13.11 利用r和theta在协调计划中找到点
章节大纲
-
Trig Riddle: I am a point. My are . What are my Cartesian coordinates?
::Trig Riddle:我是一个点。我是2,330。我的笛卡尔座标是什么?Convert Polar Coordinates to Cartesian Coordinates
::将极坐标转换为笛卡尔坐标Let's look at how to convert Polar coordinates to Cartesian coordinates. This is, essentially, the reverse of the process used to convert Cartesian coordinates to Polar coordinates.
::让我们来看看如何将极地坐标转换为笛卡尔坐标。这基本上是把笛卡尔坐标转换为极地坐标的过程的反方向。Given the point , let's find the equivalent Cartesian coordinates.
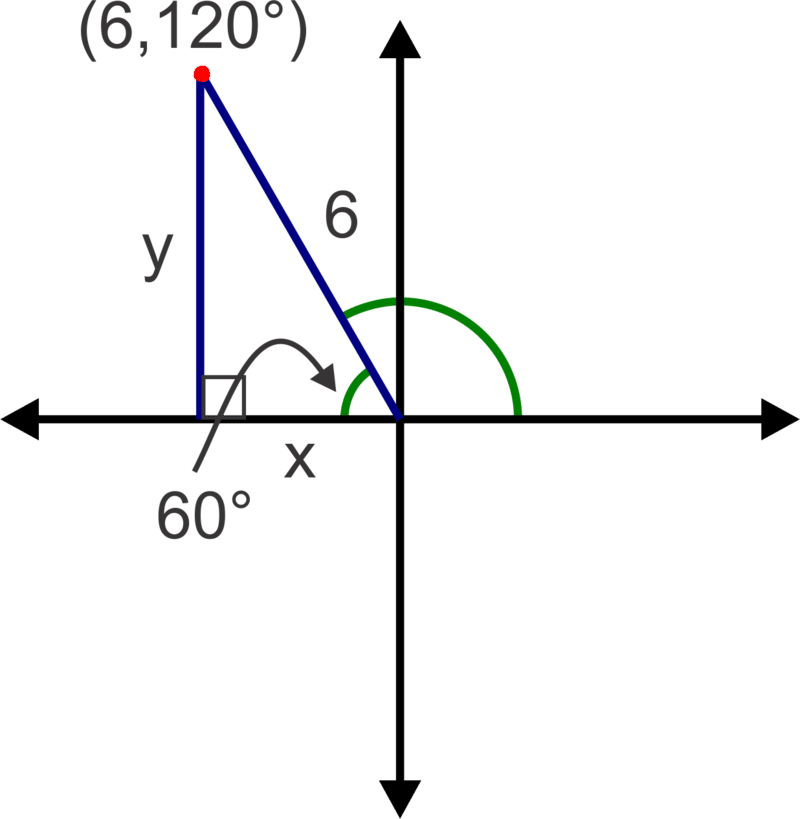
::根据点数(6,120),让我们找到等同的笛卡尔坐标。First, consider the diagram below and the right triangle formed by a perpendicular segment to the -axis and hypotenuse equal to the radius. We can find the legs of the right triangle using and thus the and coordinates of the point.
::首先, 请考虑下图和右三角形, 右三角形由直角段组成, 与 X 轴和下角等值, 等于半径。 我们可以使用右三角形的腿, 从而找到点的 x 和 y 坐标 。From the diagram we can see that the reference angle is . Now we can use right triangle trigonometry to find and . In this particular case, we can also use special right triangle ratios or the unit circle .
::从图表中我们可以看到参考角度是 60 。 现在我们可以使用右三角三角三角测量来找到 x 和 y。 在此特定情况下, 我们也可以使用特殊右三角比或单位圆 。
::{\fn黑体\fs22\bord1\shad0\3aHBE\4aH00\fscx67\fscy66\2cHFFFFFF\3cH808080}为什么? {\fn黑体\fs22\bord1\shad0\3aHBE\4aH00\fscx67\fscy66\2cHFFFFFF\3cH808080}为什么? {\fn黑体\fs22\bord1\shad0\3aHBE\4aH00\fscx67\fscy66\2cHFFFFFF\3cH808080}为什么? {\fn黑体\fs22\bord1\shad0\3aHBE\4aH00\fscx67\fscy66\2cHFFFFFF\3cH808080}为什么? {\fn黑体\fs22\bord1\shad0\3aHBE\4aH00\fscx67\fscy66\2cHFFFFFF\3cH808080}为什么?Since the point is in the second quadrant, the value should be negative giving the Cartesian coordinates .
::由于点位于第二个象限, x 值应为负值,显示笛卡尔坐标(-3,33)。Recall that every point on the unit circle was , where represented the angle of rotation from the positive axis and the radius (distance from the origin) was 1. In these problems, our radius varies as we are no longer restricted to the unit circle. In the previous problem , observe that the coordinates are essentially where 6 was the radius and was the reference angle. We could have used the angle of rotation, , and the only difference would be that the cosine ratio would be negative which would automatically make the coordinate negative. We can generalize this into a rule for converting from Polar coordinates to Cartesian coordinates:
::回顾单位圆的每个点是(cos,sin), 代表正x轴的旋转角度,半径(与原点的距离)为1. 在这些问题上,我们的半径因我们不再局限于单位圆而有所不同。 在前一个问题上, 注意坐标( x,y) 基本上( x, y) 6 =半径, 6 =半径, 60 = 6 = 参考角度。 我们本可以使用旋转角度, 120 =, 唯一的区别是, 共弦比为负, 这会自动使x坐标为负。 我们可以将这一规则概括为从极坐标转换为笛切斯坐标的规则 :
:r,)=(rcos,rsin)
Now, given the point, , let's find the Cartesian coordinates.
::现在,考虑到这一点, (10, -220), 让我们找到笛卡尔座标。Using the rule with and and the calculator:
::使用 r= 10 和 220 和计算器的规则 :
:10cos(-220),10sin(-220)=(-7.66,6.43)
Finally, given the point, , let's find the exact value of the Cartesian coordinates.
::最后,鉴于这一点,(9,11,6),让我们找出笛卡尔座标的确切价值。This time and . So, .
::这一次 r=9 和 \\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\92\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\ -92\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\92\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\92。。\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\92。。\\First, draw a diagram. From this diagram we can see that the reference angle is . Now we can use right triangle trigonometry to find and . In this particular case, we can also use special right triangle ratios or the unit circle.
::首先, 绘制图表。 从这个图表中, 我们可以看到引用角度是 30\\\\\\ 30\\\ 。 现在我们可以使用右三角三角三角测量来查找 x 和 y。 在此特定情况下, 我们也可以使用特殊的右三角比或单位圆 。
::30x2 sin 30Y2x=2cos 30302(32) 3和y=2sin}3022(12)=1Since the point is in the fourth quadrant, the value should be negative giving the Cartesian coordinates .
::由于点在第四象限,Y值应为负值,表示笛卡尔坐标(3,-1)。Examples
::实例Example 1
::例1Earlier, you were asked to find the Cartesian coordinates for a point whose Polar coordinates are .
::早些时候,有人要求你找到笛卡尔座标,以找到极地座标(2 330)所在的点。First draw a diagram. From the diagram we can see that the reference angle is . Now we can use right triangle trigonometry to find and . In this particular case, we can also use special right triangle ratios or the unit circle.
::首先绘制图表。 从图表中我们可以看到参考角度是 30\\\\\\\\\\\\\ n现在我们可以使用右三角三角三角测量来找到 x和 y。 在此特定情况下, 我们也可以使用特殊的右三角三角比或单位圆 。
::30x2 sin 30Y2x=2cos 30302(32) 3和y=2cos 302(12)=1Since the point is in the fourth quadrant, the value should be negative giving the Cartesian coordinates .
::由于点在第四象限,Y值应为负值,表示笛卡尔坐标(3,-1)。Example 2
::例2Use your calculator to find the Cartesian coordinates equivalent to the Polar coordinates .
::使用计算器找到与极地坐标(11,157)相等的笛卡尔坐标(11,157)。
:11cos157,11sin157)(-1013.4.30)
Example 3
::例3Find the exact value of the Cartesian coordinates equivalent to the Polar coordinates .
::找到相当于极地坐标(8,45)的笛卡尔座标的准确值。
:8cos45,8sin45) =(8(22),8(22) =(42,42)
Example 4
::例4Find the exact value of the Cartesian coordinates equivalent to the Polar coordinates .
::找到相当于极地坐标(5,2)的笛卡尔座标的准确值。
:5cos(2),5sin(2)) =(5(0),5(-1) =(0),5(-5) =(0)
Review
::回顾Use your calculator to find the Cartesian coordinates equivalent to the following Polar coordinates. Give your answers rounded to the nearest hundredth.
::使用您的计算器找到与以下极坐标相等的笛卡尔座标。 将答案四舍五入到最接近的一百位 。Find the exact value Cartesian coordinates equivalent to the following Polar coordinates.
::找到与以下极地坐标相等的笛卡尔座标的准确值 。Review (Answers)
::回顾(答复)Click to see the answer key or go to the Table of Contents and click on the Answer Key under the 'Other Versions' option.
::单击可查看答题键, 或转到目录中, 单击“ 其他版本” 选项下的答题键 。