细菌(细菌)和细菌(细菌)
章节大纲
-
Wouldn't you want these to be sterile?
::你不想这些不育吗?Sterilization removes and other disease-causing agents from things like surgical instruments. So, yes, of course you would want these instruments to be sterile. What would happen otherwise?
::绝育和其他致病剂从外科器械等东西中除去。所以,是的,当然,你希望这些器械不育。否则会怎样呢?Control of Bacteria
::控制细菌(细菌)和细菌Today, while many medical advances have been made to safeguard against infections by , through the use of vaccination and antibiotics , pathogens continue to threaten human life. Social advances such as food safety, hygiene, and treatment have had a great effect on reducing the threat of some pathogens.
::今天,虽然通过使用疫苗和抗生素,在预防感染方面已经取得了许多医学进步,但病原体继续威胁人的生命,诸如食品安全、卫生和治疗等社会进步对减少某些病原体的威胁产生了巨大影响。The most significant actions that reduced the incidence of were better sanitation, improved personal hygiene practices, better sewage treatment, better nutrition, and better living conditions for people. Overcrowded, unhygienic living conditions are excellent breeding grounds for disease.
::降低发病率的最重要行动是改善环境卫生、改善个人卫生习惯、改善污水处理、改善营养和改善人民生活条件。 过度拥挤、不卫生的生活条件是绝佳的疾病滋生地。Bactericide
::细菌A bactericide is a substance that kills bacteria and, preferably, nothing else. Bactericides are either disinfectants, antiseptics, or antibiotics. Disinfectants are antimicrobial agents that are applied to non-living objects (surfaces) to destroy microorganisms. Examples of disinfectants include chlorine bleach and hydrogen peroxide. Disinfectants are different from both antibiotics, which destroy microorganisms within the body, and antiseptics, which destroy microorganisms on living tissue , such as skin. However, there are some and bacteria that are not killed by disinfectants.
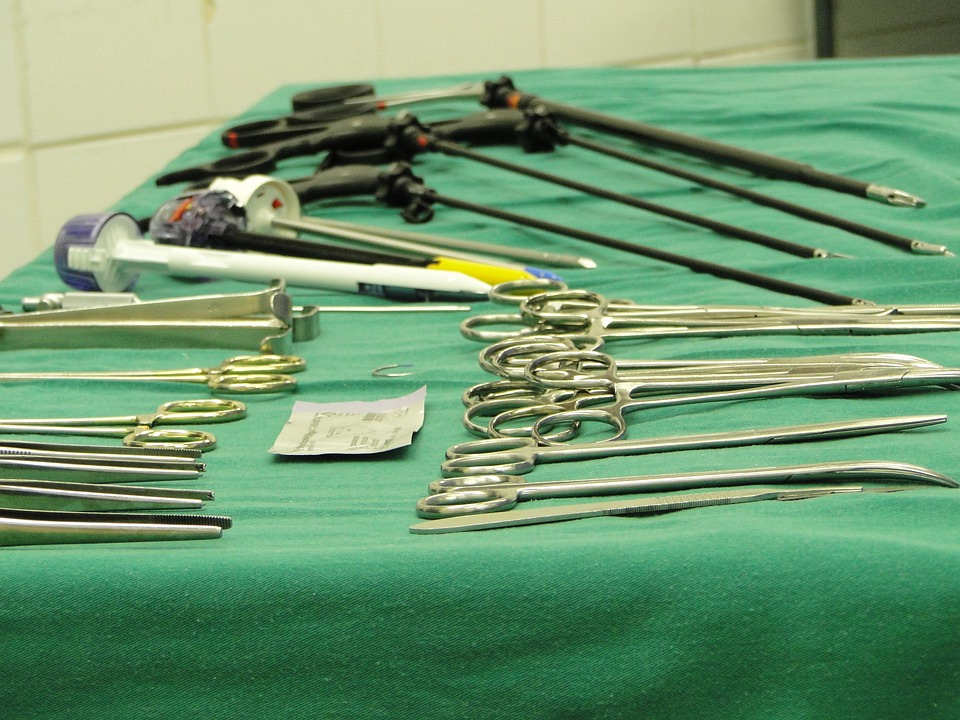
::杀菌剂是一种杀死细菌的物质,最好是其他物质。杀菌剂是消毒剂、抗菌剂或抗生素。除菌剂是用于非生物物体(表层)的抗微生物剂,用于摧毁微生物。消毒剂的例子包括氯漂白剂和过氧化氢。除菌剂不同于摧毁人体微生物的抗生素和将微生物破坏如皮肤等生物组织中的微生物的抗菌剂。但是,有些细菌和细菌并没有被消毒剂杀死。In hospitals, infections can be prevented by antiseptic measures, such as sterilizing the skin before piercing it with the needle of a syringe. Proper care of catheters and tubing that are placed in a person’s body is important to prevent infection, especially by S. aureus , as shown in Figure . Surgical and dental instruments are also sterilized to prevent contamination and infection by bacteria. Doctors, nurses, and other health care personnel are reminded to frequently wash their hands because contaminated hands are a major method of transmission for hospital-acquired illnesses, such as MRSA.
::在医院,可以通过抗消毒措施预防感染,例如在用注射器针刺穿皮肤前对皮肤进行消毒,适当护理放置在人体中的导管和管子对预防感染非常重要,尤其是S. Aureus感染,如图所示。外科和牙科工具也进行绝育,以防止细菌污染和感染。 医生、护士和其他保健人员经常被提醒洗手,因为被污染的手是传染医院疾病的主要方法,如MRSA。Staphlococcus aureus bacteria found on the inside of a catheter. The sticky-looking substance between the round cocci bacteria is biofilm, which is made of polysaccharides. Biofilm protects the bacteria from disinfectants, which makes these bacteria very likely to cause an infection in a patient.
::在导管内部发现的斯塔夫洛科库斯亚尿素细菌。圆锥菌之间的粘附物质是生物胶片,由聚沙焦素组成。生物胶片保护细菌免受消毒剂的危害,这使得这些细菌极有可能在病人体内造成感染。Sterilization
::绝育Sterilization refers to any process that kills or eliminates disease-causing agents from surfaces, equipment, foods, medications, or biological culture media. A widely-used method for heat sterilization is the autoclave. Autoclaves commonly use steam heated to 121 o C (250 o F), at 103 kPa (15 psi) above atmospheric pressure. Solid surfaces are sterilized when heated at this temperature for at least 15 minutes or to 134 o C for a minimum of 3 minutes. Proper autoclave treatment will inactivate all , bacteria, viruses, and also bacterial spores, which can be quite resistant. Ionizing radiation can be used to sterilize objects such as medical instruments and disposables. The high- energy rays cause lethal to occur in bacterial .
::绝育是指从表面、设备、食品、药物或生物培养介质中杀死或消除致病剂的任何过程。热消毒的一种广泛使用的方法是高压板。自动刀片通常使用蒸汽加热至121°C(250oF),高于大气压力103千帕(15皮西),在这种温度下加热至少15分钟或134°C至少3分钟时,固体表面被消毒。适当的自动板处理将停止所有细菌、病毒和细菌螺旋体的活化,这些细菌、病毒和细菌螺旋体可以相当耐药性。离子辐射可用于消毒,例如医疗器械和一次性物品。高能射线在细菌中造成致命作用。Pasteurization
::消省Cooking is way of killing bacteria that are in food. Most bacteria in food are killed by cooking at temperatures above 60 o C (140 o F). Pasteurization is the process of heating liquids, such as milk and fruit juice, to destroy pathogens. The process was named after its inventor, French scientist Louis Pasteur. Food can also be sterilized by irradiation. Small doses of ionizing radiation may be used to remove bacteria on food or other organic material. It is important to remember that irradiated food is not radioactive and that radiation only removes the bacteria on the food at that time. It does not prevent future contamination.
::烹饪是杀死食物中的细菌的一种方式,食物中的细菌大多在60摄氏度以上(140摄氏度)的温度下被烹饪杀死;消毒是牛奶和果汁等取暖液体销毁病原体的过程;这一过程是以发明者法国科学家路易斯·巴斯德命名的;食物也可以通过辐照消毒;小剂量的电离辐射可以用来清除食物或其他有机材料上的细菌;重要的是,必须记住辐照食物不是放射性的,辐射只会消除当时食物上的细菌;它不能防止未来的污染。