轮调的几何软件
章节大纲
-
Rotations with a Grid
::带有网格的旋转Recall that a rotation is one example of a rigid transformation . A rotation of about a given point takes each point on a shape and moves it to such that is on the circle with center and radius and
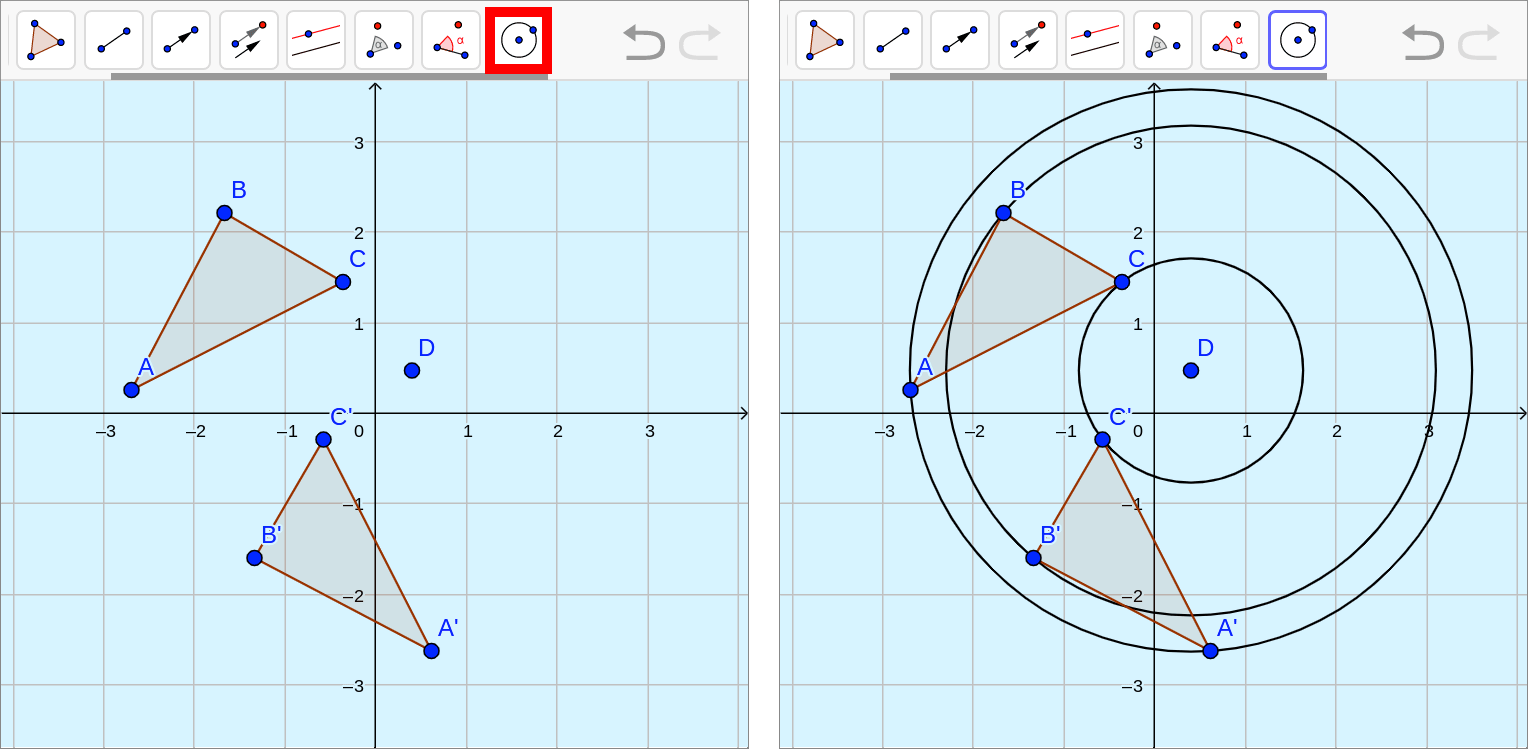
::回顾旋转是僵硬转换的一个例子。 大约一个给定点 O 的旋转在形状 P 上每个点, 并移动到 P , 这样 P 就会在圆上, 中间 O 和半径 OP 和 QPOP 。Below, quadrilateral has been rotated counterclockwise about point to create new quadrilateral (the image).
::以下四边形 ABCD 已旋转 90 / o o 点左右, 以创建新的四边形 A_B_C_D}( 图像 ) 。
Rotation W ithout a Grid
::无网格旋转When you are working on a grid (or graph paper), it's possible to perform rotations of or by using slopes to find perpendicular lines . But what if the grid is not there , o r the rotation is not a multiple of Then it is not as easy to do the rotation because there are no grid lines as a guide.
::当您在网格( 或图形纸) 上工作时, 使用斜度来查找垂直线可以进行 90 , 180 或 270 的旋转。 但是, 如果网格不在那里, 或者旋转不是90 的倍数, 那么进行旋转就不那么容易了 , 因为没有网格线作为向导 。To perform a rotation without a grid, you need to:
::要进行无网格的旋转,您需要:-
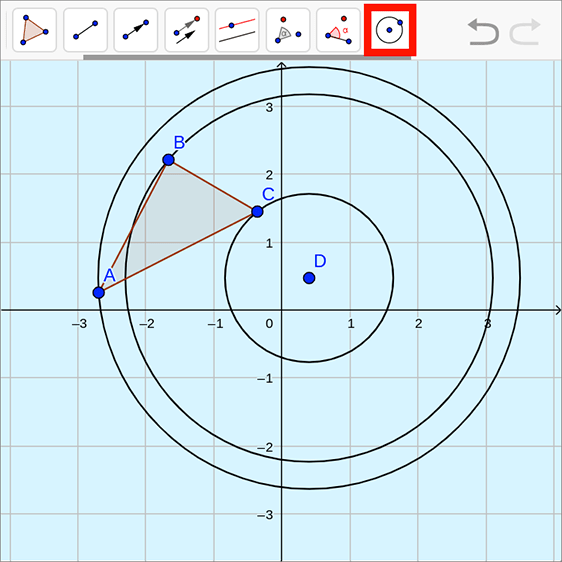
Construct a circle with center
through one of the points that define the shape.
::通过定义形状的点之一, 构造一个圆形, 以中 O 为中心 。 -
Construct a segment connecting that point that defines the shape with point
.
::构造连接此点的段段, 以此定义形状与点 O 的形状 。 -
Construct an
angle
of the given number of degrees for the rotation from this segment in the direction specified. The endpoints for this angle should be on the circle previously drawn.
::构造从此段向指定方向旋转给定的度数角度。 此角的端点应该位于先前绘制的圆上。 -
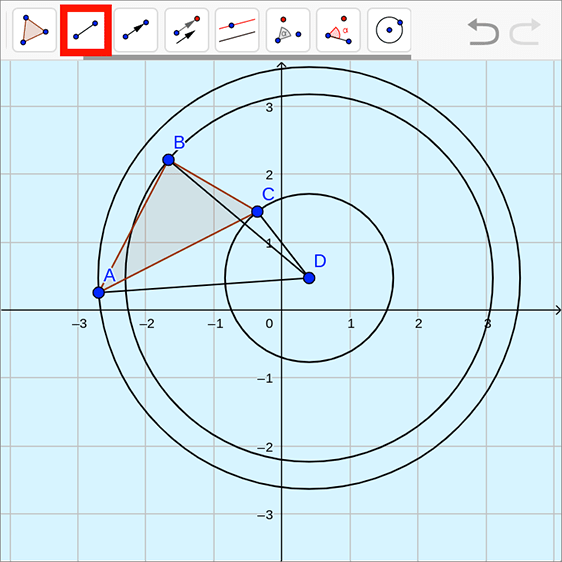
Repeat the above three steps for all the points that define the shape.
::对于定义形状的所有点,重复以上三个步骤。 -
Connect the endpoints to form the rotated image.
::连接端点以形成旋转的图像 。
Doing this by hand requires careful construction of circles and angles using a compass and a protractor . Geometry software simplifies this process, because geometry software commonly has a “rotate” tool. There are many different examples of geometry software that are free to download.
::手工完成这项工作需要使用指南针和减速器仔细构建圆圈和角度。 几何软件简化了这一过程,因为几何软件通常有一个“ 旋转” 工具。 几何软件有许多可以自由下载的不同例子。
::使用几何软件的轮调
::跟踪在互动中执行多边形旋转的步骤。To perform a rotation, first select the "polygon" tool and create your polygon.
::要执行旋转, 请先选择“ polygon” 工具, 然后创建您的多边形 。Next, use the "point" tool to create the point you will rotate the polygon about (this could be one of the points that defines the polygon, but may also be elsewhere).
::下一步, 使用“ 点” 工具来创建您将旋转多边形的点( 这可以是定义多边形的点之一, 但也可能是其他地方 ) 。Now, rotate the polygon about the point by clicking on the “rotate” tool, then the shape and then the center of rotation point. Specify the number of degrees and direction of rotation in the window that pops up.
::现在, 在点周围旋转多边形, 单击“ 旋转” 工具, 然后是形状, 然后是旋转点的中心。 指定弹出窗口的旋转度和方向 。Note that the points defining the image are labeled with prime notation. At this point you can move point to redefine the center of rotation or change your original shape and your image will move/change accordingly. Make sure to select the cursor button before attempting to move points.
::请注意, 用于定义图像的点会用质标符号标记。 在此点上, 您可以移动点 D 以重新定义旋转中心或更改您的原始形状, 您的图像会相应移动/ 更改。 在试图移动点之前, 请确定选中光标按钮 。
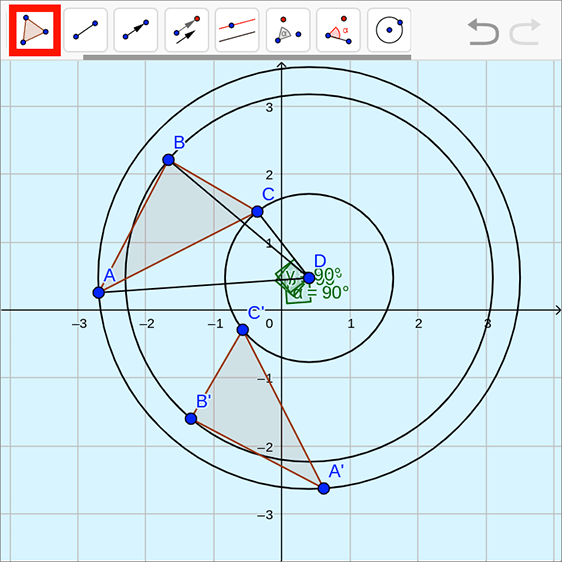
Rotation Proof
::轮调证明
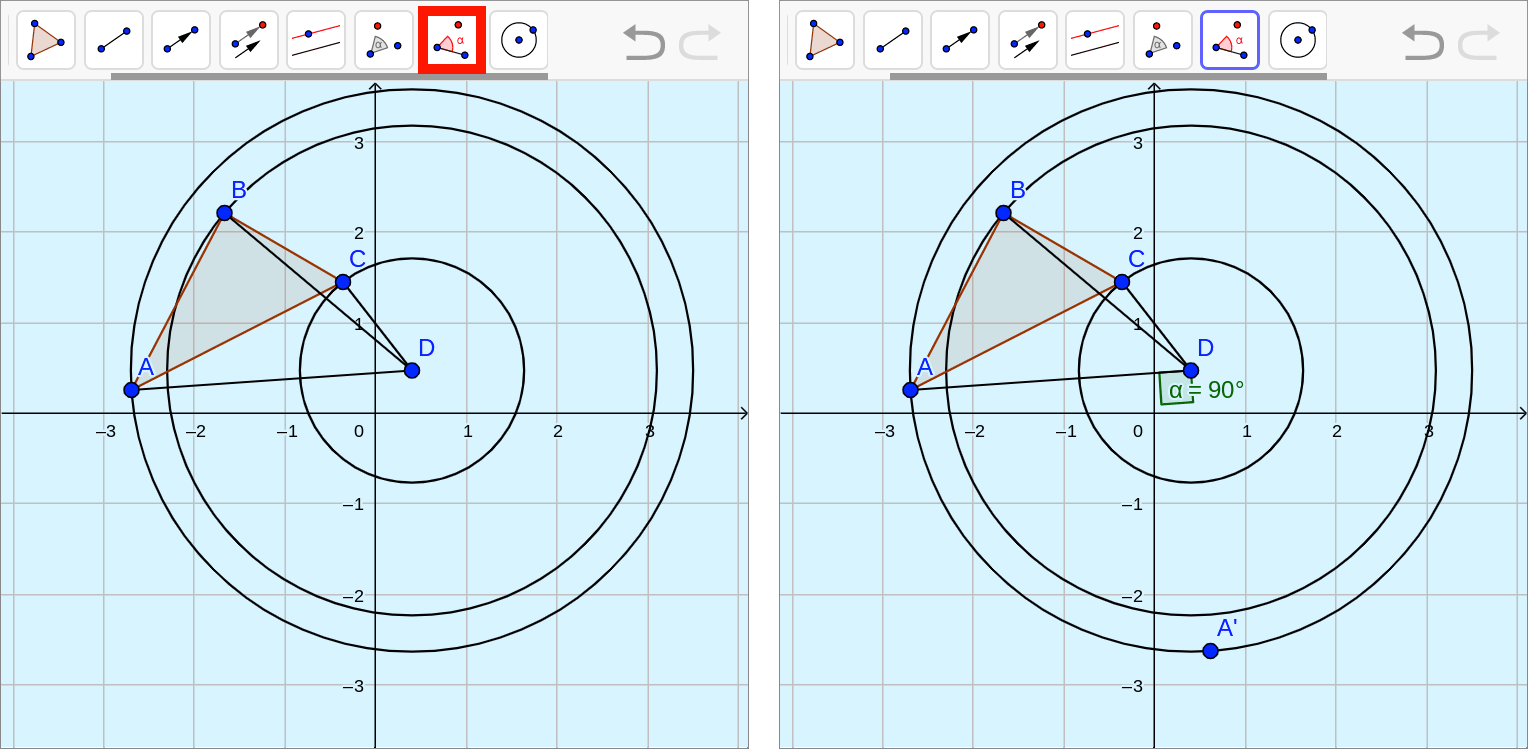
is rotated counterclockwise around point to create
::ABC 沿 D 点旋转90°C 以创建 {A_B_C} 。Show that the center of rotation is the center of circles containing and and and and
::显示旋转 D 的中心是圆圈的中心, 包括 A 、 A 、 B 、 B 、 B 、 C 和 C 。Construct circles by clicking on the “circle with center through point” tool. Construct each circle by selecting point and then one vertex of the original triangle .
::构造圆, 单击“ 圆圈, 中间穿过点” 工具。 构造每个圆圈, 选择 点 D 和 原始三角形 的一个顶点 。T he circle containing point also contains point the circle containing point also contains point and the circle containing point also contains point
::包含点A的圆也包含点A ' ,包含点B的圆也包含点B ' ,包含点C的圆也包含点C ' 。All three circles are centered at point
::所有三个圆圈都集中在D点
Performing Rotations
::执行旋转Rotate counterclockwise about point by using the "rotate" tool for each vertex of the triangle.
::使用“ rotate” 工具对三角形的每个顶点旋转“ ABC90” 。First, using the "circle with center through point" tool to construct circles with centers at point that pass through each of the three vertices that define the triangle. Use the process from the previous example problem to construct the circles.
::首先, 使用“ 圆圈与中点相交” 工具来构建圆圈, 在 D 点的圆圈中心通过 3 个圆顶的每个圆圈来定义三角形 。 使用上一个示例问题的进程来构建圆圈 。Next, selecting the "segment" tool, click on point , then on point . Repeat for vertices and to construct segments connecting each vertex with the center of the circle.
::下一步,选择“ 分区” 工具, 点击 D 点, 然后点击 A 点。 重复 顶点 B 和 C 来构造每个顶点与圆的中心 D 连接的部分 。Then, construct a angle from by selecting the “angle with given size” tool. Select point , then point , and then enter counterclockwise in the window that pops up.
::然后,从 AD 中选择“ 与给定大小对齐” 工具,从 AD 中构造一个 90 。 选择 A 点, 然后输入 D 点, 然后在弹出窗口中输入 90 。will appear.
::将出现A。Repeat for each vertex of the triangle. Then, using the "polygon" tool, connect and to form the triangle image.
::重复三角形的每个顶点。 然后, 使用“ polygon” 工具, 连接 A_ 、 B_ 和 C_ 来形成三角形图像 。Note that it isn't actually necessary to first construct the circles and line segments in order to do the rotation in this way. However, they allow you to be confident that your rotation is correct because the image points end up on the same circles as their corresponding points. Also, doing it in this way comes closest to what you would need to do to perform the construction by hand.
::请注意, 不需要首先构造圆圈和线段来进行这种旋转。 但是, 它们允许您相信您的旋转是正确的, 因为图像指向的圆圈与相应的点相同。 同时, 这样做最接近于您手动进行构造需要做什么 。Compare and contrast the 'Rotation Proof' and 'Performing Rotation' methods for explored above.
::比较并对比上面所探讨的“ 轮换证明” 和“ 履行轮换” 方法。Both methods correctly performed a rotation. The first method was faster. The second method made it more clear that each point that defined the triangle was being rotated around a circle with center . The second method shown is closer to the method you would have to use to perform a rotation by hand.
::两种方法都正确进行了旋转。 第一种方法更快。 第二种方法更清楚地说明, 定义三角形的每个点都围绕圆圈旋转, 圆心为 D。 显示的第二种方法更接近于您手动旋转时使用的方法 。
Examples
::实例实例实例实例Example 1
::例1Geometry software has a rotation function that makes it easy to rotate an object about a point. Can you perform a rotation using geometry software without using that function?
::几何软件有一个旋转功能,可以方便地将对象旋转到某个点。您可以使用几何软件进行旋转而不用该功能吗?You can perform a rotation using geometry software without the "rotate" tool by constructing circles and angles. This method was shown in the second example titled "Performing Rotations."
::您可以使用不使用“ 旋转” 工具的几何软件, 通过构建圆圈和角度来进行旋转。 此方法显示在第二个例子“ 实现旋转” 中 。Example 2
::例2Try doing the same rotation without using the "rotate" tool by constructing circles and angles as shown in the second example titled "Performing Rotations". How can you verify that you have done this correctly?
::尝试同样的旋转而不使用“ 旋转” 工具, 构建圆圈和角度, 如第二个例子“ 实现旋转 ” 所示 。 您如何验证您是否这样做正确 ?Answers will vary depending on what polygon you construct. Look back at the guidance section for help. To check that you have performed the rotation without the "rotate" tool correctly, just make sure that both images ended up in the same place.
::答案会因您构建的多边形而不同。 请回看指导部分的帮助。 要检查您是否在“ 旋转” 工具没有正确的情况下进行了旋转, 请确保两个图像最终位于同一位置 。Summary -
To perform a rotation without a grid, construct circles and angles using a compass and protractor.
::进行无网格的旋转,使用罗盘和减速器构造圆圈和角度。 -
Geometry software simplifies the rotation process with a rotate tool.
::几何软件使用旋转工具简化旋转过程。
Review
::审查审查审查审查1. Create a polygon.
::1. 创建多边形。2. Rotate the polygon counterclockwise about one of its own points using the rotate button.
::2. 使用旋转按钮逆时针旋转多边形100++ 的多边形100++ 。3. Rotate the polygon clockwise about the same point that you chose in #2 using the rotate button. What happened? Why?
::3 使用旋转按钮旋转多边形 260 顺时针旋转与您在 # 2 中选择的相同点。 发生什么了 ? 为什么 ?4. Rotate the polygon counterclockwise about a point that is not on the polygon.
::4. 逆时针旋转多边形 90++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++5. Rotate the polygon counterclockwise about the same point you used in #4 without using the rotate button by constructing circles and angles. Is your rotation correct?
::5. 逆时针旋转多边形 90++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++6. Create a regular decagon. To do this, instead of selecting “polygon”, select “regular polygon”. Plot the first two points of your polygon, then enter the number of points/sides you want your polygon to have (10).
::6. 创建正则十边形。要做到这一点,请选择“正多边形”,而不是选择“多边形”。绘制多边形的前两点,然后输入您想要多边形的点/边数(10)。7. Where would the center of rotation have to be for it to be possible to rotate the decagon less than and have the image be indistinguishable from the original decagon? Find a way to plot this center of rotation.
::7. 旋转中心要在哪里才能旋转小于360的十角形,并使图像与原十角形无法区分?找到绘制这一旋转中心的方法。8. What's the smallest number of degrees you can rotate the decagon about the point from #7 and have the image be indistinguishable from the original decagon? Test this out.
::8. 您可以将十角点从 # 7 旋转, 图像与原十角无法区分的十角点的最小度数是多少? 测试一下这个 。9. Rotations are rigid transformations which means that distance is preserved. Create a new polygon and rotate it about some point. Verify that distance has been preserved by using your geometry software to measure sides of your original polygon and their images. Select “distance or length” from one of the drop down menus. Then, click on each line segment that you want to measure to see its length.
::9. 旋转是僵硬的变换,这意味着保持距离。创建一个新的多边形并将其旋转到某个点上。通过使用您的几何软件测量原始多边形及其图像的侧面来验证保持了距离。从一个下降的菜单中选择 " 距离或长度 " 。然后,单击每个行段来测量其长度。10. Rotations are rigid transformations which means that angles are preserved. Verify that angles have been preserved by using your geometry software to measure two corresponding angles for your polygon and image from #9. Select “angle” from the same drop down menu as in #9. To find what angle you want to measure, click on the three points you would use to name the angle. You must click on the points in clockwise order for it to measure the correct angle.
::10. 旋转是硬形变换,这意味着角度得到保存。验证角度是否通过使用您的几何软件对多边形和图象的两种对应角度进行测量而得以保存。从 # 9 中从相同的下调菜单选择“ 矩形 ” 。 要找到您想要测量的角, 请单击您要用的三个点来命名角。 您必须单击时钟中的点, 以便测量正确的角度 。11. Construct a circle.
::11. 构建圆。12. Where would the center of rotation have to be for a rotation of any number of degrees to produce an image that is indistinguishable from the original circle? Test this idea.
::12. 旋转中心在哪里,必须由多少度的旋转产生与原圆无法区分的图像?测试这个想法。13. Could all rotations of circles also have been translations or reflections? Explain.
::13. 圆圈的所有轮回是否也是翻译或反思?14. Create a center of rotation that is outside of the circle.
::14. 建立一个圆外的旋转中心。15. Explore how you might be able to rotate the circle counterclockwise about the center of rotation without using the rotate button by constructing additional circles and angles.
::15. 探索如何在不使用旋转按钮的情况下,通过建造额外的圆圈和角度,在旋转中心周围反时针旋转135圆。16. Create a regular hexagon. (In the drop-down menu for create polygon there is an option to create a regular polygon.) What is the measure of each interior angle of the hexagon? Why? Rotate the hexagon this number of degrees around one of the vertices. Repeat this rotation around each vertex. What do you observe? Notice that the rotations covered the plane without any overlaps or gaps. How is this possible? Are there other regular polygons this would work for? If so, which ones, and why? Experiment.
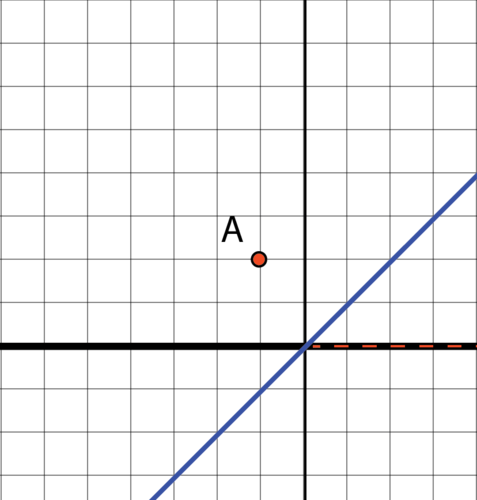
::16. 创建一个普通的六边形。 (在创建多边形的下拉菜单中,有一个选项可以创建一个普通的多边形) 六边形的每个内角的度量是多少? 为什么? 在一个顶端周围旋转这个度数的六边形。 在每个顶端上重复这个旋转。 您观察什么? 注意旋转覆盖了平面, 没有任何重叠或空隙 。 这怎么可能 ? 是否有其他的常规多边形? 如果是, 哪些多边形和为什么? 实验 。17. Consider the blue line below. If you were to rotate an image of the line 180 degrees about point A , what would be the result? How about if you rotated the line 360 degrees about point A ?
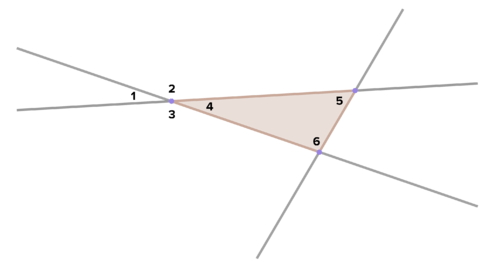
::17. 考虑下方的蓝线。如果你在A点周围旋转180度线的图像,结果会如何?如果你在A点周围旋转360度线呢?18. Look at the triangle below. Is it possible to put one copy of the triangle such that fits perfectly in place of ? Why or why not?
::18. 看看下面的三角形,是否有可能放一个三角形的复本,使4完美地取代1?为什么或为什么不?19. Create a scalene triangle. Call this A . Rotate A around a vertex. Call this image B . Now perform a translation of A that maps a side of A to the corresponding side of B . Call this triangle C . Now continue using translations to map any of the existing triangles so that one side coincides with the corresponding side on an existing image. What do you observe? Explain how this is possible in the context of the previous problem.
::19. 创建一个缩放三角形。 在顶点周围调用 A. 旋转 A 180。 调用此图像 B。 现在, 执行 A 的翻译, 绘制 A 的一面到 B 的对应一面。 调用此三角 C 。 现在, 继续使用翻译来绘制任何现有的三角形, 使一面与现有图像的对应一面相吻合 。 您观察什么? 解释在前一个问题的背景下, 这怎么可能 。Review (Answers)
::审查(答复)Click to see the answer key or go to the Table of Contents and click on the Answer Key under the 'Other Versions' option.
::单击可查看答题键, 或转到目录中, 单击“ 其他版本” 选项下的答题键 。 -
Construct a circle with center
through one of the points that define the shape.