乘法规则
章节大纲
-
Finding the probability of getting two or three heads in a row when flipping a fair coin is straightforward enough by building a frequency table. However, the process becomes somewhat unwieldy when the experiment is more complex, such as calculating the probability of pulling 3 queens in a row from a standard deck of cards. Building a frequency table for all 52 cards would be time consuming at best.
::创建一个频度表可以直接地发现在翻转一个公平硬币时一行获得两个或三个头的概率。 但是,当实验更为复杂时,这个过程变得有点不易操作,比如计算从标准牌牌牌上一行拉动三个 Q 的概率。 为所有52张卡片建立一个频率表充其量会耗费时间。
There must be an easier way, right?
::一定有更容易的方法,对吧?Multiplication Rule
::乘法规则If I bet someone $1 that I can roll a standard die and get a 6, and then do roll the die and get a 6, I would probably get my $1, along with a clap on the back and a “congratulations!” from my friends. However, if I bet someone $20 that I can roll 20 times and get 6 every time, and then I do just that, I would probably be dealing with a very angry group of people who want to know how I cheated! That’s because it would be, at best, very improbable that I could get a series of 20 6’s in a row under normal circumstances. Let’s see if we can find out just how improbable.
::我敢打赌,如果有人能赌一美元,我就可以按标准标准去死,拿到6美元,然后就滚死,拿到6美元,我也许就能从我的朋友那里得到一美元,加上拍手和“恭喜 ” 。 但是,如果我敢赌20美元,我就可以滚20次,每次得到6美元,然后我就会这样做,我可能会面对一群非常愤怒的人,他们想知道我是如何作弊的。 这是因为,在正常情况下,我最多是不可能在一排中拿到206美元的系列。 让我们看看我们能不能发现自己有多不可能做到。Let’s start with the probability of just one roll of a 6:
::让我们首先从一卷六的概率开始:Since there are 6 sides, the probability is:
::由于有6个侧面,概率如下:
::P(6)=1 结果6 可能的结果=16 或16.7%For two 6’s in a row:
::连续两六人:If we create a table of the possible rolls where the only total outcome yielding two 6’s is highlighted in blue, we get:
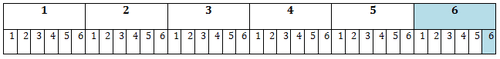
::如果我们创建一个可能的卷表, 显示产生两六分的唯一总结果以蓝色标出, 我们就会得到:KEY
::关键关键With this already pretty unwieldy table, we can see that there are 36 possible outcomes of rolling a standard die twice. Therefore, the probability of rolling two 6’s in a row is:
::在这张已经相当不易操作的桌子上,我们可以看到滚动标准死两次的结果有36种可能的结果。 因此,连续滚动2-6的概率是:
::P(2个6`s)=1 结果36 可能的结果=136或2.8%It should be apparent that things only get crazier from here, since calculating 3 6’s this way would require another row of 6 possibilities for each of the 36 outcomes of the 2 nd roll! However, look at the difference between the two probabilities:
::应该很明显的是,从这里看,事情只会变得越发疯狂,因为这样计算 3 6 将要求第二卷的36个结果中,每1个结果需要另外一排6种可能性。 但是,看看两种可能性的区别:
::P( one 6) = 16 和 P( 2 6 6 ' s) = 16x16=136The fact that the probability of getting two 6’s is of is no coincidence, of course. In fact, to understand how to calculate more complex intersections of independent compound probabilities, it may help to remember something you likely learned when practicing word problems:
::获得两个六分之十六的概率是16分之十六,这当然不是巧合。 事实上,要理解如何计算独立复合概率的更复杂的交叉点,也许可以帮助人们记住在练习文字问题时你可能学到的东西:To translate English to math, the word of and the multiplication sign · or × mean the same thing.
::将英语翻译为数学, 字词和乘法符号 / 或 x 的意思相同 。Since the probability of getting two 6’s in a row is we can say:
::因为连续两六分之一的概率 是十六分之十六的16分之一,我们可以说:
::16=16×16=136=16=16=16=16=16=16=16=16=16=16=16=16=136=16=16=16=16=16=16=16=16=16=136=16=16=16=16=16=16=16=16=16=16=16=16=16=16=136=16=16=16=16=16=16=16=16=16=16=16=16=136=16=16=16=16=16=16=16=16=16=16=16=16=16=16=16=16=16=16=16=16=16=16=16=16=16=16=16=16=16=16=16=16=16=16=16=16=16=136=16=16=16=16=16=16=16=16=16=16=16=16=16=16=16=16=16=16=16=16=16=16=16=16=16=16=16=16=16=16=16=136=16=16=16=16=16=16=136=16=16=16=16=16=16=16=16=16=16=16=16=16=16=16=16=136=16=16=16=16=16=16=16=16=136=16=16=16=16=16=136=16=16=16=16=16=16=136=16=16=16=16=16=16=16=16=16=16=136=16=16=16=16=16=16=16=16=136=16=16=16=136=16=16=16=16=136=16=16=16=16=16=16=16=16=16=16=16=16=136=16=16=16=16=16=16=16=136=16=16=16=16=16=16=16=16=16=16=16=16=16=16=16=16=16=16=136=16=16=16=16=16=16=16=16=16=16=16=16=16=16=16This is an example of the of compound probability:
::这是复数概率的一个例子:
::P(总计)=P(第1项结果)xP(第2项结果)xP(第2项结果)xP(最后结果)xP(最后结果)Now we can actually calculate the probability of 20 6’s in a row:
::现在,我们可以实际计算出 20 6 的几率:
::P( 20 618) = 16x16... 16= ( 1620) = 13, 656, 158, 440, 062, 976or approximately one in three and one-half quadrillion, which I would consider not good odds!
::或大约三分之一半的四分之一, 我认为这不是个好机会!Which also illustrates the practical impossibility of solving such a question with a frequency table, since it would take approximately 116,000,000 years just to write out the 6 th row at one number per second! (not to mention the 1 trillion sheets of paper )
::这还表明,实际上不可能用一个频率表解决这样一个问题,因为大约需要116 000 000 000年才能以每秒一个数字来写出第6行! (更不用说1万亿张纸...)Finding Theoretical Probability
::理论概率1. What would be the theoretical probability of randomly pulling a queen from a deck of 52 cards, putting it back, randomly pulling a queen again, and so on until you have pulled 5 queens in a row?
::1. 从52张牌牌的甲板上随意拉动女王,将其放回去,再随机拉动女王,等等,在连续拉动五个皇后之前,理论上的概率是多少?
The theoretical probability of pulling a single queen from a standard deck is:
::从标准甲板拉出单母后理论上的概率是:
::P(queen)=4 Q52卡片=113或7.7%If we use the multiplication rule for five pulls, we get:
::如果我们用乘法规则来进行5次拉动,我们就会得到:2. What is the theoretical probability of rolling a 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, and then 6, in order, on six successive rolls of a standard die?
::2. 将1、2、3、4、5和6的1、2、3、4、5和6按标准死亡连续六卷顺序滚动的理论概率是多少?The probability of rolling any single number on a standard die is . Use the multiplication rule:
::在标准死亡上滚动任何单个数字的概率是 16。 使用乘法规则:
::P(1-6)=16x16x16x16x16x16x16=166=146563. What is the theoretical probability that you might deal the King of Hearts, Jack of Diamonds, and then any Ace, in order, from a standard deck of cards, assuming you replace each card after drawing?
::3. 假设您在画完之后更换每张卡片,你从标准纸牌牌牌上 与红心之王、钻石之王、王牌之王、王牌之王、王牌之王进行交易的理论概率是多少?Let’s start by evaluating the individual probabilities.
::让我们从评估个人概率开始。-
::P(第一卡)=1 " 心之王52 " 总计卡=152 -
::P(第二张卡)=1 " 钻石52 杰克 " ,总卡=152 -
::P(第三张卡)=4 Aces52总卡=452=113
Now we can use the multiplication rule:
::现在我们可以使用乘法规则:
::P(心脏之王,钻石之杰克,Ace)=152x152x113=135152Earlier Problem Revisited
::重审先前的问题Finding the probability of getting two or three heads in a row when flipping a fair coin is straightforward enough by building a frequency table. However, the process becomes somewhat unwieldy when the experiment is more complex, such as calculating the probability of pulling 3 queens in a row from a standard deck of cards. Building a frequency table for all cards would be time consuming at best.
::创建一个频度表可以直接地发现在翻转一个公平硬币时一行获得两个或三个头的概率。 但是,当实验更为复杂时,这个过程变得有点不易操作,比如计算从标准牌牌牌上一行拉动三个 Q 的概率。 为所有卡建立一个频度表充其量会耗费时间 。There must be an easier way, right?
::一定有更容易的方法,对吧?Of course, now you know this isn’t even really a question anymore, the multiplication rule makes this question pretty easy:
::当然, 现在你知道这甚至不是一个真正的问题了, 乘法规则让这个问题很容易解决:
::P( 3 Q) = 152x151x150 = 1132600Examples
::实例Example 1
::例1What is the probability of rolling an odd number, followed by an even number, followed by a prime number, on three successive rolls of a 20-sided die?
::滚动一个奇数的概率是多少,然后是偶数,然后是质数,然后是连续三次20边死亡的三次卷号?Apply the multiplication rule:
::应用乘法规则: P( 总计) = P( 案例 1) xp( 案例 2)... xP( 案例 n)
::P(odd, even, prip) = P(od) ×P( even) ×P( prime) P( pod, even) = 1020x1020x820=8008008000=110 或 0.1 或 10% P( od, even, pin) = 10%Example 2
::例2What is the probability of pulling a heart, replacing it, pulling a club, replacing it, pulling a diamond, replacing it, then pulling a spade, all from a standard deck?.
::拔出一颗心 替换它 拔出一个俱乐部 替换它 拔出钻石 替换它 然后从标准甲板上拉出一个碎片的概率是多少?We can apply the multiplication rule here also:
::我们可以在此适用乘法规则:
::P(心脏、俱乐部、钻石、spade)=14×14×14×14×14=1256或0.00391或4.4%P(心脏、俱乐部、钻石、spade)=0.4%Example 3
::例3What is the probability of flipping a coin ten times in a row, and getting heads every time?
::一次翻10次硬币 一次又每次砍头的概率是多少?Since we are looking for the same outcome from the same experiment repeated ten times, we can 'shortcut' the multiplication rule by an exponent:
::既然我们在寻找同一实验的相同结果 重复了十次, 我们可以“简化”乘法规则 由推论者提出:
::P(头十倍)=(12)10=110210=11024或0.001或0.1%P(头十倍)=0.1%Example 4
::例4What is the probability of spinning red 5 times in a row on a spinner with 6 equally spaced color segments, only one of which is red?
::在有6个相同间距的彩色区块的脊柱上连续旋转5次红色的概率是多少? 其中只有1个是红色的。This one is similar to the last, in that we are looking for the same outcome of the same experiment, multiple times (5 times, in this case).
::这与最后一项相似,因为我们正在寻找同一实验的相同结果,多次(5次,在本案中)。
::P(红5次)=(165=1565=17776或0.0001或0.01%P(红5次)=0.01%Review
::回顾1. What are independent events?
::1. 什么是独立事件?2. What is the multiplication rule?
::2. 什么是乘法规则?Questions 3-7: Suppose you have an opaque bag filled with 6 red, 4 green, 7 blue and 5 purple balls.
::问题3 -7:假设你有一个不透明的袋子 装满6个红色,4个绿色,7个蓝色和5个紫色球3. What is the probability of randomly pulling a purple ball from the bag, returning it, and pulling a purple ball again on your second pull?
::3. 随机从包中拉出一个紫色球,把它还回去,再拉一个紫色球,然后再拉第二拉的概率是多少?4. What is the probability of randomly pulling a red ball from the bag, returning it, and pulling ablue ball on your second pull?
::4. 随机从包中拉出一个红色球,把它还回去,再拉一次蓝色球的可能性有多大?5. What is the probability of randomly pulling a green ball from the bag, returning it, and pulling agreen ball again on your second pull?
::5. 随机从袋子里拉一个绿色球,把它还回去,再拉一个绿色球,再拉第二个球的可能性有多大?6. What is the probability of randomly pulling a blue ball from the bag, returning it, and pulling ared ball on your second pull?
::6. 随机从包中拉出一个蓝色球,把它还回去,然后再拉上灰色球,其概率有多大?7. What is the probability of randomly pulling a purple ball from the bag, returning it, and pulling ablue ball on your second pull?
::7. 随机从包中拉出一个紫色球,把它还回去,再拉一个蓝色球,再拉一个蓝色球的可能性有多大?Questions 8 – 12: Suppose you have two standard dice, one red and one blue.
::问题8 - 12:假设你有两个标准骰子,一个红色和一个蓝色。8. What is the probability of rolling a 3 on the red die and a 5 on the blue one?
::8. 在红色死亡上滚3和蓝色死亡上滚5的概率是多少?9. What is the probability of rolling a 3 or 4 on the red die and a 5 on the blue one?
::9. 在红色死亡上滚动3或4,蓝色死亡上滚动5的概率是多少?10. What is the probability of rolling an even number on the red die and an odd on the blue one?
::10. 在红色死亡上滚动偶数和蓝色死亡上滚动奇数的可能性有多大?11. What is the probability of rolling a 6 on the red die and an odd number on the blue one?
::11. 在红色死亡上滚动一个6的概率有多大? 在蓝色死亡上滚动一个奇数的概率有多大?12. What is the probability of rolling a 1 on the red die and prime number on the blue one?
::12. 在红色死亡和蓝色死亡的质号上滚动1的概率是多少?Questions 13 – 16: Suppose you are dealing with a standard deck of cards, calculate the probability of each outcome as described, assuming you replace each card after drawing it.
::问题13 - 16:假设你处理的是标准纸牌甲板, 计算每个结果的概率, 假设您在绘制之后替换每张牌。13. Pulling a queen, then any club, then any red card.
::13. 拉一个皇后,然后是任何俱乐部,然后是红色卡片。14. Pulling the Ace of Spades, then a red 6, then any king.
::14. 拔出黑桃A,然后是红色6,然后是任何国王。15. Pulling any face card three times in a row.
::15. 连续三次拉一张长相卡。16. Pulling a face card, then an ace, then the 5 of clubs.
::16. 拉一张脸卡,然后是A,然后是梅花5。Review (Answers)
::回顾(答复)Click to see the answer key or go to the Table of Contents and click on the Answer Key under the 'Other Versions' option.
::单击可查看答题键, 或转到目录中, 单击“ 其他版本” 选项下的答题键 。 -