化学反应中的节能
章节大纲
-
The blue flame in this photo is burning inside a home furnace. The fuel is natural , and it combines with oxygen when it burns. This , called a , gives off a lot of .
::这张照片中的蓝色火焰正在家庭炉子里燃烧。 燃料是天然的, 当燃烧时与氧气结合。 这叫做“ ” , 释放了很多。Energy and Chemical Reactions
::能源和化学反应All chemical reactions involve energy. Energy is used to break bonds in reactants , and energy is released when new bonds form in products. Like the combustion reaction in a furnace, some chemical reactions require less energy to break bonds in reactants than is released when bonds form in products. These reactions, called , release energy. In other chemical reactions, it takes more energy to break bonds in reactants than is released when bonds form in products. These reactions, called endothermic reactions, absorb energy.
::所有化学反应都涉及能源。能源被用来打破反应器中的键,当产品中出现新的键时,能源就会释放出来。和炉中的燃烧反应一样,有些化学反应需要的能量比产品中债券中的键要少。这些反应被称为释放能量。在其他化学反应中,打破反应器中的键需要的能量比产品中的键要多。这些反应,称为局部热反应,吸收能量。Conservation of Energy
::保护能源Whether a chemical reaction absorbs or releases energy, there is no overall change in the amount of energy during the reaction. That’s because energy cannot be created or destroyed. This is the law of conservation of energy . Energy may change form during a chemical reaction—for example, from chemical energy to energy when gas burns in a furnace—but the same amount of energy remains after the reaction as before. This is true of all chemical reactions.
::无论化学反应吸收或释放能源,反应期间的能量数量没有总体变化。这是因为能源不能创造或摧毁。 这是节能法则。 化学反应中能源的形式可能改变 — — 例如,从化学能源到燃气炉燃烧时的能源 — — 但反应之后的能源数量与以前相同。 所有化学反应都是如此。Q: If energy can’t be destroyed during a chemical reaction, what happens to the energy that is absorbed in an ?
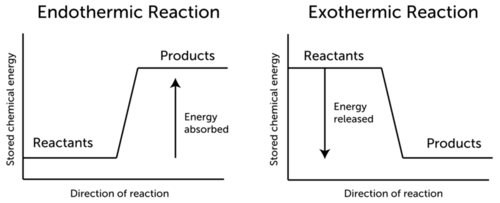
::问:如果能源无法在化学反应中被摧毁,A: The energy is stored in the bonds of the products as chemical energy. In an endothermic reaction, the products have more stored chemical energy than the reactants. This is represented by the graph on the left in the Figure . In an exothermic reaction, the opposite is true. The products have less stored chemical energy than the reactants. You can see this in the graph on the right in the Figure .
::A:能量储存在作为化学能的产品键中。在最终热反应中,这些产品储存的化学能量比反应剂多。图左侧的图表说明了这一点。在异热反应中,情况正好相反。这些产品储存的化学能量比反应剂少。在图右侧的图表中可以看到这一点。Note: ΔH represents the change in energy.
::注:#H表示能源的变化。Q: What happens to the excess energy in the reactants of an exothermic reaction?
::问题:异温反应反应反应体的超能量会怎样?A: The excess energy is generally released to the surroundings when the reaction occurs. In a home , for example, the energy that is released during combustion in the furnace is used to heat the home.
::A:反应发生时,过量能量一般会释放到周围环境。例如,在家中,炉炉燃烧期间释放的能量被用来为家暖气。Summary
::摘要-
All chemical reactions involve energy. Energy is used to break bonds in reactants, and energy is released when new bonds form in products. Endothermic reactions absorb energy, and exothermic reactions release energy.
::所有化学反应都涉及能源。 能源被用来打破反应器中的联结,当产品中出现新的联结时,能源就会释放出来。 局部热反应吸收能量,异温反应释放能量。 -
The law of conservation of energy states that matter cannot be created or destroyed. Whether a chemical reaction absorbs or releases energy, there is no overall change in the amount of energy during the reaction.
::节能法则规定,不能创造或销毁物质,无论是化学反应吸收或释放能源,反应期间的能量总量没有总体变化。
Review
::回顾-
Summarize the role of energy in chemical reactions.
::概述能源在化学反应中的作用。 -
What is the law of conservation of energy?
::什么是节能法? -
Explain how energy is conserved in an endothermic reaction.
::解释如何节能 在局部热反应。
Resources
::资源 -
All chemical reactions involve energy. Energy is used to break bonds in reactants, and energy is released when new bonds form in products. Endothermic reactions absorb energy, and exothermic reactions release energy.