The dotted line bond is to be visualized as receding into the page, while the solid triangle bond is to be visualized as coming out of the page.
::甲烷分子分子的分子几何是四面形(见图)。 H-C-H 键结角为109.5°,大于分子是平面的90°。当为甲烷这样的分子绘制结构公式时,比较好能够显示其形状的三维特性。下面的结构公式称为角度图。圆点线结角将视像为重新进入页面,而固三角联结则视像从页面中出来。Methane perspective model.
::甲烷视角模型。Summary
::摘要-
Electron pairs repel each other and influence bond angles and molecular shape.
::电子对对互相反射 影响联结角度和分子形状
Review
::回顾-
What are the bond angles in carbon dioxide?
::二氧化碳的联结角度是什么? -
What molecule has bond angles of 109.5
°
?
::哪个分子的联结角度为109.5度? -
What is the geometry of the BF
3
molecule?
::BF3分子的几何形状是什么?
-
Electron pairs repel each other and influence bond angles and molecular shape.