Valence 公债理论
章节大纲
-
What happens next?
::接下来会发生什么?We have seen that the old fish-hook idea of atoms connecting that Democritus liked so much just doesn’t work. Electrons don’t have little hooks on them, but they are the basis for connecting atoms to form molecules. You have learned how to write for molecules and predict their shape using VSEPR theory . Now it is time to apply these abilities to understand how the electrons behave in their atomic when a forms.
::我们已经看到,将民主党如此喜欢的原子连接在一起的旧的鱼钩想法是行不通的。 电子没有小钩子,但它们是将原子连接起来形成分子的基础。 你已经学会了如何用VSEPR理论为分子写作和预测其形状。 现在是时候应用这些能力来理解电子在形式上是如何在原子中表现的了。Valence Bond Theory
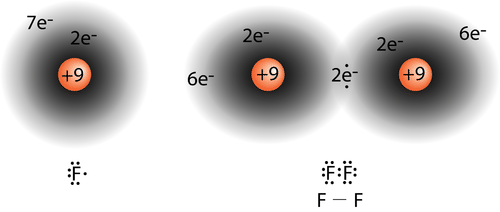
::Valence 公债理论You have learned that a covalent bond forms when the clouds of two atoms overlap with each other. In a simple H 2 molecule, the single electron in each becomes attracted to the nucleus of the other atom in the molecule as the atoms come closer together. An optimum distance, equal to the bond length, is eventually attained, and the potential energy reaches a minimum. A stable, single covalent bond has formed between the two hydrogen atoms. Other covalent bonds form in the same way as unpaired electrons from two atoms “match up” to form the bond. In a fluorine atom, there is an unpaired electron in one of the 2p orbitals. When a F 2 molecule forms, the 2p orbitals from each of the two atoms overlap to produce the F−F covalent bond. The overlapping orbitals do not have to be of the same type. In a molecule of HF, the 1s orbital of the hydrogen atom overlaps with the 2p orbital of the fluorine atom (see Figure ).
::当两个原子的云层相互重叠时,你已经学会了共价连接。在一个简单的H2分子中,随着原子的接近,每个原子中的单电子都被分子中另一个原子的核心吸引。最终达到一个最理想的距离,相当于粘结长度,而潜在的能量达到最小。两个氢原子之间形成了一个稳定、单一的共价连接。其他共价连接形式与两个原子的未处理电子“匹配”形成联系。在一个氟原子中,一个在2p轨道轨道中存在一个未处理的电子。当一个F2分子形式,两个原子的2p轨道重叠产生F-F covalent连接。重叠的轨道关系不一定是同一类型的。在高频分子中,氢原子的1s轨道与氟原子的2p轨道重叠(见图 )。A molecule of hydrogen fluoride (HF).
::氢氟化物(HFF)分子。In essence, any covalent bond results from the overlap of atomic orbitals. This idea forms the basis for a quantum mechanical theory called valence bond (VB) theory. In valence bond theory , the electrons in a molecule are assumed to occupy atomic orbitals of the individual atoms and a bond results from overlap of those orbitals.
::从本质上讲,任何共价联结都源于原子轨道的重叠。这种想法构成了被称为价值联结(VB)理论的量子机械理论的基础。 在价值联结(VB)理论中,分子中的电子假定占据了个别原子的原子轨道,而联结则产生于这些轨道的重叠。Summary
::摘要-
Electrons occupy atomic orbitals.
::电子占据原子轨道。 -
Covalent bonds result from the overlap of atomic orbitals.
::原子轨道重叠造成共价联系。
Review
::回顾-
Where are electrons according to valence bond theory?
::根据价值债券理论,电子在哪里? -
How do covalent bonds form?
::共价债券如何形成? -
Do the orbitals of the two electrons involved in the bond need to be the same?
::连接中涉及的两个电子的轨道是否必须相同?
-
Electrons occupy atomic orbitals.