磁铁和磁性
章节大纲
-
Lesson Objectives
::经验教训目标- Identify properties of magnets.
::识别磁铁的特性。
- Explain why some materials are magnetic.
::解释为什么有些材料是磁材料。
Lesson Vocabulary
::词汇表课程- magnet
::磁磁磁
- magnetic field
::磁磁场
- magnetic force
::磁力
- magnetic pole
::磁极
- magnetism
::磁力
Introduction
::导言Take a look at this futuristic-looking train in Figure . Sure, it looks cool, but do you notice anything else? That's right! Unlike a typical train, this train has no wheels. How can it have no wheels you may wonder? It doesn't need wheels because it levitates, or floats, just above the track using magnets. This is not a normal train, it is a maglev train. The word "maglev" stands for "magnetic levitation." Because it doesn't have wheels that touch the track, it has no friction. Other magnets pull the train forward along the track. This train can go very fast. It can fly over the countryside. It can reach speeds to 480 kilometers (300 miles) per hour! What are magnets and how do they exert such force? In this lesson, you’ll find out.
::看看图中的这列看似未来的列车。当然,它看起来很酷,但你注意到别的东西吗?没错!不像典型的列车,这列列列车没有轮子。它怎么会没有轮子呢?它不需要轮子,因为它用磁铁在轨道上方漂浮或漂浮。它不是普通列车,而是岩浆列车。“岩浆”一词代表的是“磁悬浮”。它没有车轮触碰轨道,也没有摩擦。其他磁铁将火车拖在轨道上。这列火车可以飞得非常快。它可以飞过农村。它可以达到每小时480公里(300英里)的速度;它能达到480公里(300英里)的速度;磁铁是什么,它们如何施加这种力量?在这个教训中,你会发现。Magnets cause this maglev train to speed along its track. Properties of Magnets
::Magnet 的属性A magnet is an object that attracts certain materials. You’re probably familiar with common bar magnets. You can see one in Figure . Like all magnets, this bar magnet has north and south poles. Magnets attract objects such as paper clips that contain iron. Iron is one type of metal that magnets attract. Magnets do not attract every type of metal. Magnets only attract iron, nickel, and cobalt. They do not attract metals like aluminum or copper. You can test this out yourself with a simple magnet.
::磁铁是一种吸引某些材料的物体。 您可能熟悉普通的铁磁铁。 您可以看到图中的磁铁。 和所有磁铁一样, 这块铁磁铁有北极和南极。 磁铁吸引物体, 如含有铁的纸片。 铁是磁铁吸引的一种金属。 磁铁不会吸引每一种类型的金属。 磁铁只吸引铁、 镍和钴。 它们不会吸引铝或铜等金属。 您可以用简单的磁铁来测试它本身 。The north and south poles of a bar magnet attract paper clips. Magnetic Poles
::磁极All magnets have two magnetic poles . The poles are regions where the magnet is strongest. The poles are called north and south. They have these names because they always line up with Earth’s north-south axis. The Earth rotates, or spins, around this imaginary line, or axis. What do you suppose would happen if you cut the bar magnet in Figure in half along the line between the north and south poles? Both halves would also have north and south poles. What if you cut each of them in half again? That's right! All of those pieces would have north and south poles as well. Pieces of a magnet always have both north and south poles.
::所有磁铁都有两个磁极。 电极是磁力最强的区域。 电极被称为北面和南面。 它们有这些名称, 因为它们总是与地球的南北轴相排。 地球绕着这个想象的线或轴旋转或旋转。 如果沿着北面和南面之间的线将条磁铁图一分为二, 你会有什么结果? 两半的电极也是北面和南面的。 如果你把两半的电极都切成两半呢? 没错! 所有这些电磁块都会有北面和南面。 磁铁的碎片总是有北面和南面的。Magnetic Force
::磁力Magnets are able to place a force on certain materials. This force is called a magnetic force . The force a magnet exerts is a little different from the forces you may normally think about. You exert a force on a book when you lift it. You also exert a force on the pedals of your bicycle. In both those cases, those forces cause a change. The change you see in both these cases is called motion. Magnets, too, can produce change. They can produce motion just like you do. Unlike you, magnets do not have to touch something to exert a force. A magnetic force is exerted over a distance. That's right, a magnet can push or pull certain items without ever touching them. That's how the maglev train works.
::磁带可以对某些材料施以力力。 这种力被称为磁力。 磁力与通常你可能想到的力略有不同。 当你举起它时, 你对一本书施以力力。 你对自行车的脚踏板也施以力。 在这两种情况下, 这些力都会产生变化。 在这两种情况下, 你所看到的改变都叫作运动。 磁力也可以产生变化。 它们可以产生运动, 就像你一样。 不像你, 磁力不需要触动某种东西来施加一种力力。 磁力会施加在一定的距离上。 没错, 磁力可以推动或拉动某些东西, 而不触动它们。 这就是磁力列列列列列的原理 。Do you know another type of force that does not require objects to touch? These forces are known as non-contact forces. Another type of non-contact force you may be familiar with is gravity. Gravity too can cause changes in motion. Gravity holds our moon in orbit without touching it. So how do these forces play a role in magnets?
::您知道另一种不需要物体触碰的力量吗? 这些力量被称为非接触力量。 您可能熟悉的另一种非接触力量是引力。 重力也可以引起运动变化。 重力将我们的月亮放在轨道上而不触碰它。 这些力量如何在磁铁中发挥作用?Think about what happens when you place two magnets next to each other. Depending on how you align the poles, different motions occur. The forces the two magnets exert on each other are either an attractive or a repulsive force. North and south poles of two magnets attract each other, while two north poles or two south poles repel each other. So, where does this force come from?
::想象一下, 当您将两块磁铁放在对方旁边时会发生什么。 取决于您如何对齐这些电线杆, 会出现不同的动作。 两块磁铁对对方施加的威力要么吸引人,要么令人厌恶。 两块磁铁的北面和南面吸引对方, 而两块北极或两块南面互相抵抗。 因此, 这股威力来自何方?Magnetic Field
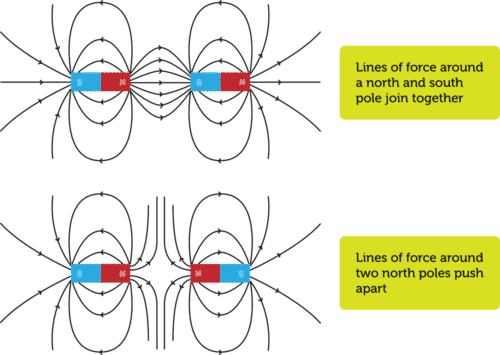
::磁场Magnets have what is called a magnetic field. This invisible field surrounds a magnet. This is the area where a magnetic force is exerted. Figure shows the magnetic field around a bar magnet. Tiny bits of iron, or iron filings, are used to help see the field. These iron filings are then placed under a sheet of glass. When the magnet is placed on the glass, it attracts the iron filings. The pattern of the iron filings shows the lines of force. These lines of force outline the magnetic field. Notice the amount of iron filings around the poles of the agent. The concentration near the poles indicates that these areas exert the strongest force.
::磁磁场有称为磁场的磁场。 这个隐形场环绕磁场。 这是磁力施加的区域 。 图显示磁力的周围磁场 。 图显示磁铁磁磁铁周围的磁场 。 少量的铁块或铁文件被用来帮助观察磁场 。 这些铁文件被放置在玻璃板下面。 当磁铁被放置在玻璃上时, 它吸引铁文件。 铁文件的图案显示了力量线 。 这些强度线勾勒了磁场 。 注意介于磁铁剂杆周围的铁文件数量 。 极附近的浓度显示, 这些地区的强度最大 。Lines of magnetic force are revealed by the iron filings attracted to this magnet. What do you think happens when two magnets are brought near each other? What happens to their magnetic fields? Interestingly, their magnetic fields interact. You can see how in Figure . The drawings show the lines of force. You can see how the north and south poles attract. When like kind poles are near each other they repel each other.
::当两块磁铁相互靠近时会怎样?它们的磁场会怎样?有趣的是,它们的磁场相互作用。你在图中可以看到这些磁场是如何相互作用的。图画显示了力量的线条。你可以看到北极和南极是如何吸引的。当同类极相邻时,它们会互相击退。When it come to magnets, there is a force of attraction between opposite poles and a force of repulsion between like poles. Magnetism and Materials
::磁力和材料Magnetism is the ability of a material to be attracted by a magnet. It also include the ability for some material to act like a magnet. No doubt you’ve handled refrigerator magnets. You can see some in Figure . You probably know they stick to a metal refrigerator. This is what holds your homework up. Maybe your little sister's drawings are hung on the fridge in this manner. Do magnets stick to all materials? Of course not. You have probably checked and they do not stick to other surfaces. They do not stick to wooden doors or glass windows. Wood and glass are not attracted to a magnet. Obviously, only certain materials are attracted to magnets.
::磁铁是一种材料能够被磁铁吸引的能力。 它也包括某些材料能够像磁铁一样行事的能力。 毫无疑问, 你处理过冰箱磁铁。 您可以在图中看到一些磁铁。 您可能知道它们会粘在金属冰箱上。 这正是你作业需要做的。 或许你妹妹的图画会以这种方式挂在冰箱上。 磁铁会粘在所有材料上吗? 当然没有。 你可能检查过它们,它们不会粘在其他表面。 它们不会粘在木门或玻璃窗上。 木和玻璃窗不会被磁铁吸引。 显然,只有某些材料被磁铁吸引。Refrigerator magnets stick to a refrigerator door because it contains iron. Why won’t the magnets stick to wooden cabinet doors? Temporary and Permanent Magnets (Advanced Topic)
::临时和永久磁(高级专题)Materials that have been magnetized may become temporary or permanent magnets. An example of each type of magnet is described below. Both are demonstrated in Figure .
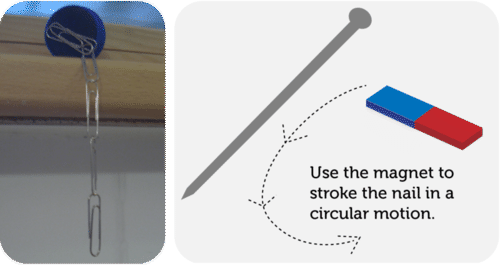
::磁化的材料可能成为暂时或永久的磁铁,以下举例说明每一种磁铁。- If you bring a bar magnet close to pile of paper clips, the paper clips will become temporarily magnetized. As a result, the paper clips will stick to the magnet. They will also stick to each other. What if you are no longer touching the magnet to the paperclips? Will the paperclips still stick together? Once the magnet is removed the paper clips will no longer be magnetized or stick together.
::如果你把铁块磁铁靠近一堆纸片剪片, 纸片剪片就会暂时被磁化。 结果, 纸片剪片会粘在磁铁上, 它们也会粘在一起 。 如果您不再触碰磁铁到纸板上呢? 纸板剪片还会粘在一起吗 ? 一旦磁铁被移走, 纸片剪片将不再被磁化或粘在一起 。
- Try something really cool. Do you think you can make a magnet? If you stroke an iron nail with a bar magnet, the nail will become a permanent (or at least long-lasting) magnet.
::尝试一些非常酷的东西。 你认为你能做磁铁吗?如果你用铁棒磁铁触摸铁钉, 铁钉就会变成永久的(或至少是长期的)磁铁。
Paper clips become temporary magnets when placed in a magnetic field. An iron nail becomes a permanent magnet when stroked with a bar magnet. Some materials are natural magnets. One of the most common is called magnetite. Magnetite is a mineral found in the earth. Magnetite is sometimes called lodestone. Figure shows a chunk of magnetite. It is able to attract iron nails and iron filings. People have known about magnetite for thousands of years. The earliest compasses used magnetite. Their magnetic pointers showed direction. The magnetite spoon compass in Figure dates back about 2000 years.
::一些材料是天然磁铁。 最常见的一种材料是磁铁。 磁铁是地球上发现的矿物。 磁铁有时被称为石石。 图显示了一块磁铁。 它能够吸引铁钉和铁文件。 人们知道磁铁已有数千年。 最早的指南针使用磁铁。 它们的磁点显示方向。 图中的磁铁勺指南针可以追溯到2000年。Magnetite naturally attracts iron nails and filings. Its natural magnetism was discovered thousands of years ago. Lesson Summary
::经验教训摘要- A magnet is an object that attracts certain materials such as iron. All magnets have two magnetic poles. Magnets have a magnetic field. It is this magnetic field that exerts a force on some materials. Opposite magnetic poles attract each other. Unlike poles repel each other.
::磁体是吸引铁等某些材料的物体。 所有磁体都有两个磁极。 磁体有磁场。 磁体是磁场。 磁场对某些材料产生一定的威力。 反磁极相互吸引。 与极相反。
- Magnetism is the ability to be attracted by a magnet. Only some metals are attracted to magnets. These metals include: iron, cobalt, and nickel. When these materials are magnetized, they become temporary or permanent magnets. Magnetite is a natural permanent magnet.
::磁铁是被磁铁吸引的能力,只有某些金属被磁铁吸引。这些金属包括铁、钴和镍。当这些材料被磁化时,它们成为暂时或永久的磁铁。磁铁是一种天然的永久磁铁。
Lesson Review Questions
::经验回顾问题Recall
::回顾- What is a magnet?
::什么是磁铁?
- Define magnetic force.
::定义磁力。
- Give examples of objects that are attracted by magnets.
::举例说明磁铁吸引的物体。
- Identify ferromagnetic materials.
::查明铁磁材料。
Apply Concepts
::应用概念- Draw magnetic field lines around the bar two magnets pictured below.
::在下面的两块磁铁周围绘制磁场线。
Points to Consider
::需要考虑的要点The northern lights that you saw in the opening photo of this chapter are caused by Earth’s magnetic field. You will read about Earth’s magnetic field in the next lesson, "Earth as a Magnet."
::在本章的开映照片中,你看到的北极光是由地球磁场造成的。下一堂课“地球是磁场”将介绍地球磁场。- If you could see Earth’s magnetic field, what do you think it would look like? ( Hint: Look at Figure .)
::如果你能看到地球的磁场,你认为它会是什么样子? (提示:看图.)
- After reading this lesson, can you predict why northern lights are most likely to be visible near Earth’s poles?
::读完这堂课后, 你能预测为什么北极光最有可能出现在地球极附近吗?
- Identify properties of magnets.