国际贸易对国际贸易的重要性
章节大纲
-
Importance of International Trade
::国际贸易对国际贸易的重要性The international market is important not just in terms of the goods and services it provides to a country, but as a market for that country’s goods and services. Because foreign demand for U.S. exports is almost as large as investment and government purchases as a component of aggregate demand, it can be very important in terms of growth.
::国际市场的重要性不仅在于它向一个国家提供的商品和服务,而且在于它作为美国商品和服务的市场。 由于外国对美国出口的需求几乎与投资和政府采购一样大,几乎与总需求一样大,因此,它对于增长可能非常重要。Universal Generalizations
::普遍化-
Trade affects neither the economy's natural level of employment nor its real wage in the long run; those are determined by the demand for and the supply curve of labor.
::贸易既不影响经济的自然就业水平,也不影响其长期的实际工资;这些工资由劳动力的需求和供应曲线决定。 -
Growth in international trade has outpaced growth in world output over the past five decades.
::过去五十年来,国际贸易的增长超过了世界产出的增长。 -
The chief determinants of net exports are domestic and foreign incomes, relative price levels, exchange rates, domestic and foreign trade policies, and preferences and technology.
::净出口的主要决定因素是国内和国外收入、相对价格水平、汇率、国内和外贸政策以及优惠和技术。 -
A change in the price level causes a change in net exports that moves the economy along its aggregate demand curve. This is the international trade effect.
::价格水平的改变导致净出口的改变,使经济沿着总需求曲线走动,这是国际贸易效应。 -
A change in net exports produced by one of the other determinants of net exports will shift the aggregate demand curve by an amount equal to the initial change net exports times the multiplier.
::由净出口的其他决定因素之一产生的净出口变化将使总需求曲线改变,其数额相当于初始变化净出口乘以乘数。
Guiding Questions
::问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问-
How does specialization facilitate trade between individuals and nations?
::专业化如何促进个人和国家之间的贸易? -
How does importing and exporting affect the economy of the United States and the trading partners of the United States?
::进出口对美国经济和美国贸易伙伴有何影响? -
What are the advantages and disadvantages of having trade barriers?
::设置贸易壁垒的利弊何在? -
How do changes made to the exchange rate impact imports and exports?
::汇率对进出口的影响如何变化?
Video: Imports, Exports, and Exchange Rates
::录像:进口、出口和汇率The Case for Trade
::贸易案例International trade increases the quantity of goods and services available to the world’s consumers. By allocating resources according to the principle of comparative advantage, trade allows nations to consume combinations of goods and services they would be unable to produce on their own, combinations that lie outside each country’s production possibilities curve.
::国际贸易增加了世界消费者可获得的商品和服务的数量。 通过按照比较优势原则分配资源,贸易允许各国消费它们无法自己生产的商品和服务的组合,而这种组合超出了每个国家的生产可能性曲线。When an economy or individual can produce more of any good per unit of labor than another country or individual, that country or person is said to have an absolute advantage . A country has a comparative advantage in the production of a good if it can produce that good at a lower opportunity cost than can other countries. If each country specializes in the production of goods in which it has a comparative advantage and trades those goods for things in which other countries have a comparative advantage, global production of all goods and services will be increased. The result can be higher levels of consumption for all.
::当一个经济体或个人能够比另一个国家或个人生产更多单位劳动力的任何商品时,据说这个国家或个人具有绝对的优势。如果一个国家能够以低于其他国家的机会成本生产该商品,那么这个国家或个人在生产该商品方面具有比较优势。如果每个国家专门生产具有比较优势的货物,并将这些货物用于其他国家具有比较优势的商品交易,那么所有货物和服务的全球生产就会增加,其结果可能是所有人的消费水平更高。If international trade allows expanded world production of goods and services, it follows that restrictions on trade will reduce world production. That is the economic case for free trade. It suggests that restrictions on trade, such as a tariff , a tax imposed on imported goods and services, or a quota , a ceiling on the quantity of specific goods and services that can be imported, reduce world living standards.
::如果国际贸易允许扩大货物和服务的世界生产,那么对贸易的限制将减少世界生产,自由贸易就是这种情况,它意味着对贸易的限制,例如关税、对进口货物和服务的税收或配额、对可进口的具体货物和服务数量的上限,将降低世界生活水平。The conceptual argument for free trade is a compelling one; virtually all economists support policies that reduce barriers to trade. Economists were among the most outspoken advocates for the 1993 ratification of the North American Free Trade Agreement ( NAFTA ), which virtually eliminated trade restrictions between Mexico, the United States, and Canada, and the 2004 Central American Free Trade Agreement ( CAFTA ), which did the same for trade between the United States, Central America, and the Dominican Republic. Most economists have also been strong supporters of worldwide reductions in trade barriers, including the 1994 ratification of the General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade ( GATT ), a pact slashing tariffs and easing quotas among 117 nations, including the United States, and the Doha round of World Trade Organization negotiations, named after the site of the first meeting in Doha, Qatar, in 2001 and still continuing. In Europe, member nations of the European Union ( EU ) have virtually eliminated trade barriers among themselves, and 15 EU nations now have a common currency, the euro, and a single central bank, the European Central Bank, established in 1999. Trade barriers have also been slashed among the economies of Latin America and of Southeast Asia. A treaty has been signed that calls for elimination of trade barriers among the developed nations of the Pacific Rim (including the United States and Japan) by 2010 and among all Pacific R im nations by 2020.
::自由贸易的概念论点是令人信服的;几乎所有经济学家都支持减少贸易壁垒的政策。经济学家是1993年批准《北美自由贸易协定》(NAFTA)的最直言不讳的倡导者之一,该协定实际上消除了墨西哥、美国和加拿大之间的贸易限制,2004年《中美洲自由贸易协定》(CAFTA)也几乎消除了美国、中美洲和多米尼加共和国之间的贸易限制。在欧洲,欧洲联盟(欧盟)成员国几乎消除了它们之间的贸易壁垒,15个欧盟国家现在拥有共同货币、欧元和1999年建立的单一中央银行欧洲中央银行。拉丁美洲经济体和东南亚经济体之间的贸易壁垒也曾被打破,包括美国在内的117个国家之间的关税减让和放宽配额,世界贸易组织多哈回合谈判在2001年在卡塔尔多哈举行第一次会议之后被命名,并且仍在继续。 在欧洲,欧洲联盟(欧盟)成员国实际上消除了它们之间的贸易壁垒,15个欧盟国家现在拥有共同货币、欧元和1999年建立的单一中央银行(欧洲央行 ) 。 拉丁美洲经济体和东南亚经济体之间的贸易壁垒也被打破了契约,包括美国在内的世界贸易组织谈判多哈回合也在2001年在卡塔尔多哈举行,而且现在仍在继续。The global embrace of the idea of free trade demonstrates the triumph of economic ideas over powerful forces that oppose free trade. One source of opposition to free trade comes from the owners of factors of production used in industries in which a nation lacks a comparative advantage.
::对自由贸易理念的全球接受表明经济思想战胜了反对自由贸易的强大力量。 反对自由贸易的一个根源来自一国缺乏比较优势的工业所使用的生产要素的拥有者。A related argument against free trade is that it not only reduces employment in some sectors but also reduces employment in the economy as a whole. In the long run, this argument is clearly wrong. The economy’s natural level of employment is determined by forces unrelated to trade policy, and employment moves to its natural level in the long run.
::反对自由贸易的一个相关论据是,它不仅减少了某些部门的就业,而且减少了整个经济的就业。 从长远看,这一论点显然是错误的。 经济的自然就业水平是由与贸易政策无关的力量决定的,而就业则从长远看也达到了其自然水平。Further, trade has no effect on real wage levels for the economy as a whole. The equilibrium real wage depends on the economy’s demand for and supply curve of labor. Trade affects neither.
::此外,贸易对于整个经济的实际工资水平没有任何影响。 平衡的实际工资取决于经济对劳动力的需求和供应曲线。 贸易对两者都没有影响。In the short run, trade does affect aggregate demand. Net exports are one component of aggregate demand; a change in net exports shifts the aggregate demand curve and affects real GDP in the short run. All other things unchanged, a reduction in net exports reduces aggregate demand, and an increase in net exports increases it.
::从短期来看,贸易确实影响着总需求,净出口是总需求的一个组成部分,净出口的变化改变了总需求曲线,在短期内影响了实际GDP。 所有其他情况都保持不变,净出口的减少降低了总需求,而净出口的增加也增加了总需求。Protectionist sentiment always rises during recessions. The recession that began in the United States in 2007 is no exception. The stimulus bill contained a provision ordering U.S. government agencies and contractors to purchase goods and services produced in the United States in preference to goods and services from other countries. Our trading partners have already begun threatening a trade war as a result of this provision. The stimulus bill does say that the “buy America first” provision should be “consistent with international obligations.” As yet, it is not clear how significant this provision would become.
::保护主义情绪在衰退期间总是在上升。 2007年在美国开始的衰退也不例外。 刺激法案包含一项条款,命令美国政府机构和承包商购买美国生产的货物和服务,而不是其他国家的货物和服务。 我们的贸易伙伴已经因为这一条款而开始威胁一场贸易战争。 刺激法案确实说“购买美国第一”条款应该“符合国际义务 ” 。 但目前还不清楚这一条款会变得多么重要。Videos: Comparative Advantage and Comparative Advantage Practice
::视频:比较优势和比较优势做法View the video below for a lesson on comparative advantage. The second video provides practice with the concept of comparative advantage.
::第二段影片提供实践的比较优势概念。The Rising Importance of International Trade
::国际贸易的日益重要重要性International trade is important, and its importance is increasing. From 1965 to 2007, world output rose by about 300%. The gains in total exports were even more spectacular; they soared by over 1,000%!
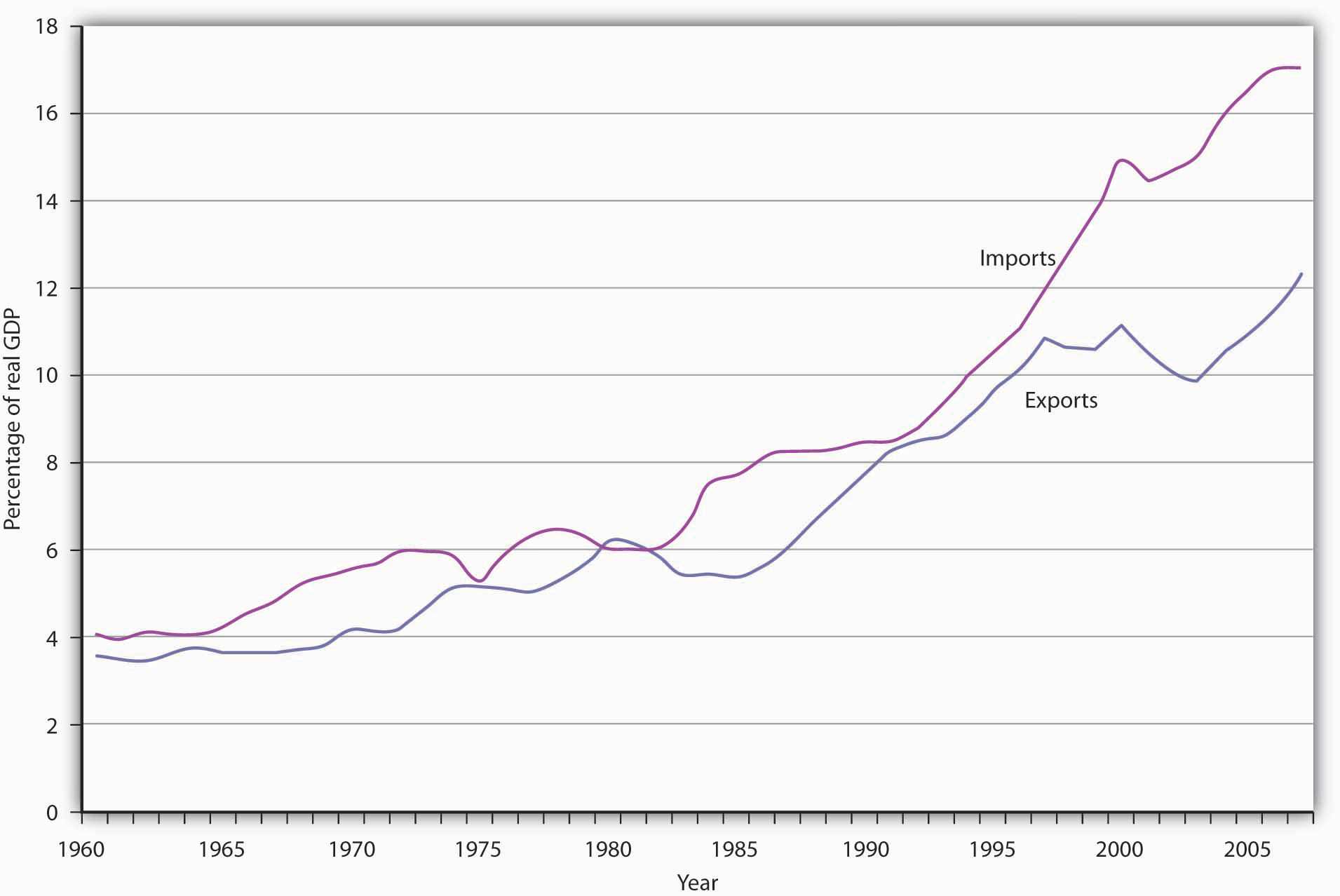
::国际贸易是重要的,其重要性正在增加。 从1965年到2007年,世界产出增长了约300 % 。 出口总量的收益甚至更加惊人;增长超过1000 % !While international trade was rising around the world, it was playing a more significant role in the United States as well. In 1960, exports represented just 3.6% of real GDP; by 2007, exports accounted for 12.4% of real GDP. Figure 7.2.1 "U.S. Exports and Imports Relative to U.S. Real GDP, 1960–2007" shows the growth in exports and imports as a percentage of real GDP in the United States from 1960 to 2007.
::当国际贸易在全世界增长的同时,它在美国也扮演着更加重要的角色。 1960年,出口只占实际GDP的3.6%;到2007年,出口占实际GDP的12.4%。 图7.2.1“1960-2007年美国相对美国实际GDP的进出口增长 ” 显示了1960-2007年美国出口和进口增长占实际GDP的百分比。Why has world trade risen so spectacularly? Two factors have been important. First, advances in transportation and communication have dramatically reduced the costs of moving goods around the globe. The development of shipping containerization that allows cargo to be moved seamlessly from trucks or trains to ships, which began in 1956, drastically reduced the cost of moving goods around the world, by as much as 90%. As a result, the numbers of container ships and their capacities have markedly increased. [1] Second, we have already seen that trade barriers between countries have fallen and are likely to continue to fall.
::世界贸易为什么如此惊人地增长?有两个因素很重要。第一,运输和通讯的进步极大地降低了全球货物运输的成本。 海运集装箱化的发展使得货物能够从卡车或火车上无缝地运到船舶,从1956年开始,这极大地降低了全世界货物运输成本的90%。 结果,集装箱船舶的数量及其能力显著增加。 [1]第二,我们已经看到国家间的贸易壁垒已经下降,而且有可能继续下降。U.S. Exports and Imports Relative to U.S. Real GDP, 1960–2007
::1960-2007年美国相对于美国实际国内生产总值的进出口情况The chart shows exports and imports as a percentage of real GDP from 1960 through the second quarter of 2007.
::图表显示,从1960年到2007年第二季度,进出口占实际国内生产总值的百分比。Source: Bureau of Economic Analysis, NIPA Table 1.1.6 (Revised December 23, 2008).
::资料来源:经济分析局,NIPA 表1.1.6(2008年12月23日修订)。Net Exports and the Economy
::净出口和经济As trade has become more important worldwide, exports and imports have assumed increased importance in nearly every country on the planet. We have already discussed the increased shares of U.S. real GDP represented by exports and by imports. We will find in this section that the economy both influences and is influenced by, net exports. First, we will examine the determinants of net exports and then discuss the ways in which net exports affect aggregate demand.
::随着贸易在全世界变得更加重要,世界上几乎每个国家的进出口都越来越重要,我们已经讨论了进出口占美国实际国内生产总值的比例增加的问题,我们在本节将发现,经济既影响又受净出口的影响。首先,我们将审查净出口的决定因素,然后讨论净出口影响总需求的方式。Determinants of Net Exports
::净出口的决定因素Net exports equal exports minus imports. Many of the same forces affect both exports and imports, albeit in different ways.
::净出口等于出口减去进口,许多同样的力量影响进出口,尽管方式不同。Income Effect
::收入对收入的影响As incomes in other nations rise, the people of those nations will be able to buy more goods and services—including foreign goods and services. Any one country’s exports thus will increase as incomes rise in other countries and will fall as incomes drop in other countries.
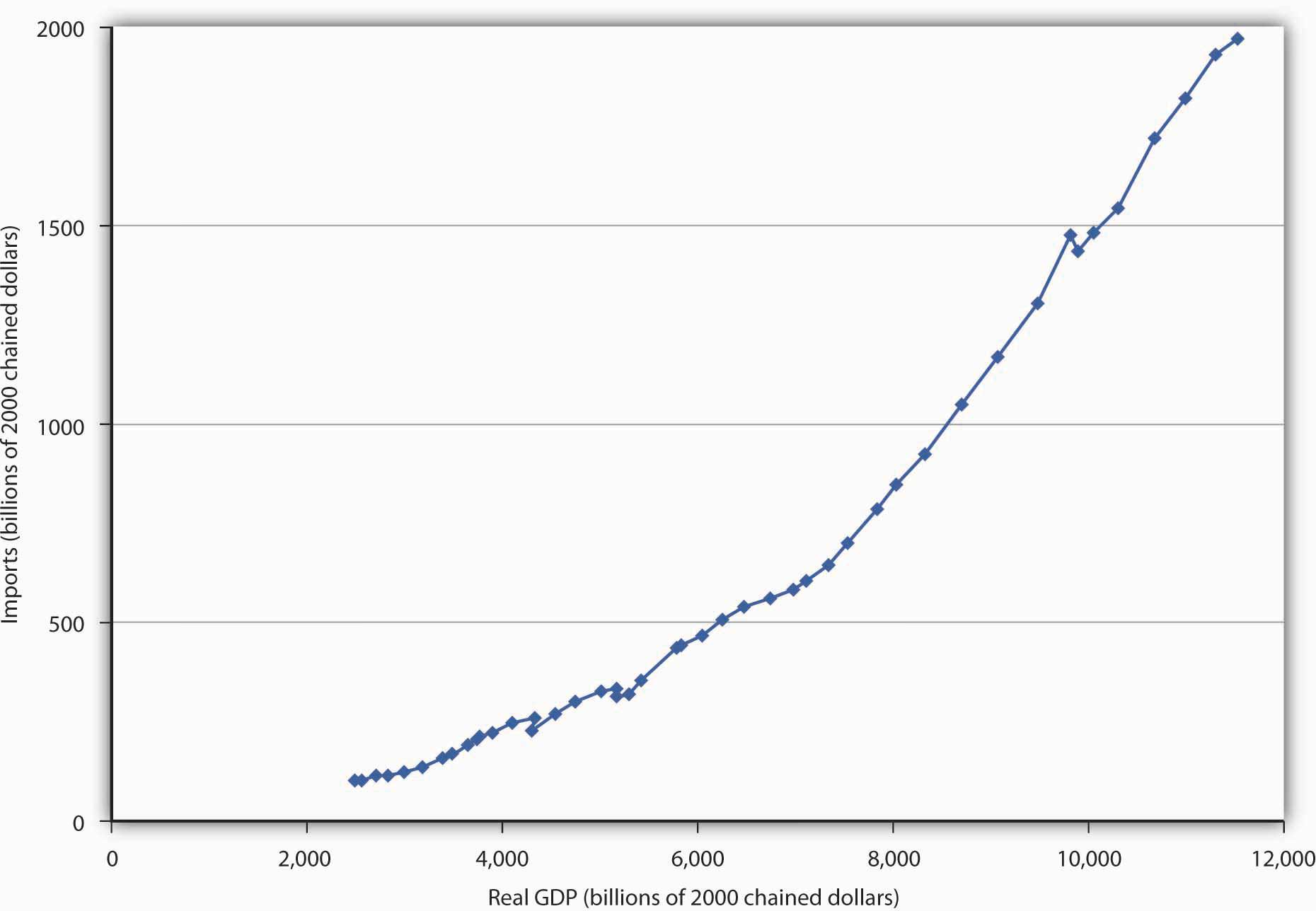
::随着其他国家的收入增加,这些国家的人民将能够购买更多的商品和服务 — — 包括外国商品和服务。 因此,任何国家的出口都会随着其他国家的收入增加而增加,并将随着其他国家的收入下降而下降。A nation’s own level of income affects its imports the same way it affects consumption. As consumers have more income, they will buy more goods and services. Because some of those goods and services are produced in other nations, imports will rise. An increase in real GDP thus boosts imports; a reduction in real GDP reduces imports. Figure 2 "U.S. Real GDP and Imports, 1960–2007" shows the relationship between real GDP and the real level of import spending in the United States from 1960 through 2007. Notice that the observations lie close to a straight line one could draw through them and resemble a consumption function.
::一个国家自身的收入水平对进口的影响与对消费的影响相同。 随着消费者收入增加,他们将购买更多的商品和服务。 由于这些商品和服务中有一部分在其他国家生产,进口将会增加。 实际GDP的增长将刺激进口;实际GDP的下降将减少进口。 图2“美国1960-2007年实际GDP和进口量 ” 显示了1960-2007年美国实际GDP与实际进口支出水平之间的关系。 图2“美国1960-2007年实际GDP与实际进口支出水平”显示了美国1960-2007年的实际GDP与实际进口支出水平之间的关系。U.S. Real GDP and Imports, 1960–2007
::1960-2007年美国实际国内生产总值和进口The chart shows annual values of U.S. real imports and real GDP from 1960 through 2007. The observations lie quite close to a straight line.
::图表显示了1960年至2007年美国实际进口量和实际GDP的年度值。 观察结果非常接近一条直线。Source : Bureau of Economic Analysis, NIPA Table 1.1.6 (Revised December 23, 2008).
::资料来源:经济分析局,NIPA 表1.1.6(2008年12月23日修订)。Relative Prices
::相对相对价格A change in the price level within a nation simultaneously affects exports and imports. A higher price level in the United States, for example, makes U.S. exports more expensive for foreigners and, for this reason, tends to reduce exports. At the same time, a higher price level in the United States makes foreign goods and services relatively more attractive to U.S. buyers and thus increases imports. A higher price level therefore reduces net exports. A lower price level encourages exports and reduces imports, increasing net exports. As we saw in the chapter that introduced the aggregate demand and supply model, the negative relationship between net exports and the price level is called the international trade effect and is one reason for the negative slope of the aggregate demand curve.
::一国内部价格水平的改变同时影响到进出口。例如,美国较高的价格水平使美国出口对外国人更贵,因此往往减少出口。与此同时,美国较高的价格水平使外国货物和服务对美国买主更具吸引力,从而增加进口。较高的价格水平因此减少了净出口。较低的价格水平鼓励出口和减少进口,增加净出口。正如我们在介绍总需求和供应模式的一章中看到的那样,净出口与价格水平之间的负关系被称为国际贸易效应,是总需求曲线负斜的一个原因。The Exchange Rate
::汇率The purchase of U.S. goods and services by foreign buyers generally requires the purchase of dollars, because U.S. suppliers want to be paid in their own currency. Similarly, purchases of foreign goods and services by U.S. buyers generally require the purchase of foreign currencies, because foreign suppliers want to be paid in their own currencies. An increase in the exchange rate means foreigners must pay more for dollars, and must thus pay more for U.S. goods and services. It therefore reduces U.S. exports. At the same time, a higher exchange rate means that a dollar buys more foreign currency. That makes foreign goods and services cheaper for U.S. buyers, so imports are likely to rise. An increase in the exchange rate should thus tend to reduce net exports. A reduction in the exchange rate should increase net exports.
::外国买家购买美国商品和服务通常需要购买美元,因为美国供应商希望用自己的货币支付。 同样,美国买家购买外国商品和服务通常需要购买外币,因为外国供应商希望用自己的货币支付。 汇率的提高意味着外国人必须支付更多的美元,从而必须支付更多的美国商品和服务。 因此,它减少了美国的出口。 与此同时,较高的汇率意味着美元购买更多的外币。 这使得美国买家的外币和服务更便宜,因此进口可能增加。 因此,汇率的提高会减少净出口。 汇率的下降应该增加净出口。Trade Policies
::贸易政策贸易政策A country’s exports depend on its own trade policies as well as the trade policies of other countries. A country may be able to increase its exports by providing some form of government assistance (such as special tax considerations for companies that export goods and services, government promotional efforts, assistance with research, or subsidies). A country’s exports are also affected by the degree to which other countries restrict or encourage imports. The United States, for example, has sought changes in Japanese policies toward products such as U.S.-grown rice. Japan banned rice imports in the past, arguing it needed to protect its own producers. That has been a costly strategy; consumers in Japan typically pay as much as 10 times the price consumers in the United States pay for rice. Japan has given in to pressure from the United States and other nations to end its ban on foreign rice as part of the GATT accord. That will increase U.S. exports and lower rice prices in Japan.
::一个国家的出口取决于其自身的贸易政策和其他国家的贸易政策。 一个国家可以通过提供某种形式的政府援助(比如对出口货物和服务的公司的特殊税收考虑、政府促进努力、研究援助或补贴 ) 来增加其出口。 一个国家的出口也受到其他国家限制或鼓励进口的程度的影响。 比如,美国寻求改变日本对美国产大米等产品的政策。 日本过去禁止大米进口,认为它需要保护自己的生产者。 这是一项代价高昂的战略;日本消费者通常支付美国大米消费价格的10倍之多。 日本向美国和其他国家施加压力,要求它们停止对外国大米的禁令,作为关贸总协定的一部分。 这将增加美国的出口,降低日本的大米价格。Similarly, a country’s imports are affected by its trade policies and by the policies of its trading partners. A country can limit its imports of some goods and services by imposing tariffs or quotas on them—it may even ban the importation of some items. If foreign governments subsidize the manufacture of a particular good, then domestic imports of the good might increase. For example, if the governments of countries trading with the United States were to subsidize the production of steel, then U.S. companies would find it cheaper to purchase steel from abroad than at home, increasing U.S. imports of steel.
::类似地,一国的进口也受其贸易政策和贸易伙伴政策的影响。 一国可以通过对某些商品和服务实行关税或配额限制其进口 — — 甚至可以禁止某些物品的进口。 如果外国政府补贴某一商品的制造,那么商品的国内进口就会增加。 比如,如果与美国贸易的国家政府补贴钢铁生产,那么美国公司就会发现从国外购买钢材比从国内购买钢材更便宜,从而增加美国钢铁进口。Preferences and Technology
::优惠和技术优惠和技术优惠和技术优惠和技术优惠和技术Consumer preferences are one determinant of the consumption of any good or service; a shift in preferences for a foreign-produced good will affect the level of imports of that good. The preference among the French for movies and music produced in the United States has boosted French imports of these services. Indeed, the shift in French preferences has been so strong that the government of France, claiming a threat to its cultural heritage, has restricted the showing of films produced in the United States. French radio stations are fined if more than 40% of the music they play is from “foreign” (in most cases, U.S.) rock groups.
::消费者的偏好是消费任何商品或服务的决定因素之一;对外国生产的商品的偏好转变将影响该商品的进口水平。 法国人对美国生产的电影和音乐的偏好促进了法国对这些服务的进口。 事实上,法国的偏好变化如此之大,以至于法国政府声称其文化遗产受到威胁,限制了在美国制作的电影的放映。 如果法国电台播放的音乐有40%以上来自“外国”(在大多数情况下,是美国)摇滚团体,那么法国广播电台就会被罚款。Changes in technology can affect the kinds of capital firms import. Technological changes have changed production worldwide toward the application of computers to manufacturing processes, for example. This has led to increased demand for high-tech capital equipment, a sector in which the United States has a comparative advantage and tends to dominate world production. This has boosted net exports in the United States.
::例如,技术变革改变了全世界的生产,将计算机应用于制造过程,这导致对高科技资本设备的需求增加,而高科技资本设备是美国具有相对优势并倾向于主宰世界生产的部门,这促进了美国的净出口。Net Exports and Aggregate Demand
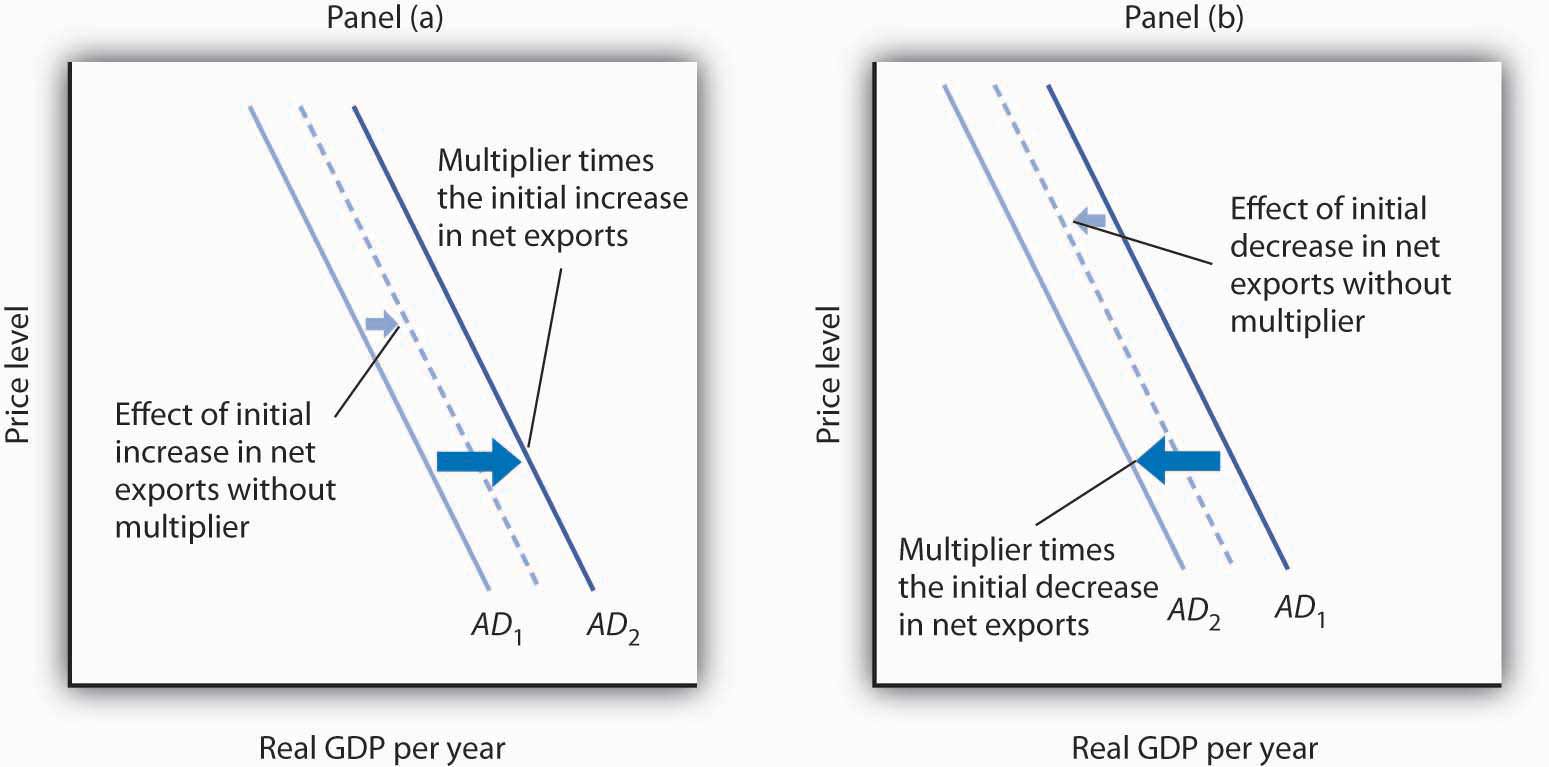
::净出口和总需求Net exports affect both the slope and the position of the aggregate demand curve. A change in the price level causes a change in net exports that moves the economy along its aggregate demand curve. This is the international trade effect. A change in net exports produced by one of the other determinants of net exports listed above (incomes and price levels in other nations, the exchange rate, trade policies, and preferences and technology) will shift the aggregate demand curve. The magnitude of this shift equals the change in net exports times the multiplier, as shown in Figure 3 "Changes in Net Exports and Aggregate Demand" . Panel (a) shows an increase in net exports; Panel (b) shows a reduction. In both cases, the aggregate demand curve shifts by the multiplier times the initial change in net exports, provided there is no other change in the other components of aggregate demand.
::价格水平的变化导致净出口的变化,使经济沿着其总需求曲线走动。这是国际贸易效应。上述净出口的其他决定因素之一(其他国家的收入和价格水平、汇率、贸易政策以及优惠和技术)产生的净出口变化将改变总需求曲线。这一变化的规模等于净出口变化乘以乘数的乘数,如图3“净出口和总需求的变化”所示。(a) 显示净出口增长;(b) 小组显示下降。在这两种情况下,总需求曲线都按净出口最初变化的乘数变化变化,但总需求的其他组成部分没有其他变化。Changes in Net Exports and Aggregate Demand
::净出口和总需求的变化In Panel (a), an increase in net exports shifts the aggregate demand curve to the right by an amount equal to the multiplier times the initial change in net exports. In Panel (b), an equal reduction in net exports shifts the aggregate demand curve to the left by the same amount.
::在小组(a)项中,净出口的增加使总需求曲线向右移动,数额等于净出口最初变化的乘数乘以;在小组(b)项中,净出口的同等减少使总需求曲线向左移动,数额相同。Changes in net exports that shift the aggregate demand curve can have a significant impact on the economy. The United States, for example, experienced a slowdown in the rate of increase in real GDP in the second and third quarters of 1998—virtually all of this slowing was the result of a reduction in net exports caused by recessions that staggered economies throughout Asia. The Asian slide reduced incomes there and thus reduced Asian demand for U.S. goods and services. We will see in the next section another mechanism through which difficulties in other nations can cause changes in a nation’s net exports and its level of real GDP in the short run.
::改变总需求曲线的净出口变化可能对经济产生重大影响。 比如,美国在1998年第二和第三季度实际GDP增长率放缓 — — 几乎所有这种放缓都是亚洲各经济体动荡不安的经济衰退导致净出口下降的结果。 亚洲的滑坡降低了亚洲的收入,从而降低了亚洲对美国商品和服务的需求。 我们将在下一节中看到另一个机制,通过该机制,其他国家的困难可以在短期内改变一个国家的净出口及其实际GDP水平。Answer the Try It! problems below to monitor your understanding of the concepts in this section.
::回答“试一下!”下面的问题是为了监测您对本节中概念的理解。Try It! Problems
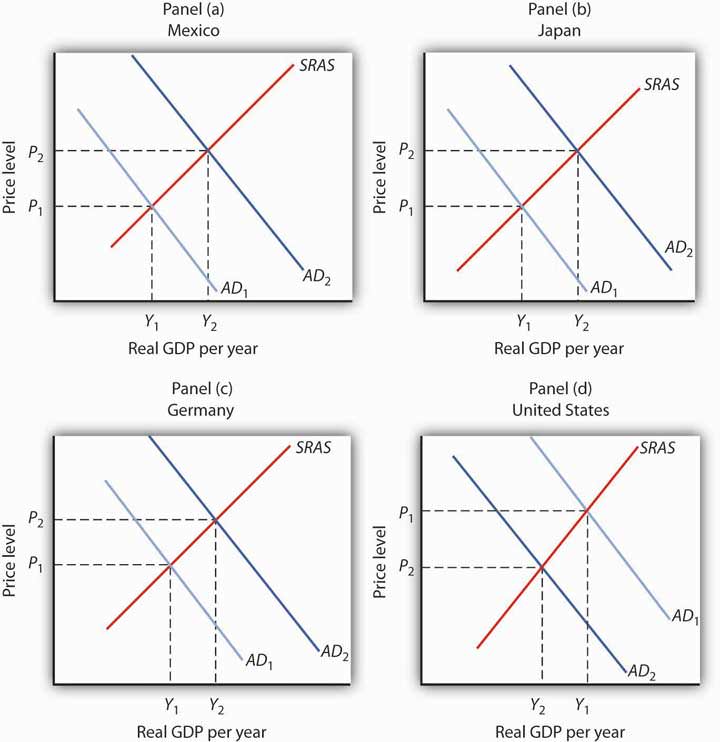
::试试看,有问题Draw graphs showing the aggregate demand and short-run aggregate supply curves in each of four countries: Mexico, Japan, Germany, and the United States. Assume that each country is initially in equilibrium with a real GDP of Y 1 and a price level of P 1 . Now show how each of the following four events would affect aggregate demand, the price level, and real GDP in the country indicated.
::绘制图表,显示墨西哥、日本、德国和美国这四个国家的供求总和短期总和曲线。假设每个国家最初都与实际GDP为Y1和价格水平为P1处于平衡状态。 现在,请显示以下四个事件对总需求、价格水平和所示国家实际GDP的影响。-
The United States is the largest foreign purchaser of goods and services from Mexico. How does an expansion in the United States affect real GDP and the price level in Mexico?
::美国是从墨西哥购买货物和服务的最大外国购买者,美国的扩张如何影响墨西哥的实际国内生产总值和价格水平? -
Japan’s exchange rate falls sharply. How does this affect the price level and real GDP in Japan?
::日本的汇率急剧下降。 这对日本的价格水平和实际GDP有何影响? -
A wave of pro-German sentiment sweeps France, and the French sharply increase their purchases of German goods and services. How does this affect real GDP and the price level in Germany?
::支持德国的情绪浪潮席卷了法国,法国人急剧增加了对德国商品和服务的购买量。 这对德国的实际GDP和价格水平有何影响? -
Canada, the largest importer of U.S. goods and services, slips into a recession. How does this affect the price level and real GDP in the United States?
Figure 4
::图4 图4ANSWERS TO TRY IT! PROBLEMS
::回答尝试它!-
Mexico’s exports increase, shifting its aggregate demand curve to the right. Mexico’s real GDP and price level rise, as shown in Panel (a).
::墨西哥的出口增长,总需求曲线向右转移。 墨西哥的实际GDP和物价水平上升(如小组(a)所示 ) 。 -
Japan’s net exports rise. This event shifts Japan’s aggregate demand curve to the right, increasing its real GDP and price level, as shown in Panel (b).
::日本的净出口增长。 这一事件将日本总需求曲线向右转移,提高了实际GDP和价格水平,正如小组(b)所示。 -
Germany’s net exports increase, shifting Germany’s aggregate demand curve to the right, increasing its price level and real GDP, as shown in Panel (c).
::德国的净出口增加,德国总需求曲线向右转移,提高价格水平和实际国内生产总值,如小组(c)所示。 -
U.S. exports fall, shifting the U.S. aggregate demand curve to the left, which will reduce the price level and real GDP, as shown in Panel (d).
::如小组(d)所示,美国出口下降,将美国总需求曲线向左移动,这将降低价格水平和实际国内生产总值。
::作为美国货物和服务的最大进口国,加拿大陷入了衰退。 这如何影响美国的价格水平和实际GDP? 图4 向美国出口增长,将其总需求曲线向右移动。 墨西哥的实际GDP和价格水平上升,如小组(a) 所示,日本的净出口上升。 此次事件将日本的总需求曲线向右转移,如小组(b) 所示,其实际GDP和价格水平上升。 德国的净出口增长,将德国总需求曲线向右转移,如小组(c) 所示,其价格水平和实际GDP上升。 美国的出口下降,将美国总需求曲线向左移动,这将降低价格水平和实际GDP,如小组(d) 所示。 -
Mexico’s exports increase, shifting its aggregate demand curve to the right. Mexico’s real GDP and price level rise, as shown in Panel (a).
-
Trade affects neither the economy's natural level of employment nor its real wage in the long run; those are determined by the demand for and the supply curve of labor.