多元多边函数
章节大纲
-
Introduction
::导言A box manufacturer constructs open boxes by cutting squares from each corner of an 8-inch by 10-inch rectangular piece of cardboard, and folding up the sides.The volume of the box is given by where is the length of each square cut from the paper. The manufacturer wants to know the size of the square to cut from each corner that will yield the box with greatest volume. To answer this question, it is helpful to look at the equation in standard form . begin with the term of the highest degree (in the case of polynomials, the one with the greatest exponent) and continue until the last term is the smallest degree. First, we must distribute in order to determine the degree of each term:This reveals that is a polynomial function . Polynomials represent a large group of models with similar characteristics. Analyzing these functions provides tools to answer questions like the one posed by the box manufacturer.Standard Form of Polynomial Functions
::多元函数的标准格式If is a polynomial function, then
::如果 P(x) 是多式函数, 那么
::P(x) = anxn+an- 1xn-1+an-2xn-2a1x+a0;where the coefficients are real numbers and the exponents are positive integers .
::当系数a, an-1, ..., a1, a1, a0 是真实数字, 指数为正整数时。The 1st nonzero coefficient , is the leading coefficient . The term is called the leading or dominant term. The degree of the polynomial is . For example, the quadratic equation has a leading coefficient of -2 and a leading term of and is of degree . The polynomial is a polynomial with a leading coefficient of 1, and the leading term is , so the degree is .
::第一非零系数(a)为主要系数。Anxn一词称为主要或主要术语。多面方程式的程度为n。例如,四面方程式f(x)2x2+3x-5,主要系数为-2,主要术语为-2,主要术语为-2x2,主要术语为-n=2。多面方程式f(x)=1是一个多面方程式,主要系数为1,主要术语为1x0=1,因此该系数为n=0。A very interesting property of polynomial functions is that they are all continuous—that is, they have no holes or breaks in the graph. In addition to their continuity, the domain of all polynomial functions is the set of all real numbers expressed in interval notation as .
::多式函数的一个非常有趣的属性是,它们都是连续的,也就是说,它们没有在图表中出现孔或断裂。除了它们的连续性外,所有多式函数的域是用间距符号表示的所有真实数字的一组(,)。To understand what a polynomial is, it is helpful to consider examples of functions that are not polynomials. For example, is not a polynomial. Its form shows that the exponent of the single term is not a positive integer.
::要理解多义是什么, 考虑非多义函数的例子是有益的。 例如, f( x) =2x 不是一个多义函数。 F( x) =2x 。 F( x) =2x=2x- 12 的表情显示, 单词的引号不是一个正整数 。Power Function (even, odd)
::Power 函数(偶,奇数)A power function is a function of the form where and i s a real number .
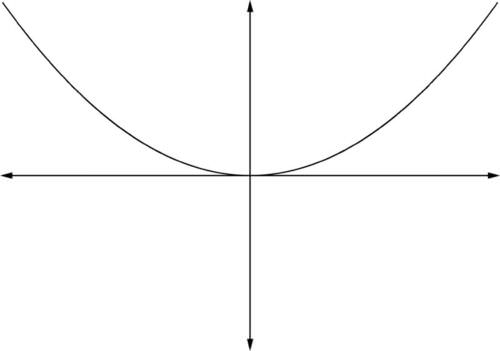
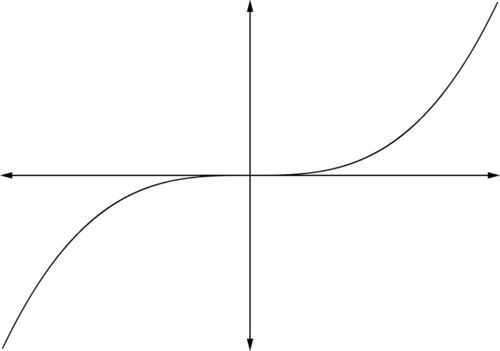
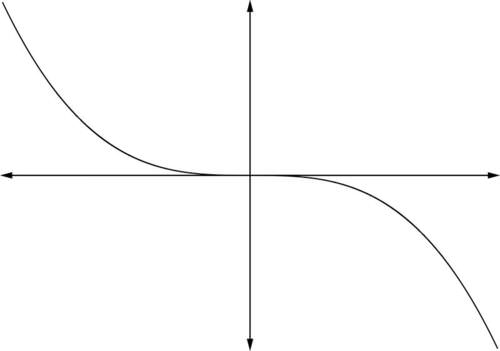
::功率函数是窗体f(x)=axn的函数,其中 a0 和 n 是实际数字。For power functions that are polynomial functions, if is even, then the power function is also called “even,” and if is odd, then the power function is “odd.” The graphs of the 1st five power functions are shown below:
::对于多功能功率函数,如果 n是偶数,则权力函数也称为“偶数”,如果 n是奇数,则权力函数是“奇数”。Notice that each power function has only one and intercept at the origin (0, 0).
::注意每个功率函数在源代码( 0, 0)只有一个 x - 和 y - 拦截 。The end behavior of power functions can be classified as follows:
::权力功能的最终行为可分类如下:-
For even powers of
and
the power function
is U-shaped. The function approaches positive infinity as
approaches positive infinity and
as
approaches
negative
infinity.
::对于 n 和 a>0 的功率, 功率函数 f( x) = 轴为 U 形。 功率接近正无穷度, 如 x 接近正无穷度, x 接近负无穷。 -
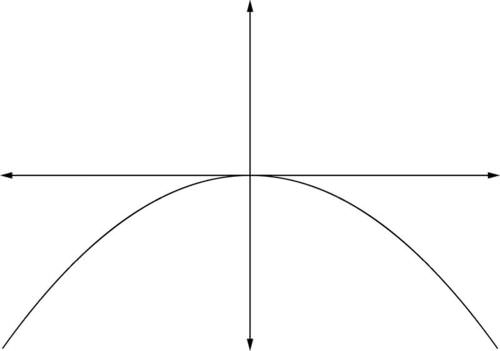
For odd powers of
and
the power function
resembles the cubing family of functions.
The function approaches positive infinity as
approaches positive infinity. Likewise, t
he function approaches negative infinity as
approaches negative infinity.
::对于 n 和 a>0 的奇数功率, 权力函数类似于函数的缩放组合。 该函数会以x 处理正无穷的方式处理正无穷。 同样, 该函数也会以负无穷的方式处理负无穷, 如 x 处理负无穷。
As with quadratics and polynomials, the leading coefficient “stretches” the graph of the function vertically when and "contracts" the graph vertically when . This leading coefficient also impacts the end behavior of the graph depending upon the degree of the polynomial. When is negative, the graph is still stretched or contracted as noted, but it is also reflected about the -axis.
::与二次方位和多面体一样,主要系数是“ 恒度 ” 1 时垂直函数的图形“ 恒度 ” 和“订约” 0 时垂直图形的“契约 ” 。 这一主要系数也根据多面体的程度影响图的末端行为。当一个数值为负值时,该图仍被拉伸或缩缩缩,但也反映 X 轴 。One of the most interesting features of the polynomial function is its graph. The zeros , the coefficients, and the degrees of the terms provide key information about how the function will be graphed. There are a number of methods that can be used to graph polynomial functions, including:
::多面函数最有趣的特征之一是其图形。零、系数和术语的度提供了该函数如何图形化的关键信息。在图形化多面函数时,可以使用若干方法,包括:-
applying
transformations
and
::应用变换和 -
graphing the zeros.
::绘制零数图。
The Graphs of Polynomial Functions Using Transformations
::使用变形的多面函数图The sum of several power functions with positive integer powers is called a polynomial. P olynomial functions can be graphed using transformations of a known graph. There are a number of ways that transformations can be applied to the graphs of power functions.
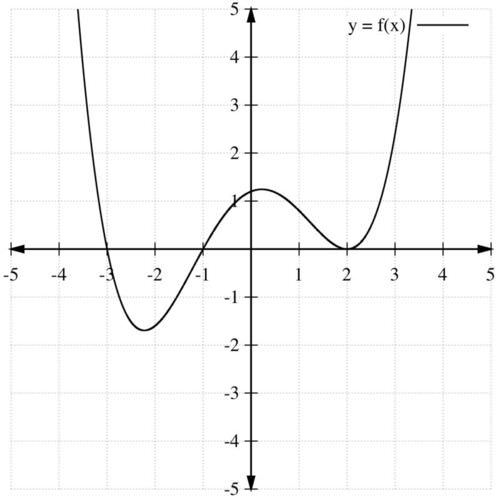
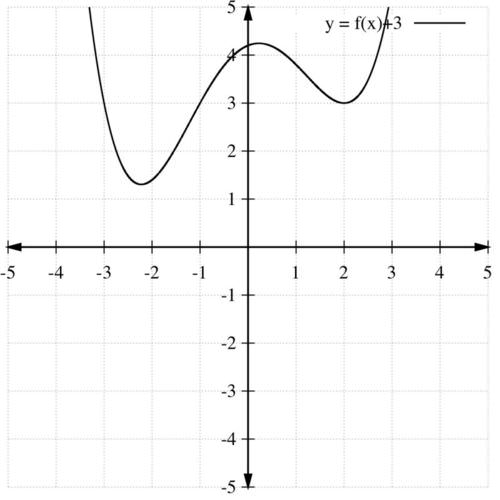
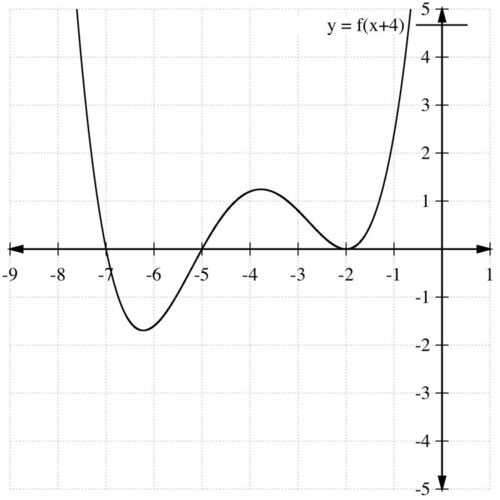
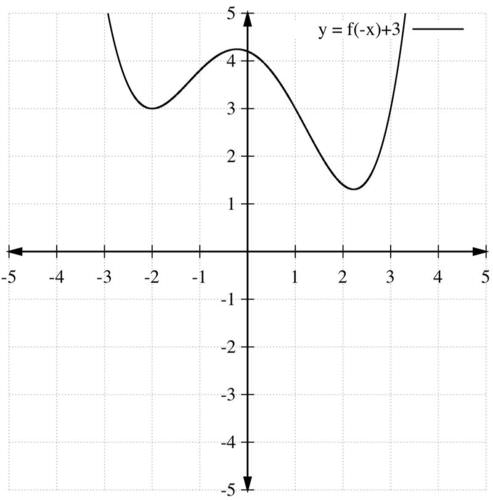
::多个具有正整数功率的功率函数的总和被称为多元体函数。多元体函数可以通过对已知图形的转换来绘制图解。变形可以应用到权力函数的图形中。The graph of is shown below. Use the graph of to graph each of the following: a) , b) , and c)
::f(x) 的图示如下。 使用 f(x) 的图示来绘制以下各图a) f(x)+3, b(b) f(x)+4) 和 c) f(x)+3 。
a) is a vertical shift of up by 3 units:
::f(x)+3 是f(x) 上升3个单位的垂直移动:b) is a horizontal shift of to the left by 4 units:
::f( x+4) 是 f( x) 向左的水平移动, 由 4 个单位向左移动 :c) is a reflection of about the -axis and a vertical shift up by 3 units:
::f( x)+3 反映了y轴的 f( x) 和 垂直向上移动 3 个单位 :Graph Polynomial Functions Using Zeros
::使用零的多倍函数Recall that the real zeros of a function or the roots of a polynomial equation coincide with the - intercepts . For example, the polynomial function
::回顾一个函数的正零或多面方程式根的函数或根根的正弦零与 X 界面相吻合。例如,多面函数
::h(x) =x3+2x2-5x-6in factored form is
::乘数形式为
::h(x) =x3+2x2-5x-6=(x+1)(x-2)(x+3)。To find the zeros, we set
::为了找到零,我们设定
::h(x)=0and solve for :
::x 的解析 :
:x+1)(x-2)(x+3)=0。
We set each factor equal to zero:
::我们设定每个系数等于0x+1)=0,(x-2)=0,(x+3)=0。
::解决所有这三个问题为我们提供了我们的三个解决办法:
::x3, - 1, 2So we say that the roots of the equation are . They are the zeros of the function . The real zeros of are also the intercepts of the graph
::所以我们说方程式的根部是+3,-1,2}。它们是函数 h(x) 的零。h(x) 的正数零也是图y=h(x) 的 x- interviews。This example illustrates a strategy for graphing a polynomial if the zeros of the function are known. To create the general shape of the graph, it is not always necessary to know the actual -values, but simply whether they are above or below the -axis, or positive or negative. To determine this, “test values” between the zeros to evaluate the function and determine if its graph is above or below the -axis between the zeros. While this cannot tell you the height ( -value) of the function between the zeros, you can use the zeros to sketch enough information about the graph to begin a thorough analysis.
::此示例显示如果函数的零为已知值, 多数值图解策略。 要创建图形的一般形状, 并非总有必要了解实际的 y 值, 只需了解这些值是否高于 X 轴或低于 X 轴, 或正值或负值。 要确定这一点, 零之间的“ 测试值” 以评价函数, 并确定其图表是否高于 0 或低于 X 轴。 虽然无法告诉您零之间函数的高度( y- value) , 您可以使用 0 来绘制关于该图形的足够信息, 以开始彻底分析 。Characteristics of Polynomial Functions
::多边函数的特征It is helpful to consider the following facts when graphing any polynomial function:
::在绘制任何多面函数图时,考虑到以下事实是有益的:Number of Zeros
::零数数If is a polynomial function with degree , then:
::如果 f( x) 是一个具有°n+% 1 的多元函数, 那么 :-
The maximum number of real zeros (
-intercepts) is
::最大实际零数为 n。 -
The maximum number of turning points of the graph, which is where the graph has either a local minimum or local maximum, is
::图形的最大转折点数为 n-1, 即图形的本地最小点或本地最大点是 n-1 。
Every polynomial function with degree has at least one zero and at most zeros (counting imaginary or complex zeros).
::具有度 n1 的每个多元函数至少有一个零,最多为nn 零(计算假想或复合零)。End Behavior by Examining the Leading Coefficient
::通过审查 " 主导系数 " 来检查 " 最终行为 "If is the leading term of a polynomial function, then the behavior of the graph as or is the same as the end behavior of one of the following :
::如果 anxn 是多元函数的首字母,那么图形作为 x 或 x 或 x 的动作与以下对象之一的结束行为相同 :1. If and even, then as and .
::1. 如果a>0和n偶数,则f(x)为x____和x____。2. If and even, then as and .
::2. 如果一个 <0和n 偶数,则 f(x) = x 和 x = 。3. If and odd, then as and as .
::3. 如果 a>0 和 n 奇数,则 f( x) = x = f( x) = f( x) 和 f( x) = x = 。4. If and odd, then as and as .
::4. 如果一个 <0和n 奇数,则 f(x) = x = f(x) = f(x) = x = f(x) = f(x) = x = 。Using the leading coefficient in this way implies that as or , then all polynomial functions look like the power function related to the leading term of the polynomial function, which is a powerful and useful generalization for analysis.
::以这种方式使用主要系数意味着,作为 x 或 x,那么所有多边函数都看起来像与多边函数主要术语有关的权力函数,这是分析的有力和有用的概括。Graphing a Polynomial Function
::图形化多面函数To summarize, the following procedure can be followed when graphing a polynomial function:
::概括地说,在绘制多元函数图时,可以遵循以下程序:-
Examine
the leading coefficient to determine the end behavior of the graph.
::检查主要系数以确定图表的最终行为。 -
Find the
-intercept(s) of
by setting
and then solving for
::通过设置 f( x) =0 来查找 f( x) 的 x 界面,然后为 x 解析 。 -
Find the
-intercept of
by setting
and finding
::通过设置 y= f(0) 和查找 y 查找 f(x) 的 Y 接口。 -
Use the
-intercept(s) to divide the
-axis into intervals, and then choose test points to determine the sign of
on each interval.
::使用 x 界面将 x 轴分隔为间隔, 然后选择测试点来确定每个间隔的 f( x) 符号 。 -
Plot the test points.
::绘制测试点。 -
If necessary, find additional points to determine the general shape of the graph.
::如有必要,请另找点来确定图表的一般形状。
Examples
::实例Example 1
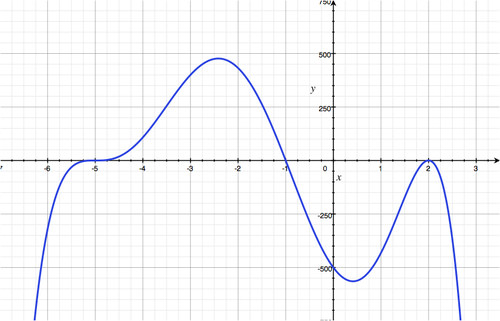
::例1Find the zeros and sketch a graph of the polynomial function
::查找零和草图,以图示显示多元函数g(x)(x-2)(x-2)(x-2)(x+2)(x+1)(x+5)(x+5)(x+5)(x+5)。Solution:
::解决方案 :Step 1: The polynomial function can be written as
::第1步:多面函数可以写为
::g(xx)(x-2)2(x+1)(x+5)3。Step 2: To solve the equation, set equal to zero:
::第2步:为解析方程式,设定 g(x) 等于 0 :
::- (x-2)、2(x+1)(x+5)3=0。Step 3: Set each term equal to 0:
::第3步:规定每个任期等于0:
::x-2=0,x+1=0,x+5=0。Step 4: Solve each:
::步骤4:解决每个问题:
::x=2,x%1,x%5。Notice the occurrence of the zeros in the function. The factor occurred twice (because it was squared), the factor occurred once, and the factor occurred three times. We say that the zero we obtain from the factor has a multiplicity and the factor has a multiplicity .
::注意函数中出现零的发生。系数(x-2)发生两次(因为它是平方),系数(x+1)发生一次,系数(x+5)发生三次。我们说,我们从系数(x-2)获得的零有多重k=2,系数(x+5)有多重k=3。Step 5: To graph , use the zeros to create a table of intervals and see whether the function is above or below the axis in each interval:
::第5步:在图g(x)中,使用零来创建间隔表,并查看函数是否高于或低于每个间隔的 x- 轴:Interval Test value
:g) (x)
Sign of
Location of graph relative to -axis -6 -320 - Below
::x=-5x=5-5 0 NA -2 432 + Above
::x=-1x=-1-1 0 NA 0 -500 - Below
::x=2x=22 0 NA 3 -2048 - Below Step 6: Finally, use this information and the test points to sketch a graph of :
::步骤6:最后,使用这些信息和测试点绘制g(x)图示:Example 2
::例2Find the zeros and sketch a graph of the polynomial function
::查找零和草图,绘制一个多元函数的图形.
::f(x) =x4 -x2 - 56.Solution:
::解决方案 :Step 1: Factor:
::第1步:因数:
:x) =x4-x2-56=(x2-8)(x2+7)。
Step 2: Set :
::第2步:设定 f(x)=0 :
:x2-8)(x2+7)=0。
Step 3: Solve each factor for 0:
::第3步:解决0的每个系数:
::x2-8=0x2=8x_822,and the 2nd factor gives
::第二因数给予
::x2+7=0x2\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\7\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\Step 4: So the solutions are and , a total of four zeros of .
::步骤4:因此,解决办法是22和i7,总共是f(x)的4个零。Only the real zeros of a function correspond to the intercepts of its graph. For this example, only the two zeros correspond to actual intercepts, but and do not, since they are complex.
::函数的正零数只对应其图形的 x- intermission。例如,只有两个零 + 22 对应实际的 x- intermissions,但+ i7 和- i7 不对应,因为它们是复杂的。Example 3
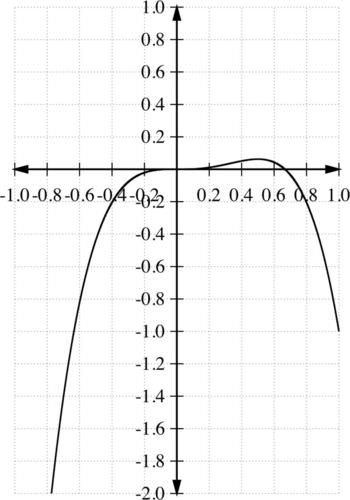
::例3Graph the polynomial function .
::图解多边函数 f(x)\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\2x3\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\Solution:
::解决方案 :Step 1: Since the leading term is then , and even. Thus, the end behavior of the graph as and is that of the 2nd case where .
::第1步:由于前一学期为-3x4,然后是 an3<0,然后是 n=4 偶数。因此,图的结尾行为为 x和 x 。Step 2: For the zeros of the function, solve for :
::第2步:对于函数的零,对x的f(x)=0进行解析:
::- 3x4+2x3=0-x3(3x-2)=0。Step 3: Solve each term set to 0:
::第3步:解决每个任期定为0:
::-x3=0or3x-2=0x=0orx=23。So there are two intercepts, at and at , with multiplicity for and multiplicity for .
::因此,在 x=0 和 x=23 上存在两个 x- 截取器, x=0 和 x= 23 上存在多个 k=3, x=0 和 x= 23 上存在多个 k=1 。The intercept is
::y - 界面是
:0,f(0))=(0,0)。
Step 4: Since the intercepts are 0 and , they divide the axis into three intervals: and . Note the sign of in these intervals:
::第4步:由于X-截取为0和23,它们将x-轴分为三个间隔,0,(0,23)和(23,()。注意这些间隔中的f(x)符号:
Interval Test Value
:fx)
Sign of
Location of points on the graph -1 -5 - below the -axis + above the -axis 1 -1 - below the -axis Step 5: The test points give three additional points to plot: and The graph is a synthesis of all of this information:
::第5步:试验点提供了另外3个点进行绘图-1,5,12,116)和(1,1)。
Example 4
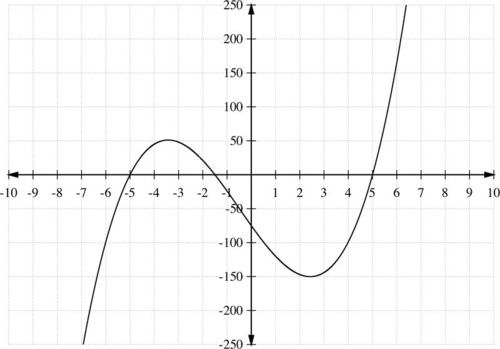
::例4Graph the polynomial function
::图形多圆函数.
::g(x)=2x3+3x2-50x-75。Solution:
::解决方案 :Step 1: Notice that the leading term is , where is odd and . This tells us that the end behavior will take the shape of the 3rd case, where as and as , for end behavior . For the and intercepts:
::第1步 : 注意, 前一学期为 2x3, 其中 n=3 是奇数, 和 an=2>0 。 这告诉我们, 最终行为将呈现第3个案例的形状, 其中 f( x) 和 f( x) 和 f( x) 和 f( x) 和 f( x) 和 x 。 对于 x- 和 y- internations 来说 :
::g(x)=02x3+3x2-50x-75=0。Step 2: F actor the polynomial by grouping:
::第2步:通过组别乘以多数值 :
:2x+3)(x2)-(2x+3)(25)=0(2x+3)(x2)-25)=0(x+5)(x-5)(2x+3)=0。
Step 3: Setting each of the factors equal to zero, we can calculate that the zeros are -5, 5, and . Divide the axis into four intervals:
::步骤3:将每个因素设定为等于零,我们可以计算零是5、5和-32。将x-轴分成四个间隔:The intercept is .
::y- 界面是 (0,f(0)) = (0,- 75) 。Step 4: Now choose test points from each interval and find :
::第4步:现在从每个间隔中选择测试点并找到 g(x) :Interval Test value Value of and its sign Location of points on graph -6 -99 below the -axis -2 21 above the -axis 0 -75 below the -axis 6 165 above the -axis Step 5: From the information obtained, we can roughly sketch the graph (below):
::步骤5:从获得的信息中,我们可以大致勾画出图表(以下):Example 5
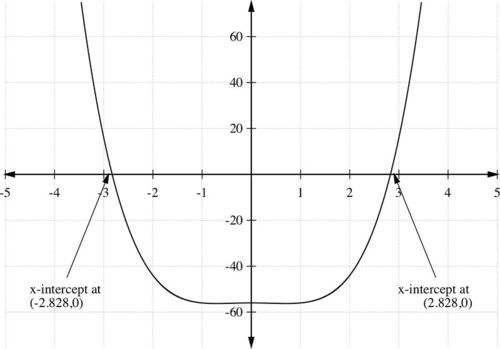
::例5Now, the manufacturer's question can be answered. The volume function is:
::现在,制造商的问题可以解答。 体积函数是: V( x) =x( 8- 2x)( 10- 2x) = 4x3- 36x2+80x,which yields the following intercepts and end behavior:
::产生以下拦截和最终行为:, , , as , and as .
:0,0,(4,0),y=(x-3)(x+3)(x-2),f(x) = x__,f(x) = x__,f(x) = x__)。
From the following graph, the maximum volume is obtained when squares that are 1.5 inches by 1.5 inches are cut from the corners of the cardboard:
::从下图中,从纸板角切开1.5英寸乘1.5英寸的方形时,最大体积为:
Review
::回顾Find the real roots for the following cubic polynomials, and graph:
::查找以下立方形多面形的根和图 :-
::y=(x- 3)(x+3)(x-2)
::y=(x- 3)(x+3)(x-2) -
::y= (x+5)(x+2)(x-2)
::y= (x+5)(x+2)(x-2) -
::y=( 3x+3)( x2+2x+6)
::y=( 3x+3)( x2+2x+6) -
::y=(x- 4)( 2x2+3)
::y=(x- 4)( 2x2+3) -
::y=(x-1)(-2x2-5x-10)
::y=(x-1)(-2x2-5x-10)
Graph the functions below using a graphing calculator or program and determine the number of real roots. Give at least one factor of each polynomial from the graphed solution:
::图形计算器或程序,然后确定真实根数。从图形解析的解决方案中至少给出每个多数值的一个系数 :-
::y=x3 - 3x2 - 2x+6 y=x3 - 3x2 - 2x+6
::y=x3 - 3x2 - 2x+6 y=x3 - 3x2 - 2x+6 -
::y=x3+x2 - 3x- 3
::y=x3+x2 - 3x- 3 -
::y=x3+2x2 - 16x- 32
::y=x3+2x2 - 16x- 32 -
::y= 2x3+13x2+9x+6
::y= 2x3+13x2+9x+6 -
::y=2x3+15x2+4x-21
::y=2x3+15x2+4x-21
Describe the following graphs (include zeros, end behavior, and test points in between):
::描述下图(包括零、结束行为和中间的测试点):-
::y=x4 - 5x2+2x+2
::y=x4 - 5x2+2x+2 -
::y=x4+3x3-x3 y=x4+3x3-x-3
::y=x4+3x3-x3 y=x4+3x3-x-3 -
::yx4+x3+4x2_x+6 yx4+x3+4x2+6
::yx4+x3+4x2_x+6 yx4+x3+4x2+6 -
::yx4 - 5x3 - 5x2+5x+6 yx4 - 5x3 - 5x2+5x+6
::yx4 - 5x3 - 5x2+5x+6 yx4 - 5x3 - 5x2+5x+6 -
::y2x4 - 4x3 - 5x2 - 4x- 4
::y2x4 - 4x3 - 5x2 - 4x- 4
Review (Answers)
::回顾(答复)Please see the Appendix.
::请参看附录。 -
For even powers of
and
the power function
is U-shaped. The function approaches positive infinity as
approaches positive infinity and
as
approaches
negative
infinity.