液溶解 - 高级
章节大纲
-
How do you slice a molecule of glucose in half?
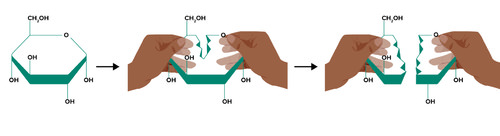
::你怎么把葡萄糖的分子切成两半?With sharp knives? Not really. But you lyse it with during a process named glycolysis. Glucose is sliced right in half from a 6-carbon molecule to two 3-carbon molecules. This is the first step and an extremely important part of . It happens all the time, both with and without oxygen. And in the process, transfers some energy to ATP .
::用锋利的刀子吗?不是。 但你在一种叫做 液解的过程里用它来解析。 葡萄糖被切成两半, 从6碳分子切成两半, 从6碳分子切成两个3碳分子。 这是第一步, 并且是其中非常重要的一部分。 它经常发生, 无论有没有氧气。 在这个过程中, 将一些能量转移到 ATP 。Glycolysis: A Universal and Ancient Pathway for Making ATP
::Glyco解析:建立ATP的普遍和古老途径When was the last time you enjoyed yogurt on your breakfast cereal, or had a tetanus shot? These experiences may appear unconnected, but both relate to that do not use oxygen to make ATP. In fact, tetanus bacteria cannot survive if oxygen is present. However, Lactobacillus acidophilus (bacteria that make yogurt) and Clostridium tetani (bacteria that cause tetanus or lockjaw) share with nearly all organisms the first stage of cellular respiration, glycolysis (the Figure ). Because glycolysis is universal, whereas aerobic (oxygen-requiring) cellular respiration is not, most biologists consider it to be the most fundamental and primitive pathway for making ATP.
::上一次你在早餐麦片上享受酸奶是什么时候,还是最后一次注射破伤风?这些经验可能看起来没有联系,但都与不使用氧气制造ATP有关。事实上,如果氧气存在,破伤风细菌就无法生存。然而,Lactobcillus酸性philus(制造酸奶的细菌)和clostridium Titani(造成破伤风或锁扎的细菌)与几乎所有生物分享了细胞呼吸的第一阶段,即液解(图 )。因为水解是普遍性的,而有氧(氧)细胞呼吸不是,大多数生物学家认为这是进行ATP的最根本和最原始的途径。Clostridium tetani bacteria are obligate anaerobes, which cannot grow in the presence of oxygen and use a variation of glycolysis to make ATP. Because they can grow in deep puncture wounds and secrete a toxin, which can cause muscle spasms, seizures, and death, most people receive tetanus vaccinations at least every ten years throughout life. Return to the overall equation for cellular respiration:
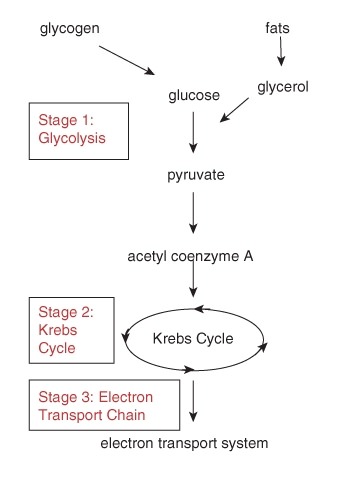
::返回到细胞呼吸的总方程:Like , the process represented by this equation is actually many small, individual chemical reactions . We grouped the reactions of photosynthesis into two stages, the and the . We will divide the reactions of cellular respiration into three stages: glycolysis, the , and the electron transport chain (the Figure ). In this concept, Stage 1, glycolysis, the oldest and most widespread pathway for making ATP, is discussed. Before diving into the details, we must note that this first stage of cellular respiration is unique among the three stages: it does not require oxygen, and it does not take place in the . The chemical reactions of glycolysis occur without oxygen in the cytosol of the (the Figure ).
::类似地, 这个等式所代表的过程其实是许多小的, 个别的化学反应。 我们将光合作用的反应分为两个阶段, 和两个阶段。 我们将细胞呼吸的反应分为三个阶段: 凝解, 电子传输链( 图 ) 。 在这个概念中, 讨论第1阶段, 凝解, 形成 ATP 的最古老和最广泛的路径 。 在跳入细节之前, 我们必须指出, 细胞呼吸的第一阶段是三个阶段中的独特阶段: 它不需要氧, 并且不会发生在 。 凝解的化学反应在没有氧气的情况下发生( 图 ) 。The many steps in the process of aerobic cellular respiration can be divided into three stages. The first stage, glycolysis, produces ATP without oxygen. Because this part of the cellular respiration pathway is universal, biologists consider it the oldest segment. Note that glycogen and fats can also enter the glycolysis pathway. The second stage is the Krebs Cycle, and the third stage is the electron transport chain. It is during the third stage that chemiosmosis produces numerous ATP molecules. Glycolysis, unlike the latter two stages of cellular respiration, takes place without oxygen in the cytosol (blue) of the cell. For many organisms, aerobic respiration continues with the Krebs cycle and the electron transport chain in the mitochondria (green). To enter the mitochondria, glucose must first be lysed into smaller molecules. The name for Stage 1 clearly indicates what happens during that stage: glyco - refers to glucose, and - lysis means "splitting." In glycolysis, within the cytosol of the cell, a minimum of eight different enzymes break apart glucose into two 3-carbon molecules. The energy released in breaking those bonds is transferred to carrier molecules, ATP and NADH . NADH temporarily holds small amounts of energy which can be used later to build ATP. The 3-carbon product of glycolysis is pyruvate , or pyruvic acid (the Figure ). (The difference between them is actually a sole hydrogen atom. Pyruvic acid: CH 3 COCOOH, pyruvate: CH 3 COCOO - .) Overall, glycolysis can be represented as:
::第一阶段的名称清楚地表明了该阶段发生的情况: 甘蓝- 指葡萄糖, 透析是指“ 分裂 ” 。 在透析中, 在细胞的细胞质中, 至少有8种不同的酶将甘蓝分解成2个3碳分子。 打破这些联系所释放的能量被转移到了载体分子、 ATP 和 NADH 。 NADH 暂时持有少量能量, 可用于以后建造 ATP 。 甘蓝解析的3碳产物是丙酸( 图 ) 。 ( 它们之间的差别实际上是唯一的氢原子。 Pyruvic 酸: CH3COOH, pyruvate: CH3COOO- 。 ) 总体而言, 解析可以表现为 :C 6 H 12 O 6 + 2NAD + + 2P i + 2ADP → 2 pyruvate + 2NADH + 2ATP
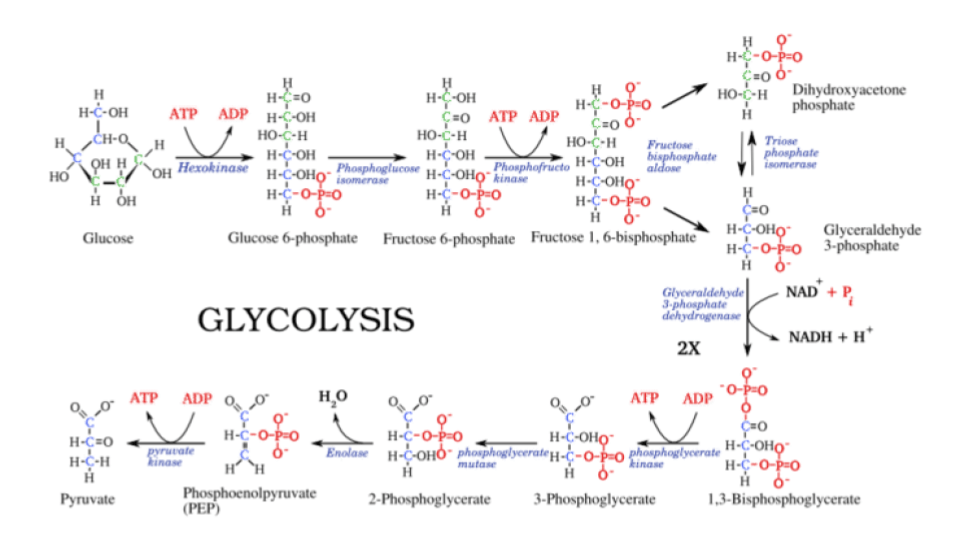
::C6H12O6+2NAD++2Pi+2ADP+2ADP+2ADP+2PH12O6+2NADH+2ATP+2NADH+2ATPIn glycolysis, glucose (C6) is split into two 3-carbon (C3) pyruvate molecules. This releases energy, which is transferred to ATP. How many ATP molecules are made during this stage of cellular respiration? Glycolysis breaks the 6-carbon molecule glucose into two 3-carbon pyruvate molecules, releasing some of the chemical energy that had been stored in glucose. However, even this equation is deceiving. Just the splitting of glucose requires many steps, each transferring or capturing small amounts of energy. Individual steps appear in the Figure . Studying the pathway in detail reveals that cells must "spend" or "invest" two ATP in order to begin the process of breaking glucose apart. Note that the phosphates produced by breaking apart ATP join with glucose, making it unstable and more likely to break apart. Later steps harness the energy released when glucose splits, and use it to build "hot hydrogens" (NAD + is reduced to NADH) and ATP (ADP + P i → ATP). If you count the ATP produced, you will find a net yield of two ATP per glucose (4 produced – 2 spent). Remember to double the second set of reactions to account for the two 3-carbon molecules that follow that pathway! The "hot hydrogens" can power other metabolic pathways, or in many organisms, provide energy for further ATP synthesis.
::然而,即使这个方程式也存在欺骗。 只是葡萄糖的分解需要许多步骤, 每一步骤转移或捕捉少量的能量。 单个步骤出现在图中 。 详细研究路径显示, 细胞必须“ 溢出” 或“ 投资” 2 APT 才能开始打破葡萄糖的过程。 请注意, 分解 ATP 产生的磷酸盐与葡萄糖结合, 使得它不稳定, 更容易分解。 以后的步骤要控制葡萄糖分解时释放的能量, 并且用它来制造“ 热氢 ” (NAD+ 减为NADH) 和 ATP ( ADP + Pi APT ) 。 如果您计算ATP 所生产的二个ATP / glucose ( 4 已经用过 2 ) , 你将会发现两种亚TP / glucose 的净产量。 。 记住, 第二组反应是计算沿这条路径的两组三碳分子的第二组 。 “ 氢” 能够驱动其他代谢路径或许多生物, 提供进一步的合成能源。To summarize: In the cytosol of the cell, glycolysis transfers some of the chemical energy stored in one molecule of glucose to two molecules of ATP and two NADH. This makes (some of) the energy in glucose, a universal fuel molecule for cells, available to use in cellular work - moving , transporting molecules across membranes, or building large organic molecules .
::总而言之:在细胞的细胞溶液中,玻璃解析将一个葡萄糖分子中储存的一些化学能量转移至ATP的两个分子和两个NADH的两个分子,这使(部分)葡萄糖中的能量成为细胞的通用燃料分子,可用于细胞工作 -- -- 移动、将分子运过膜或制造大型有机分子。Although glycolysis is universal, pathways leading away from glycolysis vary among depending on the availability of oxygen. If oxygen is unavailable, pyruvate may be converted to lactic acid or ethanol and carbon dioxide in order to regenerate NAD + , ending . Anaerobic respiration is also called , which will be discussed in another concept.
::虽然玻璃解析是普遍性的,但从玻璃解析的路径因氧气供应情况而异。 如果缺氧,气压酸或乙醇和二氧化碳可转化成抗体酸或乙醇和二氧化碳,以再生NAD+,结束。还称抗氧呼吸,将在另一个概念中讨论。If oxygen is present, pyruvate enters the mitochondria for further breakdown, releasing far more energy and producing many additional molecules of ATP in the latter two stages of aerobic respiration - the Krebs cycle and the electron transport chain. We will explore these, too, in a later section.
::如果存在氧气,回旋剂将进入米托乔因德里亚进一步分解,释放出更多的能量,并在有氧呼吸的后两个阶段 -- -- Krebs 循环和电子运输链 -- -- 产生更多的ATP分子。Summary
::摘要-
The process of cellular respiration is actually many separate reactions, which can be divided into three stages: glycolysis, the Krebs Cycle, and the electron transport chain.
::细胞呼吸过程实际上是许多不同的反应,可以分为三个阶段:液解、Krebs循环和电子运输链。 -
During glycolysis, glucose is split into two 3-carbon pyruvate molecules, using 2 ATP but generating 4 ATP, for a net gain of 2 ATP.
::在液解过程中,甘蔗糖被分成两个3碳蒸发分子,使用2个ATP,但产生4个ATP,净收益为2个ATP。 -
During glycolysis, 2 NADH are also produced.
::在水解过程中,还生产了2个NADH。
Review
::回顾-
List the three stages of cellular respiration, and contrast the first stage with the other two in terms of distribution throughout the living world, location within the cell, and use of oxygen.
::列出细胞呼吸的三个阶段,并将第一阶段与其他两个阶段相比较,从整个生物世界的分布、细胞内的位置以及氧气的使用等方面看。 -
Summarize the overall process of glycolysis, following both the path of carbon atoms and chemical energy.
::总结沿碳原子和化学能源路径进行大气解析的总体过程。 -
What molecules can enter the glycolysis pathway, besides glucose?
::除了葡萄糖,哪些分子可以进入凝解路径?
-
The process of cellular respiration is actually many separate reactions, which can be divided into three stages: glycolysis, the Krebs Cycle, and the electron transport chain.