变异原因 - 高级
Section outline
-
What does radiation contamination do?
::辐射污染有什么作用?It mutates . The Chernobyl disaster was a nuclear accident that occurred on April 26, 1986. It is considered the worst nuclear power plant accident in history. A Russian publication concludes that 985,000 excess cancers occurred between 1986 and 2004 as a result of radioactive contamination. The 2011 report of the European Committee on Radiation Risk calculates a total of 1.4 million excess cancers occurred as a result of this contamination.
::切尔诺贝利灾难是1986年4月26日发生的一次核事故,被认为是历史上最严重的核电厂事故。一份俄罗斯出版物得出结论,1986年至2004年期间,由于放射性污染,出现了985,000例超重癌症。欧洲辐射风险委员会2011年报告估计,由于这种污染,共发生140万例超重癌症。Causes of Mutation
::变异原因Is it possible for to occur spontaneously, or does there have to be a cause of the mutation? Well, the answer is that both are possible. Mutagenesis is a process by which the genetic information of an organism is changed in a stable manner, resulting in a mutation. In nature mutagenesis can lead to changes that are beneficial or harmful, or have no effect. Harmful mutations can lead to and various heritable diseases, but beneficial mutations are the driving force of evolution. In 1927, Hermann Muller first demonstrated the effects of mutations with observable changes in . He induced mutagenesis by irradiating fruit flies with X-rays,
::是否有可能自发发生,还是必须引起突变? 嗯,答案是两者都是可能的。 诱变是一个过程,即生物体的遗传信息以稳定的方式改变,导致突变。 在自然突变中,诱变可能导致有益或有害或没有效果的变化。 有害的突变可能导致和各种遗传性疾病,但有利的突变是进化的动力。 1927年,Hermann Muller首先展示了突变的影响和可观察的变化。他通过用X光照射果蝇而诱发突变,Mutagenesis may occur spontaneously or be induced. A spontaneous mutation can just happen. These mutations are not caused by an environmental factor, but occur during normal cellular processes. A spontaneous mutation may be due to a mistake during DNA replication or . Mutations may also occur during and . A mutation caused by an environmental factor, or mutagen , is known as an induced mutation . Typical mutagens include chemicals, like those inhaled while smoking, and radiation, such as X-rays, ultraviolet light, and nuclear radiation. Table lists some spontaneous mutations that are common.
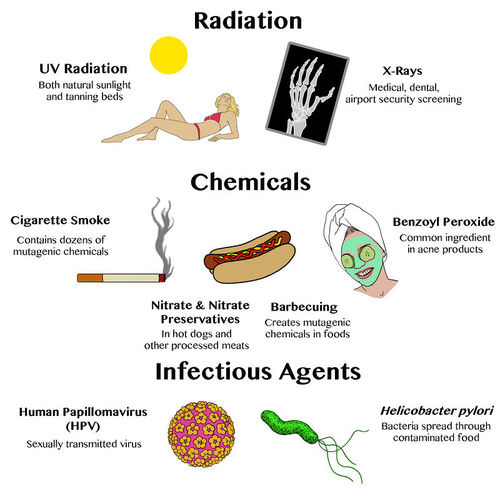
::自发突变可能自发发生,也可能诱发。自发突变可能只是发生。这些突变不是环境因素引起的,而是在正常细胞过程中发生的。自发突变可能是由于DNA复制过程中的错误,也可能是由于DNA复制过程中的错误。突变也可能发生在过程和过程期间。环境因素或诱变基因引起的突变被称为诱变。典型的诱变包括化学物质,如吸烟时吸入的化学物质,以及X光、紫外线光和核辐射等辐射。表格列出了一些常见的自发突变。Examples of Mutagens. Types of mutagens include radiation, chemicals, and infectious agents. Do you know of other examples of each type of mutagen shown here? Type Mutation Tautomerism a base is changed by the repositioning of a hydrogen atom Depurination loss of a purine base (A or G) Deamination spontaneous deamination of 5-methycytosine Transition a purine to purine, or a pyrimidine to pyrimidine change Transversion a purine becomes a pyrimidine, or vice versa Summary
::摘要-
Mutagenesis is a process by mutations, stable changes in the genetic material, are created.
::突变是产生突变的过程 基因物质的稳定变化 -
Mutations may be due to environmental factors (mutagens) or may occur spontaneously.
::变异可能是环境因素(变异因素)造成的,也可能是自发发生的。 -
Mutations may have no effect, may be beneficial, or may be harmful.
::变异可能没有效果,可能有益,也可能有害。 -
Typical mutagens include chemicals, such as those inhaled by smoking, and radiation, like X-rays, ultraviolet light, and nuclear radiation.
::典型的诱变性包括化学物质,如吸烟吸入的化学物质,以及辐射,如X光、紫外线光和核辐射。
Review
::回顾-
Define mutagenesis and mutagen.
::定义诱变和诱变。 -
List three examples of mutagens.
::列举三个诱变性的例子。 -
Distinguish between a transition and a transversion.
::区分过渡和转换。
-
Mutagenesis is a process by mutations, stable changes in the genetic material, are created.