染色体分局 - 高级
章节大纲
-
How is it assured that every cell in your body has the same DNA?
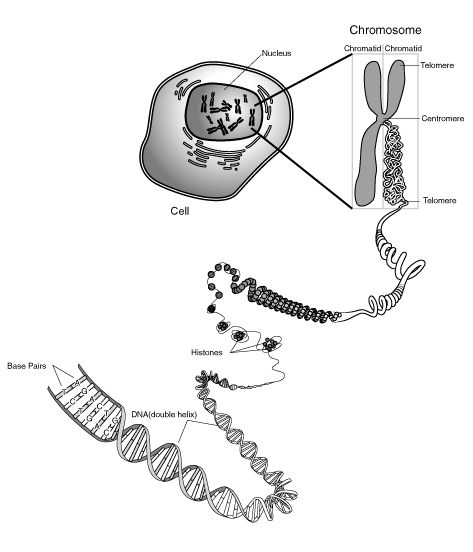
::如何保证你身体里的每个细胞 都有相同的DNA?Chromosomes, like those shown here, must form prior to , to ensure that each daughter cell receives a complete set of genetic material . Each chromosome is made of two identical sister chromatids. Each chromatid is 1/2 of the "X." Essentially, each daughter cell receives half of each "X-shaped" chromosome.
::染色体和这里显示的染色体一样,必须在......之前形成,以确保每个女儿细胞获得一整套遗传材料。每个染色体由两个相同的姐妹染色体组成。每个染色体是X的四分之一。基本上,每个女儿细胞得到每个“X形”染色体的一半。DNA, Chromosomes, and Genes
::DNA、染色体和基因contains the information necessary to make , direct a cell’s activities, and give an organism its traits. Obviously, it is a very important molecule. Actually , in human , DNA is organized into 46 molecules called chromosomes.
::DNA包含制造、指导细胞活动以及赋予生物特征所需的信息。 显然,它是一个非常重要的分子。 事实上,在人类中,DNA被组织成46个叫做染色体的分子。The information in DNA is organized into structural units scattered along the length of the DNA molecule. These units are known as genes . A gene contains the information necessary to encode an molecule or a protein. A diploid human cell has about 44,000 genes; two copies of each of about 22,000 genes. So, a single DNA molecule contains hundreds to thousands of genes. Through the process of , which involves and , different cell types use the information in different genes to make different proteins. This process gives different cell types distinct activities. Thus, a liver cell will have many different proteins than a cell, giving the two cells types distinct activities. When a cell is using the information within a gene, the segment of DNA containing that gene is unwound as chromatin , exposing the double helix to the cell machinery needed to use that information.
::DNA中的信息按分布在DNA分子长度上的结构单位排列。 这些单位称为基因。 基因包含对分子或蛋白质进行编码所需的信息。 浸泡型人类细胞有大约44,000个基因; 大约22,000个基因的两份副本。 因此, 单个DNA分子包含成百上千个基因。 不同的细胞类型通过这个过程, 涉及和 在不同基因中使用信息来制造不同的蛋白质。 这个过程提供了不同的细胞类型不同的活动。 因此, 肝细胞将拥有许多不同的蛋白质, 给两种细胞类别不同的活动。 当细胞在基因中使用信息时, 含有该基因的DNA部分作为染色体, 将双螺旋接触到使用该信息所需的细胞机器中去。Prior to cell division, the DNA must duplicate itself in a process called DNA replication . This ensures that each resulting cell receives a complete set of the organism’s genome . But how is the replicated DNA divided up evenly? This will be discussed in an additional concept.
::在细胞分解之前,DNA必须在一个称为DNA复制的过程里重复自己。 这确保了每个生成的细胞都能得到完整的生物基因组。 但复制的DNA是如何平均分配的?这将在另一个概念中讨论。What guarantees that each new cell will receive a complete set of DNA? It was the identification of chromosomes that allowed this process to be characterized. As a eukaryotic cell prepares to divide, the DNA and associated proteins (histones) coil into a chromosome ( Figure ). The DNA copies itself prior to this process, so the chromosome that forms consists of two identical chromatids, known as sister chromatids , identical copies of DNA. The two chromatids are attached at a region called the centromere . The chromatids separate from each other when the divides just prior to cell division. Thus, each new cell that results after cell division will have the complete complement of genetic material, identical to the original, or parent, cell. In human cells, this amounts to 46 chromosomes. These chromosomes come in pairs (one from each pair inherited from each parent). So these 46 chromosomes are actually two sets of 23 chromosomes each.
::是什么保证每个新细胞将获得完整的DNA集? 是什么保证了每个新细胞将获得完整的DNA集? 是什么是确定染色体, 从而可以对这一过程进行定性 。 当一个乳胶细胞准备分离时, DNA和相关蛋白质( histones) 卷状进入染色体( Figure ) 。 在这个过程之前, DNA本身复制了它本身, 因此, 由两种相同的染色体构成的染色体, 被称为姐妹染色体, 相同的DNA副本 。 两个染色体被附在一个叫做centromere的区域 。 当细胞分裂前的分隔时, 染色体会彼此分离 。 因此, 每个细胞分裂后产生结果的新细胞将拥有与原细胞或母细胞相同的基因材料的完整补充 。 在人类细胞中, 这些染色体有46个染色体组成成对子( 每对母继承一) 。 因此, 这46个染色体实际上是两套23个染色体。The DNA double helix wraps around proteins and tightly coils a number of times to form a chromosome. This figure shows the complexity of the coiling process. The chromosome comprises two identical, or sister, chromatids held together by a centromere. Each human somatic cell (a body cell, or every cell other than a gamete) normally has two sets of chromosomes, one set inherited from each parent. These cells are said to have a diploid number of chromosomes. Each set contains 23 chromosomes, for a total of 46 chromosomes. Each chromosome differs in size, from about 250 million nucleotide pairs on the largest chromosome (chromosome #1) to less than 50 million nucleotide pairs on chromosome #22. Each chromosome contains a specific set of genes, as well as regulatory elements and other nucleotide sequences, making each chromosome essential to survival.
::每个人体细胞(身体细胞,或除调色板以外的每个细胞)通常有两组染色体,每组由母体继承。这些细胞据说有染色体的分数。每组含有23个染色体,共46个染色体。每个染色体的大小各不相同,从最大的染色体染色体(染色体#1)上大约2.5亿对核核糖酸双对到22号染色体上不到5 000万对核酸双对。每个染色体都包含一套特定的基因,以及调控元素和其他核酸序列,使每种染色体都成为生存的必要条件。Homologous Chromosomes
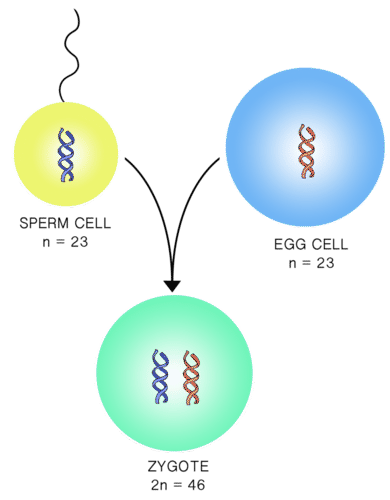
::同性恋染色体Each pair of chromosomes consists of two chromosomes that are similar in size and shape. They contain the same genes at the same loci , though they may have different . These pairs of chromosomes are known as homologous chromosomes or homologues . Upon , a zygote is formed ( Figure ). A zygote is the of a new individual. In humans, a zygote contains 23 pairs (or two sets) of chromosomes. Any cell containing two sets of chromosomes is said to be diploid. The zygote forms from the fusion of two haploid gametes . A haploid cell contains one set of chromosomes. In humans, a haploid gamete contains 23 chromosomes. Biologists use the symbol n to represent one set of chromosomes, and 2n to represent two sets.
::每对染色体由两组大小和形状相似的染色体组成。 它们在同一地方含有相同的基因, 尽管它们可能有不同的基因 。 这些染色体的配对被称为同质染色体或同族体 。 从那时起, 形成一个zygote (Figure ) 。 zygote 是一个新的个体 。 在人类中, zygote 包含23对( 或两组) 染色体。 任何包含两组染色体的细胞据说都是 diploid 。 两组杂交游戏的混合所形成的zygote 形式 。 一个 hangloid 细胞包含一组染色体 。 在人类中, 一组合合金游戏包含 23 个染色体。 生物学家使用该符号代表一套染色体, 2n 代表两组 。Homologous chromosomes form a pair, one from each parent. Homologous chromosomes are similar in size and shape, and contain the same genes, though they may have different alleles. Alleles are alternative forms of the same gene. This diagram represents two pairs of homologous chromosomes. Upon fertilization a diploid zygote is formed. In humans, a zygote has 46 chromosomes, 23 inherited from each parent. The gametes, sperm and eggs, are haploid cells, with 23 chromosomes each. Sex Chromosomes
::性染色体In humans, each set of chromosomes contains 22 autosomes and 1 sex chromosome . Autosomes are chromosomes that are not directly involved in determining the sex of an individual. The sex chromosomes contain genes that determine the sex of an individual.
::在人类中,每组染色体都包含22个异体和1个性染色体。 染色体是没有直接参与确定个人性别的染色体。 性染色体包含决定个人性别的基因。Whereas autosomes are found as homologous pairs in somatic cells, sex chromosomes come in two different sizes, shapes, and contain different genes. In many organisms, including humans, the sex chromosomes are known as the X and Y chromosomes. The Y chromosome contains genes that cause male . Therefore, any individual with a Y chromosome is male, and a male will have both an X and Y chromosome (XY). Females, without a Y chromosome, will have two X chromosomes (XX). As females have two X chromosomes, they must pass an X chromosome to all of their children. As males have both an X chromosome (inherited from their mother) and a Y chromosome, they can give either chromosome to their children. If a child inherits a Y from his father, he will be male; if a child inherits an X from her father, she will be female. It therefore is the male gamete that determines the sex of the offspring.
::虽然在体细胞中发现有同质体,但性染色体有两种不同的大小、形状和基因。在许多生物中,包括人类,性染色体被称为X和Y染色体。Y染色体含有导致男性的基因。因此,任何有Y染色体的人都是男性,男性将同时拥有X和Y染色体(XY)。没有Y染色体的女性将拥有两个X染色体(XX)。女性拥有两个X染色体,因为女性拥有两个X染色体,他们必须将X染色体传给他们的孩子。男性既拥有X染色体(母亲的遗传体),也拥有Y染色体,他们可以给孩子一个染色体。如果一个孩子继承了Y,他将成为男性;如果一个孩子继承了父亲的X,她将成为女性。因此,男性游戏决定了孩子的性别。Summary
::摘要-
As a eukaryotic cell prepares to divide, the DNA and associated proteins coil into a structure, known as a chromosome.
::当一个eukaryaty细胞准备分解时,DNA和相关蛋白质会凝结成一个结构,被称为染色体。 -
After DNA replication, a resulting chromosome will consist of two identical sister chromatids, attached at a region called the centromere.
::DNA复制后,由此产生的染色体将由两个相同的姐妹染色体组成,附于一个叫做“centromere”的区域。 -
Any cell containing two sets of chromosomes is said to be diploid; the zygote forms from the fusion of two haploid gametes.
::任何含有两组染色体的细胞,据说是浸泡细胞;由两组手动调子混合而成的zygote形态。
Review
::回顾-
Describe the structure of a chromosome.
::描述染色体的结构。 -
Differentiate between a chromatid and a homologue.
::染色体和同族体之间的区别 -
Distinguish between an autosome and a sex chromosome.
::区分异体和性染色体 -
What is the centromere?
::什么是中环? -
How does the chromosome duplicate itself?
::染色体是如何重复的?
-
As a eukaryotic cell prepares to divide, the DNA and associated proteins coil into a structure, known as a chromosome.