动动分子理论
章节大纲
-
How much oxygen is in this container?
::这个容器里有多少氧气?Approximately 20% of the atmosphere is oxygen. This is essential for life. In environments where oxygen is in low supply, it can be provided from a tank. Since gases are very compressible, a large amount of oxygen can be stored in a relatively small container. When it is released, the volume expands and the pressure decreases. The gas is then available for breathing under normal pressure.
::大约20%的大气是氧气。 这对生命至关重要。 在氧气供应量低的环境中, 可以从罐体中提供氧气。 由于气体非常压缩, 大量氧气可以储存在相对较小的容器中。 当释放时, 体积会膨胀, 压力会降低。 然后气体可以在正常压力下呼吸 。The Kinetic-Molecular Theory
::动动分子理论The kinetic-molecular theory is a theory that explains the and is based on the idea that matter is composed of tiny particles that are always in motion. The theory helps explain observable properties and behaviors of solids, , and gases . However, the theory is most easily understood as it applies to gases and it is with gases that we will begin our detailed study. The theory applies specifically to a model of a gas called an ideal gas . An ideal gas is an imaginary gas whose behavior perfectly fits all the assumptions of the kinetic-molecular theory. In reality, gases are not ideal, but are very close to being so under most everyday conditions.
::动能分子理论是一个解释这个理论的理论,它基于一个理念,即物质是由始终在运动中的微粒组成的微粒组成。该理论有助于解释固体、固体和气体的可观测特性和行为。然而,该理论最容易理解,因为它适用于气体,而正是气体,我们将开始我们的详细研究。该理论具体适用于一种称为理想气体的气体模型。理想气体是一种假冒气体,其行为完全符合动能分子理论的所有假设。在现实中,气体并不理想,但在大多数日常条件下都非常接近于理想。The kinetic-molecular theory as it applies to gases has five basic assumptions.
::适用于气体的动能分子理论有五个基本假设。-
Gases consist of very large numbers of tiny spherical particles that are far apart from one another compared to their size
. The particles of a gas may be either atoms or molecules. The distance between the particles of a gas is much, much greater than the distances between the particles of a liquid or a solid. Most of the volume of a gas, therefore, is composed of the empty space between the particles. In fact, the volume of the particles themselves is considered to be insignificant compared to the volume of the empty space.
::气体由大量微小球状微粒组成,这些微小球状微粒与其大小相比相去甚远。气体的微粒可以是原子或分子。气体的微粒之间的距离大大大于液体或固体颗粒之间的距离。因此,气体的体积大都由粒子之间的空空空空间组成。事实上,与空空空空间的体积相比,粒子本身的体积被认为是微不足道的。 -
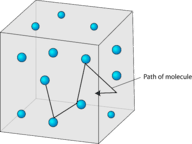
Gas particles are in constant rapid motion in random directions
. The fast motion of gas particles gives them a relatively large amount of
. Recall that kinetic energy is the
energy
that an object possesses because of its motion. The particles of a gas move in straight-line motion until they collide with another particle or with one of the walls of its container.
::气体粒子在随机方向不断快速移动。 气体粒子的快速运动给了它们相对较大的数量 。 回顾动能是物体因其运动而拥有的能量。 气体粒子以直线运动, 直到它们与另一个粒子或与容器的墙壁发生碰撞。 -
Collisions between gas particles and between particles and the container walls are elastic collisions
. An elastic collision is one in which there is no overall loss of kinetic energy. Kinetic energy may be transferred from one particle to another during an elastic collision, but there is no change in the total energy of the colliding particles.
::气体粒子之间和颗粒与容器壁之间的碰撞是弹性碰撞,弹性碰撞是没有全面丧失动能的碰撞,动能在弹性碰撞期间可能从一个粒子转移到另一个粒子,但碰撞粒子的总能量没有变化。 -
There are no forces of attraction or repulsion between gas particles
. Attractive forces are responsible for particles of a
real gas
condensing together to form a liquid. It is assumed that the particles of an ideal gas have no such attractive forces. The motion of each particle is completely independent of the motion of all other particles.
::气体粒子之间没有吸引力或反向力。 吸引力是真实气体凝聚的粒子形成液体的原因。 假设理想气体的粒子没有这种吸引力。 每个粒子的运动完全独立于所有其他粒子的运动。 -
The average kinetic energy of gas particles is dependent upon the
temperature
of the gas.
As the temperature of a sample of gas is increased, the speeds of the particles are increased. This results in an increase in the kinetic energy of the particles. Not all particles of gas in a sample have the same speed and so they do not have the same kinetic energy. The temperature of a gas is proportional to the average kinetic energy of the gas particles.
::气体粒子的平均动能取决于气体的温度。随着气体样本温度的增加,粒子的速度会加快。这导致粒子的动能增加。并非所有样本中的气体粒子都具有同样的速度,因此它们没有同样的动能。气体的温度与气体粒子的平均动能成正比。
Gas particles are in random straight-line motion according to the kinetic-molecular theory. The space between particles is very large compared to the particle size. Summary
::摘要-
Assumptions of the kinetic-molecular theory:
-
Gases consist of very large numbers of tiny spherical particles that are far apart from one another compared to their size.
::气体由大量微小球状微粒组成,与其大小相比,它们彼此相距甚远。 -
Gas particles are in constant rapid motion in random directions.
::气体粒子在随机方向不断快速移动。 -
Collisions between gas particles and between particles and the container walls are elastic collisions.
::气体粒子之间以及颗粒与容器壁之间的碰撞是弹性碰撞。 -
There are no forces of attraction or repulsion between gas particles.
::气体粒子之间没有吸引或击退的力量。 -
The average kinetic energy of gas particles is dependent upon the temperature of the gas.
::气体粒子的平均动能取决于气体的温度。
::动能分子理论的假设:气体由许多微小球粒子组成,这些微球粒子与它们的大小相差甚远。气体粒子在随机方向不断快速移动。气体粒子之间以及颗粒与容器壁之间的碰撞是弹性碰撞。气体粒子之间没有吸引力或反射力。气体粒子的平均动能取决于气体的温度。 -
Gases consist of very large numbers of tiny spherical particles that are far apart from one another compared to their size.
Review
::回顾-
Describe the motion of gas particles in a fixed container.
::描述固定容器中气体粒子的动向。 -
What kind of collisions occur between particles in a gas?
::气体中的粒子之间会发生何种碰撞? -
What is the relationship between the kinetic energy of particles in a gas and the temperature of the gas?
::气体颗粒的动能与气体温度之间的关系是什么?
-
Gases consist of very large numbers of tiny spherical particles that are far apart from one another compared to their size
. The particles of a gas may be either atoms or molecules. The distance between the particles of a gas is much, much greater than the distances between the particles of a liquid or a solid. Most of the volume of a gas, therefore, is composed of the empty space between the particles. In fact, the volume of the particles themselves is considered to be insignificant compared to the volume of the empty space.