肌肉系统收缩
章节大纲
-
What makes a muscle contract?
::是什么使肌肉合同?It starts with a signal from the or a signal from the brain . The signal goes through your nervous system to your muscle. Your muscle contracts, and your move. And all this happens incredibly fast.
::它从大脑的信号开始,或者从大脑的信号开始。信号通过你的神经系统进入你的肌肉。你的肌肉收缩,你的动作。这一切发生得太快了。Muscle Contraction
::肌肉压合A muscle contraction occurs when a muscle fiber generates tension through the movement of actin and myosin . Although you might think the term contraction means only "shortening," the overall length of a contracted muscle may stay the same or increase depending on the force working against the muscle.
::肌肉收缩发生在肌肉纤维通过动作和肌素运动产生紧张时。 尽管你可能认为“收缩”一词只意味着“收缩 ” , 但受包肌肉的总长度可能保持不变或增加,取决于对肌肉起作用的力量。The components of muscle contraction. The sacromere is the functional unit of muscle contraction; it reaches from one Z-line to the next (also shown in the Figure ). In a relaxed muscle, the actin (thin filament) and myosin (thick filament) overlap. In a muscle contraction, the filaments slide past each other, shortening the sacromere. This model of contraction is called the sliding filament mechanism.
::肌肉收缩的成分。 sacromere是肌肉收缩的功能单位; 它从一个Z线到另一个Z线( 也见于图中 ) 。 在放松的肌肉中, 阳因( 硫化物 ) 和 髓( 硫化物 ) 重叠 。 在肌肉收缩中, 纤维会相互滑过, 缩短 sacromere 。 这种收缩模式被称为滑动丝机制 。Each muscle fiber contains cellular and hundreds or thousands of myofibrils. Each myofibril is a long, cylindrical that is made up of two types of protein filaments: actin and myosin. The actin filament is thin and threadlike, while the myosin filament is thicker. Myosin has a “head” region that uses energy from ATP to “walk” along the thin actin filament ( Figure ). The overlapping arrangement of actin and myosin filaments gives its striated appearance. The actin and myosin filaments are organized into repeating units called sarcomeres , which can be seen in Figure . The thin actin filaments are anchored to structures called Z lines. The region from one Z line to the next makes up one sarcomere. When each end of the myosin thick filament moves along the actin filament, the two actin filaments at opposite sides of the sarcomere are drawn closer together, and the sarcomere shortens, as shown in Figure . When a muscle fiber contracts, all sarcomeres contract at the same time, which pulls on the fiber ends.
::每根肌肉纤维都含有细胞和成百上千的肌纤维。 每根肌纤维都是长长的圆柱形丝, 由两种蛋白丝组成: 动作和肌质。 活动丝细细细细, 细细细, 细细细细, 细细细的细细细丝, 细细细的细细细丝, 从ATP到“ 行走” 的“ 头” 区域, 沿着细细细细的丝状线( Figure ) 使用能量。 动作和肌质丝的重叠安排呈现出它的闪亮的外观。 动作和肌质的细细细细细细丝被组织成重复的单位, 称为 sarrcomeres, 这在图中可以看到。 从一个Z线到下一个线的细细细细细细的细细细细的细细丝系, 在图中显示的细细细细细细的纤维, 。When each end of the myosin thick filament moves along the actin filament, the two actin filaments at opposite sides of the sacromere are drawn closer together, and the sarcomere shortens.
::当肌肤厚厚的丝状物的两端 沿着丝状物的线状物运动时, 两端的丝状物 更紧密地拉在一起, 腐蚀物的缩短。The Neuromuscular Junction
::神经肌肉交叉口For skeletal (voluntary) , contraction occurs as a result of conscious effort that comes from the brain. The brain sends nerve signals in the form of action potentials to the motor neuron (see Figure ) that innervates the muscle fiber. In the case of some reflexes , the signal to contract can originate in the spinal cord , through a reflex arc . Involuntary muscles, such as the heart or smooth muscles in the gut and vascular system, contract as a result of non-conscious brain activity or stimuli endogenous to the muscle itself. Other actions, such as body motion, , and chewing, have a reflex aspect to them; the contractions can be initiated consciously or unconsciously but are continued through unconscious reflexes. You can learn more about action potentials and reflex arcs in the "The Nervous System: lesson.
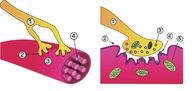
::对于骨骼(自愿)来说,收缩是大脑自觉努力的结果。大脑以运动神经(见图)潜入肌肉纤维的动作潜力的形式发出神经信号(见图 ) 。 在一些反射中,收缩信号可以通过反射弧从脊髓中产生。 非自愿肌肉,如腹部和血管系统中的心脏或光滑肌肉,由于非意识大脑活动或肌肉本身的刺激而收缩。 其他动作,如身体运动、和咀嚼,也有反射方面;收缩可以有意识或无意识地启动,但通过不意识的反射持续。你可以更多地了解“神经系统:教训”中的动作潜力和反射弧。(Left) A simplified diagram of the relationship between a skeletal muscle fiber and a motor neuron at a neuromuscular junction. 1. Axon, 2. synaptic junction, 3. muscle fiber, 4. myofibril. (Right) A close-up view of a neuromuscular junction. The neurotransmitter acetylcholine is released into the synapse and binds to receptors on the muscle cell membrane. The acetylcholine is then broken down by enzymes in the synapse. 1. Presynaptic terminal, 2. sarcolemma, 3. synaptic vesicles, 4. acetylcholine receptors, 5. mitochondrion.
::1. Axon, 2. 合成交叉口, 3. 肌肉纤维, 4. 直肠杆菌。 (右) 神经肌肉交叉口的近视。神经分质乙酰胆碱被释放到突触中,并与肌肉细胞膜上的受体结合。然后,乙酰胆碱通过神经突触中的酶破裂。 1. 先发性末端, 2. 沙本菌, 3. 突触性微粒, 4. 乙酰激素受体, 5. 线粒子体。The Sliding Filament Theory
::平滑的浅层理论The widely accepted theory of how muscles contract is called the sliding filament model (also known as the sliding filament theory), which is shown in Figure . The presence of calcium ions (Ca 2+ ) allows for the interaction between actin and myosin. In the resting state, these proteins are prevented from coming into contact. Two other proteins, troponin and tropomyosin, act as a barrier between the actin and myosin, preventing contact between them. When Ca 2+ binds to the actin filament, the shape of the troponin-tropomyosin complex changes, allowing actin and myosin to come into contact with each other. Below is an outline of the sliding filament theory .
::广泛接受的肌肉契约如何被称为滑动丝质模型的理论(也称为滑动丝质理论),如图所示。钙离子的存在(Ca2+)使得行为与肌素相互作用。在休息状态,这些蛋白无法接触。另外两个蛋白质(troponin和tropomyosin)作为行为与肌素之间的屏障,防止它们之间的接触。当Ca2+与行为丝质结合时,即Troponin-tropomyosin复杂变化的形状,允许行为和肌素相互接触。下面是滑动丝质理论的概要。-
An
action potential
(see the
Nervous and Endocrine Systems
chapter) arrives at the
axon terminal
of a motor neuron.
::行动潜力(见神经和内分泌系统一章)到达运动神经元的轴终端。 -
The arrival of the action potential activates voltage-gated calcium channels at the axon terminal, and calcium rushes into the
.
::行动潜力的到来将激活xxon终端的电压加热钙渠道,而钙会冲进...。 -
Calcium causes
vesicles
containing the
neurotransmitter
acetylcholine to fuse with the plasma membrane, which releases acetylcholine into the
synaptic cleft
between the axon terminal and the motor end plate of the skeletal muscle fiber.
::钙导致含有神经分质乙酰胆碱的微粒与等离子膜结合,该等离子膜将乙酰胆碱释放到xon终端与骨骼肌肉纤维运动端板之间的合成裂缝中。 -
Activation of the acetylcholine receptors on the muscle fiber membrane opens sodium/potassium channels, which triggers an action potential in the muscle fiber.
::肌肉纤维膜上乙酰胆碱受体的活化开启钠/钾渠道,触发肌肉纤维的活化潜力。 -
The action potential spreads through the muscle fiber's network, depolarizing (or reducing the negative charge of) the inner portion of the muscle fiber.
::行动潜力通过肌肉纤维的网络扩散 使肌肉纤维的内部分极化(或减少负电荷) -
The depolarization activates specialized storage sites throughout the muscle, called the sarcoplasmic reticulum, to release calcium ions (Ca
2+
). The sarcoplasmic reticulum is a special type of
smooth endoplasmic reticulum
found in smooth and skeletal muscle that contains large amounts of Ca
2+
, which it stores and then releases when the
is depolarized.
::非极化激活了整个肌肉的专门储存点,称为石化中脊柱,以释放钙离子(Ca2+),而石化中脊柱则是在光滑和骨骼肌肉中发现的一种特殊的光滑的内极中脊外膜,含有大量的Ca2+,储存起来,然后在脱冰时释放出来。 -
The calcium ions bind to actin filaments of the myofibrils and activate the actin for attachment by the myosin heads.
::钙离子绑在一起 粘合着细丝的肌肤 并激活阳因 以被鼻涕头附加。 -
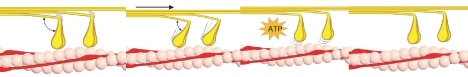
Activated myosin binds strongly to the actin filament. Upon strong binding, myosin rotates at the myosin-actin interface, which bends a region in the “neck” of the myosin “head,” as shown in
Figure
.
::活性髓素与阳性细丝紧密结合。 在强力结合下,素在肌内活性界面旋转,它弯曲了“头”的“颈部 ” ( 如图1所示 ) 。 -
Shortening of the muscle fiber occurs when the bending neck of the myosin region pulls the actin and myosin filaments across each other. Meanwhile, the myosin heads remain attached to the actin filament, as shown in
Figure
.
::肌肉纤维的减短发生在麻风地区弯曲的颈部拉扯肌和肌丝时。 与此同时,如图所示,肌头仍与肌丝相连。 -
The binding of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) allows the myosin heads to detach from actin. While detached, ATP breaks down to adenosine diphosphate and an inorganic phosphate (ADP + Pi). The breaking of the
chemical bond
in ATP gives energy to the myosin head, allowing it to bind to actin again.
::甲氧基磷酸酯(ATP)的装配允许头从阳性中分离出来。 分解后,甲氧基磷酸酯分解为乙氧基磷酸酯和无机磷酸酯(ADP + Pi ) 。 甲氧基磷酸酯化学联结的断裂给头注入了能量,使其能再次结合。 -
Steps 9 and 10 repeat as long as ATP is available and Ca
2+
is present on the actin filament. The collective bending of numerous myosin heads (all in the same direction) moves the actin filament relative to the myosin filament, which causes a shortening of the sacromere. Overall, this process results in a muscle contraction. The sarcoplasmic reticulum actively pumps Ca
2+
back into itself. Muscle contractions stop when Ca
2+
is removed from the immediate environment of the myofilaments.
::步骤 9 和 10 重复, 只要 ATP 有 ATP , Ca2+ 就会出现在 阳性丝上。 无数 头的集体弯曲( 都朝着同一方向) 将 阳性丝 与 肌质丝 相对地移动 , 从而缩短 sacromere 。 总的来说, 这一过程导致肌肉收缩 。 振动的 矩形 积极 泵 Ca2+ 返回到自己身上 。 当 Ca2+ 被清除出我的阴性丝环境时, 肌肉收缩停止 。
The process of actin and myosin sliding past one another is called cross-bridge cycling, and it occurs in all muscle types. Myosin is a molecular motor that moves along the passive actin. Each thick myosin filament has little extensions or “heads” that “walk” along the thin actin filaments during contraction. In this way, the thick filament slides over the thin filament. The actin filaments transmit the force generated by myosin to the ends of the muscle, which causes the muscle to shorten.
::动作和肌素滑过对方的过程被称为跨桥自行车,它在所有肌肉类型中都有发生。 肌素是一种分子运动,沿着被动的动作运动。 每根厚厚的肌丝都有细长或“头”的“长长”,在收缩期间沿着细细的丝状“行走 ” 。 这样一来,厚的丝质滑过薄的丝质。 细细的丝质将肌素产生的力量传送到肌肉的尽头,导致肌肉缩短。Motor Units
::机动机动车It is important to remember that the sliding filament theory applies to groups of individual muscle fibers that, along with their motor neuron, are called a motor unit. A single momentary contraction is called a muscle twitch. A twitch is the response to a single stimulus that can involve a number of motor units. As a stimulus increases, more motor units are stimulated to contract until a maximum level is reached, at which point the muscle cannot exert any more force.
::必须记住,滑动丝丝理论适用于个别肌肉纤维群体,这些肌肉纤维与其运动神经元一起被称为运动单元。 一次瞬间收缩被称为肌肉抽动。 抽动是对可能涉及若干运动单元的单一刺激的响应。 随着刺激的增加,更多的运动单元被刺激收缩,直到达到最高水平,肌肉无法再施加任何力量。Each muscle fiber contracts on an "all or nothing" principle; a muscle fiber either contracts fully or not at all, and all the fibers in a single motor unit contract at the same time. When a muscle is required to contract during , not all motor units are contracted at the same time. Most movements require only a small amount of the total force possible by the contraction of an entire muscle. As a result, our nervous system grades the intensity of muscle contractions by using different numbers of motor units at a time.
::每个肌肉纤维在“全部或无”原则下签订合同;肌肉纤维要么完全合同,要么完全合同,要么完全合同,同时在单一运动单位合同中签订所有纤维。当要求肌肉在......期间签订合同时,并非所有运动单位同时签订合同。大多数运动只需要整个肌肉收缩所可能达到的总力的一小部分。因此,我们的神经系统通过使用不同数量的运动单位进行肌肉收缩的强度分级。Cardiac Muscle Contractions
::心心肌肉压合Cardiac muscle is adapted to be highly resistant to fatigue; it has a large number of that allow continuous aerobic respiration , numerous myoglobins (oxygen storing pigment), and a good supply, which provides nutrients and oxygen. The heart is so tuned to aerobic metabolism that it is unable to pump well when there is a lack of blood to the heart muscle tissue , which can lead to a heart attack .
::心肌经过改造,对疲劳具有很强的抗药性;它拥有大量允许持续有氧呼吸、大量血球素(氧素储存色素)和提供营养素和氧气的良好供应。 心脏如此适应有氧新陈代谢,以至于当心脏肌肉组织缺乏血液时无法正常抽水,这可能导致心脏病发作。Unlike skeletal muscle, which contracts in response to nerve stimulation, and like certain types of smooth muscle, cardiac muscle is able to initiate contraction by itself. As a result, the heart can still beat properly even if its connections to the are completely severed. A single cardiac muscle cell left without input will contract rhythmically at a steady rate; if two cardiac muscle cells are in contact, whichever one contracts first will stimulate the other to contract and so on. This inherent ability to contract is controlled by the autonomic nervous system .
::与骨骼肌肉不同,骨骼肌肉与神经刺激有关,与某些类型的光滑肌肉不同,心脏肌肉本身也能够引发收缩。 因此,即使心脏与骨骼的连接完全断裂,心脏仍然可以正常跳动。 一个没有投入的单心肌肉细胞会以稳定的速度同步收缩;如果两个心脏肌肉细胞处于接触状态,无论哪一个合同首先会促进另一类合同的收缩,等等。这一固有的合同能力由自主神经系统控制。If the rhythm of cardiac muscle contractions is disrupted for any reason (for example, in a heart attack or a cardiac arrest), erratic contractions called fibrillation can result. Fibrillation, which is life threatening, can be stopped by use of a device called a defibrillator. Defibrillation consists of delivering a therapeutic dose of electrical energy to the heart, which depolarizes part of the heart muscle. The depolarization stops the fibrillation and allows a normal heartbeat to start up again. Most types of defibrillators are operated by medical personnel only. However, you may be familiar with an automated external defibrillator (AED), which is shown in Figure .
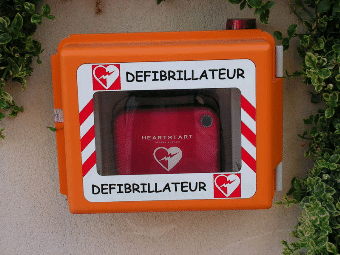
::如果心脏肌肉收缩的节奏因任何原因而中断(例如心脏病发作或心脏停跳),可以导致被称为纤维纤维化的不规律的收缩。纤维化是一种生命威胁,可以通过使用一种叫做除颤器的装置加以阻止。纤维化包括向心脏提供治疗性电能剂量,使心脏肌肉部分脱极。脱极停止了纤维化,允许正常心跳重新开始。大多数类型的除颤器只由医务人员操作。不过,你可能熟悉一个自动外部除颤器(AED),如图所示。A wall-mounted automated external defibrillator (AED). Defibrillators are used to “shock” fibrillating cardiac muscle back into the correct rhythm. AEDs are designed to be able to diagnose fibrillation in a person who has collapsed, meaning that a bystander can use them successfully with little or no training. They are usually found in areas where large groups of people may gather such as train stations, airports, or at sports events.
::挂在墙上的自动外部除颤器(AED) 。 防颤器被用来“震动”心脏肌肉,以正确的节奏恢复“震动 ” 。 设计AED能够诊断崩溃者身上的纤维发炎,这意味着旁观者可以在很少或没有受过训练的情况下成功使用它们。 通常在火车站、机场或体育赛事等大量人群聚集的地区发现。Smooth Muscle Contraction
::平滑肌肉压合Smooth muscle-containing tissue , such as the stomach or urinary bladder , often must be stretched, so elasticity is an important characteristic of smooth muscle. Smooth muscle (like cardiac muscle) does not depend on motor neurons to be stimulated. However, motor neurons of the autonomic nervous system do reach smooth muscle, causing it to contract or relax depending on the type of neurotransmitter that is released. Smooth muscle is also affected by . For example, the hormone oxytocin causes contraction of the uterus during childbirth.
::软肌肉组织,如胃部或膀胱,往往必须伸展,因此弹性是光滑肌肉的一个重要特征。 柔滑肌肉(如心脏肌肉)并不取决于需要刺激的运动神经元,然而,自动神经系统的运动神经元确实达到滑动肌肉,导致肌肉收缩或放松,取决于释放的神经分质的类型。光滑肌肉还受到以下因素的影响:例如,荷尔蒙催产素在分娩期间导致子宫萎缩。The intestinal tract contains smooth muscle that moves food along by contracting and relaxing in a process called peristalsis.
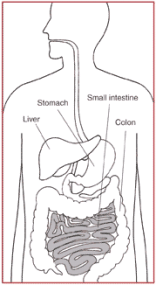
::肠道中含有光滑的肌肉,在被称为常态的过程中,通过收缩和放松来移动食物。Similar to the other muscle types, smooth muscle contraction is caused by the sliding of myosin and actin filaments over each other. However, calcium initiates contractions in a different way in smooth muscle than in skeletal muscle. Smooth muscle may contract phasically with rapid contraction and relaxation, or tonically with slow and sustained contraction. The reproductive, digestive, respiratory, and urinary tracts, skin, eye, and vasculature all contain smooth muscle. For example, the ability of vascular smooth muscle ( veins and arteries) to contract and dilate is critical to the regulation of . Smooth muscle contracts slowly and may maintain the contraction (tonically) for prolonged periods in , bronchioles , and some sphincters. In the digestive tract, smooth muscle contracts in a rhythmic peristaltic fashion. It rhythmically massages products through the digestive tract, shown in Figure , as the result of phasic contractions.
::与其他肌肉类型相似,肌肉的滑动是肌质滑动和细丝相互滑动的结果,但是,钙以与骨骼肌肉不同的不同方式在光滑的肌肉中引发收缩; 滑滑的肌肉可能以快速收缩和放松的速度收缩,或以缓慢和持续的收缩而收缩; 生殖、消化、呼吸和尿道、皮肤、眼睛和血管都包含光滑的肌肉; 例如,血管滑动的肌肉(动脉和动脉)收缩和放大的能力对调节. 滑动的肌肉合同缓慢,并可能在支气管和一些螺栓中长期保持收缩(质上); 在消化的胃,以有节奏的渗透方式,滑动的肌肉链条,通过消化道进行有节奏的按摩产品,如图所示,通过消化的收缩的结果。Summary
::摘要-
The sliding filament theory is the widely accepted theory of how motor neurons cause muscle contractions.
::滑动丝质理论是人们广泛接受的关于运动神经元如何导致肌肉收缩的理论。 -
Motor neurons in skeletal muscle activate calcium channels, causing myosin heads to attach to actin. This shortening of the sarcomere causes the muscle to contract.
::骨骼肌肉活性钙导管中的运动神经元,导致骨髓头附着在行动上。这样缩短石墨使肌肉收缩。 -
All the muscle fibers in a motor unit contract fully or not at all. Our nervous system grades the intensity of muscle contractions by using different numbers of motor units at a time.
::我们的神经系统通过一次使用不同数量的机动设备来分辨肌肉收缩强度。 -
Unlike skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle is able to initiate contraction by itself.
::与骨骼肌肉不同的是,心脏肌肉本身可以引发收缩。 -
Motor neurons of the autonomic nervous system activate smooth muscle, causing it to contract or relax depending on the type of neurotransmitter that is released. Smooth muscle is also affected by hormones.
::自动神经系统运动神经元激活光滑肌肉,根据释放的神经分质的类型,使其收缩或放松。 光滑肌肉也受到荷尔蒙的影响。
Review
::回顾-
What is the most widely accepted theory of how motor neurons initiate muscle contractions? What ions play a key role in this theory?
::最普遍接受的关于运动神经元如何引发肌肉收缩的理论是什么?什么离子在这一理论中起着关键作用? -
How does cardiac muscle contraction differ from skeletal muscle contraction?
::心脏肌肉收缩与骨骼肌肉收缩有何不同? -
What is fibrillation? How does a defibrillator work?
::什么是纤维化?除颤器怎么工作? -
Can a muscle fiber vary how much it contracts?
::肌肉纤维能改变多少合同吗?
-
An
action potential
(see the
Nervous and Endocrine Systems
chapter) arrives at the
axon terminal
of a motor neuron.