函数的近似根根 : 牛顿的方法
章节大纲
-
We want to look at finding the roots of a polynomial. Sometimes the polynomial cannot be easily factored, and other algebraic methods (e.g., the quadratic equation) are not applicable, or do not work. When faced with a mathematical problem that cannot be solved with simple algebraic means, calculus sometimes provides a way of finding approximate solutions.
::我们想要寻找多元数学的根。 有时,多元数学不能很容易地被考虑在内,而其他代数方法(如二次方程)则不适用,或者无效。 当数学问题无法用简单的代数方法解决时,计算有时会提供找到近似解决方案的途径。Newton's Method
::牛顿方法A simple example will help introduce Newton’s Method for approximating the roots of a polynomial equation.
::一个简单的例子将有助于引入牛顿的“接近多面方程式根部的方法 ” 。Let's say you want to compute without using a calculator or a table. Any ideas how this could be done? Try thinking about this problem in a different way, so that you make use of linearization .
::假设您想要计算 5 而不使用计算器或表格。 任何想法如何做到这一点? 尝试用不同的方式来思考这个问题, 这样您就可以使用线性化 。Assume that we are interested in solving the quadratic equation:
::假设我们有兴趣解决二次方程式:
:xx) =x2-5=0
We know this equation has the roots .
::我们知道这个方程式有根 x5。The idea here is to find the linearization of at an appropriate point, and then solve the linear equation for . This is an added twist to the linearization problem!
::这里的想法是在一个适当点找到 f( x) 的线性化, 然后解开 x 的线性方程。 这是线性化问题的额外转折 !How to choose the linearization point? Since , this mean .
::如何选择线性点? 自 4 < 5 < 9, 这意味着 2 < 5 < 3 。We choose the linear approximation of to be near (but, could also could be selected).
::我们选择 f(x) 的线性近似值, 以接近 x0=2 (但也可以选择 x0=3) 。and
:xx)=x2-5和f(2)1
and .
::f_(x)=2x和f_(2)=4。Using the linear approximation formula,
::使用线性近似公式,
:xx) f(x0)+f*(x0)+f*(x0)(x-x0)\*1+(4)(x-2)\*1+4x-8*4x-9。
Notice that this equation is much easier to solve than .
::注意此方程比 f( x) =x2 - 5=0 更容易解析 。Setting and solving for , we obtain,
::设置 f(x)=0 和解析 x, 我们获得,
::4-9=0x=94=2.25。This is a fairly good approximation, since a calculator would give , lower by 0.014. We can actually make this approximation to the root of even better by repeating what we have just done but using the latest estimate , a number that is even closer to the actual value of .
::这是一个相当不错的近似值, 因为计算器会给出 x=2.23607, 低于 0.014 。 我们实际上可以通过重复我们刚才所做的, 来使f( x) 根的近似值更好, 但使用最新的估计值 x1= 2. 25=94, 这个数字更接近于实际值为 5 。and
:xx)=x2-5和f(2.25)=116
and
::f_(x)=2x和f_(2)=92Using the linear approximation again,
::再次使用线性近似,
::f(x) f(x1) +f*(x1)(x1)(x-x1) 116+92(x-94) 92x-16116。Solving for by setting , we obtain
::设置 f(x)=0, 溶解 x 的 f(x)=0, 我们获得
::x=x2=16172=2.23611which is an even better approximation than .
::比x1=94更接近。We could continue this process generating a better approximation to , as shown in the table, where the last estimate approximates the correct answer to 5 places. Thank goodness for calculators!
::我们可以继续这一进程,从而更接近于5,如表所示,最后的估计接近于5个地方的正确答案。 感谢计算者!
::n 内
::xn 进
:fxn)
::f_( xn)
:fxn) f_(xn)
::xn-f(xn) f_(xn)1
2
-1
4
-0.25
2.25
2
2.25
0.0625
4.5
0.01389
2.23611
3
2.23611
0.00019
4.47222
0.00004
2.23607
4
2.23607
--
--
--
--
This is the basic idea of Newton’s Method . Here is a summary of the method:
::这是牛顿方法的基本概念。 以下是方法摘要:-
Given the function
, find
.
::根据函数 f(x),请查找 f_(x) 。 -
Estimate the first approximation,
, to a solution of the equation
. Use a graph to help in finding the first approximation if necessary (see Figure below).
::估计第一个近似值为x0, 以解析公式 f(x)=0。 必要时使用图表帮助寻找第一个近近近值(见下图)。 -
Use the current approximation
to find the next approximation,
, by using the recursion relation.
::使用当前近似 xn 使用递归关系查找下一个近似 xn+1 。
::xn+1=xn-f(xn)f_(xn)xn。-
Repeat the previous step until the desired level of convergence occurs.
::重复前一步骤,直至达到预期的趋同水平。
Note that in some cases, Newton’s Method does not converge .
::请注意,在一些情况下,牛顿的方法并不趋同。Examples
::实例Example 1
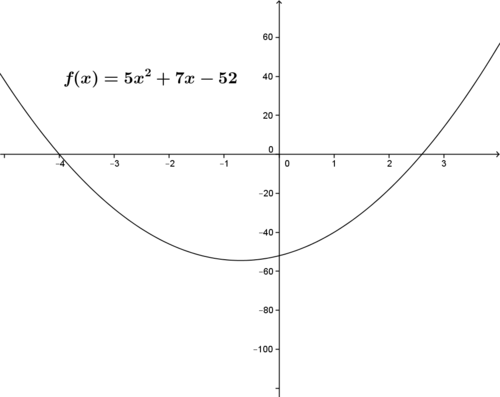
::例1Compare the solutions to in the interval [2, 3] from using the Quadratic formula and using Newton’s Method.
::将使用二次曲线公式和使用牛顿方法的(x)=5x2+7x-52的间隔[2, 3]中的 f(x)=5x2+7x-52的解决方案比较。The function is shown in the figure.
::函数在图中显示。For , use of the quadratic formula gives the exact solution in the interval.
::对于 f(x) = 5x2+7x-52=0, 使用四方形公式给出准确的溶液x=2.6 间隔。Use of Newton’s Method with an initial estimate of , yields the results shown in the table.
::使用牛顿方法,初步估计为x0=3,得出表中所列结果。
::n 内
::xn 进
:fxn)
::f_( xn)
:fxn) f_(xn)
::xn-f(xn) f_(xn)1
3
14
37
0.3784
2.6216
2
2.6216
0.7151
33.216
0.0215
2.6001
3
2.6001
0.0033
33.001
0.0001
2.6000
4
2.6000
--
--
--
--
The technique rapidly converges to a solution.
::技术迅速趋于一致,找到解决办法。Example 2
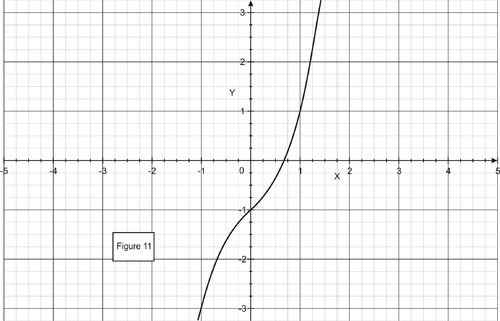
::例2Use Newton’s method to find the roots of the polynomial .
::使用 牛顿 的方法来查找 monnomilal f( x) =x3+x-1 的根根 。The problem is to solve the equation .
::问题是解决f(x)=x3+x- 1=0的方程式。The equations we need are:
::我们需要的方程式是:
:xx)=x3+x-1)
.
::f_(x) = 3x2+1 。Using the recursion relation,
::使用循环关系,
::xn+1=xn-f(xn)f_(xn)=xn-xn3+xn-13xn2+1。To help us find the first approximation, we make a graph of . As the figure suggests, set .
::为了帮助我们找到第一个近似值, 我们绘制一个 f( x) 的图形。 如图所示, 设置 x1=0. 6 。Then using the recursion relation, we can generate :
::然后使用循环关系, 我们可以生成x1 :
::xn+1=xn-xn3+xn-13xn2+1x2=0.6-(0.6)3+(0.6)-13(0.6)2+1=0.6884615。By using the recursion relation several times, we can find and as shown in the table.
::通过多次使用递归关系,我们可以找到表所示的 x3 和 x4 。
::n 内
::xn 进
:fxn)
::f_( xn)
:fxn) f_(xn)
::xn-f(xn) f_(xn)1
0.6
-0.184
2.08
-0.0884615
0.6884615
2
0.6884615
0.01477796
2.4219377
0.0061017
0.6823598
3
0.6823598
0.00007669
2.3968445
0.0000320
0.6823278
4
0.6823278
--
--
--
--
We conclude that the solution to the equation is about 0.6823.
::我们的结论是,公式x3+x-1=0的解决方案约为0.6823。Example 3
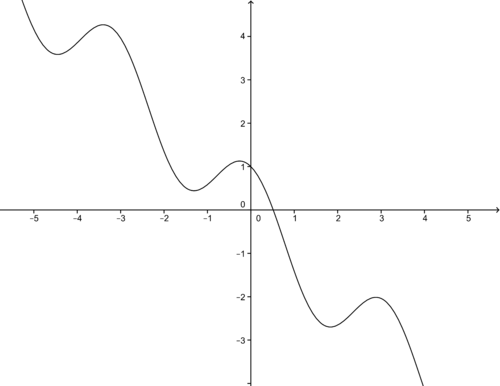
::例3Use Newton’s Method to show to find the root of .
::使用 牛顿 的 方法来显示 f( x) = cos *( 2x) - x 的根 。The equations we need are:
::我们需要的方程式是:
:xx) =cos(2x)-x
:xx)%2sin(2x)- 1
Using the recursion relation,
::使用循环关系,
::xn+1=xnf( xn) f*( xn) =xn-cos *( 2xn)-xn-2sin *( 2xn)- 1To help us find the first approximation, we make a graph of . As the figure suggests, set the first estimate at 0.5.
::为了帮助我们找到第一个近似值,我们绘制一个f(x)的图表。如图所示,将第一个估计数定为0.5。Using the recursion relation several times gives the table values:
::使用递归关系多次给出表格值:
::n 内
::xn 进
:fxn)
:fxn) f_(xn)
1
0.500000
0.0403023
-0.0152168
2
0.515022
-0.0002400
0.0000884
3
0.514933
-0.0000000
0.0000000
4
0.514933
--
--
We conclude that the solution to the equation is 0.514933.
::我们的结论是,对等方程的解决方案为0.514933,cos(2x)-x=0。Review
::回顾For all the problems, use Newton’s Method to find the roots.
::使用牛顿的方法找出根源。-
.
::x3+3=0。 -
.
::-x+3-1+x=0。 -
in the interval [-1, 0].
::间距[-1,0]4x2-x-2。 -
.
::4x3 - 6x2 - 1; -
.
::5 e- x+x3 。 -
.
::xxxx。 -
in the interval [-1, 0].
::间隔[-1,0] x5-7x2+2。 -
in the interval [0, 1].
::x5-7x2+2 间隔 [0, 1] 。 -
in the interval [4, 5].
::间隔内 x2cosx-x [4, 5] 。 -
in the interval [7, 8].
::间隔中的 x2cosx-x [7、8] 。 -
to five decimal places, starting with initial guess
.
::f(x) =x- 2sin(x) 到小数点后五位位数, 从最初的猜测x0=3开始 。 -
to three decimal places, starting with initial guess
.
::f(x) = 6x3 - 4x+1 到小数点后三位位数, 从初始猜数x0=1.2开始 。 -
to five decimal places, starting with initial guess
.
::f(x) = ln (x) ×(ln (x)+4)+1 到小数点后五个位数, 从最初的猜测x0=1开始 。 -
to six digits of accuracy, starting with initial guess
.
::f(x)=tan(x)-csc(x)至精度的六位数,从最初的猜测x0=0.7开始。 -
to four digits of accuracy, starting with initial guess
.
::f(x) = tan- 1(x) +cos(x) 至 4 位数的精确度, 从初始猜数 x02 开始 。
Review (Answers)
::回顾(答复)Click to see the answer key or go to the Table of Contents and click on the Answer Key under the 'Other Versions' option.
::单击可查看答题键, 或转到目录中, 单击“ 其他版本” 选项下的答题键 。 -
Given the function
, find
.