分类学 - 高级
章节大纲
-
In biology , what would classification refer to?
::在生物学中,分类是指什么?There are millions and millions of , so classifying organisms into proper categories can be a difficult task. To make it easier for all scientists, a classification system had to be developed.
::因此,将生物体分类为适当类别可能是一项困难的任务。 为了方便所有科学家,必须开发一个分类系统。Taxonomy
::分类学Billions of years of evolution on Earth have resulted in a huge variety of different types of organisms. For more than two thousand years, humans have been trying to organize this great diversity of life. The classification system introduced by the Swedish botanist Carolus Linnaeus in the early 1700s has been the most widely used classification for almost 300 years.
::地球上数十亿年的进化导致了各种各样的生物。 两千年多来,人类一直试图组织这种巨大的生命多样性。 瑞典植物学家卡罗尔斯·林瑙斯在1700年代初引入的分类制度是近300年来最广泛使用的分类制度。Scientific classification is a method by which biologists organize living things into groups. It is also called taxonomy . Groups of organisms in taxonomy are called taxa (singular, taxon ). You may already be familiar with commonly used taxa, such as the and species. A kingdom is a major grouping of organisms, such as plants or . A species includes only organisms of the same type, such as humans ( Homo sapiens ) or lions ( Panthera leo ). The modern biological definition of a species is a group of organisms that are similar enough to mate and produce fertile offspring together. In a classification system, kingdoms, species, and other taxa are typically arranged in a hierarchy of higher and lower levels. Higher levels include taxa such as kingdoms, which are more inclusive. Lower levels include taxa such as species, which are less inclusive.
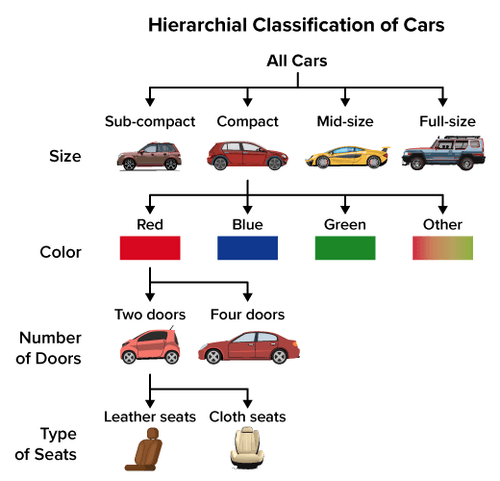
::科学分类是生物学家将生物组织成群体的一种方法,它也称为分类学。分类学中的生物群称为分类学( singulal, excon)。你们可能已经熟悉常用的分类学,例如物种和物种。王国是一个主要的生物群,例如植物或物种。一个物种只包括同类生物体,例如人类(Homo sapiens)或狮子(Panthera leo) 。一个物种的现代生物定义是一个生物群,足以同时交配和产生肥沃后代。在一个分类制度中,王国、物种和其他分类学通常是在更高层次和较低层次上排列的。更高层次包括诸如王国等更具包容性的分类学。较低层次包括诸如物种等的分类学,而这种分类则不那么广泛。This type of hierarchical classification can be demonstrated by classifying familiar objects. For example, a classification of cars is shown in Figure . The highest level of the classification system includes all cars. The next highest level groups cars on the basis of size. Then, within each of the size categories, cars are grouped according to first one trait, then another trait, and so on. Higher taxa (for example, compact cars) include many different cars. Lower taxa (for example, compact cars that are blue and have two doors and cloth seats) contain far fewer cars. The cars in lower taxa are also much more similar to one another.
::此类等级分类可以通过对熟悉物体进行分类来证明。例如,图中显示了汽车分类。分类制度的最高层包括所有汽车。下一个最高层根据大小将汽车分组。然后,在每一大小类别中,汽车按先一个特点、然后另一个特点等等分组。高级分类群(例如,紧凑汽车)包括许多不同的汽车。下层分类群(例如,蓝色的紧凑汽车,有两扇门和布座)包含的汽车要少得多。下层分类群中的汽车也相似得多。Cars can be classified or grouped based on various traits. In this classification, the most inclusive groups are the size categories, such as all compact or mid-size cars. The most exclusive groups in this classification share several additional traits, including color, number of doors, and type of seats. Note that just one group for each trait is further divided as an example. Why Biologists Classify
::为什么生物学家分类Why do biologists classify organisms? The major reason is to make sense of the incredible diversity of life on Earth. Scientists have identified millions of different species of organisms. Among animals, the most diverse group of organisms is the insect. More than one million different species of have already been described. An estimated nine million insect species have yet to be identified. A tiny fraction of insect species is shown in the beetle collection in the Figure .
::生物学家为何对生物进行分类?主要的原因是了解地球上令人难以置信的生命多样性。科学家已经查明了数百万种不同的生物。在动物中,最多样化的生物群体是昆虫。已经描述了100多万种不同的物种。估计有900万种昆虫物种尚未查明。图中甲虫的收集中显示了一小部分昆虫物种。Only a few of the more than one million known species of insects are represented in this beetle collection. Beetles are a major subgroup of insects. According to some estimates, beetles makeup about 40 percent of all insect species and possibly up to 25 percent of all known species of organisms. As diverse as insects are, there may be even more species of , another major group of organisms. Clearly, there is a need to organize the tremendous diversity of life. Classification allows scientists to organize and better understand the basic similarities and differences among organisms. This knowledge is necessary to understand the present diversity and the past evolutionary on Earth.
::同昆虫一样,昆虫的种类可能更多,是另一大类生物。显然,需要组织生命的巨大多样性。分类使科学家能够组织和更好地了解生物的基本相似性和差异。这种知识对于了解地球上目前的多样性和过去的演进是必要的。Early Classification Systems
::早期分类制度One of the first known systems for classifying organisms was developed by Aristotle. Aristotle was a Greek philosopher who lived more than 2,000 years ago. He created a classification system called the “Great Chain of Being” (See Figure ). Aristotle arranged organisms in levels based on how complex, or “advanced,” he believed them to be. There were a total of eleven different levels in his system. At the lower levels, he placed organisms that he believed were less complex, such as plants. At higher levels, he placed organisms that he believed were more complex. Aristotle considered humans to be the most complex organisms in the natural world. Therefore, he placed them near the top of his great chain, just below angels and other supernatural beings.
::亚里士多德是最早已知的生物分类系统之一,由亚里士多德开发。亚里士多德是希腊哲学家,在2000多年前就曾生活过。他创建了一个称为“大生活链”的分类系统(见图 ) 。 亚里士多德根据复杂程度或“先进程度”将生物排列在一定水平上。 他认为这个系统共有11个不同的水平。 在较低水平上,他安置了他认为不太复杂的生物,如植物。 在较高水平上,他安置了他认为更为复杂的生物。 亚里士多德特认为人类是自然世界中最复杂的生物。 因此,他把生物置于他伟大的链的最顶端, 就在天使和其他超自然生物的下面。The Great Chain of Being was Aristotle’s way of classifying organisms. The basis of Aristotle’s classification was the presumed complexity of organisms. On that basis, Aristotle placed plants near the bottom of the classification and humans near the top. Aristotle also introduced two very important concepts that are still used in taxonomy today: genus and species. Aristotle used these two concepts in ways that are similar to, but not as precise as, their current meanings. He used the term species to refer to a particular type of organism. He thought each species was unique and unchanging. He used the term genus (plural, genera ) to refer to a more general grouping of organisms that share certain traits. For example, he grouped animal species with similar reproductive structures together in the same genera.
::亚里士多德还引入了当今在分类学中仍然使用的两个非常重要的概念:基因和物种。亚里士多德使用这两个概念的方式与它们当前的含义相似,但并不精确。他用物种一词指某类生物。他认为每种物种都是独特和不变的。他用基因(多元、基因)一词指具有某些特征的更一般性的生物组。例如,他将具有类似生殖结构的动物组群放在同一个基因组中。As early naturalists learned more about the diversity of organisms, they developed different systems for classifying them. All these early classification systems, like Aristotle’s, were based on obvious physical traits, either of form or function. For example, in one classification system, animals were grouped together on the basis of similarities in movement . In this system, bats and were grouped together as flying animals, and fishes and whales were grouped together as swimming animals.
::早期自然学家们对生物的多样性有了更多了解,他们开发了不同的分类系统。 所有这些早期分类系统,如亚里士多德的分类系统,都基于明显的物理特征,无论是形式还是功能。 比如,在一个分类系统中,动物根据运动的相似性被组合在一起。 在这个系统中,蝙蝠被组合在一起,作为飞行动物,鱼类和鲸鱼被组合在一起,作为游泳动物。Summary
::摘要-
Taxonomy is the scientific classification of organisms.
::分类学是对生物进行科学分类。 -
Scientists classify organisms in order to make sense of the tremendous diversity of life on Earth.
::科学家对生物进行分类,以便了解地球上生命的巨大多样性。
Review
::回顾-
Define taxonomy.
::定义分类学。 -
Explain why biologists need to classify organisms.
::解释为什么生物学家需要将生物分类。 -
What is the most diverse group of animals?
::最多样化的动物群是什么? -
Create a hierarchical taxonomy to classify writing implements, such as pens and pencils. Use a diagram to show your taxonomy.
::创建一个等级分类系统, 用于分类写作工具, 如笔和铅笔。 使用图表显示您的分类 。
-
Taxonomy is the scientific classification of organisms.