8.12 曲线下区域
Section outline
-
You probably remember Becca and her track meet from earlier lessons. She won her race after pulling away from the pack in a hard push at the finish, and her boyfriend got a great picture of her just as she began pulling away. We have learned that by using , she could actually calculate her speed at the moment the picture was taken, and then with the second derivative she could calculate her acceleration similarly.
::你可能记得贝卡和她的履历在早期的课上相遇。她赢得了比赛,因为她从球队的球队中拉了出来,在球队的比赛结束时,她很努力地推开了球队,而她男朋友在她开始拉开球时得到了她一幅很棒的照片。我们了解到,通过使用这个球队,她可以计算出照片拍摄时的速度,然后用第二个衍生物来计算她的加速度。In this lesson we will discuss the integral , which is the process that would allow Becca to calculate the distance she actually covered during a given interval of the race, even though her speed was not constant!
::在这个教训中, 我们将讨论一个整体, 这个过程可以让贝卡计算自己在比赛的某一段时间里 实际所覆盖的距离, 即使她的速度并不稳定!Area Under the Curve
::曲线下区域To understand integration , consider the area under the curve y = f ( x ) for the interval from x = a to x = b in the figure below.
::为了解整合情况,请在下图中考虑曲线y = f(x)下从 x = a 到 x = b 之间的区域。One way to calculate the area is to fill the region with rectangles. If the region is curved, the rectangles will not fit exactly, but we can improve the approximation by using rectangles of thinner width. If we continue to make the rectangles thinner and thinner, the area under the curve would reach the exact area under the curve. This is the limiting process that we discussed. In other words, the area under the curve is the limit of the total area of the rectangles as the widths of the rectangles approach zero.
::计算区域的方法之一是用矩形填充区域。 如果区域被弯曲, 矩形将不完全合适, 但我们可以通过使用较薄宽度的矩形来改进近似。 如果我们继续使矩形变薄, 曲线下的区域会达到曲线下的确切区域。 这就是我们讨论的限制进程。 换句话说, 曲线下的区域是矩形总面积的界限, 也就是矩形接近零的宽度。Consider again the figure above. The interval from x = a to x = b is subdivided into n equal subintervals. Rectangles are drawn in each subinterval. Each rectangle touches the curve at its upper right corner. The height of the first rectangle is f ( x 1 ), the second f ( x 2 ), and the last is f ( x n ). Since the length of the entire interval from a to b is b - a , then the width of each subinterval is b − a b . We will refer to this width as ∆ x . (The Greek letter ∆ is Delta and thus “delta x ”.) That is,
::再考虑上面的图。 从 x = a 到 x = b 的间距被细分为 n 等值的子间替值。 矩形在每个次间替中绘制。 每个矩形都在其右上角碰过曲线。 第一个矩形的高度是 f(x1), 第二个 f(x2), 最后一个是 f(xn)。 由于从 a 到 b 的整个间距的长度是 b - a, 那么每个次间替的宽度是 b - a 。 我们称此宽度为 {x. (希腊字母 是 Delta, 因此是“ delta x ” ) , 也就是说,-
-
-
-
- Δ x = b − a n
-
-
-
is defined as the width of each subinterval. The area of the first rectangle is f ( x 1 ) Δ x , the second is f ( x 2 ) Δ x , and so on. Thus the total area A n of the n rectangles, is the sum of all areas:
::第一个矩形的面积是 f(x1)\x,第二个是 f(x2)\x,等等。因此, n矩形的总面积是所有区域的总和 :A n = f ( x 1 ) Δ x + f ( x 2 ) Δ x + . . . + f ( x n ) Δ x = n ∑ i = 1 f ( x i ) Δ x To make use of the , we make the width of each rectangle approach 0 , which is equivalent to making the number of rectangles, n , approach infinity. By doing so, we find the exact area under the curve,
::要使用 , 我们使每个矩形方向 0 的宽度, 相当于 矩形, n 的宽度, 无穷无尽。 这样, 我们就可以在曲线下找到准确的区域 ,-
-
-
- lim n → ∞ A n = lim n → ∞ n ∑ i = 1 f ( x i ) Δ x .
-
-
This limit is defined as the definite integral and it is denoted by
::这一限制被定义为一个明确的整体,其用意是:-
-
-
- ∫ b a f ( x ) d x .
-
-
The Definite Integral
::绝对综合A definite integral gives us the area between the x -axis and a curve over a defined interval.
::一个确定的整体为我们提供了 X 轴与一个曲线之间的区域, 跨度为一定的间隔 。The Definite Integral (The Limit Method) -
The area between a curve
f
(
x
) and the
x
-axis over the interval [
a
,
b
] can be calculated by
- A = ∫ b a f ( x ) d x = lim n → ∞ n ∑ i = 1 f ( x i ) Δ x
-
where
- Δ x = b − a n
- is the width of the subintervals.
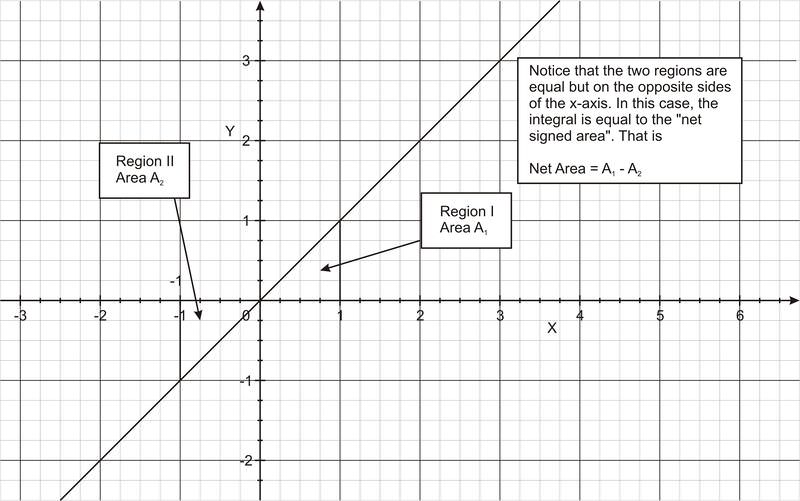
It is important to keep in mind that the area under the curve can assume positive and negative values. It is more appropriate to call it “the net signed area”. Example 2 below illustrates this point.
::必须牢记,曲线下的区域可以假定正值和负值,将它称为“净签名区域”更为恰当,下面的例2说明了这一点。Examples
::实例Example 1
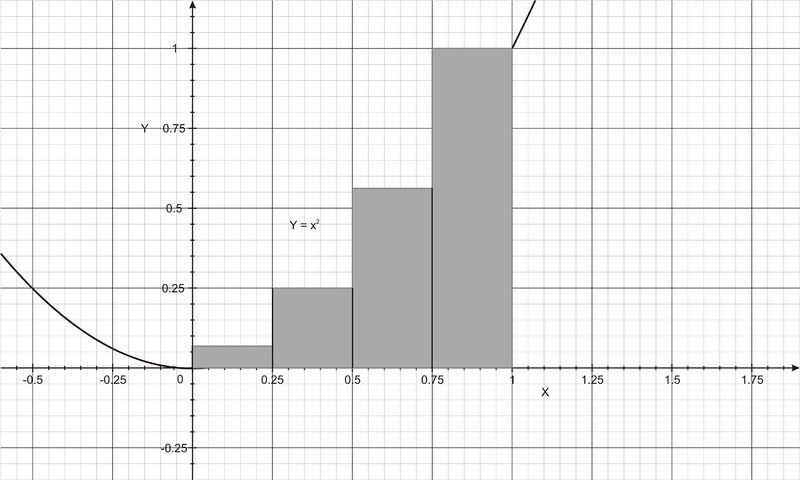
::例1Calculate the area between the curve y = x 2 and the x -axis from x = 0 to x = 1.
::计算曲线 y = x2 与 x 轴 = 0 到 x = 1 之间的区域。We divide the region into n number of subintervals, each of width ∆x (see figure below).
::我们将该区域分为每宽度 x(见下图)的n次隔年数(见下图)。First find ∆x.
::第一个发现是xx。Δ x = b − a n = 1 − 0 n = 1 n The next step is to find x i .
::下一步是发现它。x i = a + i Δ x = 0 + i ⋅ 1 n = i n Therefore, f ( x i ) = x 2 i = ( i n ) 2 Using the integration formula
::因此,f(xi)=x2i=( in)2A = ∫ b a f ( x ) d x = lim n → ∞ n ∑ i = 1 f ( x i ) Δ x = ∫ 1 0 x 2 d x = lim n → ∞ n ∑ i = 1 ( i n ) 2 ( 1 n ) = lim n → ∞ n ∑ i = 1 i 2 n 3 Since we are summing over i , not n , the summation becomes,
::因为我们在消音,不是,总和变成,A = lim n → ∞ 1 n 3 n ∑ i = 1 i 2 = lim n → ∞ 1 n 3 ( 1 2 + 2 2 + 3 2 + . . . + n 2 ) But since n ∑ i = 1 i 2 = n ( n + 1 ) ( 2 n + 1 ) 6 then
::但从此以后, i=1i2=n( n+1)( 2n+1) 6thenA = lim n → ∞ 1 n 3 n ( n + 1 ) ( 2 n + 1 ) 6 lim n → ∞ 1 6 ( 2 + 3 n + 1 n 2 ) Taking the limit,
::采取限制,A = 1 6 ( 2 + 3 ( 0 ) + ( 0 ) ) = 1 3 Thus the area under the curve is (1/3).
::因此,曲线下的区域是(1/3)。Example 2
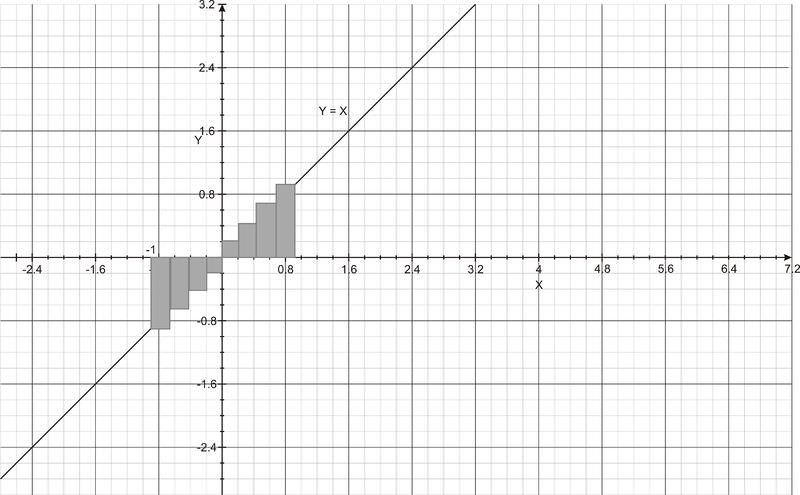
::例2Find the area between the curve y = x and the x -axis from x = -1 to x = 1.
::查找曲线 y = x 与 x 轴之间的区域,从 x = - 1 到 x = 1 = 1 。As you can see in figure a, the integral represents the total areas of all the rectangles above and below the x -axis. First, we divide the region into two regions, one above x -axis and one below the x -axis. Then we divide each region into n subintervals, each of width ∆ x (figure b).
::如图a所示,整体体代表 X 轴上下所有矩形的总区域。首先,我们将该区域分为两个区域,一个区域高于 X 轴,一个区域低于 x 轴。然后,我们将每个区域分为 n 次数,每个宽度为 x(图b)。Region I: Find ∆x and x i .
::区域一: 查找 x 和 xi 。Δ x = 1 − 0 n = 1 n
::*x=1-0n=1nx i = a + i Δ x = 0 + i ( 1 n ) = i n f ( x i ) = i n
::f( 十一) = 英寸Region II: Again, find ∆ x and x i .
::区域二:再次,请找到 xandxi。Δ x = − 1 − 0 n = − 1 n
::{\fn黑体\fs22\bord1\shad0\3aHBE\4aH00\fscx67\fscy66\2cHFFFFFF\3cH808080}一号一号一号一号一号一号一号一号一号一号一号一号一号一号一号一号一号一号一号一号一号一号一号一号一号一号一号一号一号一号一号一号一号一号一号一号一号一号一号一号一号一号一号一号一号一号一号一号一号一号一号一号一号一号一号一号一号一号一号一号一号一号一号一号一号一号一号一号一号一号一号一号一号一号一号一号一号一号一号一号一号一号一x i = b + i Δ x = − 1 + i ( − 1 n ) = − 1 − i n f ( x i ) = − 1 − i n
::f( 十一)\%1- inThe integral represents the net area of the two regions I and II:
::组成部分代表第一和第二个区域的净面积:A = A 1 − A 2 = ( area above x-axis in [ a , b ] ) − ( area below x-axis in [ a , b ] ) Thus,
::A=A1-A2=([a,b]-(a,b]中x轴以上区域)-(a,b]中x轴以下区域)A = lim n → ∞ n ∑ i = 1 f ( x i ) Δ x − lim n → ∞ n ∑ i = 1 f ( x i ) Δ x = lim n → ∞ n ∑ i = 1 ( i n ) ( 1 n ) − lim n → ∞ n ∑ i = 1 ( − 1 − i n ) ( 1 n ) = lim n → ∞ n ∑ i = 1 ( i n 2 ) − lim n → ∞ n ∑ i = 1 ( − 1 n − i n 2 ) = lim n → ∞ 1 n 2 n ∑ i = 1 i − [ lim n → ∞ − 1 n + lim n → ∞ 1 n 2 n ∑ i = 1 i ] = lim n → ∞ 1 n 2 n ( n + 1 ) 2 − [ 0 + lim n → ∞ 1 n 2 n ( n + 1 ) 2 ] = 1 2 − [ 1 2 ] = 0 We conclude that the net area is zero.
::我们的结论是,净面积为零。Example 3
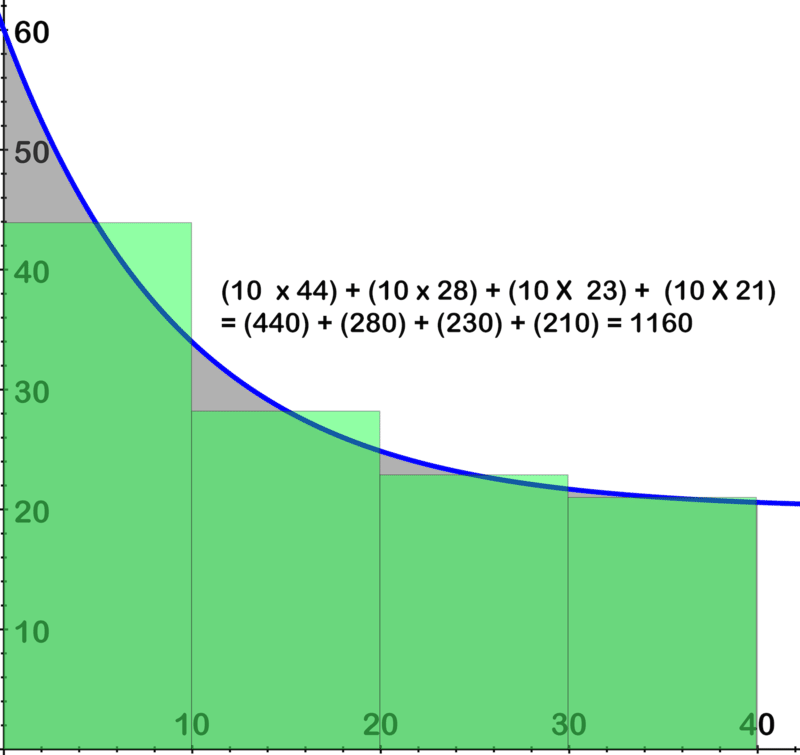
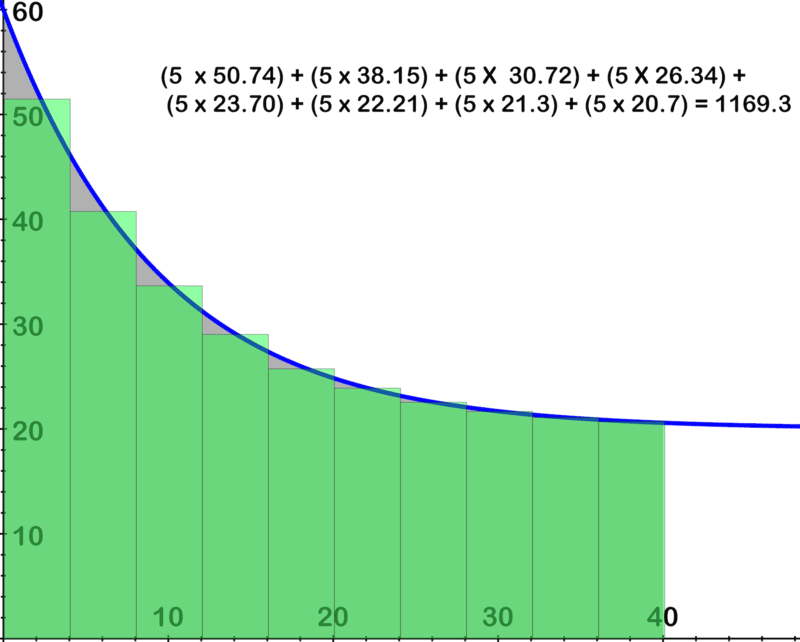
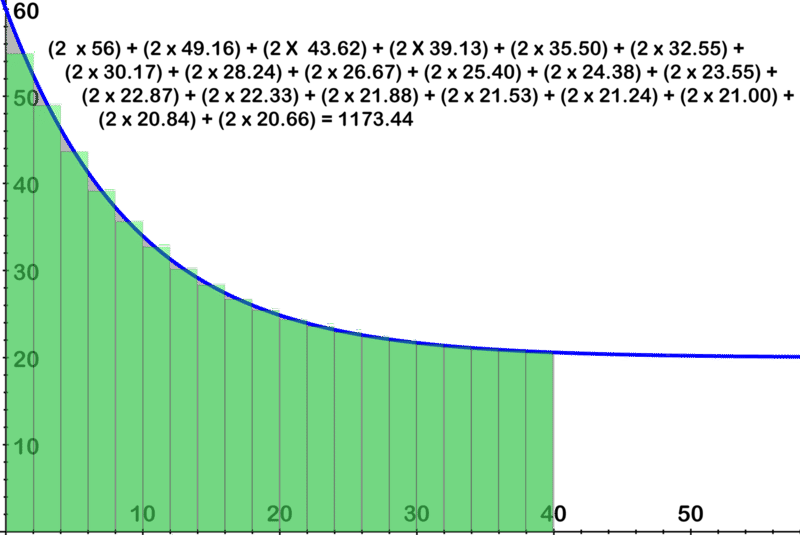
::例3Approximate the definite integral between x = 0 and x = 40 by calculating the areas of rectangles which fill the area in the image below. Use at least 3 successively narrower sizes of rectangles.
::x = 0 和 x = 40 之间,通过计算在下方图像中填充区域的区域的矩形区域,大致是 x = 0 和 x = 40 之间的确定整体。使用至少3个相继较窄的矩形大小。The equation of the curve in the image is: y = 60 − 40 ( 1 − 9 10 x ) .
::图像中的曲线方程式是:y=60-40(1-910x)。∴ the closest approximated area is 1173.44 units (The actual calculated area is 1174.0373)
::最接近的区域为1173.44个单位(实际计算区域为1174.0373个)。Example 4
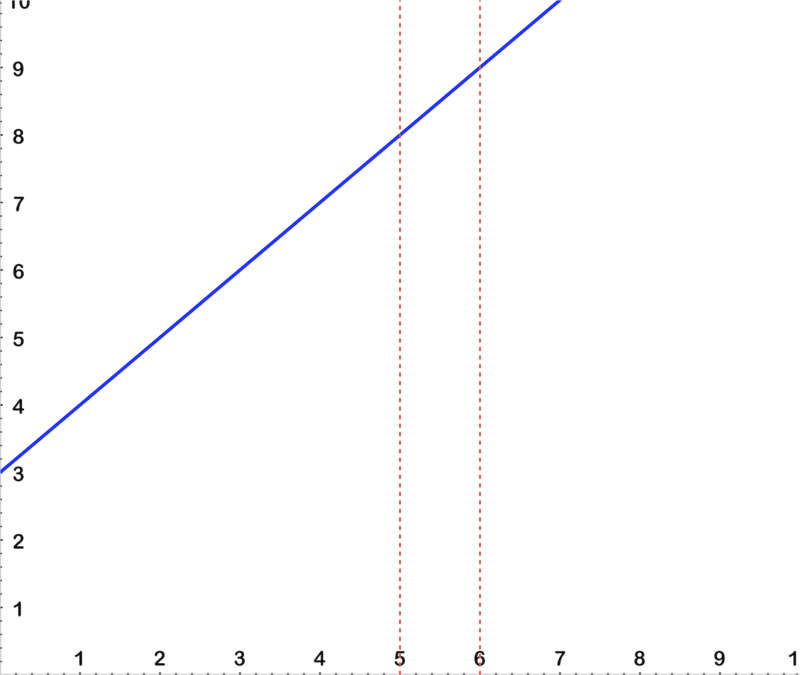
::例4Approximate the area under y = x + 3 on the interval [5,6] using the middle with 5 subintervals.
::y = x + 3下区域以 [5,6] 间距接近[5,6] ,中间为 5 次间距。Sketch of graph:
::图表的边距 :First, we divide the interval [5,6] into pieces:
::首先,我们把间隔[5,6]分成几个部分:Between x = 5 and x = 5.2, the middle value is 5.1 + 3 = 8.1
::x=5至x=5.2之间,中间值为5.1+3=8.1Between x = 5.2 and x = 5.4, the middle value is 5.3 + 3 = 8.3
::x = 5.2和x = 5.4之间,中间值为5.3 + 3 = 8.3Between x = 5.4 and x = 5.6, the middle value is 5.5 + 3 = 8.5
::x = 5.4 和 x = 5.6之间,中间值为 5.5 + 3 = 8.5Between x = 5.6 and x = 5.8, the middle value is 5.7 + 3 = 8.7
::x = 5.6 和 x = 5.8,中间值为 5.7 + 3 = 8.7Between x = 5.8 and x = 6, the middle value is 5.9 + 3 = 8.9
::x = 5.8至x = 6,中间值为 5.9 + 3 = 8.9Adding these, we get 42.5.
::加上这些,我们得到42.5美元。To get the Riemann sum, take this answer and multiply by the width of each segment: 0.2
::要获得Riemann总和, 请选择这个答案, 乘以每个段的宽度 : 0.2 。∴ 8.5 is our approximated area.
::约8.5是我们大致所在的区域。Example 5
::例5Approximate the area between y = 3x 2 + x + 5 and the x-axis on the interval between x = 2 and x = 5 using the right Riemann Sum with 2 subintervals.
::在x=2和x=5之间的间隔处,使用右边的Riemann Sum和2个次间距,靠近y = 3x2 + x + 5和x = 5之间的X轴之间的区域。First, we divide the interval [2,5] into subintervals: Between x = 2 and x = 3.5, the right value is 3(3.5) 2 + (2.5) + 5 = 42.25 Between x = 3.5 and x = 5, the right value is 3(5) 2 + (5) + 5 = 85 Adding these, we get 127.25. Take this answer and multiply by the width of each segment: 1.5.
::首先,我们将间隔[2,5]分为次隔年数:在x=2和x=3.5之间,正确的值为3(3.5)2+(2.5)+5=42.25在x=3.5和x=5之间,正确的值为3(5)2+(5)+5=85加上这些,我们得到127.25。用这个答案并乘以每个段的宽度:1.5。∴≈ 190.88 is the area
::190.88是这个区域Example 6
::例6Use a definite integral to find the area under the curve y = 5 x 2 + 2 x + 4 on the interval [0, 3].
::在 y= 5x2+2x+4 曲线下的间隔 [0, 3] 中找到区域, 使用一个确定的组成部分 。∫ 3 0 5 x 2 + 2 x + 4 d x = 5 3 x 3 + x 2 + 4 x | 5 4
::=305x2+2x+4dx=53x3+x2+4x**54Review
::回顾-
Use the limit method to find the area under the curve of
f
(
x
) = x
2
in the interval [0, 2].
::使用限值方法在间隔 [0, 2] 中查找 f(x) = x2 曲线下的区域。
Find the area between the curve and the x-axis:
::查找曲线和 X 轴之间的区域 :-
Curve
y
=
x
on the interval
x
= 1 to
x
= 3.
::曲线 y = x 间隔 x = 1 = x = 3。 -
Curve
y
= -
x
from
x
= 1 to
x
= 3.
::曲线 y = -x 从 x = 1 到 x = 3。 -
Curve
y
=
x
from
x
= -3 to
x
= 3.
::曲线 y = x 从 x = - 3 到 x = 3 = 3。 -
Approximate the area under
y
=
2
x
+
3
on the interval [0,3] using the middle Riemann Sum for y with 6 subintervals.
::y=2x+3下地区在间隔[0][3]下,使用中间里格曼 Sum, 与 y 和 6 次间隔。
Find the area under the curve:
::查找曲线下的区域 :-
y
=
3
on [4, 5]
::[4、5] y=3 on [4、5] -
y
=
3
x
+
1
on [1, 5]
::y=3x+1, [1, 5] -
y
=
1
x
on [3, 4]
::y=1x [3、4] -
y
=
2
x
+
4
on [5, 6]
::[5、6] y=2x+4 -
y
=
5
x
3
+
4
x
2
+
x
+
2
on [2, 5]
::y= [2, 5x3+4x2+x2] 时 y= 5x3+4x2+x2 -
y
=
1
x
on [3, 7]
::y=1x [3、7] -
y
=
3
x
2
+
2
x
on [5, 6]
::y=3x2+2x [5、6] -
y
=
4
on [2, 6]
::y=4, [2, 6] -
y
=
2
x
2
+
4
x
+
5
on [1, 5]
::y= 2x2+4x+5 [1, 5] -
Sketch
y
=
x
2
and
y
=
x
on the same coordinate system and then find the area of the region enclosed between them.
::在同一坐标系统上标出折叠 y = x2 和 y = x,然后在它们之间找到区域区域。
Review (Answers)
::回顾(答复)Click to see the answer key or go to the Table of Contents and click on the Answer Key under the 'Other Versions' option.
::单击可查看答题键, 或转到目录中, 单击“ 其他版本” 选项下的答题键 。 -