基因表达式的 Eukaryod 语义调控 - 高级
章节大纲
-
On or Off? On or Off? On or Off?
::开还是走 开还是走 开还是走 开还是走?That is the key question. Why are some genes expressed and others are not? Why do different types have different ? How do different cell types have different functions? The answers to those questions are related. Gene regulation in eukaryotes is a highly regulated process usually involving many proteins, which either bind to each other or bind to the .
::这是关键问题。为什么有些基因表现出来,而另一些基因没有表现出来?为什么不同类型是不同的?不同的细胞类型有不同的功能?不同的细胞类型如何有不同的功能?对这些问题的答案是相互联系的。 Eukaryotes 的基因监管是一个监管严密的过程,通常涉及许多蛋白质,它们要么相互捆绑,要么与蛋白质捆绑。Eukaryotic Gene Regulation
::Eukaryatic 基因规范All your cells have the same DNA and therefore the same genes, yet they have different proteins because they express different genes. In eukaryotic cells , the start of is one of the most complex aspects of gene regulation. Transcriptional regulation involves the formation of an initiation complex involving interactions between a number of , cis- regulatory elements , and enhancers , distant regions of DNA that can loop back to interact with a gene’s promoter . These regulatory elements occur in unique combinations within a given cell type, resulting in only necessary genes being transcribed in certain cells. Transcription factors , or trans-acting factors, bind to a DNA strand, usually interacting with cis-regulatory elements, allowing RNA polymerase to bind and start transcription.
::你所有的细胞都拥有相同的DNA,因此,同样的基因,但是它们都有不同的蛋白质,因为它们表现了不同的基因。在衣冠状细胞中,基因调节的最复杂方面之一是开始的。 定型监管包括形成一个启动复合体,其中涉及若干精密调节元素和强化元素之间的相互作用,以及增强元素,DNA的遥远区域,它们可以回转与基因的促进者互动。 这些调控元素在特定细胞类型中以独特的组合形式出现,导致某些细胞中只有必要的基因被转录。 定型因子或转动因,与DNA捆绑在一起,通常与精密调节元素互动,允许RNA聚合酶捆绑并开始转录。Each gene has unique cis-regulatory sequences, only allowing specific transcription factors to bind. However, there are common regulatory sequences found in most genes. The TATA box is a cis-regulatory element found in the promoter of most eukaryotic genes. It has the DNA sequence 5'-TATAAA-3' or a slight variant, and has been highly conserved throughout evolution. When the appropriate cellular signals are present, RNA polymerase binds to the TATA box, completing the initiation complex. A number of transcription factors first bind to the TATA box while other transcription factors bind to the previously attached factors, forming a multi-protein complex. It is only when all the appropriate factors are bound that RNA polymerase will recognize the complex and bind to the DNA, initiating transcription.
::每个基因都有独特的精密序列,只允许特定的转录因子捆绑。然而,大多数基因中都有共同的调制因子。TATA框是大多数尿道基因的促进者中发现的一个精密要素。它有DNA序列 5'-TATAAA-3' 或一个微小变体,并且在整个进化过程中都得到了高度保护。当适当的细胞信号出现时,RNA聚合酶与TATA盒捆绑在一起,完成启动综合体。许多转录因子首先与TATA盒绑在一起,而其他转录因子则与先前的附录因捆绑在一起,形成多蛋白综合体。只有当所有适当因素都受约束时,RNA聚合酶才会认识到复杂之处,并与DNA绑在一起,并开始转录。One of the more complex eukaryotic gene regulation processes is during . What genes must be turned on and when during development must that genes be expressed so that tissues and organs form from simple cells?
::比较复杂的电子营养基因调节过程之一是在过程期间。 在开发过程中,什么基因必须开动,什么时候必须表达基因才能使组织和器官从简单的细胞中形成?Regulation of Gene Expression During Development
::开发过程中基因表达监管What makes the heart form during development? What makes the skin form? What makes a structure become an arm instead of a leg? These processes occur during development because of a highly specific pattern of . This intensely regulated pattern of gene expression turns genes on in the right cell at the right time, such that the resulting proteins can perform their necessary functions to ensure proper development. Transcription factors play an extremely important role during development. Many of these proteins can be considered master regulatory proteins , in the sense that they either activate or deactivate the transcription of other genes and, in turn, these secondary gene products can regulate the expression of still other genes in a regulatory cascade. Homeobox genes and gap genes are important classes of transcription factors utilized during development.
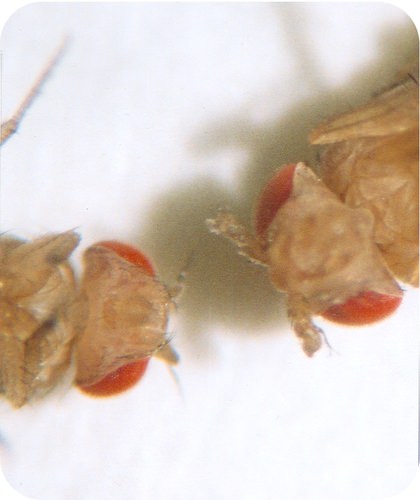
::发育过程中的心脏形态是什么? 皮肤形态是什么? 是什么使结构变成手臂而不是腿? 是什么使结构变成手臂而不是腿? 这些过程是在发育过程中发生的,因为有非常具体的模式。 这种受到严格管制的基因表达模式在正确的细胞里,在正确的时间里使基因在正确的细胞里发生变化,因此由此产生的蛋白质可以发挥必要的功能以确保适当的发展。 移植因素在发展过程中发挥着极为重要的作用。 这些蛋白质中有许多可以被视为管理性的主蛋白质,即它们可以激活或取消其他基因的转录,反过来,这些次级基因产品可以调节其他基因在监管层中的表达。 Homeobox 基因和差距基因是开发过程中使用的重要转录因素类别。Effect of Hox Gene Mutation. Scientists caused a mutation in a hox gene of this fruit fly. As a result of the mutation, a leg grew out of its head where an antenna should have developed (fly on right). Normal fly (fly on right).
::霍克斯基因变异的效果。 科学家引发了这一果蝇的Hox基因基因突变。 由于突变,一只腿从头部长出来,而天线本应在那里( 向右飞行 ) 。 普通飞行( 向右飞行 ) 。Homeobox Genes
::主邮箱 GenesHomeobox genes contain a highly conserved DNA sequence known as a homeobox and are involved in the regulation of genes important to development. A homeobox is a 180 base pairs long highly conserved segment of DNA; it encodes a 60 amino acid within the protein known as the homeodomain , which can bind DNA through a helix-turn-helix motif. Proteins with a homeodomain are therefore transcription factors. These factors typically switch on series of other genes, for instance, the genes needed to encode the proteins to make a leg.
::Homeobox 基因含有高度保存的DNA序列,称为homeobox, 并参与管理对发展十分重要的基因。 Homeobox 是180对长期高度保存的DNA基配; 它在蛋白质中编码了60氨酸, 称为homeodomain, 可以通过螺旋- 转弯- helix motif 将DNA捆绑起来。 因此, 蛋白质与 homeodomemain 是转录因素。 这些因素通常转换为其他基因系列, 例如, 将蛋白质编码成腿所需的基因 。The homeobox genes were first found in the fruit fly Drosophila melanogaster in the lab of Walter Gehring at the University of Basel, Switzerland, and then in the African clawed frog Xenopus laevis in the group of Eddy De Robertis at the same institution. Homeobox genes have subsequently been identified in many other , from to and mammals including humans. Homeobox genes have even been found in , for example the unicellular yeasts, and in plants.
::在瑞士巴塞尔大学Walter Gehring实验室的果蝇Drosophila melanogaster中,首先发现了软木箱基因,然后在同一所Eddy De Robertis组的非洲爪蛙Xenopus Laevis中发现了软木箱基因。后来在许多其他动物中发现了软木箱基因,包括人类和哺乳动物。软木箱基因甚至还在一些植物中发现了,例如单细胞酵母和植物中的软木箱基因。A particular subgroup of homeobox genes are the Hox genes . Protein products of Hox genes function in patterning the body, providing the placement of certain body parts during development. In other words, Hox genes determine where limbs and other body segments will grow in a developing fetus or larva . in any one of these genes can lead to the growth of extra, typically non-functional body parts in invertebrates . The Antennapedia mutation in Drosophila results in a leg growing from the head in place of an antenna. A mutation in a vertebrate Hox genes usually results in miscarriage.
::霍克斯基因的蛋白质产物在构造身体时发挥作用,在发育过程中提供某些身体器官的放置。换句话说,霍克斯基因决定胎儿或幼虫发育过程中的四肢和其他身体部分会在哪里生长。在这些基因的任何一种基因中,都可能导致无脊椎动物增加额外、通常不起作用的身体部分。德罗索比拉的天线突变导致从天线头上长出一条腿。脊椎动物Hox基因的突变通常会导致流产。Mutations in homeobox genes can produce easily visible phenotypic changes. An example of a homeobox mutation in Drosophila is known as antennapedia , which results in a fly with legs where the antennae should be. Another homeobox mutation results in a fly with a second pair of wings . Furthermore, the duplication of homeobox genes can produce new body segments, further demonstrating the importance of these genes.
::软木箱基因中的突变可以产生易见的眼部变化。 德罗索比拉的一例软木箱突变被称作天线,它导致一只腿上有天线的苍蝇。另一个软木箱突变可以产生第二对翅膀的苍蝇。此外,对软木箱基因的重复可以产生新的身体部分,进一步证明了这些基因的重要性。Gap Genes
::差距基因A gap gene controls the shape of a developing zygote early in its development. Many of these genes were first identified in Drosophila based on the discovery of mutant embryos and flies. The products of these genes, when mutated, produce gaps in a rather uniform arrangement of cells. These gaps will result in the loss of a body segment in the developing embryo, causing a gap in the normal body plan. Therefore, each gap gene is critical for the development of a section of the organism . Each gap gene is expressed in a vertical band or segment in the early embryo. This segment correlates with the region that is absent in the mutant ( Figure ).
::突变胚胎和苍蝇发现后,这些基因的产物在突变后,在相当统一的细胞安排中产生差距。这些差距将导致胚胎发育中身体部位的丧失,导致正常身体计划出现差距。因此,每个差距基因对于有机体的某一部分发育至关重要。每个差距基因在早期胚胎中以垂直波段表示。这个部分与变种(图示 ) 中不存在的区域有关。One example of a gap gene is the Krüppel gene, which regulates the activity of a number of other genes. Krüppel literally means "cripple" in German, named for the crippled appearance of mutant larva. Gap genes are defined by the effect of a mutation in that gene, and Krüppel is one such effect. Other gap genes are known as tailless and knirps (a "squirt or whippersnapper"). Gap genes encode transcription factors which directly effect the expression of additional genes involved in embryo segmentation , called the pair-rule genes . Pair-rule genes are expressed in alternating segments within the developing embryo. Pair-rule genes have very creative names, such as even-skipped, hairy, odd-skipped, odd-paired, sloppy paired and fushi tarazu , which is Japanese for “few segments.”
::差距基因的一个例子就是管理许多其他基因活动的Krüppel基因。 Krüppel字面上的意思是德国语的“cripple ” , 以变异幼虫的畸形外形命名。 差距基因由突变该基因的影响来界定,而Krüppel就是这种影响之一。 其他差异基因被称为无尾和kniprps (“quirt 或 hippernapper ” ) 。 差距基因编码了直接影响到胚胎分解中涉及的其他基因表达的分解因素,称为对等分界基因。 等分界基因在发育中的胚胎中以交替的分块来表达。 等相形基因具有非常创造性的名称,如均位、毛、奇形、奇形、奇形、奇形、毛状配对和毛状等,而日本语系为“细片部分 ” 。Gap genes control the expression of other genes within specific regions of cells in the developing organism. This allows specific genes to be expressed in certain cells at the appropriate stage of development.
::基因差距控制着发育中的有机体中细胞特定区域内其他基因的表达方式,从而使特定基因能够在开发的适当阶段在某些细胞中表达。Complex Regulation
::复杂条例Gap genes themselves are under the effect of maternal effect genes, such as bicoid and nanos. Gap genes also regulate each other to achieve their precise striped expression patterns. The maternal effect is when the phenotype of offspring is partly determined by the phenotype of its mother, irrespective of genotype . This often occurs when the mother supplies mRNA or proteins to the egg , affecting early development. In developing Drosophila, maternal effects include axis determination.
::差距基因本身受母性影响基因的影响,如双胞胎和纳米基因; 差距基因还相互调节,以达到精确的分层表达模式; 母性效应是,不论基因类型如何,后代的苯型部分由其母亲的苯型决定,这经常发生在母亲向蛋提供mRNA或蛋蛋蛋蛋蛋蛋时,影响早期发育; 在开发Drosophia时,母性效应包括轴心测定。The bicoid maternal effect gene is transcribed in the nurse cells of the mother and then the mRNA is transferred to the oocyte. Mutant embryos from homozygous mutant bicoid mothers fail to produce head and thorax structures.
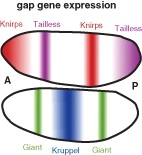
::母体的护士细胞转录出母体对母体的双细胞影响基因,然后将MRNA转至卵细胞中,同质体变异体母体的异体胚胎无法产生头部和胸腔结构。Gap gene expression. Shown is the expression pattern of four gap genes, Krüppel, Giant, Knirps, and Tailless, in a developing Drosophilia embryo. Note how the expression of these genes creates an unique pattern resulting in gaps in what was a rather uniform arrangement of cells.
::差距基因表达方式。 Shown是四种差距基因的表达模式, Krüppel, Giant, Knirps, 和无尾无尾,在正在发育的Drosophilia胚胎中。 注意这些基因的表达方式如何形成一种独特的模式,导致细胞结构中一种相当统一的模式存在差距。The bicoid protein activates a number of gap genes. Bicoid encodes a homeodomain-containing transcription factor , and is expressed in a gradient within the embryo. Bicoid positions gap and pair rule gene expression along the anterior-posterior axis of the developing Drosophila embryo.
::生物蛋白质会激活一些空白基因。 生物体会编码含有本族生物的转录因子,以胚胎内的梯度表示。 生物体在发育中的德罗索比亚胚胎的内侧轴沿线,在生物体位置和成对规则基因表达上存在差距和对等规则。The intricate and complex regulation of these developmental genes is demonstrated by the regulation of the Krüppel gene. Like other gap genes, Krüppel is specifically expressed in certain segments of the developing embryo. This gene is up and down regulated by five proteins: bicoid, hunchback, tailless, knirps and giant. Krüppel is activated when the bicoid protein gradient declines steeply at the central part of the embryo, and inhibited by high levels of hunchback, and high levels of giant and tailless, which establishes the anterior boundary of Krüppel expression. Krüppel is also inhibited by knirps and activated by low levels of bicoid and low levels of hunchback, which establishes the posterior boundary of Krüppel expression.
::这些发育基因的复杂和复杂的监管表现在对Krüppel基因的监管上。与其他差距基因一样,Krüppel在发育中的胚胎的某些部分中表现得特别明确,这种基因由五种蛋白质(bicorid)、驼背、尾巴、克尼普斯和巨型)来来回调节。当生物蛋白质梯度在胚胎的核心部分急剧下降,并受到高水平的驼背和高水平的巨型和尾巴的抑制,从而形成Krüppel表达的近端边界时,Krüppel也会受到knirps的抑制,并且受到低水平的双细胞和低水平的驼背的激活,后者确定了Krüppel表达的后方边界。Summary
::摘要-
Homeobox genes are involved in the regulation of genes important to development. They encode transcription factors.
::Homeobox基因参与管理对发展十分重要的基因,它们编码了转录系数。 -
Gap genes control the shape of a developing zygote early in its development. Gap mutants are missing segments in their embryos. These genes are highly regulated.
::差距基因在发育初期就控制着正在发育的zygote的形状。差距变种人在胚胎中缺少部分。这些基因受到高度管制。
Review
::回顾-
Why is gene regulation an important aspect of development?
::为什么基因管制是发展的一个重要方面? -
What is a homeobox gene? A gap gene? Why are these genes important?
::什么是原声盒基因?什么是空隙基因?为什么这些基因重要? -
Give three examples of gap genes and discuss their mutations.
::举三个差距基因的例子,讨论它们的突变。 -
What is meant by a maternal effect gene?
::母性效应基因意味着什么? -
The homeobox is a sequence of ______ nucleotides in the DNA that codes for a polypeptide consisting of ________ amino acids.
::主机箱是DNA中核糖核酸的序列 用于编码由氨基酸组成的聚虫酸。 -
What would cause a grasshopper whose thorax bears two pairs of legs and one pair of antennae? A grasshopper usually has antennae on its head.
::何以导致一个长着两双腿和一对天线的头? 一只头上通常有天线。
-
Homeobox genes are involved in the regulation of genes important to development. They encode transcription factors.