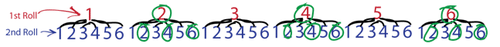复类活动的交叉交错
Section outline
-
There is a classic example of probability studies involving a coin flip. Everyone knows that the probability of getting heads on a single flip is 50%, which means that every time you flip it, there is also a 50% probability of getting tails. The question is, if you have flipped a coin 99 times and got heads every time, what is the probability of getting heads the next time?
::有关硬币翻转的概率研究是一个典型的例子。 人人都知道,在一次翻转上获得头部的概率是50%,这意味着每次翻转时,也有50%的尾部概率。 问题是,如果你每次翻转99下硬币,每次翻转99下,头部,那么下一次获得头部的概率是多少?
After this lesson on the intersection of compound events, we’ll return to this question and see how it does (and doesn’t!) fit with the concept.
::我们将会回到这个问题, 看看这是否符合这个概念。Intersection of Compound Events
::复类活动的交叉交错It should make sense intuitively that the more specific or restricted you make the details of an event , the less probable it becomes for that event to occur. The concept of calculating the total probability of multiple events strung together is the same idea.
::应该直觉地说,你越是具体或受限,事件的细节就会越少发生的可能性。 计算多重事件总概率是同一个概念。If I flip a coin once there are only two possible outcomes :
::如果我翻硬币一次,就只有两种可能的结果:
:头)或(尾)
If I flip the coin twice, there are four possibilities:
::如果我翻翻硬币两次, 有四种可能性:
::H+T或H+H或T+H或T+H或T+TWe know there are a total of four possible outcomes from two coin flips: , , , and , and only one of them: , results in the outcome we want to calculate. Using the simple probability formula, we get:
::我们知道,从两个硬币翻转中共有四个可能的结果:HT、HH、TH和TT,其中只有一个:HH,我们想要计算的结果。使用简单的概率公式,我们得到:
::P(HH)=1 结果4Calculating Probability
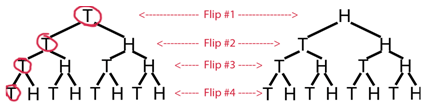
::计算概率1. What is the probability of flipping a coin four times and getting tails all four times?
::1. 翻翻硬币四次和得到尾巴四次的可能性有多大?Create a table listing all of the possible outcomes:
::创建列出所有可能结果的表格 :Now we can look at the bottom row and see that there are a total of 16 possibilities, only one of which is four tails in a row. The probability, therefore, is:
::现在,我们可以看一看底行,看一看总共16种可能性,其中只有一种是一行的四个尾巴。因此,概率是:
::P(4尾尾尾尾尾尾尾尾尾尾尾尾尾尾尾尾尾尾尾尾尾尾尾尾尾尾尾尾尾尾尾尾尾尾尾尾尾尾尾尾尾尾尾尾尾尾尾尾尾尾尾尾尾尾尾尾尾尾尾尾尾尾尾尾尾尾尾尾尾尾尾尾尾尾尾尾尾尾尾尾尾尾尾尾尾尾尾尾尾尾尾尾尾尾尾尾尾尾尾尾尾尾尾尾尾尾尾尾尾尾尾尾尾尾尾尾尾尾尾尾尾尾尾尾尾尾尾尾尾尾尾尾尾尾尾尾尾尾尾尾尾尾尾尾尾尾尾尾尾尾尾尾尾尾尾尾尾尾尾尾尾尾尾尾尾尾尾尾尾尾尾尾尾尾尾尾尾2. What is the probability of rolling two even numbers in a row on a standard six-sided die?
::2. 在标准的六面死亡中连续两次翻滚两个偶数的可能性有多大?Create a table listing all possible outcomes:
::创建列出所有可能结果的表格 :
::P(两个偶数)=9 有利结果36 总结果=936=14Reducing to:
::减少:
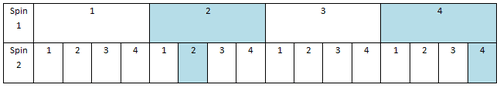
::P(两个偶数)=14或25%3. What is the probability of spinning two 2’s in a row OR two 4’s in a row on a spinner with the numbers 1-4?
::3. 以数字1-4在脊柱上连续旋转2 2 或 2 或 2 或 2 或 连续旋转4 的概率是多少?Create a table listing all possible outcomes, and highlight the favorable ones:
::创建一个列出所有可能结果的表格, 并突出显示有利的结果 :Out of a total of 16 possible outcomes, only 2 fit our description, which gives us:
::在总共16项可能的成果中,只有2项符合我们的描述,即:
::P( 2- 秒或 4- 秒) = 2 有利结果 16 可能的结果= 216= 18= 18 或 12.5%Earlier Problem Revisited
::重审先前的问题The question is, if you have flipped a coin 99 times and got heads every time, what is the probability of getting heads the next time?
::问题是,如果你已经翻了99次硬币 每次都有头, 下次有头的概率是多少?This is a very common example of something called the gambler’s fallacy. It is not a good example of calculating the intersection of compound events because of the way it is worded . The question as written is essentially asking about a single flip of the coin, which is always , because a coin has no memory.
::这是赌徒谬误的一个非常常见的例子。 它不是计算复合事件交叉点的好例子,因为它的用词方式。 书面的问题基本上是关于硬币的一翻一翻,它总是5050,因为硬币没有记忆。From the standpoint of an example of what we have been studying in this chapter, the more useful, and dramatically more difficult question would be:
::从我们在本章中研究的一个例子的角度来看,更有用、更困难的问题是:What is the probability of flipping a coin 100 times and getting heads every time?
::翻硬币一百次 每次都砍头的概率是多少?See the difference? The first question assumes that 99 flips have already occurred and asks about the last flip, the second question asks about all 100 flips.
::看到不同之处了吗?第一个问题假定99个翻转已经发生, 并询问最后一个翻转,第二个问题问所有100个翻转。If you want to know the probability of flipping 100 heads in a row, you could either draw a really long chart of all of the possibilities (like the one in Example A, but much longer), or you could use the that we will be learning in the next lesson. Check it out!
::如果您想知道一次翻转100个头的概率, 您可以绘制一个非常长的图表, 显示所有的可能性( 如例A中的图表, 但要长得多) , 或者您可以使用我们在下一个课程中学习的图表 。 请看看 !Example 1
::例1Example 1
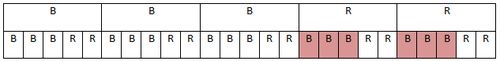
::例1What is the probability of pulling 1 red marble, replacing it, then pulling another red marble out of a bag containing 4 red and 2 white marbles?
::从一个装有4个红色和2个白色大理石的大理石的袋子里拉出另一个红色大理石的可能性有多大?Make a chart:
::绘制图表: 第一次拉: r r r www_ 第二次拉: rrww rrwww rrwww rrwww rrwww rrwww rrwww rrwww rrwww rrrww_The four sets of four red “ ’s” represent the favorable outcomes out of the total of 36, therefore
::四套红色 " r " 代表总共36套中的有利结果,因此P(2红色)=1636=49或44.44=*_________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________Example 2
::例2What is the probability of a spinner landing on “2” and then a “3”, or “6” if there are 6 equally spaced points on the spinner?
::如果在“2”和“3”或“6”上有6个相等的空格点,旋转器降落在“2”和“3”或“6”上的概率是多少?Make a chart:
::绘制图表:第一个旋转:12 3 456_第二个旋转: 1 2 3 4 5 5 6 6 1 2 2 3 4 4 5 6 1 2 3 4 4 4 5 6 2 3 4 4 5 6 4 6 4 6 4 6 4 6 6 4 6 4 6 6 4 6 4 6 6 4 6 4 6 4 6 4 6 6 4 6 6 4 6 6 4 6 6 6 4 6 6 4 6 4 6 4 6 6 4 6 6 6 6 6 4 6 6 6 6 4 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 1 6 6 6 1 6 1 6 1 6 1 6 1 6 1 6 1 6 1 6 1 6 1 6 1 6 6 1 6 6 1 6 1 6 1 6 1 6 6 6 6 1 6 6 6 1 6 1 6 1 6 6 6 6 6 1 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 1 6 1 6 1 6 1 6 1 6 1 6 1 6 1 6 1 6 1 6 1 6 1 6 1 6 1 6 1 6 1 6 1 6 1 6 1 6 1 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 1 6 6 6 6 6 1 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 1 6 1 6 1 6 1 6 1 6 1 6 1 6 1 6 6 6 6 6The red numbers 3 and 6 represent the two favorable outcomes out of 36 total, therefore
::红色数字3和6是总共36项中的2项有利结果,因此P(2和3或6)=236或118或5.55=____________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________Example 3
::例3What is the probability of pulling a red and then a black card at random from a standard deck (replacing the first card after drawing)?
::从标准甲板随机拉红色和黑色卡的概率(在绘制第一个牌之后替换第一个牌)是多少?There are 26 black and 26 red cards in the deck, so the probability on the first pull is On the second pull, we again have a 50% chance of favorable outcome , but that 50% only applies to the half of the first pulls that were favorable. Therefore:
::甲板上有26张黑卡和26张红色卡片,因此,第一次拉动的概率是P(red)=26 红色卡片52 共卡片=2652=12=12或50%。第二次拉动,我们再次有50%的有利结果,但50%仅适用于第一次拉动的半数。因此:P(red) = 26 红色卡片52 共卡片=2652=12或50%。5025%的50%。Example 4
::例4What probability of picking a red and then a green marble from a bag with 5 red and 1 green marbles in it (replacing the first marble after the draw)?
::从装有5个红色和1个绿色大理石的袋子中取出红色和绿色大理石的几率如何(取代抽取后的第一个大理石)?Make a chart:
Of the 36 possible outcomes, only 5 fit the description of red the first time, and green the second time (noted by the red “ ’s”. Therefore
::绘制图表: 第一次拉: rrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrr36, 在36个可能的36个结果中, 第一次只有5个符合红色的描述,第二次绿(用红色“ gs”表示)。 因此, P( 红色然后是绿色)=536Example 5
::例5What is the probability of shaking the hand of a student wearing red and then a student wearing blue if you randomly shake the hands of two people in a row in a room containing 3 students in blue and 2 in red?
::身穿红衣、身着蓝衣、身着红衣、身穿蓝衣的学生, 若在一间有3名身穿蓝衣、2名身穿红衣的学生的房间里, 连排与两人握手,Make a chart:
::绘制图表:So, out of the 25 possible handshake possibilities, 6 of them fit the requirements of red first, then blue:
::所以,在25个可能的握手可能性中, 其中6个符合红先,然后蓝色的要求:
::P(红后蓝色)=625Review
::回顾Questions 1-6: Suppose you have an opaque bag filled with 4 red and 3 green balls. Assume that each time a ball is pulled from the bag, it is random, and the ball is replaced before another pull.
::问题1-6:假设你有一个装满4个红球和3个绿球的不透明袋子。假设每次从袋子里拉出一个球,它都是随机的,球就会在另一个球拉之前被替换。1. Create a chart of all possible outcomes of an experiment consisting of pulling one ball from the bag at random, noting the color and replacing it, then pulling another.
::1. 绘制一个实验的所有可能结果的图表,该实验包括随机从包中拉出一个球,注意颜色并替换它,然后拉出另一个球。2. How many possible outcomes are there?
::2. 有多少可能的结果?3. What is the probability of randomly pulling a red ball from the bag, returning it, and pulling agreen ball on your second pull?
::3. 随机从包中拉出一个红色球,还回去,再拉一次绿球的可能性有多大?4. What is the probability of randomly pulling a red ball both times?
::4. 两次随机拉红色球的可能性有多大?5. What is the probability of pulling a green ball both times?
::5. 两次拉绿色球的可能性有多大?6. Is the probability of pulling a red followed by a green different than pulling a green followed by a red?
::6. 拉红色之后加绿色的概率是否不同于拉绿色之后加红色的概率?Questions 7 – 12: Suppose you have two standard dice, one red and one blue.
::问题7 - 12:假设你有两个标准骰子, 一个红色和一个蓝色。7. Construct a probability distribution table or diagram for an experiment consisting of one roll of the red die followed by one roll of the blue one.
::7. 为由一卷红色死亡和一卷蓝色死亡构成的实验建立一个概率分布表或图表。8. How many possible outcomes are there?
::8. 有多少可能的结果?9. Is there an apparent mathematical relationship between the number of sides on the dice and the number of possible outcomes?
::9. 骰子上方数与可能的结果数之间是否存在明显的数学关系?10. What is the probability of rolling a 2 on the red die and a 1, 3, or 5 on the blue one?
::10. 在红色死亡和蓝色死亡上滚2和1、3或5的概率是多少?11. What is the probability of rolling an even number on the red die and an odd on the blue one?
::11. 在红色死亡上滚动偶数和蓝色死亡上滚动奇数的可能性有多大?12. Do the probabilities of a particular outcome change based on which die is rolled first? Why or why not?
::12. 特定结果变化的概率是否首先取决于死亡的概率?为什么或为什么不是?Questions 13 – 16: Suppose you have a spinner with 5 equally-spaced color sections: red, blue, green, yellow, and orange.
::问题13 - 16:假设你有一个带有5个平空颜色的脊柱:红色、蓝色、绿色、黄色和橙色。13. Construct a probability distribution detailing the possible outcomes of three consecutive spins. You may wish to use only the first letter, or a single color-coded hash mark, to represent each possibility, as there will be many of them.
::13. 构造一个概率分布, 详细描述连续三个旋转的可能结果。 您可能希望只使用第一个字母, 或一个颜色编码的散列标记, 来代表每一种可能性, 因为其中有许多 。14. How many possible outcomes are there?
::14. 有多少可能的结果?15. Is there an apparent mathematical relationship between the number of sections on the spinner, the number of spins, and the number of possible outcomes? If so, what is the relationship?
::15. 旋转器上各部分的数目、旋转次数和可能的结果数目之间是否有明显的数学关系?如果有,那关系是什么?16. What is the probability of spinning red, then green, and then orange?
::16. 旋转红色、绿色和橙色的概率是多少?Review (Answers)
::回顾(答复)Click to see the answer key or go to the Table of Contents and click on the Answer Key under the 'Other Versions' option.
::单击可查看答题键, 或转到目录中, 单击“ 其他版本” 选项下的答题键 。