翻译 - 高级
Section outline
-
How does a cell use the information in its DNA?
::细胞如何使用DNA中的信息?To transcribe means "to paraphrase or summarize in writing." The information in is transcribed - or summarized - into a smaller version - - that can be used by the . This process is called transcription. Only certain specific "segments" - genes - in the DNA are transcribed at any one time.
::转录中的信息是可被转录的,或者被归纳成一个较小的版本。这个过程叫做转录。DNA中只有某些特定的“部分”——基因——在任何时候都被转录。Transcription
::翻译Transcription is “DNA → RNA.” In other words, transcription is the transfer of the genetic instructions from DNA to RNA. During transcription, a complementary copy of RNA is made. Whereas in DNA replication both strands of the DNA double helix are used as templates, in transcription only one strand is needed. RNA polymerase enzymatically “reads” a template strand of DNA, known as the coding strand, to synthesize the complementary RNA strand. Transcription is usually divided into 3 stages, appropriately named initiation , elongation and termination . In eukaryotes , transcription can be additionally divided into 5 stages: preinitiation, initiation, promoter clearance, elongation and termination.
::转录法是“DNA ” 。 换句话说,转录法是将基因指令从DNA转基因到RNA。在转录法中,对RNA做了补充拷贝。在DNA复制中,DNA双螺旋的两部分都用作模板,而在转录法中,只需要一股模板。 RNA 聚合酶酶酶酶酶酶“读”一种称为编码线的DNA模板,以合成补充性RNA线。转录法通常分为三个阶段,适当命名为启动、延长和终止。在eukaryotes中,转录法可以再分为五个阶段:启动、启动、促进清除、延长和终止。Overview of Transcription. Transcription uses the sequence of bases in a strand of DNA to make a complementary strand of mRNA. Triplets are groups of three successive nucleotide bases in DNA. Codons are complementary groups of bases in mRNA. Every triplet, or codon, encodes for a unique amino acid.
::Trancripation使用DNA链中基数的序列,以形成一个补充的 mRNA。三联体是DNA中连续三个核酸基数的一组。 Codon是 mRNA中两个基数的互补组。每个三联体,或codon,都为一种独特的氨基酸编码。PreInitiation
::启动前In eukaryotes, preinitiation of transcription is a step that determines if transcription will proceed. This step is involved in the regulation of , and will be further discussed in those concepts. The process is also highly regulated in prokaryotic cells , but is a much less complicated process than that in eukaryotic cells .
::在 eukaryotes 中, 开始转录前是一个决定转录是否会进行的步骤。 这一步骤涉及对...的监管,并将在这些概念中进一步讨论。 这个过程在 prokaryotes 细胞中也受到高度监管,但比在eukarytells 细胞中的过程复杂得多。Briefly, during preinitiation, RNA polymerase binds to a promoter sequence in the presence of specific . RNA polymerase II , and therefore the initiation of transcription, requires the presence of a core promoter sequence in the DNA. The TATA box is a highly characterized core promoter sequence found in most eukaryotic promoters. The TATA box is the binding site for a transcription factor known as TATA-binding (TBP), which is itself a subunit of another transcription factor, called Transcription Factor II D (TFIID). Only after this factor and a number of other factors bind to this complex can RNA polymerase complete the preinitiation complex and initiate transcription. The rate of transcription is modulated by additional activators and repressors.
::简言之,在启动前,RNA聚合酶在有特定的.RNA聚合酶二号的情况下与促销器序列结合,从而启动转录程序,需要DNA中有一个核心促销器序列。TATA盒是大多数含水促销器中发现的一个高度特征的核心促销器序列。TATA盒是连接调试因数(TATA-绑定(TBP)的固定站点,它本身就是另一个转录因子的子单位,称为Tranationing因数II D(TFIID)。只有在这一因数和与该综合体相关的若干其他因素之后,RNA聚合器才能完成启动转录程序。转录率由额外的活性器和抑制器调节。The complete preinitiation complex contains:
::完整的启动前综合设施包括:-
the core promoter sequence
::核心促进器序列 -
various transcription factors
::各种转录系数 -
RNA polymerase
::RNA 聚合酶 -
activators and repressors.
::振动器和抑制器
RNA Polymerase
::RNA 聚合酶RNA polymerase, which is also known as DNA-dependent RNA polymerase, is an that produces RNA using a DNA template. RNA polymerase enzymes are essential to life and are found in all organisms . In biochemical terms, RNA polymerase is a nucleotidyl transferase that polymerizes ribonucleotides at the 3' end of an RNA transcript. While have one type of RNA polymerase, eukaryotes have multiple types, each responsible for the sun thesis of a distinct set of RNAs.
::RNA聚合酶也称为DNA依赖的RNA聚合酶,是一种使用DNA模板生产RNA的聚合酶,RNA聚合酶对生命至关重要,存在于所有生物中,在生化术语中,RNA聚合酶是一种核分裂基转移酶,在RNA笔录的3 结尾处聚合了核分裂基转移酶,有一种RNA聚合酶,而eukaryotes具有多种类型,每个类型都对一套不同的RNA的太阳原理负责。-
RNA polymerase I synthesizes a pre-rRNA 45S, which matures into 28S, 18S and 5.8S rRNAs which will form the major RNA components of the
.
::RNA 聚合酶I合成了RRNA前45S,成熟为28S、18S和5.8S RNA,它们将成为RNA的主要组成部分。 -
RNA polymerase II synthesizes mRNAs and most snRNA and microRNAs. Due to the high level of regulation needed for proper transcription, a wide range of transcription factors is necessary for RNA polymerase II to bind to a gene's promoter. These will be discussed in the
Regulation of Gene Expression (Advanced)
concepts.
::RNA 聚合酶II合成 mRNAs和大多数SnRNAs和微RNAs,由于对正确转录需要高度监管,RNA 聚合酶II需要一系列广泛的转录因子,才能与基因促进者捆绑在一起,这些因子将在基因表达(高级)规范概念中讨论。 -
RNA polymerase III synthesizes tRNAs, rRNA 5S and other small RNAs.
::RNA聚合酶III合成tRNAs、RRNA 5S和其他小型RNA。 -
RNA polymerases IV and V synthesize siRNA in plants.
::RNA 聚合酶IV和V合成的工厂中的硅氨酸合成聚合酶。
Initiation
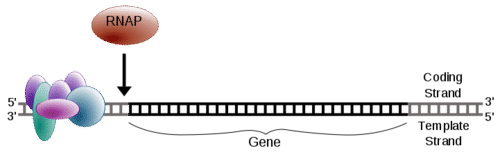
::启动Initiation of transcription only occurs when all transcription factors are aligned along the promoter correctly. Transcription factors are usually proteins that bind to the DNA sequence of the promoter. Once all these factors are in place, RNA polymerase can begin transcription.
::只有在所有转录系数都正确与促销者一致的情况下,才开始转录; 转录系数通常是与促销者的DNA序列联系在一起的蛋白质; 一旦所有这些因素都到位, RNA 聚合酶就可以开始转录。Transcription begins with the binding of RNA polymerase to the promoter of a gene. An eukaryotic promoter signals the approximate start of a gene. The promoter usually includes specific sequences that are recognized by transcription factors, which are proteins that aid in the binding of RNA polymerase to the correct place on the DNA. The transcription initiation complex formed by the promoter, transcription factors, and RNA polymerase signals the start, or initiation, of transcription. The DNA unwinds as the hydrogen bonds between the bases are broken, and produces a small open complex, which allows RNA polymerase to “read” the DNA template and begin the synthesis of RNA.
::RNA聚合酶与基因促销者的结合开始于RNA聚合酶与基因促销者的结合。 an eukaryocyproducer 表示基因的大致起点。 促销者通常包括经转录系数确认的具体序列, 即有助于将RNA聚合酶结合到DNA正确位置的蛋白质。 由促销者组成的转录启动综合体、 转录系数和 RNA聚合酶预示转录的开始或开始。 脱氧后作为基地间氢系的链条被打破, 并产生一个小的开放综合体, 使RNA聚合酶能够“ 读” DNA模板并开始合成RNA。Initiation. Notice that a set of transcription factors must bind to the promoter in the proper orientation prior to RNA polymerase (RNAP) binding and initiating transcription.
::启动. 通知说,一套转录系数必须在RNA聚合酶(RNAP)约束和启动转录之前,对正确方向的促进者具有约束力。Promoter Clearance
::推动者清除Soon after initiation the RNA polymerase must clear the promoter. During this time the transcriptional process is unstable. There is a tendency for the complex to release the RNA transcript and produce truncated unstable messages. This is called abortive initiation and is common for both eukaryotes and . This process can continue until the the transcription elongation complex is formed. Once the newly synthesized mRNA transcript reaches approximately 23 nucleotides long, abortive initiation is no longer and issue and elongation will continue until termination. This, like most of the remainder of transcription, is an energy-dependent process, consuming ATP .
::RNA聚合酶在启动后不久必须清除促销者。 在此期间, 转录过程不稳定。 综合体发布 RNA 记录并生成短发不稳定信息的趋势。 这被称为中止启动, 对eukaryotes和eukaryotes都是常见的。 这一过程可以持续到转录延展综合体形成为止。 一旦新合成的 mRNA 记录长到大约23个核核桃, 中止启动就不再存在, 发行和延长将持续到终止。 这与大部分转录过程一样, 是一个依赖能源的过程, 消耗 ATP 。Elongation
::长长Transcription elongation involves the further addition of RNA nucleotides and the change to a transcriptional complex. As the RNA transcript is assembled, DNA in front of RNA polymerase unwinds by breaking the hydrogen bonds between the bases, and transcription continues. As transcription progresses, RNA nucleotides are added to the 3' end of the growing RNA transcript. The DNA template (non-coding) strand is read in the 3' → 5' direction, so the complementary RNA stand in created in the 5' → 3' direction. This produces an RNA molecule from 5' → 3', an exact copy of genetic instructions in the DNA coding strand. Of course the newly made RNA is composed of RNA nucleotides with uracil bases and ribose sugars.
::随着RNA笔录的收集,RNA 聚合酶的DNA在RNA 之前通过打破基底之间的氢系而释放出来,转录还在继续。随着转录的进展,RNA 核酸将添加到不断增长的RNA笔录的3端。DNA模板(非编码)线在3' 5' 方向上读,因此在5' 3'方向上创建了补充RNA站。这产生了一种RNA分子,从5' 3' 3'开始,这是DNA编码线中基因指示的准确复制件。当然,新制成RNA由RNA 核糖核酸和糖组成。The transcriptional complex has a short DNA-RNA hybrid , an 8 base-pair stretch in which the newly made RNA is temporarily hydrogen bonded to the DNA template strand. Once the hydrogen bonds are broken, the RNA is released from the DNA transcription complex. Unlike DNA replication, mRNA transcription can involve multiple RNA polymerases, allowing numerous mRNAs to be produced from a single copy of the gene. This step also involves a proofreading mechanism that can replace an incorrectly added RNA nucleotide.
::转录式综合体有一个短的DNA-RNA混合体,这是8个基底孔段,其中新制RNA暂时被与DNA模板束连接氢。一旦氢联结破裂,RNA就会从DNA转录式综合体中释放出来。与DNA复制不同,MRNA转录可涉及多个RNA聚合酶,允许从基因的单一副本中产生许多 mRNA。这一步骤还包含一个校对机制,可以取代错误添加的RNA核核酸。Elongation. As RNA polymerase reads the template strand, the mRNA is synthesized. Notice that a few of the RNA nucleotides are temporarily hydrogen bonded to the DNA nucleotides.
::随着RNA聚合酶读取模板条,将合成MRNA。请注意,一些RNA核糖核酸是暂时与DNA核糖核酸结合的氢。Termination
::解雇The termination of transcription in prokaryotes and eukaryotes is very different. Though both involve the detachment of the RNA from the DNA template, how this occurs is surprisingly distinct. Bacteria use two different strategies for transcription termination, Rho-dependent and Rho-independent termination. In Rho-dependent termination , a protein factor called "Rho" destabilizes the RNA-DNA hybrid, releasing the newly synthesized mRNA from the elongation complex. In Rho-independent termination, RNA transcription stops when the newly synthesized RNA molecule forms a hairpin loop followed by a run of uracils. This structure is the signal for the detachment of the RNA from the DNA. The DNA is now ready for .
::在prokaryotes 和 eukaryotes 中, 笔录的终止非常不同。 虽然两者都涉及RNA与DNA模板的分离, 但这种情况是如何发生的却令人惊讶地不同。 细菌对笔录的终止使用两种不同的策略, Rho- 依赖和Rho- 独立终止。 在Rho- 独立终止中, 一个叫做“ Rho” 的蛋白质因素破坏了RNA- DNA 混合体的稳定, 从延展综合体释放了新合成的 mRNA。 在Rho- 独立终止中, RNA 笔录停止了新合成的 RNA 分子形成一个发光环, 并随后运行了一种泌尿素。 这个结构是RNA 的离脱氧核糖核糖核酸的信号。 DNA现在可以用于 。The termination of transcription in eukaryotes is less well understood. The RNA polymerase transcribes a polyadenylation signal. Polyadenylation is the addition of a string of A’s to the mRNA’s 3’ end and will be discussed in the : mRNA (Advanced) concept. However, soon after the transcription of this signal, proteins cut the RNA transcript free from the RNA polymerase and the enzyme eventually falls off the DNA. This process produces a pre-mRNA, an mRNA that is not quite ready to be translated.
::以 eukaryotes 完成转录的过程不太为人所知。 RNA 聚合酶转录成一个多词形信号。 多词形是将A的字符串加到 mRNA 3 结尾处,并将在 : mRNA ( Advanced) 概念中讨论。 但是,在这个信号转录后不久,蛋白质将RNA 转录从RNA 聚合酶中解脱出来,酶最终会从DNA中掉下来。 这个过程产生了一个MRNA预产期,一个尚未完全准备好翻译的 mRNA。Steps of Transcription. Transcription occurs in the three steps - initiation, elongation, and termination - shown here.
::吊销步骤 。 吊销发生在此处显示的三个步骤中 - 启动、 延长和终止 - 。Summary
::摘要-
Transcription is the transfer of the genetic instructions from DNA to RNA.
::解密是指将基因指示从DNA转至RNA。 -
Transcription begins with the binding of RNA polymerase to the promoter of a gene.
::RNA聚合酶与基因促销者捆绑在一起,
Review
::回顾-
What is protein synthesis?
::什么是蛋白质合成? -
What is transcription?
::什么是转录? -
Describe the steps of transcription.
::描述笔录的步骤。 -
Compare Rho-dependent and Rho-independent termination.
::比较Rho依赖和Rho独立终止合同。
-
the core promoter sequence