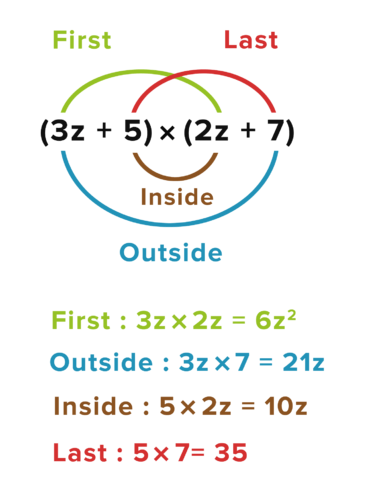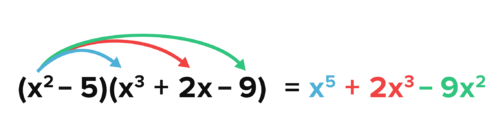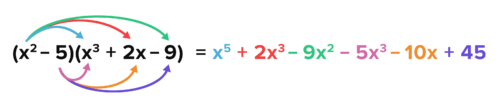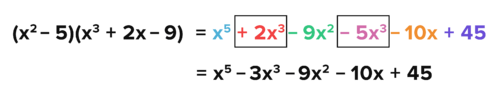乘以多边多边形
章节大纲
-
Learning Objectives
::学习目标-
Find the area of a rectangle or square with
polynomial
side lengths.
::查找矩形或正方形区域,其边长为多面。 -
Understand that polynomials
function
much like integers
when multiplied
.
::理解多数值函数与乘以整数时的整数非常相似 。 -
Multiply
using the box and FOIL methods
, and in
a real-world context.
::使用盒子和FOIL方法乘法, 在现实世界中。 -
Know and apply the
binomial
theorem
.
::了解并应用二元论定理。
Introduction: Area
::导言:面积Architects use computer programs that scale shapes.
::建筑师使用计算机程序 来缩放形状Which of the following rectangles has a greater area?
::以下哪个矩形的面积更大?The area of a rectangle can be found by multiplying the length by the width. You would be correct in saying that the area of rectangle A is 60 square units, and the area of rectangle B is 15 square units. While this is correct, there is not enough information to assume that the square units used in rectangle A and rectangle B are the same size. This fluid nature of scale is something that computer programs use to model shapes. Engineers use 3-D modeling programs to design objects with dimensions that are scaled within the program. Architects use computer programs that scale shapes in both 2 and 3 dimensions. As dimensions change, polynomial expressions are created using relative dimensions and a scale factor to find side lengths, perimeters, areas, volumes, etc.
::矩形 矩形 区域 的 矩形 区域 可以 以 宽度 乘以 长度 来 找到 矩形 区域 的 区域 。 您的描述是正确的 : 矩形 A 区域是 60 平方 单位 , 矩形 B 区域是 15 平方 单位 。 虽然这是对的, 但没有足够信息可以假定矩形 A 和 矩形 B 的 方形 单位是 相同的大小 。 比例表的这种流动性质是计算机程序用来模拟形状的 。 工程师们使用 3 - D 建模 程序来设计在程序内缩放大小 的物体。 建筑师们使用 计算机 程序 , 以 2 和 3 维 的 大小 形状为形状 。 由于 尺寸的变化, 尺寸变化, 多数值表达方式是使用相对尺寸和 尺度系数 来找到边长、 周界、 区域、 体积等 。Use the interactive below to explore how to represent area with polynomials .
::使用下面的交互方式来探索如何以多面形表示区域 。
Extension: Multiplying Polynomials by Monomials
::扩展名: 以单数乘以多边数Use the interactive below to review the before applying it in the next activity .
::使用以下互动关系来审查在下次活动中应用之前的情况。
Activity 1: Multiplying Polynomials
::活动1:乘数聚合体As with addition and subtraction , multiplying polynomials works much the same way as multiplying integers . The example below illustrates this using what is called the “box method.” In this method, the polynomials are broken up into expanded form and the terms are written across the columns and rows of a box. Each cell represents the product of the term at the top of the column and term at the start of the row.
::与添加和减法一样,多数值的乘法与乘法整数的乘法基本相同。下面的例子用所谓的“框法”来说明这一点。在这个方法中,多数值以扩大的形式分解,术语在框的列和行之间写出。每个单元格在列的顶部代表术语的产物,在行的起始处则代表术语的产物。Multiplying 3059 x 215 with the box method.
::用盒式方法乘以 3059 x 215 。Multiplying 3059 x 215 in expanded form with the box method.
::乘以 3059 x 215 乘以盒式法的扩大型号 。This method is particularly useful for multiplying polynomials with many terms. The boxes help organize the process of multiplying each term in the first polynomial by each term in the second.
::此方法对于以多个术语乘以多个术语特别有用。 框有助于组织第一个多术语中每个术语乘以第二个术语的过程 。Example
::示例示例示例示例Find the product of ( x 2 + 4 x − 7 ) ( x 3 − 8 x 2 + 6 x − 11 )
::查找 (x2+4x-7)(x3-8x2+6x-11) 的产品To begin, align the two polynomials along the top and the left side of a rectangle, making a row or column for each term.
::要开始, 将两个多面形对齐, 沿着矩形的顶部和左侧对齐, 每个词组设置一行或列 。Multiplying a polynomial by a trinomial using the box method.
::使用框法用三角乘法乘以多数值。Each small rectangle represents the product of the term at the top of the column and the start of the row. Once all small rectangles are filled, combine like terms to simplify.
::每个小矩形代表词词在列的顶部和行首的产物。一旦所有小矩形都填满,则将词词合并来简化。Use the interactive below to find the product of the polynomials above.
::使用下面的交互方式查找以上多面体的产物。
Activity 2: FOIL
::活动2:FOILExample
::示例示例示例示例The length of a rectangular garden plot is 3 x − 1 feet. The width of the plot is x + 5 feet. Write a polynomial to model the area of the garden plot.
::矩形花园地块的长度为 3x-1 英尺。 地块的宽度为 x+5 英尺。 写一个多面形图来模拟花园地块的面积 。3x-1 by x+5 garden plot
::3x-1 x+5 花园地块As shown in the introduction, the area of the rectangular garden plot is the product of the length and the width.
Area = ( 3 x − 1 ) ( x + 5 )
::如导言部分所示,矩形花园地块面积是长度和宽度的产物。面积=(3x-1)(x+5)Using the box method to multiply integers takes advantage of the distributive property.
::使用框法乘以整数利用分配属性。Distributive Property
::分配财产a ( x + y ) = ( a ⋅ x ) + ( a ⋅ y )The same way that 3 is distributed to each term in the expression 3 ( 4 x − 2 ) , ( 3 x − 1 ) is distributed to each term in ( x + 5 ) , like this:
::在(x+5)中,以同样方式将3个词分配给3个词(3(4x-2)、(3x-1)和(x+5)中的每个词,例如:( 3 x − 1 ) ( x + 5 ) = ( 3 x − 1 ) ⋅ x + ( 3 x − 1 ) ⋅ 5
:3x-1(x+5)=(3x-1)x+(3x-1)5)
D istribute again to get the following:
::再次分配以获得以下内容:( 3 x − 1 ) ( x + 5 ) = ( 3 x − 1 ) ⋅ x + ( 3 x − 1 ) ⋅ 5 = ( 3 x ⋅ x ) + ( − 1 ⋅ x ) + ( 3 x ⋅ 5 ) + ( − 1 ⋅ 5 )
:3x-1(x+5)=(3x-1)xx+(3x-1-1)5=(3xxx)+(1xx)+(1xx)+(3x)5)+(1x-5)+(1x-5)
Simplify the resulting expression to obtain the answer.
::简化生成的表达式以获取答案 。( 3 x ⋅ x ) + ( − 1 ⋅ x ) + ( 3 x ⋅ 5 ) + ( − 1 ⋅ 5 ) = 3 x 2 − x + 15 x − 5 = 3 x 2 + 14 x − 5
:3xxx)+(-1xx)+(3x)+(3x)5+(-1x)5+(-15)=3x2-x+15x-5=3x2+14x-5)
Answer: 3 x 2 + 14 x − 5
::答复:3x2+14x-5By the end of the process, each term in the first polynomial is multiplied by each term in the second polynomial. When multiplying binomials, use the mnemonic FOIL to help remember this.
::进程结束时, 第一个多义中的每个词会乘以第二个多义中的每个词。 当乘以二进制时, 请使用 Mnemonic FOIL 来帮助记住这一点 。Multiplying (3z + 5)(2z + 7) with the FOIL method.
::与FOIL方法乘以(3z+5)(2z+7)。P olynomial multiplication can be extended to trinomials.
::多元乘法可延伸至三元乘法。Example
::示例示例示例示例Find the following product:
::查找以下产品x2-5)(x3+2x-9)
M ultiply any polynomials using a method similar to the FOIL method which requires you to multiply each term in the first polynomial by each term in the second polynomial, then combine like terms. To be gin , t ake the x 2 in the first polynomial and multiply it by every term in the second polynomial.
::使用类似于 FIIL 方法的方法乘以任何多边名词,该方法要求您在第一个多边名词中将第一个多边名词乘以第二个多边名词中的每个术语,然后将类似术语合并。要开始,在第一个多边名词中采用 x2 乘以第二个多边名词中的每个术语。Now, multiply the -5 by every term in the second polynomial.
::现在,在第二个多元体中,乘以 - 5 乘以每个术语。Lastly, combine any like terms. In this example, only the x 3 terms can be combined.
::最后,将任何类似术语结合起来,在这个例子中,只有 x3 术语可以合并。Answer: x 5 − 3 x 3 − 9 x 2 − 10 x + 45
::答复: x5-3x3-9x2-10x+45
CK-12 PLIX Interactive
::CK-12 PLIX 交互式互动M ultiply a binomial and a trinomial with distribution.
::乘以二进制和三进制分布。
Activity 3: The Binomial Theorem
::活动3:二子论理Example
::示例示例示例示例Multiply ( x + 2 ) 3
::乘数 (x+2) 3When raising a polynomial to a power, a common mistake is simply distributing the power to each of the terms inside the " data-term="Parentheses" role="term" tabindex="0"> parentheses .
::当向一个大国提出一个多名制时,一个常见的错误就是简单地将权力分配给括号内的每个用语。( x + 2 ) 3 ≠ ( x 3 + 2 3 )
:x+2)3 (x3+23)
Instead consider what the exponent means: multiply the base by itself 2 times.
::反之,考虑一下指数的含义:将基数本身乘以2倍。( x + 2 ) 3 = ( x + 2 ) ( x + 2 ) ( x + 2 )
:x+2)3=(x+2)(x+2)(x+2)(x+2)
T hree polynomials can be multiplied the same as you would multiply three numbers: multiply two of the polynomials and multiply that product by the third.
::3个多元数可以乘以与您乘以3个数字相同的倍数:2个多元数乘以2,并将该产品乘以3。( x + 2 ) ( x + 2 ) ( x + 2 ) = ( x 2 + 4 x + 4 ) ( x + 2 ) = x 3 + 6 x 2 + 12 x + 8
:x+2)(x+2)(x+2)(x+2)=(x2+4x+4)(x+2)=x3+6x2+12x+8)
Answer: x 3 + 6 x 2 + 12 x + 8
::答复: x3+6x2+12x8When binomials are raised to a power, the coefficients form an interesting pattern which is referred to as the Binomial Theorem.
::当二进制被提升到权力时,系数形成一种有趣的模式,称为二进制定理。The Binomial Theorem
::二元论论A method for finding the expansion of a binomial to any power without multiplying it out.Use the interactive below to explore this pattern and how it can be used to raise a binomial to a power quickly.
::使用下面的交互方式来探索这个模式, 以及如何使用它来快速提升一个二元论的力量 。Discussion Question : What other patterns do you see in Pascal’s Triangle? Explain each pattern to the best of your ability. (Example: The sum of each row is 2 n )
::讨论问题:您在帕斯卡尔三角洲中还看到什么其他模式? 尽你最大能力解释每一种模式。 (例如:每行的总和是2n)
Wrap-Up: Review Questions
::总结:审查问题The video below demonstrates how to multiply polynomials.
::下面的影片展示了如何乘数多元论。
Ext ension : Binomial Corkboard
::扩展名: Binomial 纸板Explore the interactive below for more practice multiplying polynomials.
::探索下面的互动, 以便更多练习 乘以多面体 。Summary
::摘要-
The "box method" can be used to multiply polynomials. Align the terms of one polynomial across the top and the terms of the other polynomial along the side. Multiply each pair of terms and combine like terms.
::“ 框方法” 可用于乘以多义 。 将一个多义词的术语对齐, 将另一多义词的术语对齐, 将另一多义词的术语对齐。 将每一对术语乘以一对, 并合并类似术语 。 -
FOIL is another method that can be used to multiply polynomials. Distribute each term from one polynomial to the other polynomial. Next, simplify and combine like terms.
::FOIL 是另一个可以用来乘以多面体的方法。 将每个术语从一个多面体分配到另一个多面体。 下一步, 简化和合并类似术语 。 -
The
Binomial Theorem
is a method for finding the expansion of a binomial to any power.
::Binomial定理是找到将二进制扩展至任何权力的方法。 -
Use the Binomial Theorem to expand expressions in the form
(
a
+
b
)
n
.
::使用 Binomial 定理来展开窗体(a+b)n 中的表达式。 -
The coefficients of the Binomial Theorem can be arranged to build Pascal's Triangle.
::Binomial定理的系数可以安排 建造帕斯卡尔三角。
-
Find the area of a rectangle or square with
polynomial
side lengths.