双分拆
章节大纲
-
When waves strike a small slit in a wall, they create circular wave patterns on the other side of the barrier. This is seen in the image above, where ocean waves create precise circular waves. The circular waves undergo constructive and destructive interference , which generates a regular interference pattern.
::当海浪在墙上小片裂开时,它们会在屏障的另一侧形成循环波形。 从上图中可以看出,海洋波形成精确的循环波。 循环波受到建设性和破坏性的干扰,经常产生干扰模式。Diffraction and Interference
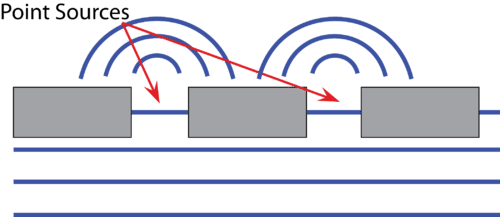
::违法行为和干涉When a series of straight waves strike an impenetrable barrier, the waves stop at the barrier. However, the last particle of the medium at the back corner of the barrier will create circular waves from that point, called the point source. This can be seen in the image below. This phenomenon is called , and it occurs in liquid, sound, and light waves. While the waves become circular waves at the point source, they continue as straight waves where the barrier does not interfere with the waves.
::当一连串直波撞击一个不可穿透的屏障时,波浪会停在屏障上。然而,在屏障后角的介质最后的粒子会从那个点产生圆形波,称为点源。从下面的图像中可以看到这种现象。这种现象被称作,在液体、声音和光波中发生。当波浪变成点源的圆形波时,它们会继续作为直波,而屏障不会干扰波浪。Any two waves in the same medium undergo as they pass each other. At the location where the two waves collide, the result is essentially a summation of the two waves. In some places, a wave crest from one source will overlap a wave crest from the other source. Since both waves are lifting the medium, the combined wave crest will be twice as high as the original crests. Nearby, a wave trough will overlap another wave trough and the new trough will be twice as deep as the original. This is called constructive interference because the resultant wave is larger than the original waves. Within the interference pattern, the amplitude will be twice the original amplitude. Once the waves pass through each other and are alone again, their amplitudes return to their original values.
::在同一介质中, 任何两个波都会相互穿行。 在两个波相撞的地点, 结果基本上是两个波的相撞。 在有些地方, 一个源的波峰会重叠另一个源的波峰。 由于两个波峰都升起介质, 合并波峰会比原来的波峰高一倍。 靠近一点, 一个波谷会重叠另一个波谷, 新波谷会比原来的更深。 这被称为建设性干扰, 因为由此产生的波比最初的波要大。 在这种干扰模式下, 振幅将是最初的波峰的两倍。 一旦波浪经过对方, 并且再次孤立起来, 它们的振幅就会回到原来的值 。In other parts of the wave pattern, crests from one wave will overlap troughs from another wave. When the two waves have the same amplitude, this interaction causes them to cancel each other out. Instead of a crest or a trough, there is nothing. When this cancellation occurs, it is called destructive interference.
::在波状的其他部分,一个波的顶峰会与另一个波的底部重叠。 当两个波的宽度相同时, 这种交互作用会迫使它们相互取消。 而不是一个顶或底部, 没有什么。 当取消时, 它被称为破坏性干扰 。.It is easy to see how waves emanating from multiple sources, such as drops of rainwater in still water, create interference patterns. But a single source of waves can create interference patterns with itself as a result of diffraction.
::很容易看出来自多种来源(如静水中的雨水滴)的波浪是如何造成干扰模式的。 但单一的波浪源会因分裂而造成干扰模式。The Double Slit Experiment
::双分线实验A similar situation to the raindrops above occurs when straight waves strike a barrier containing two slits. These waves are cut off everywhere except for where the waves that pass through the two slits. The medium in the slits again acts as a point source to produce circular waves on the far side of the barrier.
::当直波撞上一堵有两条断裂的屏障时,与上面的雨滴情况相似,这些波浪被切断,但穿过两条断裂处的波浪除外,断裂处的介质再次作为点源,在屏障的远端产生循环波。As long as these two circular waves have the same , they interfere constructively and destructively in a specific pattern. This pattern is called the wave interference pattern and is characterized by light and dark bands. The light bands are a result of constructive interference and the dark bands occur because of destructive interference.
::只要这两波循环波相同,它们就以具体的方式建设性地和破坏性地干预,这种模式被称为波的干扰模式,以光和暗带为特征,光带是建设性干扰的结果,黑暗波段是破坏性干扰的结果。In the early 1800s, light was assumed to be a particle. There was a significant amount of evidence to point to that conclusion, and famous scientist Isaac Newton's calculations all support the particle theory . In 1803, however, Thomas Young performed his famous Double Slit Experiment to prove that light was a wave. Young shined a light onto the side of a sealed box with two slits in it, creating an interference pattern on the inside of the box opposite the slits. As seen above, interference patterns are characterized by alternating bright and dark lines. The bright lines are a result of constructive interference, while the dark lines are a result of destructive interference. By creating this interference pattern, Young proved light is a wave and changed the course of physics .
::1800年代初,光被假定为一个粒子。有相当多的证据表明了这一结论,著名的科学家Isaac Newton的计算都支持粒子理论。然而,在1803年,Thomas Young进行了他著名的双光实验,以证明光是波。Young用两条缝隙将光照到密封盒子的侧面,在裂缝对面的盒子内侧制造了干扰模式。如上所示,干扰模式的特点是光线和暗线交替。光线是建设性干扰的结果,而暗线则是破坏性干扰的结果。通过制造这种干扰模式,Young证明光是波,改变了物理过程。Calculating Wavelength from Double Slit Pattern
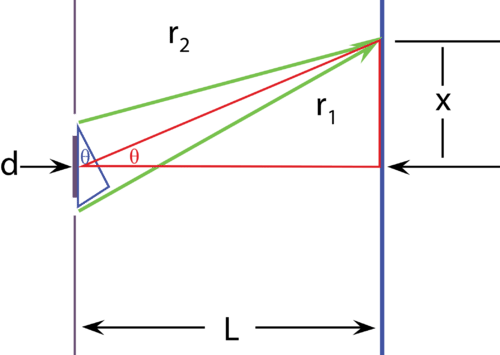
::从双切分模式计算波长Using the characteristics of the double slit interference pattern, it is possible to calculate the wavelength of light used to produce the interference. To complete this calculation, it is only necessary to measure a few distances. As can be seen below, five distances are measured. In the sketch, L is the from the two slits to the back wall where the interference pattern can be seen. d is the distance between the two slits. To understand x , look again at the interference pattern shown above. The middle line, which is the brightest, is called the central line . The remaining lines are called fringes . The lines on either side of the central line are called the first order fringes, the next lines are called the second order fringes, and so on. x is the distance from the central line to the first order fringe.
::使用双线干扰模式的特性, 可以计算产生干扰的光的波长。 完成此计算, 只需要测量几条距离即可 。 从下面可以看到, 测量了五条距离 。 在草图中, L 是从两条斜线到后墙的距离, 可以看到干扰模式 。 d 是两条斜线之间的距离 。 要理解 x, 请再次查看上面显示的干扰模式 。 中间线是最亮的, 被称为中线 。 其余的直线被称为边缘 。 中线两边的直线被称为第一顺线边缘, 下一条直线被称为第二顺线边缘, 依此推。 x 是中线到第一顺线的距离 。r 1 and r 2 are the distances from the slits to the first order fringe. We know that the fringes are a result of constructive interference, and that the fringe is a result of the crest of two waves interfering. If we assume that r 2 is a whole number of wavelengths (confirm for yourself that this is a logical assumption), then r 1 must be one more wavelength. This is because r 1 and r 2 are the distances to the first order fringe. Mathematically, we can let
::r1 和 r2 是从断裂到第一阶边缘的距离。 我们知道边缘是建设性干扰的结果, 边缘是两波干扰的柱子的结果。 如果我们假设 r2 是整个波长数( 确定这是逻辑假设) , 那么 r1 必须是再一个波长。 这是因为 r1 和 r2 是到第一阶边缘的距离。 从数学角度讲, 我们可以允许 r1 和 r2 。r 2 = n λ and r 1 = n λ + λ , where λ is the wavelength and n is a constant.
::r2=n和r1=n, 其中为波长, n为常数。Using this relationship, we determine that r 1 − r 2 = λ .
::利用这种关系,我们确定 r1 -r2\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\i\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\Looking again at the diagram, the red and blue triangles are similar, which means that the ratios of corresponding sides are the same. The ratio of x to L in the red triangle is equal to the ratio of λ to d in the blue triangle. From this, we can determine that the wavelength is dependent on x, d, and L:
::再看看图表,红三角和蓝三角是相似的,这意味着对应边的比重相同。红三角中x对L的比例等于+++d的比例。从这个角度,我们可以确定波长取决于 x、d和L:λ = x d L
::xdL dL dL dL dL dL dL dL dL dL dL dL dL dLExample
::示例示例示例示例Monochromatic light falls on two narrow slits that are 0.0190 mm apart. A first order fringe is 21.1 mm from the central line. The screen (back wall) is 0.600 m from the slits. What is the wavelength of the light?
::单色光落在两条窄切线上,两条窄切线为0.0190毫米。第一线边缘距中线21.1毫米。屏幕(背壁)距断线0.600米。光的波长是多少?λ = x d L = ( 0.021 m ) ( 0.000019 m ) ( 0.600 m ) = 6.68 × 10 − 7 m
::*xdL=(0.021米)(0.00019米)(0.600米)=6.68×10-7米)Use the Marina simulation below to interact with waves that are traveling at a steady and wavelength toward the shore. The peaks of these waves are represented as horizontal lines at the top of the screen. The point in the middle between two lines indicates a wave trough, where the water is lowest. If you adjust the wavelength with the slider you will notice that shorter wavelengths are represented by lines closer together. Have fun learning about the concept of double slit diffraction in this real-world setting:
::使用下面的 Marina 模拟来与以稳定波长向海岸行驶的波浪进行互动。 这些波浪的峰值以屏幕顶部的水平线表示。 两行中间的点表示波槽, 水位最低 。 如果您使用滑动器调整波长, 您将会注意到, 较短波长由更近的线条代表 。 有趣的是, 学习这个现实世界环境中双斜折叠的概念 :Further Reading
::继续阅读-
Gratings
::格 数
Summary
::摘要-
The last particle of medium at the back corner of an impenetrable barrier will act as a point source and produce circular waves.
::不可穿透屏障后角最后的介质粒子将作为点源并产生环波。 -
Diffraction is the bending of waves around a corner.
::破坏是一角的波浪弯曲 -
Constructive interference occurs when two wave crests overlap, doubling the wave amplitude at that location.
::当两个波峰重叠,使该地点的波浪振幅翻了一番时,就会发生建设性干扰。 -
Destructive interference occurs when a wave crest overlaps with a trough, causing them to cancel out.
::当波峰与沟槽重叠,导致它们取消时,就会发生破坏性干扰。 -
Light is a wave, and creates an interference pattern in the double slit experiment.
::光是波, 并造成干扰模式 在双重割裂实验。 -
An interference pattern consists of alternating bright and dark lines; the bright lines are called fringes.
::干扰模式包括交替的亮线和暗线;亮线称为边缘线。 -
In a double slit experiment, the wavelength can be calculated using this equation:
λ
=
x
d
L
::在双切实验中,波长可以用这个方程式来计算:xdL
Review
::回顾-
Destructive interference in waves occurs when
-
two troughs overlap.
::两条干线重叠。 -
crests and troughs align.
::柱和槽对齐。 -
two crests overlap.
::两处山顶重叠。 -
a crest and a trough overlap.
::山脊和干线重叠。
::当两个槽相互重叠时,波浪的破坏性干扰就会发生。 峰顶和底部对齐。 两个顶部对齐。 一个顶部和底部对齐。 -
two troughs overlap.
-
Bright bands in interference patterns result from
-
destructive diffraction.
::破坏性破坏。 -
destructive interference.
::破坏性干扰。 -
constructive diffraction.
::建设性违规。 -
constructive interference.
::建设性干涉。
::干扰模式的亮带源于破坏性的破坏性破坏、破坏性的干扰、建设性破坏、建设性干扰。 -
destructive diffraction.
-
In a double slit experiment with slits
1.00
×
10
−
5
m
apart, light casts the first bright band
3.00
×
10
−
2
m
from the central bright spot. If the screen is 0.650 m away, what is the wavelength of this light?
-
510 nm
::510纳米 -
390 nm
::390纳米 -
430 nm
::430纳米 -
460 nm
::460纳米
::在两条切片1.00×10-5米相隔的双切实验中,光从中央亮点投出第一支3 00×10-2米的亮度,如果屏幕距离0.650米,这种光的波长是多少? 510 nm 390 nm 430 nm 460 nm -
510 nm
-
Violet light falls on two slits separated by
1.90
×
10
−
5
m
. A first order bright line appears 13.2 mm from the central bright spot on a screen 0.600 m from the slits. What is the wavelength of the violet light?
::紫色灯光落在两条截断线上,以190×10-5米隔开。 第一道亮线从中央亮点显示13.2毫米。 紫色灯光的波长是多少? -
Suppose in the previous problem, the light was changed to yellow light with a wavelength of
5.96
×
10
−
7
m
while the slit separation and distance from screen to slits remained the same. What would be the distance from the central bright spot to the first order line?
::假设在前一个问题中,光线被改为黄色光,波长5.96×10-7米,而从屏幕到切片的割裂距离和距离保持不变。 从中央亮点到第一层线的距离是多少? -
Light with a wavelength of
6.33
×
10
−
7
m
is used in a double slit experiment. The screen is placed 1.00 m from the slits and the first order line is found 65.5 mm from the central bright spot. What is the separation between the slits?
::6.33×10-7米的波长为6.33×10-7米的光用于双切试验。屏幕从切片处放置在1.00米处,从中心亮点发现第一道线65.5毫米。 切片之间的分离是什么?
Explore More
::探索更多Use this resource to answer the questions that follow.
::使用此资源回答下面的问题 。-
When the amplitude of waves add, it is called _________________ interference.
::当波浪的振幅增加时,它被称为“干扰”。 -
When the amplitude of waves subtract, it is called _________________ interference.
::当波浪的振幅减慢时,它被称为“干扰”。 -
What do we call the phenomenon of light bending around a corner?
::转弯到角落的灯光现象叫什么来着?
-
Gratings