生化化合物
章节大纲
-
Carbs Galore
::卡布斯·加洛尔What do all of these foods have in common? All of them consist mainly of large compounds called , often referred to as "carbs." Contrary to popular belief, carbohydrates are an important part of a healthy diet. They are also one of four major classes of biochemical compounds.
::所有这些食物有什么共同之处?它们都主要由称为“碳”的大型化合物组成。 与流行的信仰相反,碳水化合物是健康饮食的重要组成部分。它们也是四大类生化化合物之一。Chemical Compounds in Living Things
::活物中的化学化合物The compounds found in living things are known as biochemical compounds (or biological molecules). Biochemical compounds make up the and other structures of organisms . They also carry out life processes. Carbon is the basis of all biochemical compounds, so carbon is essential to life on Earth. Without carbon, life as we know it could not exist.
::在生物物质中发现的化合物被称为生化化合物(或生物分子),生物化学化合物构成生物体的结构和其他结构,它们也进行生命过程。碳是所有生化化合物的基础,因此碳是地球上生命必不可少的。没有碳,我们知道生命不可能存在。Carbon is so basic to life because of its ability to form stable bonds with many elements , including itself. This property allows carbon to create a huge variety of very large and complex molecules. In fact, there are nearly 10 million carbon-based compounds in living things!
::碳是生命的基础,因为它能够与包括自身在内的许多元素形成稳定的联系。 这种特性使得碳能够创造大量非常大和复杂的分子。 事实上,在生物中,有近1,000万种碳化合物。Most biochemical compounds are very large molecules called polymers . A polymer is built of repeating units of smaller compounds called monomers . Monomers are like the individual beads on a string of beads, and the whole string is the polymer. The strings of beads pictured are simple models of polymers in biochemical compounds.
::大部分生化化合物都是称为聚合物的大型分子。 聚合物是由称为单体的较小化合物的重复体组成的聚合物。 单体就像一串珠子上的单个珠子,整个链子是聚合物。 所描绘的珠子链是生化化合物中的简单的聚合物模型。Classes of Biochemical Compounds
::生化化合物类别Although there are millions of different biochemical compounds in Earth's living things, all biochemical compounds contain the elements carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. Some contain only these elements, while others contain additional elements, as well. The vast number of biochemical compounds can be grouped into just four major classes: carbohydrates, , , and .
::尽管地球生物中存在数百万种不同的生化化合物,但所有生化化合物都含有碳、氢和氧等元素。有些含有这些元素,而另一些则包含额外的元素。 大量生化化合物可以分为四大类:碳水化合物、碳水化合物、碳水化合物和碳氢化合物。Carbohydrates
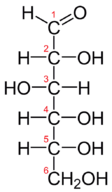
::碳水合物Carbohydrates include sugars and starches. These compounds contain only the elements carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. In living things, carbohydrates provide energy to cells, store energy, and form certain structures (such as the cell walls of plants). The monomer that makes up large carbohydrate compounds is called a monosaccharide . The sugar glucose , represented by the chemical model , is a monosaccharide. It contains six carbon atoms (C), along with several atoms of hydrogen (H) and oxygen (O). Thousands of glucose molecules can join together to form a polysaccharide , such as starch .
::碳水化合物包括糖和淀粉,这些化合物仅含有碳、氢和氧元素。在生物物质中,碳水化合物为细胞、储存能量和形成某些结构(如植物的细胞壁)提供能量。构成大型碳水化合物的单体称为单碳酸盐。由化学模型代表的糖甘甘蔗是一种单碳酸盐。它包含六个碳原子(C),以及若干氢原子(H)和氧原子(O)。成千上万的葡萄糖分子可以联合形成一个聚碳酸盐,如淀粉。Model of a monosaccharide (glucose) molecule
::单沙焦化(葡萄糖)分子模型Lipids
::唇唇Lipids include fats and oils. They contain primarily the elements carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen, although some lipids contain additional elements, such as phosphorus. Lipids function in living things to store energy, form , and carry messages. Lipids consist of repeating units that join together to form chains called fatty acids . Most naturally occurring fatty acids have an unbranched chain of an even number (generally between 4 and 28) of carbon atoms.
::利皮包括脂肪和油,主要含有碳、氢和氧等元素,尽管有些脂质含有其他元素,如磷; 利皮在活物中发挥作用,储存能量、形态和传递信息; 利皮包括重复的单位,它们共同组成称为脂肪酸的链条。 大部分自然产生的脂肪酸有平均数量(一般在4到28之间)的碳原子链条。Proteins
::蛋白质Proteins include , antibodies , and many other important compounds in living things. They contain the elements carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, and sulfur. Functions of proteins are very numerous. They help cells keep their shape, compose , speed up chemical reactions , and carry messages and materials. The monomers that make up large protein compounds are called amino acids . There are 20 different amino acids that combine into long chains (called polypeptides) to form the building blocks of a vast array of proteins in living things.
::蛋白质包括, 抗体, 以及生物中许多其他重要的化合物。 它们包含碳、 氢、 氧、 氮和硫元素。 蛋白质的功能非常多。 它们帮助细胞保持形状、 合成、 加速化学反应, 并传递信息与材料。 构成大型蛋白化合物的单体被称为氨基酸。 有20种不同的氨基酸结合成长链( 称为聚苯醚 ) , 形成生物中大量蛋白质的构件。Nucleic Acids
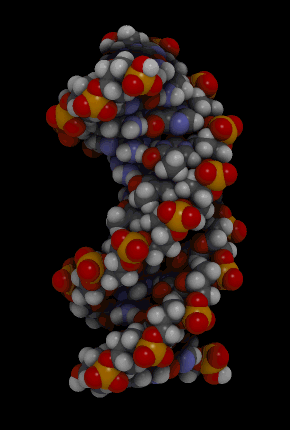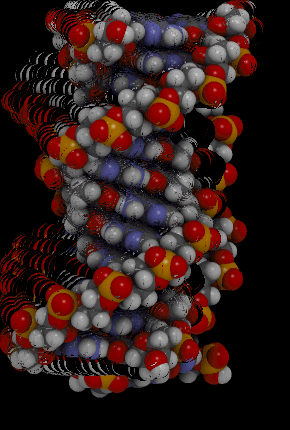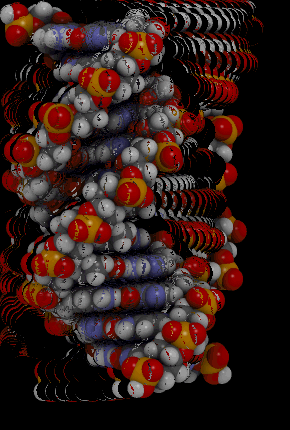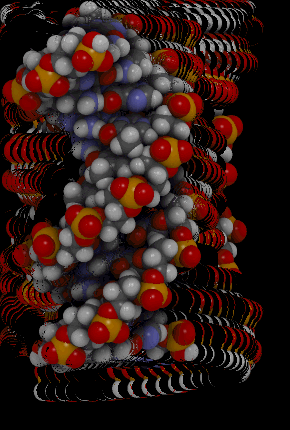
::核酸Nucleic acids include the molecules (deoxyribonucleic acid) and (ribonucleic acid). They contain the elements carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, and phosphorus. Their functions in living things are to encode instructions for making proteins, to help make proteins, and to pass instructions between parents and offspring. The monomer that makes up nucleic acids is the nucleotide . All nucleotides are the same, except for a component called a nitrogen base. There are four different nitrogen bases, and each nucleotide contains one of these four bases. The sequence of nitrogen bases in the chains of nucleotides in DNA and RNA makes up the code for , which is called the . The animation below represents the very complex structure of DNA, which consists of two chains of nucleotides.
::核糖核酸包括分子(脱氧核糖核酸)和(核糖核酸),它们包含碳、氢、氧、氮和磷元素。它们在生物物质中的功能是将蛋白质制作指令编码,帮助制造蛋白质,并在父母和后代之间传递指令。构成核糖核酸的单体是核酸。所有核酸都是相同的,但一个称为氮基的成分除外。有四个不同的氮基,每个核酸包含这四个基体中的一个。DNA和RNA中核酸链中的氮基序列构成代号。下面的动画代表了非常复杂的DNA结构,由两个核糖核酸链组成。This rotating DNA model shows the complexity of this two-stranded nucleic acid.
::这种旋转式DNA模型 显示了这种两层核酸的复杂性Summary
::摘要-
Biochemical compounds are carbon-based compounds found in living things. They make up cells and other structures of organisms and carry out life processes. Most biochemical compounds are large molecules called polymers that consist of many repeating units of smaller molecules, which are called monomers.
::生化化合物是活物中发现的碳基化合物,它们组成细胞和其他生物结构,并进行生命过程,大多数生化化合物是大型分子,称为聚合物,由许多较小的分子(称为单体)的重复单元组成。 -
There are millions of biochemical compounds, but all of them fall into four major classes: carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids.
::生物化学化合物数以百万计,但都分为四大类:碳水化合物、脂类、蛋白质和核酸。 -
Carbohydrates include sugars and starches. They provide cells with energy, store energy,
and
make up organic structures, such as the cell walls of plants.
::碳水化合物包括糖和淀粉,它们为细胞提供能源、储存能源,并构成有机结构,如植物的细胞壁。 -
Lipids include fats and oils. They store energy, form cell membranes, and carry messages.
::嘴唇包括脂肪和油,它们储存能量,形成细胞膜,并传递信息。 -
Proteins include enzymes, antibodies, and numerous other important compounds in living things. They have many functions — helping cells keep their shape, making up muscles, speeding up chemical reactions, and carrying messages and materials.
::蛋白质包括酶、抗体和生物中许多其他重要化合物。 它们有许多功能 — — 帮助细胞保持形状、形成肌肉、加速化学反应、传递信息和材料。 -
Nucleic acids include DNA and RNA. They encode instructions for making proteins, help make proteins, and pass encoded instructions from parents to offspring.
::核酸包括DNA和RNA。它们编码了蛋白质制作说明,帮助制造蛋白质,并将父母的编码指示传给后代。
Review
::回顾1. Why is carbon so important to life on Earth?
::1. 为什么碳对地球上的生命如此重要?2. What are biochemical compounds?
::2. 什么是生化化合物?3. Describe the diversity of biochemical compounds and explain how they are classified.
::3. 描述生化化合物的多样性,并解释如何将其分类。4. Identify two types of carbohydrates. What are the main functions of this class of biochemical compounds?
::4. 查明两种碳水化合物:这一类生化化合物的主要功能是什么?5. What roles are played by lipids in living things?
::5. 脂肪在生物中起什么作用?6. The enzyme amylase is found in saliva. It helps break down starches in foods into simpler sugar molecules. What type of biochemical compound do you think amylase is?
::6. 氨基酶在唾液中找到,有助于将食物中的淀粉碎成简单的糖分子。7. Explain how DNA and RNA contain the genetic code.
::7. 解释DNA和RNA是如何包含遗传代码的。8. What are the three elements present in every class of biochemical compound?
::8. 每一类生化化合物中存在的三个要素是什么?9. For each of the following terms: nucleic acid; amino acid; monosaccharide; protein; nucleotide; polysaccharide...
::9. 下列术语中的每一术语:核酸;氨基酸;单沙酸;蛋白质;核酸;聚沙酸...a. Classify it as a monomer or a polymer.
::a. 分类为单体或聚合物。b. Match each monomer with its correct polymer.
::b. 将每一单体与正确的聚合物匹配。c. Identify which class of biochemical compound is represented by each monomer/polymer pair.
::c. 确定每对单体/聚合物代表哪一类生化化合物。10. Is glucose a monomer or a polymer ? Explain your answer.
::10. 葡萄糖是单体还是聚合物?11. What is one element contained in proteins and nucleic acids, but not in carbohydrates?
::11. 蛋白质和核酸所含的一个要素是什么,但不包括碳水化合物?12. Describe the relationship between proteins and nucleic acids.
::12. 描述蛋白质和核酸之间的关系。13. Why do you think it is important to eat a diet that contains a balance of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats?
::13. 为什么你认为必须吃含有碳水化合物、蛋白质和脂肪平衡的饮食?Explore More
::探索更多The video below discusses the importance of the element carbon.
::以下视频讨论碳元素的重要性。
Watch the video below to learn more about polymers and monomers.
::观看下面的录像,以了解更多聚合物和单体。 -
Biochemical compounds are carbon-based compounds found in living things. They make up cells and other structures of organisms and carry out life processes. Most biochemical compounds are large molecules called polymers that consist of many repeating units of smaller molecules, which are called monomers.