内分泌
章节大纲
-
Think about all the processes that need to be controlled. How is it all done?
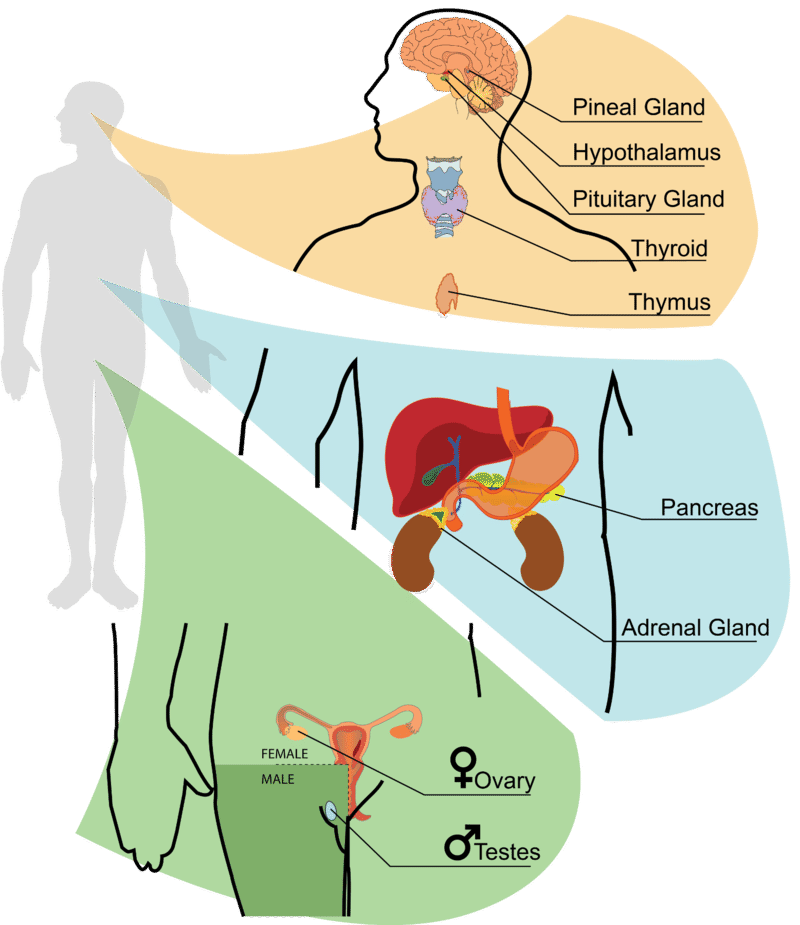
::想想所有需要控制的进程。这一切是如何完成的?This concept just mentions some of the processes controlled by . But, as you can see, they function in different organ systems throughout the body. This complex control takes numerous glands that are also located throughout the body.
::这个概念只是提到一些由 . 控制的过程。 但是, 正如你可以看到的, 它们在整个身体的不同器官系统里运作。 这种复杂的控制需要很多腺, 这些腺也存在于整个身体中。Other Endocrine Glands
::其他内分泌Thyroid and Parathyroid Glands
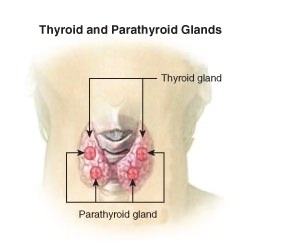
::甲状体和甲甲状腺The thyroid is one of the largest endocrine glands in the body. This butterfly-shaped gland is found in the neck, wrapped around the trachea , as shown in Figure , and is controlled by the hypothalamus and pituitary. The hormones released by the thyroid control how quickly the body uses energy , makes , and how sensitive the body should be to other hormones. Thyroid hormone generally controls the pace of all of the processes in the body; this pace is related to your metabolism . If there is too much thyroid hormone, every function of the body tends to speed up. The thyroid gland regulates body temperature by secreting two hormones that control how quickly the body burns calories . Hyperthyroidism (overactive thyroid) and hypothyroidism (underactive thyroid) are the most common problems of the thyroid gland.
::甲状腺是体内最大的内分泌腺体之一。如图所示,在颈部中发现了蝴蝶状腺,缠绕在气管周围,由下脑和垂体控制。甲状腺控制所释放的荷尔蒙对身体的能量使用速度、制造速度和体体体应对其他荷尔蒙的敏感性如何。甲状腺激素一般控制身体所有过程的步伐;这种速度与你的代谢有关;如果甲状腺激素过多,身体的每个功能都会加速。甲状腺腺调节体温,对两种荷尔蒙进行保密,以控制身体烧热的速度。甲状腺超强和甲状腺下甲状腺是甲状腺最常见的问题。The position of the thyroid and parathyroid glands. A person can have more than four parathyroid glands.
::甲状腺和甲状腺、甲状腺、甲状腺、甲状腺、甲状腺、甲状腺、甲状腺、甲状腺、甲状腺、甲状腺、甲状腺、甲状腺、甲状腺、甲状腺、甲状腺、甲状腺、甲状腺、甲状腺、甲状腺、甲状腺、甲状腺、甲状腺、甲状腺、甲状腺、甲状腺、甲状腺、甲状腺和甲状腺。The thyroid hormones thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3) regulate the rate of metabolism and affect growth and many other systems in the body. As a result, problems with under-secretion or over-secretion of thyroid hormones affect many body systems.
::甲状腺激素甲状腺激素甲状腺素(T4)和三碘二苯胺(T3)调节新陈代谢率,影响身体的生长和许多其他系统,因此甲状腺激素的保密不足或过度保密问题影响到许多身体系统。The element iodine is very important for making both T3 and T4. If a person’s diet does not have enough iodine, their thyroid cannot work properly, and the person develops an iodine deficiency disease called goiter. Low amounts of T3 and T4 in the , due to insufficient levels of iodine, cause the pituitary to secrete large amounts of thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH), which causes abnormal growth of the thyroid gland. The addition of small amounts of iodine to mass produced foods, such as table salt, has helped reduce the occurrence of iodine-deficiency in developed countries. The thyroid also produces the hormone calcitonin, which plays a role in calcium . The hormones secreted by the thyroid are listed in Table .
::碘元素对于制造T3和T4都非常重要。 如果一个人的饮食缺乏足够的碘,他们的甲状腺就无法正常工作,而这个人患上一种被称为甲状腺的缺碘性疾病。 由于碘含量不足,甲状腺3和T4的含量较低,导致大量甲状腺刺激激素(TSH)的疏漏,导致甲状腺腺异常生长。 将少量碘添加到大量生产的食品中,如食盐,有助于减少发达国家缺碘的发病率。甲状腺还产出激素卡西通宁,在钙中发挥作用。 甲状腺隐含的激素在表格中列出。Hormones Secreted by the Thyroid and Parathyroid Glands Location Hormone Target Function Thyroid Triiodothyroine (T3) and Thyroxine (T4)
::三碘多丁(T3)和甲氧基(T4)Calcitonin
::卡尔西托宁Name- Body
- cells
Increase metabolic rate and stimulate mental and physical growth. Increases calcium absorption by bones and lowers blood calcium levels.
::增加代谢率,刺激精神和身体发育,增加骨头吸收钙和降低血钙水平。Parathyroid Parathyroid hormone (PTH) Cells of the bone, , and intestines Regulates blood calcium levels. Parathyroid Glands
::甲虫菊酯The parathyroid glands are usually located behind the thyroid gland, but they are visible in Figure . Parathyroid hormone (PTH) maintains blood calcium levels within a narrow range so that the nervous and muscular systems can work properly. When blood calcium levels drop below a certain point, calcium-sensing receptors in the parathyroid gland release parathyroid hormone (PTH) into the blood. PTH has effects that are opposite to the effects of calcitonin. It increases blood calcium levels by stimulating certain bone cells to break down bone and release calcium. It also increases gastrointestinal calcium absorption by activating vitamin D , and it promotes calcium uptake by the kidneys. The hormones secreted by the parathyroid glands are listed in Table .
::类甲状腺通常位于甲状腺后方,但图中可见。类甲状腺激素(PTH)保持在狭窄范围内的血钙水平,以便神经和肌肉系统能够正常工作。当血钙水平下降到某一点以下时,类甲状腺中的钙感应受体将类甲状腺激素(PTH)释放到血液中。PTH的效果与钙素的效果相反。它通过刺激某些骨细胞破裂和释放钙而增加血钙水平。它也通过激活维生素D而增加胃肠钙的吸收,并且它促进肾脏吸收钙。表内列出了由类甲状腺腺体分解的激素。Pineal Gland
::松果园The hormone melatonin is made in the pea-sized pineal gland , which is located at the base of the brain . Production of melatonin by the pineal gland is under the control of the hypothalamus, which receives information from the retina about the daily patterns of light and darkness. Very little is currently known about the functions of melatonin, but scientists have found that it is involved in sleep cycles (circadian cycles), the onset of , and immune function. Melatonin secretion also responds to seasonal changes in light, which could be a reason why getting out of bed on a dull, rainy morning can be so difficult, as the boy in Figure probably knows.
::荷尔蒙melatonin 是在位于大脑底部的豆状松树腺中制造的。 松树腺生产Melatonin 是在低丘陵的控制之下,它从视网膜中获取有关日光和黑暗模式的信息。 目前对Melatonin的功能知之甚少,但科学家发现它涉及到睡眠周期(环礁循环 ) 、 开始和免疫功能。 Melatonin 分泌也回应了季节性光的变化,这可能是为什么在一个无趣、雨天的早晨从床上出来会变得如此困难的原因,图中的男孩可能知道这一点。Very little is currently known about the role of melatonin, but scientists do know that it is involved in sleep cycles. It is produced by the pineal gland, the retina, and the intestines. Production of melatonin by the pineal gland is influenced by the hypothalamus, which receives information from the retina about the daily patterns of light and darkness.
::目前对梅拉托宁的作用知之甚少,但科学家确实知道它涉及睡眠周期。 它由松树腺、视网膜和肠组成。 松树腺生产梅拉托宁受低丘脑影响,后者从视网膜中获取关于日光和黑暗模式的信息。Pancreas
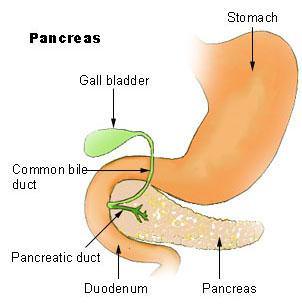
::胰腺The pancreas is both an exocrine gland and an endocrine gland; it secretes pancreatic juice containing digestive and several important hormones. It is located just below and behind the stomach , as shown in Figure . The endocrine cells of the pancreas are grouped together in areas called islets of Langerhans , which are shown in Figure . The islets produce the amino acid-based hormones insulin , glucagon , and somatostatin. Insulin and glucagon are both involved in controlling blood glucose levels. Insulin is produced by beta cells and causes excess blood glucose to be taken up by liver and muscle cells, where it is stored as glycogen, a polysaccharide . Glucagon is produced by alpha cells and stimulates liver cells to break down stores of glycogen into glucose, which is then released into the blood. An alpha cell is another type of endocrine cell that is found within the islets of Langerhans. The hormones secreted by the pancreas are listed in Table .
::如图所示,胰腺的内分泌细胞聚集在称为Langerhans小岛的地区,如图所示。小岛产生氨基酸激素的胰岛素、甘蓝和索马托斯塔丁。胰岛素和甘茄都是控制血糖水平的分泌物。胰岛素和甘茄素是乙型细胞生产的,导致肝脏和肌肉细胞吸收过多的血糖,并储存为甘蓝,一种聚氨酯是一种聚氨酯,由甲型细胞产生,刺激肝细胞将甘油的储存分解成葡萄糖,然后释放到血液中。一种甲型细胞是另一种类型的内分泌细胞,在兰格汉小湾内发现。盘中列出了由丙烯秘密的激素。The location of the pancreas in relation to the stomach and gall bladder. The hormone-producing Islet cells are found in groups throughout the pancreas.
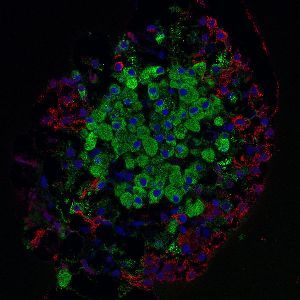
::胰腺与胃和胆囊有关的位置,在全胰腺各处的分组中发现了产生激素的突厥岛细胞。A micrograph of an islet of Langerhans that was isolated from a rat pancreas. Each islet in a human pancreas contains approximately 1,000 cells and is 50 to 500 micrometers in diameter. Cell nuclei are stained blue, insulin-producing beta cells are green, and glucagon-producing alpha cells are red.
::从大鼠胰腺中分离出来的兰格汉斯岛的缩微图。人类胰腺中的每一小岛大约有1,000个细胞,直径为50至500微米。细胞核是染色蓝色的,产生胰岛素的乙型细胞是绿色的,而产生甲型腺的甲型细胞是红色的。Hormones Secreted by the Pancreas Hormone Effects Insulin Glucagon
::Insulin Glucagon 外观Amylin
::艾米林Somatostatin (inhibitory hormone)
::Somatostatain(内生激素)Ghrelin
::格里林Reduces blood glucose concentration. Raises blood glucose concentration.
::降低血糖浓度 提高血糖浓度Suppresses glucagon secretion.
::抑制凝胶分泌Suppresses the release of insulin, glucagon, and pancreatic enzymes.
::抑制胰岛素、甘油和胰岛素酶的释放。Stimulates appetite.
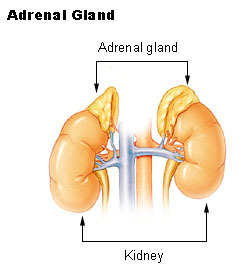
::刺激食欲The location of the adrenal glands above the kidneys.
::肾上腺在肾上腺上方的位置。Adrenal Glands
::肾上腺An adrenal gland is located above each of the kidneys, as shown in Figure . Each adrenal gland is separated into two structures: the adrenal medulla, which is the center of the gland, and the adrenal cortex, which is the outer layer. The medulla and the cortex work as two separate endocrine glands.
::肾上腺位于每个肾上腺上方,如图所示。每一肾上腺分为两个结构:肾上腺中枢和外层肾上皮层。脑下腺和皮下皮上腺作为两个单独的内分泌腺发挥作用。The adrenal medulla is the core of the adrenal gland. Secretion of hormones from the medulla is controlled by the sympathetic . The cells of the medulla are the body's main source of the hormones adrenaline (epinephrine) and noradrenaline (norepinephrine). These hormones are part of the fight-or- flight response that is initiated by the sympathetic nervous system. The hormones boost the supply of oxygen and glucose to the brain and , while suppressing other non-emergency bodily processes such as digestion .
::肾上腺素是肾上腺肿的核心,脑膜激素的分泌由同情者控制。脑膜细胞是体内肾上腺素(肾上腺素)和肾上腺素(肾上腺素)的主要来源。这些激素是同情性神经系统引发的抗争或飞行反应的一部分。荷尔蒙刺激了大脑的氧气和葡萄糖供应,同时抑制了其他非紧急身体过程,如消化。The adrenal cortex is the site of steroid hormone synthesis. Some cells make cortisol, while other cells make androgens such as testosterone . Other cells of the cortex regulate and electrolyte concentrations by secreting aldosterone, which helps to regulate . In contrast to the medulla, which is controlled directly by the nervous system, the cortex is regulated by hormones secreted by the pituitary gland and the hypothalamus.
::肾上腺皮层是类固醇荷尔蒙合成的场所。有些细胞制造皮质素,而其他细胞则制造睾丸酮等激素。皮层的其他细胞通过隔离阿氏酮来调节和电解浓度,这有助于调节。与由神经系统直接控制的梅杜拉相比,皮层受到由垂垂体腺和下丘脑隔离的激素的调节。Cortisol is an important steroid hormone that is often called the "stress hormone" because it is involved in the body's response to stress and in restoring homeostasis after a stressful event such as when (good) stress is caused by running around a soccer field (football pitch for non-American-English speakers), as shown in Figure . Cortisol increases blood pressure, blood sugar levels, and has an immunosuppressive effect. Long-term stress causes prolonged cortisol secretion, hyperglycemia, and weakening of the immune system . Excess levels of cortisol in the blood result in Cushing's syndrome—symptoms of which include rapid weight gain, a round face, excess sweating, and thinning of the skin and mucous membranes.
::Cortisol是一种重要的类固醇激素,通常被称为“紧张激素”,因为它涉及身体对压力的反应和在压力事件之后恢复自闭症,例如(好的)压力是由足球场周围跑动造成的,如图所示(为非美裔英语者提供足球球场),如图所示。Cortisol会增加血压、血糖水平和免疫抑制效应。长期压力造成长期的理醇分泌、高血糖和免疫系统衰弱。骨质激素在血液中造成超量的血压导致Cushing综合症——其症状包括快速体重增加、圆脸、超量出血、皮肤和粘膜变薄。Regular activity through sports is a good way of allowing your body to respond naturally to its stress hormones, which prepare the body for quick movements or prolonged activity.
::通过体育定期活动是使身体能够自然地应对压力激素的好办法,这种激素为身体快速移动或长期活动做好准备。Hormones of the Adrenal Glands Location Hormone Function Adrenal cortex - Mineralcorticoids (such as aldosterone)
- Glucocortocoids (such as cortisol)
- Gonadotropins
- Regulate sodium reabsorption and potassium elimination in the kidneys.
- Depress immune response , provide stress resistance, and help in fat, protein, and metabolism.
- Stimulate the release of sex hormones that develop the sexual characteristics of both males and females.
Adrenal medulla - Epinephrine (adrenaline)
- Norepinephrine (noradrenaline)
- "Fight or flight" hormone, plays a central role in short-term responses to stress, increases heart rate and the supply of blood and oxygen to the brain.
- Increases alertness and has physical effects similar to those caused by epinephrine.
Epinephrine, also called adrenaline, is a “fight or flight” hormone that is released from the adrenal medulla when stimulated by the sympathetic nervous system. Epinephrine plays a central role in short-term stress reactions—the body’s response to threatening, exciting, or environmental stressors such as high noise levels or bright lights. When secreted into the bloodstream, it binds to multiple receptors and has many effects throughout the body. Epinephrine increases heart rate, dilates the pupils, and constricts in the skin and gut while dilating arterioles in leg muscles. It increases blood sugar levels and, at the same time, begins the breakdown of in fat cells. It also “turns down” non-emergency bodily processes such as digestion. Similar to other stress hormones, such as cortisol, epinephrine depresses the immune system.
::肾上腺素也被称为肾上腺素,是一种在有同情心的神经系统刺激下从肾上腺内膜中释放出来的“战斗或飞行”激素。 肾上腺素在短期应激反应中发挥着核心作用 — — 身体对威胁、兴奋或环境压力反应的反应,如高噪音或亮光。 当它被隐藏在血液流中时,它会与多种受体相连,并在整个身体中产生许多影响。 肾上腺素会增加心率,使学生膨胀,皮肤和内脏受限,同时对腿肌肉的动脉进行分泌。 它会增加血糖水平,同时开始在脂肪细胞中进行分解。 它还会“下降”非紧急身体过程,比如消化。 类似其他压力激素,比如皮质素,肾上腺素抑制免疫系统。Stress also releases norepinephrine in the brain. Norepinephrine has similar actions in the body to those of adrenaline, such as increasing blood pressure. Norepinephrine is also psychoactive because it affects alertness, which would be helpful for studying, as shown in Figure . The hormones secreted by the adrenal cortex and medulla are listed in Table .
::肾上腺素与肾上腺素相似,如血压增加; 肾上腺素也具有精神活性,因为它会影响警觉性,如图所示,对研究有帮助。Thinking about an upcoming exam can cause your adrenal glands to produce adrenaline (epinephrine). Your body’s stress response can cause you to feel “stressed out” but can also motivate you to study.
::思考即将到来的考试可能导致你的肾上腺产生肾上腺肾上腺素(肾上腺素 ) 。 你的身体压力反应可以让你感到“紧张 ” , 但也能够激励你学习。Gonads
::戈纳The ovaries of females and the testes of males are the gamete producing organs , or gonads . Ovaries in females are homologous to testes in males. In addition to producing gametes (an exocrine action), the gonads are endocrine glands that produce steroid sex hormones. Sex hormones are responsible for the secondary sex characteristics that develop at puberty. Puberty is the process of physical changes that occur when the sex organs mature and a person becomes capable of reproducing. During puberty, among other changes, males begin producing and females begin menstrual cycles.
::雌性卵巢和雄性睾丸是发芽的器官,或者说鼻腺。雌性卵巢与雄性卵巢是同质的;除产生蛋白质外(排泄作用),甲状腺是产生类固醇性激素的内分泌腺;性荷尔蒙是青春期发育的第二性特征;胚胎是性器官成熟和人能够再生时发生的身体变化过程;青春期期间,除其它变化外,男性开始生产,女性开始月经周期。Luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle stimulating hormone (FSH), which are both secreted by the pituitary gland, are called gonadotropins because they are tropic hormones of the gonads. Recall that tropic hormones trigger the production of hormones in other endocrine glands. The secretion of LH and FSH are, in turn, controlled by gonadotropin-releasing hormone from the hypothalamus. The production of gonadotropin-releasing hormone, in turn, is subject to the estrogen feedback from the gonads.
::液化荷尔蒙(LH)和泡泡刺激激素(FSH)都由垂死腺所隐匿,被称为gonadotropin(gonnads),因为它们是淋病的热带荷尔蒙。回顾热带荷尔蒙会引发其他内分泌腺的荷尔蒙。LH和FSH的分泌反过来又会受到低脑丘下液化激素的分泌控制。制成gonadontropin-releasy 激素反过来又会受到甲状腺的雌激素反馈。In males, LH triggers the production of sex hormones called androgens in the testes. The main androgen produced by the testes is testosterone. Testosterone causes an increase in mass and bone density and is also responsible for the secondary sex characteristics of males such as facial hair, as shown in Figure . The testes also produce small amounts of estrogen in the form of estradiol, which is believed to be important for sperm formation. On average, the human adult male body produces about eight to ten times more testosterone than an adult female body.
::在雄性中,LH引发睾丸中性激素和rogens的产生,睾丸产生的主要阳性激素是睾丸酮,睾丸酮导致质量和骨头密度增加,并造成男性的第二性特征,如面部毛发等,如图所示。睾丸还产生少量雌激素,其形式为雌激素,被认为对精子形成很重要。平均而言,成年男性体内的睾丸酮比成年女性体内的雌激素多8至10倍。Hormones Produced by Gonads Organ Hormone Target Function Ovaries Estrogen Bone cells and cells of sex organs Promotes growth and of female sex organs.
::促进女性性器官的成长和性器官的生长。Maintains uterine lining.
::维持子宫衬。Testes Progesterone
::Progsterone(先列)Testosterone
::睾酮Bone cells, muscle cells, and cells of sex organ Stimulates growth and development of male sex organs and sex drive. The male hormone testosterone stimulates the growth of facial hair. Many men develop facial hair in the later years of puberty, usually between the ages of 15 and 18. The amount of facial hair on a man's face varies between individuals and also between ethnic groups. For example, men from many East Asian or West African backgrounds typically have much less facial hair than those of Western European, Middle Eastern, or South Asian descent.
::男性荷尔蒙睾酮刺激了面部毛发的增长。 许多男性在青春期后几年长出面部毛发,通常年龄在15-18岁之间。 一个人脸上的面部毛发数量在个人之间和族裔群体之间各不相同。 比如,来自许多东亚或西非背景的男性的面部毛发通常比西欧、中东或南亚血统的男性少得多。In females, a rise in LH concentration triggers the production of estrogen and progesterone by the ovaries. Estrogen causes the release of an egg from the ovaries, and progesterone prepares the uterus for possible implantation by a fertilized egg. The placenta is an endocrine gland of because it secretes the hormones estrogen, human chorionic gonadatropin, and progesterone, which are important for maintaining a pregnancy (shown in Figure ). The hormones secreted by the male and female gonads are listed in Table .
::在雌性体内,LH浓度的上升引发卵巢产生雌激素和蛋白质,雌激素导致卵蛋的释放,蛋白质为子宫进行编织,以便通过受精卵植入。胎盘是一种内分泌腺,因为它会分泌对保持妊娠至关重要的激素雌激素、人类血清色素和蛋白酮(见图 )。Maintaining correct hormone levels (especially progesterone) throughout pregnancy is important for carrying a pregnancy to full term.
::在整个怀孕期间保持正确的荷尔蒙水平(特别是前列腺酮)对于怀孕至整个怀孕期非常重要。Other Hormone-Producing Tissues and Organs
::其他产生激素的组织和机构Several organs that are generally non-endocrine in function, such as the stomach, the , the kidneys, and the heart, have cells that secrete hormones. For example, the kidneys secrete erythropoietin (EPO), a hormone that regulates red blood cell production, and the heart secretes atriopeptin, a hormone that reduces water and sodium levels in the blood, which decreases blood pressure. Ghrelin is a hormone that stimulates appetite and is produced by certain cells that line the stomach. Certain cells secrete hormones that can interfere with homeostasis.
::一些通常不是内分泌功能的器官,如胃、肾和心脏,都有分泌荷尔蒙的细胞。例如,肾分泌红血球生产激素(EPO),一种调节红细胞生产的激素,以及心脏分泌亚利皮丁(Atriopetin),一种减少血液水和钠水平的荷尔蒙,降低血压。格里林是一种激素,刺激食欲,由胃内某些细胞生成。某些细胞分泌激素可以干扰顺势。Summary
::摘要-
The thyroid is relatively large, is controlled by the hypothalamus and pituitary gland, and releases hormones that control the speed of the body's use of energy.
::甲状腺相对较大,由下脑膜和脑垂状腺控制,释放荷尔蒙,以控制人体使用能量的速度。 -
The parathyroid glands regulate blood calcium levels.
::甲状腺类甲状腺调节血液中的钙含量。 -
The pineal gland releases melatonin, the purposes of which scientists remain unclear about.
::松树腺释放了米拉托宁 科学家们对它的目的仍不清楚 -
The pancreas releases hormones that regulate blood sugar levels.
::胰腺释放出控制血糖水平的荷尔蒙 -
The adrenal gland releases adrenaline and noradrenaline, which help the body respond to and recover from stress.
::肾上腺素释放肾上腺素和抗肾上腺素,帮助身体应对和从压力中恢复。 -
The gonads are the glands that release sex hormones; in women they are ovaries, and in men they are the testes.
::Gonnad是释放性荷尔蒙的腺;在妇女中,她们是卵巢,在男子中,她们是睾丸。
Review
::回顾-
What is the primary purpose of the thyroid?
::甲状腺的主要目的是什么? -
What does the pancreas do?
::胰腺会做什么? -
What happens when a person is frightened?
::当一个人害怕时会怎么样?