联邦储备体系
章节大纲
-
The Federal Reserve System
::联邦储备体系The Federal Reserve System was established in 1913 as the nation’s central bank. It is owned by private member banks, not by the government. It regulates financial institutions, conducts monetary policy, provides services to the government, maintains the payment system, and enforces consumer protection laws. In addition, it supervises member banks, bank holding companies, and international operations of commercial banks, it maintains the country’s currency, clears checks, and oversees truth-in-lending laws.
::美联储体系成立于1913年,是国家的中央银行,由私人成员银行而不是政府所有。 它监管金融机构,执行货币政策,向政府提供服务,维护支付系统,执行消费者保护法。 此外,它监督成员银行、银行控股公司和商业银行的国际业务,维护国家货币,清查和监督披露真相法。Universal Generalizations
::普遍化-
The Federal Reserve works to strengthen and stabilize the nation’s monetary system.
::美联储致力于加强和稳定国家货币体系。 -
The Federal Open Market Committee makes decisions about the growth of the money supply.
::联邦开放市场委员会就货币供应的增长作出决定。 -
The Fed has a broad range of responsibilities, regulating both banks and laws to protect consumers.
::美联储负有广泛的责任,对银行和法律进行监管,以保护消费者。
Guiding Questions
::问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问 问-
What is a difference between National banks and State Banks in regard to the Fed?
::就美联储而言,国家银行和国家银行之间有什么区别? -
What is the main role of the Board of Governors for the Federal Reserve System?
::联邦储备系统理事会的主要作用是什么?
- Marriner S. Eccles Federal Reserve Headquarters, Washington D.C.

Some of the most influential decisions regarding monetary policy in the United States are made behind these doors. (Credit: modification of work by “squirrel83”/Flickr Creative Commons)
The Federal Reserve Banking System and Central Banks
::联邦储备银行系统和中央银行In making decisions about the money supply, a central bank decides whether to raise or lower interest rates and, in this way, to influence macroeconomic policy whose goal is low unemployment and low inflation. The central bank is also responsible for regulating all or part of the nation’s banking system to protect bank depositors and ensure the health of the bank’s balance sheet.
::在货币供应决策方面,央行决定是提高还是降低利率,从而影响以低失业率和低通胀为目标的宏观经济政策。 央行还负责监管国家全部或部分银行系统,以保护银行存款人并确保银行资产负债表的健康。The organization responsible for conducting monetary policy and ensuring that a nation’s financial system operates smoothly is called the central bank . Most nations have central banks or currency boards. Some prominent central banks around the world include the European Central Bank, the Bank of Japan, and the Bank of England. In the United States, the central bank is called the Federal Reserve—often abbreviated as just “the Fed.” This section explains the organization of the U.S. Federal Reserve and identifies the major responsibilities of a central bank.
::负责实施货币政策和确保国家金融体系顺利运作的组织被称为中央银行。 大多数国家都设有中央银行或货币委员会。 全世界一些著名的央行包括欧洲央行、日本银行和英格兰银行。 在美国,央行被称为美联储 — — 通常简称为“美联储 ” 。 这一节解释了美联储的组织,并确定了央行的主要责任。Structure/Organization of the Federal Reserve
::联邦储备基金的结构/组织Unlike most central banks, the Federal Reserve is semi-decentralized. It mixes government appointees with representation from private-sector banks. At the national level, it is run by a Board of Governors, consisting of seven members appointed by the President of the United States and confirmed by the Senate. Appointments are for 14-year terms and they are arranged so that one term expires January 31 of every even-numbered year. The purpose of the long and staggered terms is to insulate the Board of Governors as much as possible from political pressure so that policy decisions can be made based only on their economic merits. Additionally, except when filling an unfinished term, each member only serves one term, further insulating decision-making from politics. Policy decisions of the Fed do not require congressional approval, and the President cannot ask for the resignation of a Federal Reserve Governor as the President can with cabinet positions.
::与大多数中央银行不同,美联储实行半分权制,将政府任命者与私营部门银行的代表混为一谈,在国家一级,它由一个理事会管理,理事会由7名成员组成,由美国总统任命并经参议院确认;任命为期14年,每偶数年度的1月31日任满;长期和交错任期的目的是尽可能避免理事会受到政治压力,以便只能根据他们的经济优势作出决策;此外,除了完成一个未完成的任期,每个成员只任职一个任期,进一步从政治上做出决策;美联储的政策决定不需要国会批准,总统不能要求联邦储备局总督辞职,因为总统可以担任内阁职位。One member of the Board of Governors is designated as the Chair. For example, from 1987 until early 2006, the Chair was Alan Greenspan. From 2006 until 2014, Ben Bernanke held the post. The current Chair, J erome Powell , was sworn-in in February 2018. The Fed Chair is first among equals on the Board of Governors. While he or she has only one vote, the Chair controls the agenda and is the public voice of the Fed, so he or she has more power and influence than one might expect.
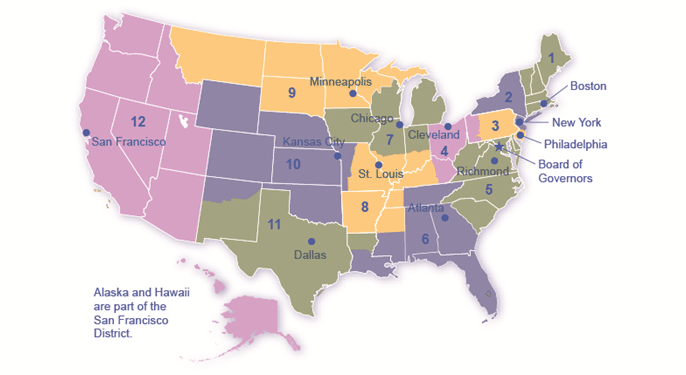
::例如,从1987年到2006年初,主席是艾伦·格林斯潘,从2006年到2014年,本·伯南克担任该职位,现任主席杰罗姆·鲍威尔于2018年2月宣誓就职,美联储主席在理事会中是首任平等成员之一,尽管只有一票,但主席控制着议程,是美联储的公开声音,因此他或她拥有比人们预期更大的权力和影响力。The Federal Reserve is more than the Board of Governors. The Fed also includes 12 regional Federal Reserve banks, each of which is responsible for supporting the commercial banks and economy generally in its district. The Federal Reserve districts and the cities where their regional headquarters are located are shown in 1. The commercial banks in each district elect a Board of Directors for each regional Federal Reserve bank, and that board chooses a president for each regional Federal Reserve district. Thus, the Federal Reserve System includes both federally and private-sector appointed leaders.
::联邦储备局比联邦储备局多,还包括12家联邦储备局地区银行,每个银行都负责支持其所在地区的商业银行和经济,联邦储备局地区及其地区总部所在的城市显示为1. 每个地区的商业银行为联邦储备局的每个地区银行选举一个董事会,而联邦储备局则为每个地区联邦储备局地区选择一个主席,因此联邦储备局系统包括联邦和私营部门任命的领导人。- The Twelve Federal Reserve Districts
There are twelve regional Federal Reserve banks, each with its district.
Video: What Does a Central Bank Do?
::录像:中央银行是做什么的?The Federal Reserve
::美联储The Federal Reserve, like most central banks, is designed to perform three important functions: to conduct monetary policy that promotes stability of the financial system, to provide banking services to commercial banks and other depository institutions, and to provide banking services to the federal government.
::联邦储备基金与大多数中央银行一样,旨在履行三项重要职能:执行促进金融体系稳定的货币政策;向商业银行和其他存款机构提供银行服务;向联邦政府提供银行服务。The first two functions are sufficiently important that we will discuss them in their own modules; the third function we will discuss here.
::前两个职能非常重要,我们将在各自模块中讨论;我们将在这里讨论第三个职能。The Federal Reserve provides many of the same services to banks as banks provide to their customers. For example, all commercial banks have an account at the Fed where they deposit reserves. Similarly, banks can obtain loans from the Fed through the “discount window” facility, which will be discussed in more detail later. The Fed is also responsible for check processing. When you write a check, for example, to buy groceries, the grocery store deposits the check in its bank account. Then, the physical check (or an image of that actual check) is returned to your bank, after which funds are transferred from your bank account to the account of the grocery store. The Fed is responsible for each of these actions.
::美联储向银行提供许多与银行向客户提供的相同服务,例如,所有商业银行在美联储设有存款准备金的账户。类似地,银行可以通过“贴现窗口”机制从美联储获得贷款,稍后将对此进行详细讨论。美联储还负责支票处理。例如,当您开支票购买杂货时,杂货店将支票存入其银行账户。然后,将实物核对(或实际核对的图像)退回您的银行,随后资金从您的银行账户转到杂货店的账户。美联储负责每项行动。On a more mundane level, the Federal Reserve ensures that enough currency and coins are circulating through the financial system to meet public demands. For example, each year the Fed increases the amount of currency available in banks around the Christmas shopping season and reduces it again in January.
::在更平凡的层面上,美联储确保足够的货币和硬币通过金融系统流通以满足公众需求。 比如,每年美联储在圣诞节购物季节前后增加银行可用货币的数量,并在1月份再次减少。Finally, the Fed is responsible for assuring that banks are in compliance with a wide variety of consumer protection laws. For example, banks are forbidden from discriminating on the basis of age, race, sex, or marital status. Banks are also required to publicly disclose information about the loans they make for buying houses and how those loans are distributed geographically, as well as by sex and race of the loan applicants.
::最后,美联储负责确保银行遵守各种消费者保护法,例如禁止银行因年龄、种族、性别或婚姻状况而实行歧视。 银行还必须公开披露它们为购买房屋提供的贷款信息,以及这些贷款在地理上是如何分配的,以及贷款申请人的性别和种族。The most prominent task of a central bank is to conduct monetary policy, which involves changes to interest rates and credit conditions, affecting the amount of borrowing and spending in an economy. Some prominent central banks around the world include the U.S. Federal Reserve, the European Central Bank, the Bank of Japan, and the Bank of England.
::央行最重要的任务是实施货币政策,这涉及到利率和信贷条件的改变,影响到一个经济体的借贷和支出数额。 全世界一些著名的中央银行包括美国联邦储备银行、欧洲央行、日本银行和英格兰银行。 央行的货币政策包括利率和信贷条件的改变,这影响到一个经济体的借贷和支出数额。The Problem of the Zero Percent Interest Rate Lower Bound
::零0%利率下下限的问题Most economists believe that monetary policy (the manipulation of interest rates and credit conditions by a nation’s central bank) has a powerful influence on a nation’s economy. Monetary policy works when the central bank reduces interest rates and makes credit more available. As a result, business investment and other types of spending increase, causing GDP and employment to grow.
::多数经济学家认为货币政策(一国央行操纵利率和信用条件)对国家经济具有强大的影响力。 当央行降低利率并增加信贷供应时,货币政策就会起作用。 结果,企业投资和其他类型的支出增长导致GDP和就业增长。But what if the interest rates banks pay are close to zero already? They cannot be made negative, can they? That would mean that lenders pay borrowers for the privilege of taking their money. Yet, this was the situation the U.S. Federal Reserve found itself in at the end of the 2008–2009 recession. The federal funds rate, which is the interest rate for banks that the Federal Reserve targets with its monetary policy, was slightly above 5% in 2007. By 2009, it had fallen to 0.16%.
::但是,如果利率银行已经接近零了呢? 利率银行支付利率已经接近零了呢? 它们不能变成负数吗? 这意味着放款人支付借款人拿到钱的特权。 然而,美国联邦储备基金在2008—2009年衰退结束时就陷入了这样的境地。 2007年,联邦储备基金利率(即联邦储备基金货币政策所针对银行的利率)略高于5 % 。 到2009年,该利率下降到0.16 % 。The Federal Reserve’s situation was further complicated because fiscal policy, the other major tool for managing the economy, was constrained by fears that the federal budget deficit and the public debt were already too high. What were the Federal Reserve’s options? How could the monetary policy be used to stimulate the economy? The answer, as we will see in this chapter, was to change the rules of the game.
::美联储的情况更加复杂,因为财政政策 — — 管理经济的另一个主要工具 — — 受到了担心联邦预算赤字和公共债务已经过高的制约。 美联储有什么选择? 如何用货币政策刺激经济? 正如我们在本章中所看到的,答案是改变游戏规则。Money, loans, and banks are all tied together. Money is deposited in bank accounts, which is then loaned to businesses, individuals, and other banks. When the interlocking system of money, loans, and banks works well, economic transactions are made smoothly in goods and labor markets and savers are connected with borrowers. If the money and banking system does not operate smoothly, the economy can either fall into recession or suffer prolonged inflation.
::货币、贷款和银行都是捆绑在一起的。 货币存放在银行账户中,然后借给企业、个人和其他银行。 当货币、贷款和银行的互连系统运转良好时,经济交易在商品和劳动力市场上顺利进行,储蓄者与借款人有联系。 如果货币和银行系统运作不顺利,经济可能陷入衰退或长期通货膨胀。The government of every country has public policies that support the system of money, loans, and banking, but these policies do not always work perfectly. This chapter discusses how monetary policy works and what may prevent it from working perfectly.
::每个国家的政府都有支持货币、贷款和银行体系的公共政策,但这些政策并不总是完美运作。 本章讨论了货币政策如何运作以及哪些因素可能阻止货币政策完美运作。How a Central Bank Executes Monetary Policy
::中央银行如何执行货币政策The most important function of the Federal Reserve is to conduct the nation’s monetary policy. Article I, Section 8 of the U.S. Constitution gives Congress the power “to coin money” and “to regulate the value thereof.” As part of the 1913 legislation that created the Federal Reserve, Congress delegated these powers to the Fed. Monetary policy involves managing interest rates and credit conditions, which influences the level of economic activity, as described in more detail below.
::美联储最重要的职能是实施国家货币政策。 美国《宪法》第8条第1款赋予国会“硬币”和“调节其价值”的权力。 作为1913年建立美联储的立法的一部分,国会将这些权力下放给美联储。 货币政策涉及利率和信用条件的管理,这影响到经济活动水平,详见下文。A central bank has three traditional tools to implement monetary policy in the economy:
::中央银行有三种在经济中执行货币政策的传统工具:Open market operations
::开放市场业务Changing reserve requirements
::变动准备金所需经费Changing the discount rate
::改变贴现率In discussing how these three tools work, it is useful to think of the central bank as a “bank for banks”—that is, each private-sector bank has its own account at the central bank. We will discuss each of these monetary policy tools in the sections below.
::在讨论这三个工具如何发挥作用时,将中央银行视为“银行银行”是有用的,也就是说,每个私营部门银行在中央银行有自己的账户。 我们将在下文各节讨论这些货币政策工具。Open Market Operations
::开放市场业务The most commonly used tool of monetary policy in the U.S. is open market operations. Open market operations take place when the central bank sells or buys U.S. Treasury bonds in order to influence the quantity of bank reserves and the level of interest rates. The specific interest rate targeted in open market operations is the federal funds rate. The name is a bit of a misnomer since the federal funds rate is the interest rate charged by commercial banks making overnight loans to other banks. As such, it is a very short term interest rate, but one that reflects credit conditions in financial markets very well.
::美国最常用的货币政策工具是开放市场业务。 当中央银行出售或购买美国国库债券以影响银行储备数量和利率水平时,公开市场业务就发生。 公开市场业务中的具体利率是联邦基金利率。 其名称有点错误,因为联邦基金利率是商业银行向其他银行提供过夜贷款的利率。 因此,它是一个非常短的利率,但能很好地反映金融市场的信用条件。The Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) makes the decisions regarding these open market operations. The FOMC is made up of the seven members of the Federal Reserve’s Board of Governors. It also includes five voting members who are drawn, on a rotating basis, from the regional Federal Reserve Banks. The New York district president is a permanent voting member of the FOMC and the other four spots are filled on a rotating, annual basis, from the other 11 districts. The FOMC typically meets every six weeks, but it can meet more frequently if necessary. The FOMC tries to act by consensus; however, the chairman of the Federal Reserve has traditionally played a very powerful role in defining and shaping that consensus. For the Federal Reserve, and for most central banks, open market operations have, over the last few decades, been the most commonly used tool of monetary policy.
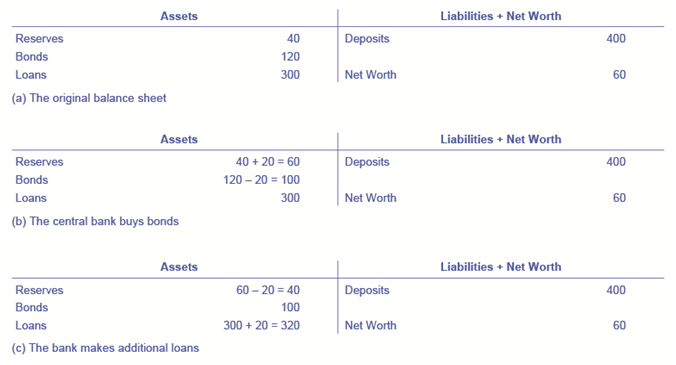
::联邦开放市场委员会(FOMC)负责决定这些公开市场运作。FOMC由联邦储备委员会的七位成员组成。它还包括五名投票成员,轮流从地区联邦储备银行中抽出。 纽约区主席是FOMC的永久投票成员,其他四个点每年轮流从其他11个区填补。 FOMC通常每六个星期开会一次,但必要时可以更频繁地开会。 FOMC试图以协商一致的方式行事;但是,联邦储备委员会主席传统上在确定和形成这一共识方面发挥了非常强大的作用。 对于联邦储备委员会和大多数央行来说,开放市场业务在过去几十年中一直是最常用的货币政策工具。To understand how open market operations affect the money supply, consider the balance sheet of Happy Bank, displayed in 1. 1 (a) shows that Happy Bank starts with $460 million in assets, divided among reserves, bonds and loans, and $400 million in liabilities in the form of deposits, with a net worth of $60 million. When the central bank purchases $20 million in bonds from Happy Bank, the bond holdings of Happy Bank fall by $20 million and the bank’s reserves rise by $20 million, as shown in 1 (b). However, Happy Bank only wants to hold $40 million in reserves (the quantity of reserves that it started with in 1) (a), so the bank decides to loan out the extra $20 million in reserves and its loans rise by $20 million, as shown in 1 (c). The open market operation by the central bank causes Happy Bank to make loans instead of holding its assets in the form of government bonds, which expands the money supply. As the new loans are deposited in banks throughout the economy, these banks will, in turn, loan out some of the deposits they receive, triggering the money multiplier.
::为了了解开放市场业务如何影响货币供应,请考虑到《快乐银行》的资产负债表,1 (a)中显示的《快乐银行》资产负债表显示,快乐银行从4.6亿美元的资产开始,分为储备金、债券和贷款,以及4亿美元以存款形式负债开始,净值为6 000万美元。 当中央银行从《快乐银行》购买2 000万美元的债券时,“快乐银行”的债券持有量下降了2 000万美元,银行的储备额上升了2 000万美元(如1 (b)中所示 ) 。 然而,《快乐银行》只想要持有4 000万美元的准备金(其起始准备金数量为1 (a) ) , 因此,银行决定借出额外的2 000万美元的准备金,并将贷款增加2 000万美元(如1 (c)中所示 ) 。 中央银行的公开市场运作导致《快乐银行》贷款而不是以政府债券形式持有资产,政府债券扩大了货币供应。 随着新贷款被存入整个经济体的银行,这些银行将反过来借出它们收到的一些存款,从而触发货币的倍增倍。Where did the Federal Reserve get the $20 million that it used to purchase the bonds? A central bank has the power to create money. In practical terms, the Federal Reserve would write a check to Happy Bank, so that Happy Bank can have that money credited to its bank account at the Federal Reserve. In truth, the Federal Reserve created the money to purchase the bonds out of thin air—or with a few clicks on some computer keys.
::美联储从哪得到用来购买这些债券的2 000万美元? 央行拥有创造资金的权力。 实际上,美联储会向幸福银行开支票,这样美联储就可以把这笔钱记入其在美联储的银行账户。 事实上,美联储创建了这笔钱,用空机购买这些债券 — — 或者点击电脑钥匙。Open market operations can also reduce the quantity of money and loans in an economy. Figure (a) shows the balance sheet of Happy Bank before the central bank sells bonds in the open market. When Happy Bank purchases $30 million in bonds, Happy Bank sends $30 million of its reserves to the central bank, but now holds an additional $30 million in bonds, as shown in Figure (b). However, Happy Bank wants to hold $40 million in reserves, as in Figure (a), so it will adjust down the quantity of its loans by $30 million, to bring its reserves back to the desired level, as shown in Figure (c). In practical terms, a bank can easily reduce its quantity of loans. At any given time, a bank is receiving payments on loans that it made previously and also making new loans. If the bank just slows down or briefly halts making new loans, and instead adds those funds to its reserves, then its overall quantity of loans will decrease. A decrease in the quantity of loans also means fewer deposits in other banks, and other banks reducing their lending as well, as the money multiplier discussed in Money and Banking takes effect. And what about all those bonds? How do they affect the money supply?
::开放市场经营也可以减少经济体的货币和贷款数量。 图(a)显示了中央银行在公开市场出售债券之前的幸福银行资产负债表。当快乐银行购买3 000万美元的债券时,快乐银行向中央银行发放了3 000万美元的储备,但现在又持有额外的3 000万美元的债券,如图(b)所示。 但是,快乐银行希望持有4 000万美元的储备,如图(a)所示,这样它将将其贷款数量调低3 000万美元,使其储备恢复到图(c)所示的预期水平。实际上,银行可以很容易减少贷款数量。在任何特定时间,银行接受其以前发放的贷款,并发放新的贷款。如果银行只是放慢或短暂停止发放新贷款,而是将这些资金加入其储备,那么其贷款总额就会减少。贷款数量的减少也意味着其他银行的存款减少,而其他银行的贷款也减少,因为货币和银行业中讨论的增值效应。这些债券会如何影响货币供应?
Changing Reserve Requirements
::变动准备金需求A second method of conducting monetary policy is for the central bank to raise or lower the reserve requirement, which, as we noted earlier, is the percentage of each bank’s deposits that it is legally required to hold either as cash in their vault or on deposit with the central bank. If banks are required to hold a greater amount in reserves, they have less money available to lend out. If banks are allowed to hold a smaller amount in reserves, they will have a greater amount of money available to lend out.
::实施货币政策的第二种方法是央行提高或降低储备要求,正如我们早些时候指出的那样,储备要求是每个银行依法必须持有的存款的百分比,这些存款要么作为现金存放在其保险库中,要么作为存款存放在中央银行。 如果银行被要求持有更多的储备,它们可以借出的资金就更少了。 如果允许银行持有较少的储备,它们将拥有更多的贷款资金。In early 2015, the Federal Reserve required banks to hold reserves equal to 0% of the first $14.5 million in deposits, then to hold reserves equal to 3% of the deposits up to $103.6 million, and 10% of any amount above $103.6 million. Small changes in the reserve requirements are made almost every year. For example, the $103.6 million dividing line is sometimes bumped up or down by a few million dollars. In practice, large changes in reserve requirements are rarely used to execute monetary policy. A sudden demand that all banks increase their reserves would be extremely disruptive and difficult to comply with, while loosening requirements too much would create a danger of banks being unable to meet the demand for withdrawals.
::2015年初,美联储要求银行持有相当于头1,450万美元存款的0 % 的储备,然后持有相当于存款的3 % 的储备,高达1.036亿美元,以及超过1.036亿美元的任何金额的10 % 。 准备金需求几乎每年都有小幅变化。 比如,1.036亿美元的分界线有时会涨幅或降幅几百万美元。 实际上,储备需求的大幅变化很少用于实施货币政策。 突然要求所有银行增加其准备金将极具破坏性且难以遵守,而放松要求将造成银行无法满足提款需求的危险。Changing the Discount Rate
::更改贴现率The Federal Reserve was founded in the aftermath of the Financial Panic of 1907 when many banks failed as a result of bank runs. As mentioned earlier, since banks make profits by lending out their deposits, no bank, even those that are not bankrupt, can withstand a bank run. As a result of the Panic, the Federal Reserve was founded to be the “lender of last resort.” In the event of a bank run, sound banks, (banks that were not bankrupt) could borrow as much cash as they needed from the Fed’s discount “window” to quell the bank run. The interest rate banks pay for such loans is called the discount rate. (They are so named because loans are made against the bank’s outstanding loans “at a discount” of their face value.) Once depositors became convinced that the bank would be able to honor their withdrawals, they no longer had a reason to make a run on the bank. In short, the Federal Reserve was originally intended to provide credit passively, but in the years since its founding, the Fed has taken on a more active role with monetary policy.
::美联储是在1907年金融恐慌之后成立的,当时许多银行都因银行破产而破产。 如前所述,由于银行通过放贷而获利,因此没有任何银行,甚至那些没有破产的银行,能够承受银行的运行。 由于恐慌,美联储是“最后的贷款人 ” 。 如果银行破产,美联储(没有破产的银行 ) 可以从美联储的贴现“窗口”中借出足够多的现金来压倒银行的运行。 利率银行为这类贷款支付的利率被称为贴现率。 (因为贷款是用银行的未偿贷款“贴现 ” , 银行的面值。 )一旦存款人确信银行能够兑现其提款,他们就没有理由再在银行里逃钱了。 简言之,美联储原本打算被动地提供信贷,但自其成立以来的几年里,美联储在货币政策中扮演了更加积极的作用。So, the third traditional method for conducting monetary policy is to raise or lower the discount rate. If the central bank raises the discount rate, then commercial banks will reduce their borrowing of reserves from the Fed, and instead call in loans to replace those reserves. Since fewer loans are available, the money supply falls and market interest rates rise. If the central bank lowers the discount rate it charges to banks, the process works in reverse.
In recent decades, the Federal Reserve has made relatively few discount loans. Before a bank borrows from the Federal Reserve to fill out its required reserves, the bank is expected to first borrow from other available sources, like other banks. This is encouraged by Fed’s charging a higher discount rate, than the federal funds rate. Given that most banks borrow little at the discount rate, changing the discount rate up or down has little impact on their behavior. More importantly, the Fed has found from experience that open market operations are a more precise and powerful means of executing any desired monetary policy.
::因此,实施货币政策的第三个传统方法就是提高或降低贴现率。 如果央行提高贴现率,那么商业银行就会减少向美联储的储备借款,而要求用贷款来取代这些储备。 由于可获得的贷款较少,货币供应下降,市场利率上升。 如果央行降低向银行收取的贴现率,这一过程就会发生逆转。 近几十年来,美联储提供了相对较少的贴现贷款。 在银行从美联储借款以补足其所需储备之前,预期该银行将首先从其他来源(如其他银行)借款。 美联储的贴现率高于联邦基金利率,这鼓励了美联储收取更高的贴现率。 由于大多数银行的贴现率很少,改变贴现率或降低贴现率不会对其行为产生什么影响。 更重要的是,美联储从经验中发现,开放市场业务是执行任何理想货币政策的更精确和有力的手段。In the Federal Reserve Act, the phrase “...to afford means of rediscounting commercial paper” is contained in its long title. This tool was seen as the main tool for monetary policy when the Fed was initially created. This illustrates how monetary policy has evolved and how it continues to do so.
::在《联邦储备法》中,“买得起商业票据再贴现手段”的短语载于其长标题中。 这一工具在美联储最初成立时被视为货币政策的主要工具。 这说明了货币政策是如何演变的,以及它如何继续发展。A central bank has three traditional tools to conduct monetary policy: open market operations, which involves buying and selling government bonds with banks; reserve requirements, which determine what level of reserves a bank is legally required to hold; and discount rates, which is the interest rate charged by the central bank on the loans that it gives to other commercial banks. The most commonly used tool is open market operations.
::央行有三种实施货币政策的传统工具:公开市场业务,涉及与银行买卖政府债券;储备要求,确定银行依法必须持有的储备水平;以及贴现率,即中央银行对其给予其他商业银行的贷款收取的利率。 最常用的工具是开放市场业务。Check It Out:
::检查它 :Video: Regulation Z
::视频:Z条Answer the self check questions below to monitor your understanding of the concepts in this section.
::回答下面的自我核对问题,以监测你对本节概念的理解。
Self Check Questions
::自查问题1. What is the purpose of the Federal Reserve System?
::1. 联邦储备体系的目的是什么?2. What do the Federal Reserve District Banks do?
::2. 联邦储备区银行是做什么的?3. What is the main role of the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC)?
::3. 联邦开放市场委员会(开放市场委员会)的主要作用是什么?4. What is the role of the Federal Reserve in dealing with State Member Banks?
::4. 美联储在与成员国成员银行打交道方面起什么作用?5. Name 2 other roles of the Federal Reserve System.
::5. 列出联邦储备系统的其他两个作用。 -
The Federal Reserve works to strengthen and stabilize the nation’s monetary system.