10.2 关键价值
Section outline
-
What are critical values ? Why is it important to know if a test is left, right, or two-tailed, when calculating critical values?
::关键值是什么?为什么在计算关键值时必须知道测试是左、右还是双尾的?Critical Values
::关键价值When you calculate the probability that a range of values will occur given a random variable with a particular distribution , you often use a z -score reference or calculator.
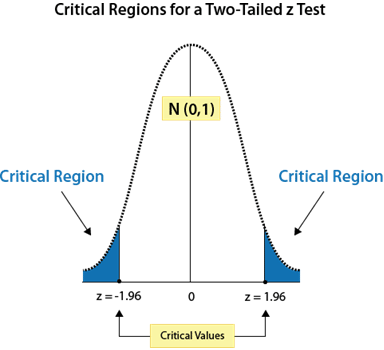
::当计算一个数值范围的概率时,如果给定一个带有特定分布的随机变量,通常会使用z-score 引用或计算器。Critical values are the values that indicate the edge of the critical region . Critical regions (also known as rejection regions ) describe the entire area of values that indicate you reject the null hypothesis . In other words, the critical region is the area encompassed by the values not supportive of the default assumption - the area of the ‘tails’ of the distribution.
::关键值是表示关键区域边缘的值。 关键区域( 也称为拒绝区域) 描述整个数值区域, 表明您拒绝无效假设。 换句话说, 关键区域是不支持默认假设的值所包含的区域 — — 分布的“ 尾部” 区域。In this lesson, we will use a table to find critical values. Although critical values may refer to other types of distributions, for the moment we will be dealing only with the Z -score critical values of a normal distribution. There is a table of Z -score values that you may refer to here:
::在此教训中, 我们将使用一个表格来查找关键值。 虽然关键值可能指其他类型的分布, 但关键值可能指其他类型的分布, 目前我们只处理正常分布的 Z - 关键值 。 您可以在此引用一个 Z - 关键值列表 :Z 0.00 0.01 0.02 0.03 0.04 0.05 0.06 0.07 0.08 0.09 Z 0.0 0.5
0.504
0.508
0.512
0.516
0.5199
0.5239
0.5279
0.5319
0.5359
0.0 0.1 0.5398
0.5438
0.5478
0.5517
0.5557
0.5596
0.5636
0.5675
0.5714
0.5753
0.1 0.2 0.5793
0.5832
0.5871
0.591
0.5948
0.5987
0.6026
0.6064
0.6103
0.6141
0.2 0.3 0.6179
0.6217
0.6255
0.6293
0.6331
0.6368
0.6406
0.6443
0.648
0.6517
0.3 0.4 0.6554
0.6591
0.6628
0.6664
0.67
0.6736
0.6772
0.6808
0.6844
0.6879
0.4 0.5 0.6915
0.695
0.6985
0.7019
0.7054
0.7088
0.7123
0.7157
0.719
0.7224
0.5 0.6 0.7257
0.7291
0.7324
0.7357
0.7389
0.7422
0.7454
0.7486
0.7517
0.7549
0.6 0.7 0.758
0.7611
0.7642
0.7673
0.7704
0.7734
0.7764
0.7794
0.7823
0.7852
0.7 0.8 0.7881
0.791
0.7939
0.7967
0.7995
0.8023
0.8051
0.8078
0.8106
0.8133
0.8 0.9 0.8159
0.8186
0.8212
0.8238
0.8264
0.8289
0.8315
0.834
0.8365
0.8389
0.9 1.0 0.8413
0.8438
0.8461
0.8485
0.8508
0.8531
0.8554
0.8577
0.8599
0.8621
1.0 1.1 0.8643
0.8665
0.8686
0.8708
0.8729
0.8749
0.877
0.879
0.881
0.883
1.1 1.2 0.8849
0.8869
0.8888
0.8907
0.8925
0.8944
0.8962
0.898
0.8997
0.9015
1.2 1.3 0.9032
0.9049
0.9066
0.9082
0.9099
0.9115
0.9131
0.9147
0.9162
0.9177
1.3 1.4 0.9192
0.9207
0.9222
0.9236
0.9251
0.9265
0.9279
0.9292
0.9306
0.9319
1.4 1.5 0.9332
0.9345
0.9357
0.937
0.9382
0.9394
0.9406
0.9418
0.9429
0.9441
1.5 1.6 0.9452
0.9463
0.9474
0.9484
0.9495
0.9505
0.9515
0.9525
0.9535
0.9545
1.6 1.7 0.9554
0.9564
0.9573
0.9582
0.9591
0.9599
0.9608
0.9616
0.9625
0.9633
1.7 1.8 0.9641
0.9649
0.9656
0.9664
0.9671
0.9678
0.9686
0.9693
0.9699
0.9706
1.8 1.9 0.9713
0.9719
0.9726
0.9732
0.9738
0.9744
0.975
0.9756
0.9761
0.9767
1.9 2.0 0.9772
0.9778
0.9783
0.9788
0.9793
0.9798
0.9803
0.9808
0.9812
0.9817
2.0 2.1 0.9821
0.9826
0.983
0.9834
0.9838
0.9842
0.9846
0.985
0.9854
0.9857
2.1 2.2 0.9861
0.9864
0.9868
0.9871
0.9875
0.9878
0.9881
0.9884
0.9887
0.989
2.2 2.3 0.9893
0.9896
0.9898
0.9901
0.9904
0.9906
0.9909
0.9911
0.9913
0.9916
2.3 2.4 0.9918
0.992
0.9922
0.9925
0.9927
0.9929
0.9931
0.9932
0.9934
0.9936
2.4 2.5 0.9938
0.994
0.9941
0.9943
0.9945
0.9946
0.9948
0.9949
0.9951
0.9952
2.5 2.6 0.9953
0.9955
0.9956
0.9957
0.9959
0.996
0.9961
0.9962
0.9963
0.9964
2.6 2.7 0.9965
0.9966
0.9967
0.9968
0.9969
0.997
0.9971
0.9972
0.9973
0.9974
2.7 2.8 0.9974
0.9975
0.9976
0.9977
0.9977
0.9978
0.9979
0.9979
0.998
0.9981
2.8 2.9 0.9981
0.9982
0.9982
0.9983
0.9984
0.9984
0.9985
0.9985
0.9986
0.9986
2.9 3.0 0.9987
0.9987
0.9987
0.9988
0.9988
0.9989
0.9989
0.9989
0.999
0.999
3.0 3.1 0.999
0.9991
0.9991
0.9991
0.9992
0.9992
0.9992
0.9992
0.9993
0.9993
3.1 3.2 0.9993
0.9993
0.9994
0.9994
0.9994
0.9994
0.9994
0.9995
0.9995
0.9995
3.2 3.3 0.9995
0.9995
0.9995
0.9996
0.9996
0.9996
0.9996
0.9996
0.9996
0.9997
3.3 3.4 0.9997
0.9997
0.9997
0.9997
0.9997
0.9997
0.9997
0.9997
0.9997
0.9998
3.4 3.5 0.9998
0.9998
0.9998
0.9998
0.9998
0.9998
0.9998
0.9998
0.9998
0.9998
3.5 3.6 0.9998
0.9998
0.9999
0.9999
0.9999
0.9999
0.9999
0.9999
0.9999
0.9999
3.6 3.7 0.9999
0.9999
0.9999
0.9999
0.9999
0.9999
0.9999
0.9999
0.9999
0.9999
3.7 3.8 0.9999
0.9999
0.9999
0.9999
0.9999
0.9999
0.9999
0.9999
0.9999
0.9999
3.8 3.9 1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
3.9 Z 0.00 0.01 0.02 0.03 0.04 0.05 0.06 0.07 0.08 0.09 Z In the next lesson, we will discuss how to identify a test as Left, Right, or Two-tailed. For now, the problems will specify which type you are working with since it affects the location of the critical value(s), and therefore the area of the critical region.
::在下一个教训中,我们将讨论如何确定左、右或双尾测试。 现在,问题将具体指出您正在和哪类人合作,因为它影响到关键值的位置,因此也影响到关键区域的区域。If you have completed the prior lesson(s) on Z -scores, you should recognize Z -score critical values as the Z -scores associated with a given percentage. The reason there is another term, critical values , instead of just Z -scores , is that the concept of critical values is also applicable to other types of distributions, such as the student’s t -score distribution discussed in the lesson Degrees of Freedom .
::如果您已经完成了以前关于Z-scores(Z-scores)的课程, 您应该承认Z- slocks( Z) 关键值是与某个百分比相关的Z- scores( Z) 。 原因是另一个术语, 关键值,而不仅仅是Z- scores( Z) , 关键值的概念也适用于其他类型的分布, 如自由度课中讨论的学生的 T- pores 分布 。Determining Critical Values
::确定关键价值What is the critical value for a 95% confidence level , assuming a two-tailed test ?
::假设进行双尾测试,95%的置信度的临界值(ZZZ)是多少?A 95% confidence level means that a total of 5% of the area under the curve is considered the critical region.
::95%的置信度意味着曲线下总面积的5%被视为关键区域。Since this is a two-tailed test, of of the values would be in the left tail, and the other 2.5% would be in the right tail. Looking up the -score associated with 0.025 on a reference table, we find 1.96. Therefore, +1.96 is the critical value of the right tail and -1.96 is the critical value of the left tail.
::由于这是一个双尾测试, 52.5%的值中有12个在左尾, 而另外的2.5%在右尾。 在查找参考表格上与 0.025 相关的 Z 值时, 我们发现有1. 96. 因此, +1. 96 是右尾的临界值, 而 - 1.96 是左尾的临界值 。The critical value for a 95% confidence level is .
::95%的置信度的关键值是/-1.96。Sketching the Z-Score
::切除 Z - 分数Sketch the Z -score critical region for the previous example.
::将Z核心关键区域涂抹为上一个例子。Sketch the graph of the normal distribution with the given values and mark the critical values from Ex. A, then shade the area from the critical values away from the center. The shaded areas are the critical regions.
::用给定值绘制正态分布图, 并标出Ex. A 的临界值, 然后将区域与中点之间的关键值隔开。 阴影区域是关键区域 。Finding the Critical Value
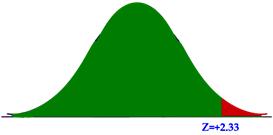
::查找关键值What would be the critical value for a right-tailed test with ?
::使用 0.01 进行右尾试验的关键价值是什么?If , then the area under the curve representing , the alternative hypothesis , would be 99%, since (alpha) is the same as the area of the rejection region. Using the Z -score reference table above, we find that the Z -score associated with 0.9900 is approximately 2.33.
::如果++0.01,则代表H1的曲线下区域为99%,则替代假设为99%,因为α(阿尔法)与拒绝区域的面积相同。 使用上文的Z-级参考表,我们发现与0.9900相关的Z-级区域约为2.33。It appears that the critical value is .
::看来关键值是2.33。Let’s see if that answer makes sense. Since this is a right-tailed test, is on the right end of the graph, and is on the left. A Z -score of +2.33 is well to the right of the center of the graph, splitting the area under the curve from that point to the left, and indicating that the values supporting the default hypothesis encompass nearly the entire graph. Since the initial question specified , indicating that only 1% of the area is in the critical region, is quite reasonable.
::让我们看看这个答案是否有道理。 由于这是一个右尾试验, α在图的右端, 1在左边。 Z-score +2.33 与图的右侧相当, 将曲线下的区域从该点向左分割, 并表明支持默认假设的值几乎包含整个图。 由于初始问题指定了 0.01 , 显示只有1%的区域位于关键区域, 2.33 相当合理 。Earlier Problem Revisited
::重审先前的问题What are critical values? Why is it important to know if a test is left, right, or two-tailed, when calculating critical values?
::关键值是什么?为什么在计算关键值时必须知道测试是左、右还是双尾的?Critical values are the values which separate the area indicating the null hypothesis should be rejected from the area suggesting it not be rejected. It is important to know what kind of test you are dealing with, because the critical value is often calculated from a probability range, and the Z-score of that range changes depending on what portion of the distribution you are evaluating.
::关键值是指将表示无效假设的区域与表示无效假设不应拒绝的区域分开的数值。重要的是要知道您正在处理的测试是什么类型,因为关键值通常是从概率范围计算的,而该区域中的 Z 值变化取决于您正在评价的分布的哪一部分。Vocabulary
::词汇表Critical values are values separating the values that support or reject the null hypothesis.
::关键值是指将支持或拒绝无效假设的数值分开的数值。Critical regions are the areas under the distribution curve representing values that support the null hypothesis.
::关键区域是分布曲线下代表支持无效假设的数值的区域。Examples
::实例Example 1
::例1What would be the critical value for a left-tailed test with ?
::用 0.01 进行左尾测试的关键值是什么 ?A left-tailed test with would have 99% of the area under the curve outside of the critical region. If we use a reference to find the Z-score for 0.99, we get approximately 2.33. However, a Z-score of 2.33 is significantly to the right of the center of the distribution, including all the area to the left and only leaving a very small alpha value on the right. While we are indeed looking for a critical value with only a very small alpha, this is a left-tailed test, so the critical value we need is negative .
::0.01 的左尾测试将拥有关键区域外曲线下99%的区域。 如果我们使用引用来找到 Z 值为 0.99, 我们得到的值约为 2.33 。 但是, Z 值为 2.33 的 Z 值在分布中心右侧是显著的, 包括左边所有区域, 而在右边只留下一个非常小的阿尔法值 。 虽然我们确实在寻找一个只有非常小的阿尔法的关键值, 但这是一个左尾值的测试, 因此我们需要的关键值是负的 。
::2.33Example 2
::例2What would be the critical region for a two-tailed test with ?
::使用 0.08 进行双尾测试的关键区域是什么?We are looking for the critical region here, but let’s start by finding the critical values. This is a two-tailed test, so half of the alpha will be in the left tail, and half in the right. That means that we are looking for a positive/negative critical value associated with an alpha of 0.04, which indicates that we need to find the Z -score for . Referring to the Z -score table, we see that 0.96 corresponds to approximately 1.75. The critical values, then are +/- 1.75, and the critical region would be .
::我们在这里寻找关键区域,但让我们从找到关键值开始。 这是一个双尾测试, 所以一半的阿尔法在左尾部, 一半在右侧。 这意味着我们正在寻找一个正/负关键值, 与一个0.04的阿尔法相关, 这表明我们需要找到Z级(1-0.04=0.96), 提到Z级表, 我们发现0.96相当于大约1.75。 关键值是+/- 1.75, 而关键区域将是+1. 751.75。Example 3
::例3What would be the for a right-tailed test with a critical value of ?
::使用关键值为+1.76的右尾量测试的α值是什么?The area under the curve associated with a Z -score of 1.76, according to the reference table above, is 0.9608. Since 96.08% of the area is to the left of , that leaves approximately as the area in the critical region.
::根据上表的参考表,与1.76兹分数相关的曲线下区域为0.9608,因为96.08%的区域位于1.76小段的左侧,留下的关键区域面积约为1-0.9608=0.0392。Review
::回顾For questions 1-9, identify the critical value(s) for each :
::对于问题1-9,确定每个α的关键值:1. , left-tailed
::1. 0.05,左尾尾2. , right-tailed
::2. 0.02, 右零售3. , two-tailed
::3. 0.05,双尾双尾4. , left-tailed
::4. 0.02,左尾尾5. , right-tailed
::5. 0.01, 右零售6. , two-tailed
::6. 0.01,双尾双尾7. , left-tailed
::7. 0.1,左尾尾8. , right-tailed
::8. 0.1, 右尾尾尾9. , two-tailed
::9. 0.1,双尾For questions 10-15, find for the given critical value(s):
::对于问题10-15, 找到给定关键值的α值 :10. , right-tailed
::10.1.28,右零售11.
::11. 1.65至1.65美元。12. , left-tailed
::12.3.10 左尾尾13.
::13. 2.58至2.58美元14. , left-tailed
::14.1.65,左零售15. , right-tailed
::15. 2.33, 右零售Review (Answers)
::回顾(答复)Click to see the answer key or go to the Table of Contents and click on the Answer Key under the 'Other Versions' option.
::单击可查看答题键, 或转到目录中, 单击“ 其他版本” 选项下的答题键 。