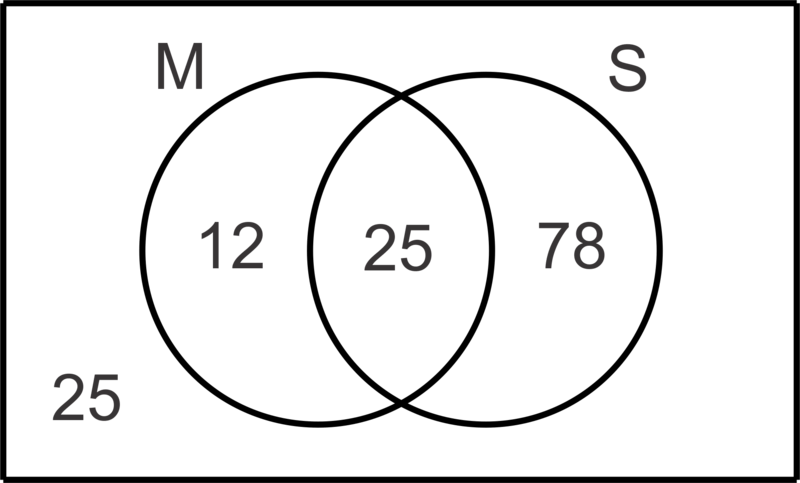12.13 使用活度图和有条件概率的概率
Section outline
-
Freezy's Ice Cream Stand is testing out two new flavors, Pumpernickel Brickel and Dandy Cotton Candy. A poll conducted by Freezy's showed that 32 customers liked Pumpernickel Brickel, 58 customers liked Dandy Cotton Candy, 12 liked both flavors, and 22 liked neither flavor. What is a probability that one of those customers selected at random would like Dandy Cotton Candy?
::Freezy进行的一项民意测验显示,有32位顾客喜欢Pumpernickel Brickel,58位顾客喜欢Dandy Cotton Candy,12位顾客喜欢两种口味,22位顾客不喜欢两种口味。 随机挑选的顾客中,有一位喜欢Dandy Cottond Candy的可能性是什么?Probability Using a Venn Diagram
::使用 Ven 图表的概率It is often useful to use a to visualize the probabilities of multiple events. In #1 below we explore the use of a Venn diagram to determine the probabilities of individual events, the intersection of events and the compliment of an event . In #3 we will continue to explore the concept of a and how to use a Venn diagram to solve these problems as well as the formula for conditional probability.
::通常使用一种方法来想象多个事件的概率是有用的。 在下面的 # 1 中, 我们探索使用一个 Venn 图表来确定单个事件的概率、 事件的交叉和对事件的赞美。 在 # 3 中, 我们将继续探索一个概念以及如何使用 Venn 图表来解决这些问题, 以及有条件概率的公式 。Let's use the Venn diagram below to find the following probabilities.
::让我们使用下面的文恩图 来发现以下的概率。Notice that the sum of all the values in the diagram is . This diagram represents the entire sample space for two events, and .
::注意图中所有数值的总和是 0.4+0.3+0.2+0.1=1. 此图代表A和B两个事件的全部样本空间。-
::P(A)项
To find the , we will add the probability that only occurs to the probability that and occur to get . So .
::要找到 P( A) , 我们将会加上一个概率, 即 A 和 B 的发生概率只有 A 发生于 0.4+0. 3 = 0. 7。 所以 P( A) = 0. 7 。-
::P(B) P(B)
Similarly, .
::同样,P(B)=0.2+0.3=0.5。-
::PA__________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
Now, is the value in the overlapping region 0.3.
::现在,P(AB)是重叠区域0.3的值。
::PA__________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________. Which can also be found using the formula .
::P(AB) =0. 4+0. 3+0. 2=0. 9。 也可以使用公式P(A)+P(B)-P(AB) = 0. 7+0. 5-0.3=0. 9 。
:AB________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
needs to be determined by finding where in the diagram everything outside of overlaps with everything outside of . That will be the region outside of both circles and that probability is 0.1. Another way to think of this is , or .
::P(AB) 需要通过在图表中找到A以外的所有东西与B以外的所有东西的重叠之处来确定。 这将是两个圆圈以外的区域, 概率为0.1。 另一种思考方式是 P(AB) , 或 1-P(AB) 。De Morgan's Law
::德摩根法There are a couple of equivalent set notations on probabilities and they are called De Morgan’s Laws.
::也被称为德摩根法则。for sets or for probabilities.
:AB) (AB) 或 P (AB) P (AB) 或概率。
and
::和for sets or for probabilities.
:AB) (AB) 或 P (AB) P (AB) 或概率。
Now, let's solve the following problems.
::现在,让我们解决以下的问题。-
Given
,
and
, find
and
.
::鉴于P(A)=0.6,P(B)=0.3,P(A)=0.7,见P(A)B和P(A)B。
First, we can use the formula for the union of two sets to determine the intersection.
::首先,我们可以使用两组组合的公式来确定交叉点。
::P(A)+P(B)-P(AB)=P(AB)0.6+0.3-P(AB)=0.70.9-0.7=P(AB)-0.2=P(AB)Now we can use De Morgan’s Law to find .
::现在,我们可以利用德摩根的法律来找到P(AB)。
::P(AB)=P(AB)1-P(AB)=1-0.2=0.8。We could have also created a Venn diagram for the probabilities and interpreted and the regions outside union with the regions outside which would be everything in the Venn diagram except the overlap of the two regions or .
::我们还可以制作一份文恩图,说明概率和解释P(AB)以及A联盟以外的区域与B以外的区域,这是文恩图中的一切,但两个区域或P(AB)的重叠除外。-
The data from a survey of 140 students showed that 37 study music, 103 play a sport and 25 do neither. Create a Venn diagram to illustrate the data collected and then determine the probability that if a student is selected at random,
::对140名学生的调查数据显示,37人学习音乐,103人玩运动,25人两者兼而有之。 创建一个文恩图表来说明所收集的数据,然后确定如果随机挑选学生,
-
he or she will study music
::他(或她)将学习音乐 -
he or she will study music given that he or she plays a sport.
::他(她)将学习音乐,因为他(她)参加运动。
Let represent the set of students who study music and represent the set of students who play sports. First let’s determine the number of students that study music and play a sport to fill in the overlapping region in the diagram and then we can find the other values.
::让M代表一组学习音乐的学生,而S代表一组玩体育的学生。 首先,让我们决定研究音乐和玩体育的学生人数,以填充图表中的重叠区域,然后找到其他的价值观。
::n(M)+n(S)-n(MS)=n(MS)37+103-n(MS)=115n(MS)=25-
The probability that a randomly selected student studies music is the number of students who study music divided by the total number of students surveyed or
.
::随机选择的学生学习音乐的概率是学习音乐的学生人数除以接受调查的学生总数或P(M)=n(M)140=371400.264。 -
The probability that a randomly selected student will study music given that he/she plays a sport is called a conditional probability. We use the notation
to represent the
given that
has already occurred. To find this probability using a Venn diagram, we find the number of student who study music and play a sport and divide by the number of students who play a sport or
. Think of it this way, when we say that we know that the student plays a sport, then the numerator is limited to those students who study music and play a sport and the denominator is limited to those who play a sport.
::随机选择的学生学习音乐的概率是,他/她玩运动的概率被称为有条件的概率。我们使用P(MS)标记来代表P(M),因为S已经出现。为了用Venn图表来发现这一概率,我们发现学习音乐和玩运动的学生人数,并且按照参加运动的学生人数或P(MS)=n(MS)n=251030.243来区分,这样想想,当我们说我们知道学生玩运动时,那么分子仅限于那些学习音乐和玩运动的学生,分母仅限于那些参加运动的学生。
There is also a formula for conditional probability:
::有条件概率也有一个公式:P(AB)=P(AB)P(B)In the context of our problem, it is: .
::就我们的问题而言,是:P(MS)=P(MS)P(S)=25140103140=25140140140=25140140140103=25103。Notice that the resulting probability is the same as previously determined. Either method can be used.
::注意由此产生的概率与先前确定的相同。 这两种方法都可以使用。Examples
::实例Example 1
::例1Earlier, you were asked to find the probability that one of those customers selected at random would like Dandy Cotton Candy.
::早些时候,有人要求你 找到一个随机挑选的顾客 喜欢丹迪棉花糖的概率The Venn diagram for this situation would show 12, the number of customers who like both flavors, as the intersection. The number of customers who like only the Pumpernickel flavor would therefore be while the number of customers who like only the Cotton Candy flavor would be . Since there are 21 customers who like neither flavor, the total number of customers polled is and the probability that one of those customers chosen at random would like the Cotton Candy flavor is .
::这种情形的文恩图将显示12个,即喜欢两种口味的客户数量,作为交叉点。因此,只喜欢南瓜尼可口味的客户数量将是32-12=20,而只喜欢棉花糖果口味的客户数量将是58-12=46。由于21个客户不喜欢两种口味,因此接受调查的客户总数是12+20+46+22=100,随机选择的客户中喜欢棉花口味的客户可能为58100=58%。Example 2
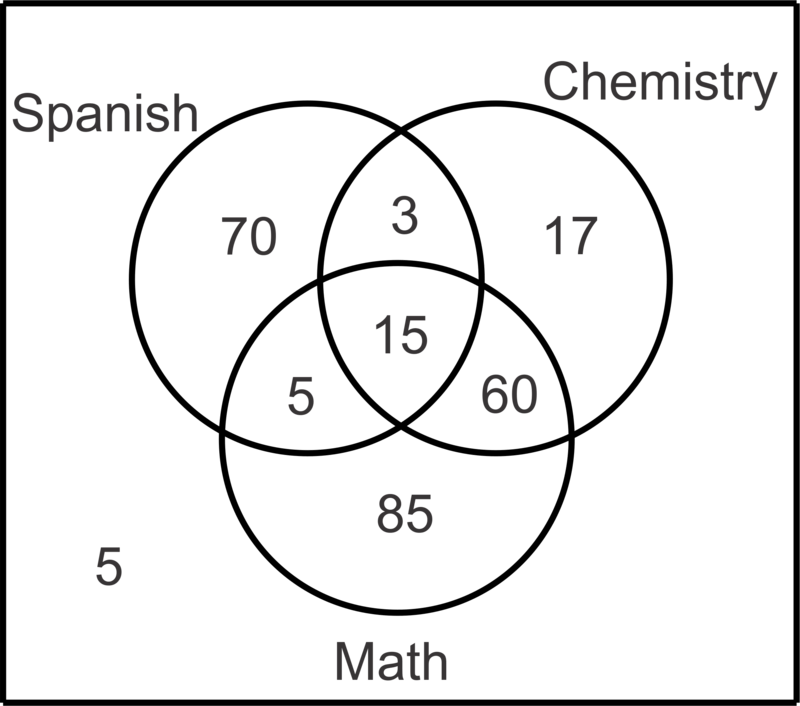
::例2In a class of 260 seniors, 93 study Spanish, 95 study Chemistry, 165 study Mathematics, 18 study Spanish and Chemistry, 75 study Chemistry and Math, 20 study Math and Spanish and 15 study all three subjects. Make a Venn diagram to illustrate the data and then find the probability that a student selected at random studies:
::在260名高年级学生中,有93人学西班牙语,95人学化学,165人学数学,18人学西班牙语和化学,75人学化学和数学,20人学数学和西班牙语,15人学这三个科目。just Spanish
::只是西班牙语
:SMC)=70260=7260.269
Math and Chemistry but not Spanish
::数学和化学,但不是西班牙语
:MCS)=60260=3130.231
none of these subjects
::这些主题无一是这些主题。
::P(MCS)=5260=1520.0192Spanish, given that he/she studies Math
::西班牙语,鉴于他/她学习数学
::P(SM) = P(SM) P(M) = 20260165260= 4330. 121Example 3
::例3Given , and , find and .
::鉴于P(AB)=0.4,P(AB)=0.2和P(AB)=0.3,见P(B)和P(AB)。The information gives us the Venn diagram:
::信息为我们提供了文恩图:The missing value, , must be 0.1 in order for the total of the probabilities in the sample space to equal 1. Thus, . .
::缺失值 P(B) {A}) 必须为 0.1, 样本空间的概率总额必须等于 1. 1。 因此, P(B) = 0.5。 P(A) (B) = P(A) B) = 0. 40.5= 45=0. 8。Review
::回顾For questions 1-3, find the indicated probabilities given , and .
::关于问题1-3,请找到P(A)=0.5、P(B)=0.65和P(AB)=0.75所示的概率。-
::PA__________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ -
:AB________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
-
::P(BA)
For questions 4-6, find the indicated probabilities given , and .
::关于问题4-6,见P(A)=0.6、P(B)=0.8和P(AB)=0.2所示概率。-
:AB________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
-
::P(BA) -
::PA__________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
For questions 7-9, find the indicated probabilities given , and .
::关于问题7-9,见P(A)B=0.3、P(B)A=0.2和P(A)B=0.8所示概率。-
::PA__________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ -
::P(A)项 -
::P(BA) -
Given
,
and
, find
.
::鉴于P(A)=2P(B),P(AB)=0.8和P(AB)=0.1,请找到P(A)。 -
The international club at a school has 105 members, many of whom speak multiple languages. The most commonly spoken languages in the club are English, Spanish and Chinese. Use the Venn Diagram below to determine the probability of selecting a student who:
-
does not speak English.
::不会说英语。 -
speaks Spanish given that he/she speaks English.
::鉴于heshe说英语,讲西班牙语。 -
speaks English given that he/she speaks Chinese.
::说英语,因为heshe说中文。 -
speaks Spanish and English but not Chinese.
::讲西班牙语和英语,但不是中文。
::学校的国际俱乐部有105名成员,其中许多人讲多种语言,俱乐部中最常用的语言是英语、西班牙语和中文,使用下面的Venn图表来确定选择学生的概率:不讲英语;讲西班牙语,因为英语;讲英语,因为讲中文;讲西班牙语和英语,但不是中文。 -
does not speak English.
Review (Answers)
::回顾(答复)Click to see the answer key or go to the Table of Contents and click on the Answer Key under the 'Other Versions' option.
::单击可查看答题键, 或转到目录中, 单击“ 其他版本” 选项下的答题键 。 -