同位素同位素同位素
章节大纲
-
Is this creature a space alien? It may look alien, but the sketch is actually just a scientist wearing a special suit to protect himself from harmful radiation. The scientist is working with radioactive chemicals called isotopes. Not all isotopes are radioactive, but many of them are. To understand why, you first need to know what isotopes are.
::这个生物是外星人吗?它看起来可能是外星人,但素描其实只是个穿着特别外衣保护自己免受有害辐射的科学家。科学家正在研究放射性化学物质,叫做同位素。并非所有同位素都是放射性的,但其中许多是放射性的。为了理解原因,你首先需要知道什么是同位素。What Are Isotopes?
::什么是伊索托邦?All atoms of the same have the same number of , but some may have different numbers of . For example, all carbon atoms have six protons, and most have six neutrons as well. But some carbon atoms have seven or eight neutrons instead of the usual six. Atoms of the same element that differ in their numbers of neutrons are called isotopes . Many isotopes occur naturally. Usually one or two isotopes of an element are the most stable and common. Different isotopes of an element generally have the same physical and chemical properties. That’s because they have the same numbers of protons and electrons.
::同一原子的所有原子数量相同,但有些原子的数量可能不同。例如,所有碳原子有6个质子,大多数也有6个中子。但有些碳原子有7个或8个中子,而不是通常的6个。同一元素的原子被称为同位素。许多同位素自然发生。一个元素的一至两个同位素通常是最稳定和最常见的。一个元素的不同同位素一般具有相同的物理和化学特性。这是因为它们的质子和电子数量相同。An Example: Hydrogen Isotopes
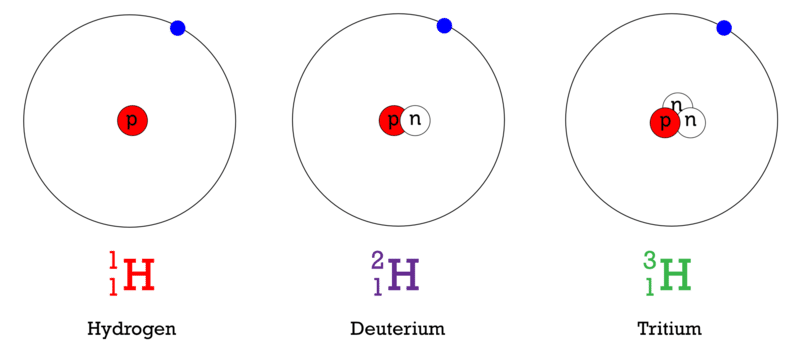
::示例: 氢伊索托端Hydrogen is an example of an element that has isotopes. Three isotopes of hydrogen are modeled in the Figure . Most hydrogen atoms have just one proton and one and lack a neutron. These atoms are just called hydrogen. Some hydrogen atoms have one neutron as well, these atoms are the isotope named deuterium. Other hydrogen atoms have two neutrons, these atoms are the isotope named tritium.
::氢是具有同位素元素的一个例子。在图中以三种氢同位素为模型。大多数氢原子只有一个质子和一个质子,并且缺乏中子。这些原子被称为氢。有些氢原子也有一个中子,这些原子是同位素叫做。其他氢原子有两个中子,这些原子是同位素叫做。Q: The mass number of an is the sum of its protons and neutrons. What is the mass number of each isotope of hydrogen shown above?
::Q: a 的质数是其质子和中子的总和。上面显示的每种氢同位素的质量数是多少?A: The mass numbers are: hydrogen = 1, deuterium = 2, and tritium = 3.
::A:质量数字是:氢 = 1, = 2, = 3。Naming Isotopes
::命名异形For most elements other than hydrogen, isotopes are named for their mass number. For example, carbon atoms with the usual 6 neutrons have a mass number of 12 (6 protons + 6 neutrons = 12), so they are called carbon-12. Carbon atoms with 7 neutrons have an atomic mass of 13 (6 protons + 7 neutrons = 13). These atoms are the isotope called carbon-13.
::对于除氢以外的大多数元素,同位素按其质量数命名。例如,通常有6个中子的碳原子质量数为12个(6个质子+6个中子=12),因此称为碳-12。7个中子的碳原子原子原子质量为13个(6个质子+7个中子=13)。这些原子是称为碳-13的同位素。Q: Some carbon atoms have 8 neutrons. What is the name of this isotope of carbon?
::问题:有些碳原子有8个中子。碳同位素的名称是什么?A: Carbon atoms with 8 neutrons have an atomic mass of 14 (6 protons + 8 neutrons = 14), so this isotope of carbon is named carbon-14.
::A:8个中子的碳原子原子原子质量为14个(6个质子+8个中子=14个),所以这一碳同位素称为碳-14。Stability of Isotopes
::伊索托邦的稳定Atoms need a certain ratio of neutrons to protons to have a stable nucleus . Having too many or too few neutrons relative to protons results in an unstable, or radioactive, nucleus that will sooner or later break down to a more stable form. This process is called . Many isotopes have radioactive nuclei, and these isotopes are referred to as . When they decay, they release particles that may be harmful. This is why radioactive isotopes are dangerous and why working with them requires special suits for protection. The isotope of carbon known as carbon-14 is an example of a radioisotope. In contrast, the carbon isotopes called carbon-12 and carbon-13 are stable.
::原子需要一定比例的中子和质子才能有一个稳定的核。 相对于质子的中子太多或太少导致不稳定或放射性核。 这个过程被称为 。 许多同位素有放射性核, 这些同位素被称为 。 当它们衰减时, 它们释放出可能有害的粒子。 这就是为什么放射性同位素是危险的, 并且与它们合作需要特殊保护。 碳14的碳同位素是放射性同位素的一个例子。 相比之下, 碳-12 和碳- 13 的碳同位素是稳定的。Summary
::摘要-
Atoms of the same element that differ in their numbers of neutrons are called isotopes. Different isotopes of an element generally have the same physical and chemical properties because they have the same numbers of protons and electrons.
::与中子数量不同的同元素原子称为同位素,元素的不同同位素一般具有相同的物理和化学特性,因为它们的质子和电子数量相同。 -
Most hydrogen atoms lack a neutron and are just called hydrogen. Hydrogen atoms with one neutron are the isotope known as deuterium, and those with two neutrons are the isotope named tritium.
::大部分氢原子都缺乏中子,仅称为氢,一个中子的氢原子是同位素,两个中子的氢原子是称为的同位素。 -
For most elements other than hydrogen, isotopes are named for their mass number, which is the number of protons plus neutrons. For example, carbon with a mass number of 14 is called carbon-14.
::对于除氢以外的大多数元素,同位素按质数命名,即质子加中子的数量。例如,质量为14的碳称为碳-14。 -
Atoms need a certain ratio of neutrons to protons to have a stable nucleus. If they have too many or too few neutrons relative to protons, they are radioactive and will decay to more stable forms. Isotopes with radioactive nuclei are called radioisotopes.
::原子需要一定比例的中子和质子才能有一个稳定的核。如果它们相对于质子有太多或太少的中子,那么它们就是放射性的,会腐蚀成更稳定的形态。 放射性核的同位素叫做放射性同位素。
Review
::回顾-
What are isotopes?
::什么是同位素? -
Why do different isotopes of an element generally have the same physical and chemical properties?
::为什么元素的不同同位素通常具有相同的物理和化学特性? -
Describe the three isotopes of hydrogen.
::描述氢的三个同位素。 -
Relate the concepts of isotope and mass number.
::将同位素和质量编号的概念联系起来。 -
All oxygen atoms have eight protons, and most have eight neutrons as well. What is the mass number of an oxygen isotope that has nine neutrons? What is the name of this isotope?
::所有氧原子都有8个质子,大多数也有8个中子。一个含9个中子的氧同位素的质量数量是多少?这个同位素叫什么名字? -
Why are many isotopes radioactive?
::为什么许多同位素是放射性的?
Explore More
::探索更多Watch the video about isotopes of carbon. Then answer the questions below.
::观看关于碳同位素的视频。 然后回答下面的问题。-
How does carbon-14 form?
::碳-14如何形成? -
Carbon-14 slowly decays over time because it is radioactive. Why does the percent of carbon-14 remain the same in living organisms?
::碳-14由于放射性而逐渐衰减。 为什么碳-14在活生物体中的百分比保持不变? -
How can the percent of carbon-14 in a dead organism be used to estimate the amount of time that has passed since the organism died?
::如何利用死亡生物体中碳-14的百分率来估计自该生物体死亡以来所经过的时间?
-
Atoms of the same element that differ in their numbers of neutrons are called isotopes. Different isotopes of an element generally have the same physical and chemical properties because they have the same numbers of protons and electrons.