8.13 微积分的基本理论原理
Section outline
-
Velocity due to gravity can be easily calculated by the formula: v = gt , where g is the acceleration due to gravity (9.8m/s 2 ) and t is time in seconds. In fact, a decent approximation can be calculated in your head easily by rounding 9.8 to 10 so you can just add a decimal place to the time.
::由于重力造成的速率很容易用公式来计算: v = gt, g 是重力加速度(9.8m/s2), t 是秒以内的时间。事实上,通过四舍五入9.8到10,可以很容易地在你的头上计算出一个像样的近似值,这样您就可以在时间上加上小数位数。Using this function for velocity, how could you find a function that represented the position of the object after a given time? What about a function that represented the instantaneous acceleration of the object at a given time?
::3⁄4 ̄ ̧漯BFundamental Theorem of Calculus
::微积分的基本理论Antiderivatives
::抗抗药剂If you think that evaluating areas under curves is a tedious process you are probably right. Fortunately, there is an easier method. In this section, we shall give a general method of evaluating definite integrals (area under the curve) by using antiderivatives.
::如果您认为在曲线下评价区域是一个乏味的过程, 您可能是对的。 幸运的是, 有一个比较容易的方法。 在本节中, 我们将给出一种一般的方法, 通过使用抗降解剂来评价确定的整体性( 曲线下的区域 ) 。Definition: The Antiderivative - If F ' ( x ) = f ( x ), then F '( x ) is said to be the antiderivative of f ( x ).
There are rules for finding the antiderivatives of simple power functions such as f ( x ) = x 2 . As you read through them, try to think about why they make sense, keeping in mind that differentiation reverses integration .
::找到f(x) = x2. 等简单功率函数的抗衍生物有规则。 正如您从这些函数中读到的, 试着思考它们为什么有意义, 同时铭记区别会逆转整合。Rules of Finding the Antiderivatives of Power Functions -
The Power Rule
::权力规则
-
-
- where C is constant of integration and n is a rational number not equal to -1.
-
A Constant Multiple of a Function Rule
::函数常数多次规则
-
-
- where k is a constant.
-
Sum and Difference Rule
::总和和差额和差额
-
The Constant Rule
::常数规则
- where k is a constant. (Notice that this rule comes as a result of the power rule above.)
The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus
::微积分的基本理论The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus makes the relationship between and integrals clear. Integration performed on a function can be reversed by differentiation.
::微积分的基本理论使整体体与整体体之间的关系变得清晰明了,对功能的整合可以通过区别对待而逆转。The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus -
If a function
f
(
x
) is defined over the interval [
a
,
b
] and if
F
(
x
) is the antidervative of
f
on [
a,
b
], then
-
We can use the relationship between differentiation and integration outlined in the Fundamental Theorem of Calculus to compute definite integrals more quickly.
::我们可以利用《微积分基本理论》中概述的差别和融合之间的关系,更快地计算确定的整体体。Examples
::实例Example 1
::例1Evaluate
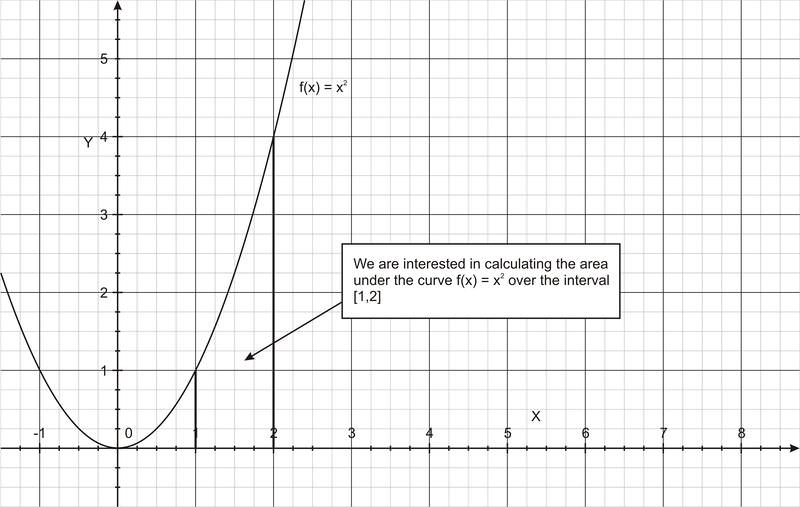
::评估12x2dx。This integral tells us to evaluate the f ( x ) = x 2 , which is a parabola over the interval [1, 2], as shown in the figure below.
::如下图所示,本元件要求我们评估 f(x) = x2,这是间隔[1, 2] 的抛物线。To compute the integral according to the Fundamental Theorem of Calculus, we need to find the of f ( x ) = x 2 . It turns out to be F ( x ) = (1/3) x 3 + C , where C is a constant of integration . How can we get this? Think about the functions that will have derivatives of x 2 . Take the derivative of F ( x ) to check that we have found such a function. (For more specific rules, see the box after this example). Substituting into the Fundamental Theorem,
::要根据微积分的基本理论计算集成, 我们需要找到 f( x) = x2 的 f( x) = x2 。 它被证明是 F( x) = ( 1) x3 + C, C 是常态集成的 C。 我们如何得到这个 ? 想想具有 x2 衍生物的函数 。 使用 F( x) 的衍生物来检查我们找到的函数 。 (关于更具体的规则, 请参见此示例后的框 ) 。 替换为基本理论 ,So the area under the curve is (7/3) units 2 .
::因此曲线下的区域是(7/3)单位2。Example 2
::例2Evaluate
::评估 x3dx。Since , we have
::*xndx=1n+1xn+1+C以来,我们已经有了To check our answer we can take the derivative of and verify that it is , the original function in our integral.
::为了检查我们的答案, 我们可以使用14x4+C的衍生物 来验证它是否是x3, 也就是我们整体中的原始函数。Example 3
::例3Evaluate
::评估5x2dx。Using the constant multiple of a power rule, the coefficient 5 can be removed outside the integral:
::使用权力规则的常数倍数,系数5可在整体体之外删除:
::=5x2dx=5x2dxThen we can integrate:
::然后我们可以整合:Again, if we wanted to check our work we could take the derivative of and verify that we get .
::再说一次,如果我们想检查一下我们的工作 我们可以拿53x3+C的衍生物 来证实我们得到了5x2Example 4
::例4Evaluate
:3x3-4x2+2)dx。
Using the sum and difference rule we can separate our integral into three integrals:
::使用总和和差异规则,我们可以将我们不可分割的组成部分分为三个组成部分:
:3x3 - 4x2+2)dx=
::3dx)-4(x2dx)+(2dx)
::314x4-413x3+2x+C34x4-43x3+2xCExample 5
::例5Evaluate
::评估25xxx。The evaluation of this integral represents calculating the area under the curve from x = -2 to x = 3, shown in the figure below.
::该积分的评价表示下图所示曲线y=x下从 x = -2 = x = = 3 的面积的计算。So the area under the curve is 5.57.
::因此曲线下的区域是5.57。Example 6
::例6Use the Fundamental Theorem of Calculus to solve: .
::使用微积分的基本理论解析 : 46dxxx。Given what we know, that if F(x) = ln x, then F'(x) =
::根据我们所知 如果F(x) = 内x, F'(x) = 1xThus, we apply the Fundamental Theorem of Calculus:
::因此,我们适用微积分的基本理论:
::46dxxx=lnxx*46= F(6) - F(4) = [ln(6)] - [ln(4)] = 0.4055
::= F(6) - F(4) = [ln(6)] - [ln(4)] = 0.4055Example 7
::例7Use the Fundamental Theorem of Calculus to solve: .
::使用微积分的基本理论解析 : @% 2p2p3cos( x) dx 。Given what we know, that if F(x) = 3sin(x), then F'(x) = 3cos(x)
::根据我们所知,如果F(x) = 3sin(x),那么F'(x) = 3cos(x)So we apply the Fundamental Theorem of Calculus:
::因此,我们应用微积分的基本理论:
::=2p2p3costx=3sin(x) =2p2p2p= F(8) - F(0) = [3sin(2p)] - [3sin(-2p)] = 1 - 0 = 0
::F(8) - F(0) = [3sin(2p)] - [3sin(-2p)] = 1 - 0 = 0Review
::回顾Evaluate the integral:
::评估整体:-
Evaluate the integral
::评估 =%035xdx -
Evaluate the integral
::评估积分 #%01x4dx -
Evaluate the integral
::评估#14(x-3)dx
Find the integral:
::查找积分 :-
Find the integral of (
x
+ 1)(2
x
- 3) from -1 to 2.
::查找 -1 到 2 的( x + 1)( 2x - 3) 的内装件。 -
Find the integral of
from 0 to 9.
::查找 x 从 0 到 9 的积分。 -
Find
::查找 #% 10 - 3dx -
Find
::查找 #%13dx -
Find
::查找\\ pp2- 4cos( x) dx -
Find
::查找 #% 02- dx -
Find
::查找 # 27dxxx -
Find
::查找 20x+5dx -
Find
::查找\\ p3p26sin( x) dx -
Find
::查找 67dxxx
Challenge yourself:
::挑战你自己:-
Sketch y = x
3
and y = x on the same coordinate system and then find the area of the region enclosed between them (a) in the first quadrant and (b) in the first and third quadrants.
::在同一坐标系统上,在(a)第一个象限和(b)第一个和第三个象限之间找到区域内的面积,然后在(a)第一个象限和(b)第一个和第三个象限之间找到。 -
Evaluate the integral
where
R
is a constant.
::评估 R 是常数的 {RR( R2 x2) dx 。
Review (Answers)
::回顾(答复)Click to see the answer key or go to the Table of Contents and click on the Answer Key under the 'Other Versions' option.
::单击可查看答题键, 或转到目录中, 单击“ 其他版本” 选项下的答题键 。