8.5 阴性行为
Section outline
-
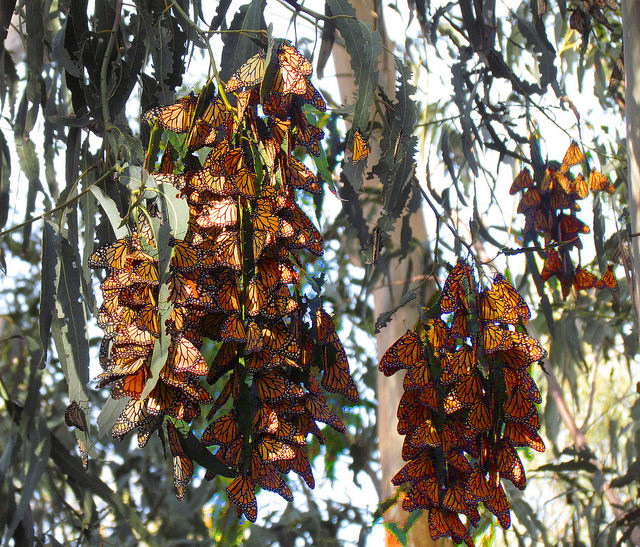
What are these butterflies doing?
::这些蝴蝶在做什么?Monarch butterflies gather in large groups as they migrate 2,500 miles south each fall. They return to the north in the spring. This migration is a cycle that repeats every year.
::每年秋天向南迁移2500英里,大宗蝴蝶聚集成大群,春季返回北方。 这种迁移是每年重复的循环。Cycles of Behavior
::行为周期Many change in a regular way. They go through cycles. Some cycles of behavior repeat each year. Other cycles of behavior repeat every day.
::经常发生许多变化。 它们经过周期。 某些行为周期每年重复。 其他行为周期每天重复。Yearly Cycles
::年周期An example of a behavior with a yearly cycle is hibernation . Hibernation is a state in which an animal’s body processes are slower than usual, and its body temperature falls. An animal uses less energy than usual during hibernation. This helps the animal survive during a time of year when food is scarce. Hibernation may last for weeks or months. Animals that hibernate include species of bats , squirrels, and snakes.
::每年周期行为的一个例子是冬眠。 休眠是动物身体过程比通常慢,体温下降的状态。 动物在冬眠期间使用能量比通常少。 这有助于动物在食物稀少的一年中生存。 休眠可能持续数周或数月。 冬眠包括蝙蝠、松鼠和蛇等种类的动物。Most people think that bears hibernate. In fact, bears do not go into true hibernation. In the winter, they go into a deep sleep. However, their body processes do not slow down very much. Their body temperature also remains about the same as usual. Bears can be awakened easily from their winter sleep.
::大部分人认为熊是冬眠。 事实上,熊并没有进入真正的冬眠。 在冬天,他们进入了深睡眠。 但是,他们的身体过程并没有减慢很多。他们的体温也和往常一样。 熊从冬眠中很容易被唤醒。Another example of a behavior with a yearly cycle is migration . Migration is the movement of animals from one place to another. Migration is an that is triggered by changes in the environment. For example, animals may migrate when the days get shorter in the fall. Migration is most common in , , and . In the Northern Hemisphere, many species of birds, including robins and geese, travel south for the winter. They migrate to areas where it is warmer and where there is more food. They return north in the spring. A flock of migrating geese is pictured below ( Figure ).
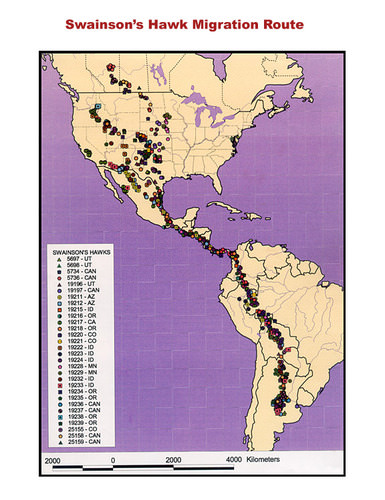
::每年周期行为的另一个例子是移徙。移徙是动物从一个地方迁徙到另一个地方。移徙是由环境变化引发的。例如,当秋季的天数缩短时,动物可能会移徙。移徙在北半球最为常见。在北半球,许多鸟类种类,包括野猪和鹅,都往南游过冬季。它们移徙到温暖的地方,食物较多。它们会在春季向北返回。下面是一群迁徙的鹅(图示)。These geese are flying south for the winter. Flocks of geese migrate in V-shaped formations. Some animals migrate very long distances. The map shown below shows the migration route of a species of hawk called Swainson’s hawk ( Figure ). About how many miles do the hawks travel from start to finish? Are you surprised that birds migrate that far? Some species of birds migrate even farther. Whales also are known to migrate thousands of miles each year to take advantage of warmer waters in the winter months. The great migration of millions of zebra, wildebeest and other antelope in East Africa also occurs yearly. Each year around 1.5 million wildebeest and 300,000 zebra (along with other antelope) go in search of food and water, traveling a distance of around 1800 miles.
::某些动物长途迁徙。 下面的地图显示了被称为Swainson的鹰(Figure ) 的鹰类的迁徙路线。 有关鹰类从头到尾旅行多少英里? 你对鸟类迁徙如此之远感到惊讶吗? 一些鸟类迁徙得更远。 鲸类每年迁徙数千英里,以利用冬季几个月的温暖水域。 东非数百万斑马、野生动物和其他羚羊每年也大量迁徙。 每年大约有150万只野生动物和30万只斑马(连同其他蚂蚁 ) , 去寻找食物和水,在1800英里的远处旅行。The migration route of Swainson’s hawk starts in North America and ends in South America. Scientists learned their migration route by attaching tiny tracking devices to the birds. The birds were then tracked by satellite. On the migration south, the hawks travel almost 5,000 miles from start to finish. Birds and other migrating animals follow the same routes each year. How do they know where to go? It depends on the species. Some animals follow landmarks, such as rivers or coastlines. Other animals are guided by the position of the sun, the usual direction of the wind, or other clues in the environment.
::鸟类和其他迁徙动物每年沿同样的路线走。 他们怎么知道去向? 取决于物种。 有些动物沿着山标, 如河流或海岸线。 其他动物则以太阳的位置、 风向的通常方向或环境的其他线索为指导。Daily Cycles
::每日周期Many animal behaviors change at certain times of day, day after day. For example, most animals go to sleep when the sun sets and wake up when the sun rises. Animals that are active during the daytime are called diurnal . Some animals do the opposite. They sleep all day and are active during the night. These animals are called nocturnal . Examples of nocturnal animals include bats, foxes, possums, skunks and coyotes. Many mammals (including humans), insects, and birds are diurnal.
::许多动物行为在白天的某些时间、一天又一天地改变。例如,大多数动物在太阳落下时睡觉,太阳升起时醒来。白天活跃的动物被称为阴极动物。有些动物则相反。他们白天睡觉,晚上活动。这些动物被称为夜夜。夜间动物的例子包括蝙蝠、狐狸、负鼠、昆虫和野狼。许多哺乳动物(包括人类)、昆虫和鸟类都是阴极的。Animals may eat and drink at certain times of day as well. Humans have daily cycles of behavior, too. Most people start to get sleepy after dark and have a hard time sleeping when it is light outside. Daily cycles of behavior are called circadian rhythms .
::动物也可以在某天的某个时间吃喝。人类也有日常行为周期。 大多数人在天黑后开始入睡,在天亮时很难睡觉。 日常行为周期被称为环形节奏。In many species, including humans, circadian rhythms are controlled by a tiny structure called the biological clock . This structure is located in a gland at the base of the brain . The biological clock sends signals to the body. The signals cause regular changes in behavior and body processes. The amount of light entering the helps control the biological clock. The clock causes changes that repeat every 24 hours.
::在许多物种中,包括人类在内, 螺旋节奏被一个叫做生物钟的小结构所控制。 这种结构位于大脑底部的腺中。 生物钟会向身体发出信号。 这些信号会定期改变行为和身体过程。 进入时的光量会帮助控制生物钟。 时数会每24小时发生一次变化。Summary
::摘要-
Yearly cycles of behavior include hibernation and migration.
::每年的行为周期包括休眠和移徙。 -
Daily cycles of behavior, including sleeping and waking, are called circadian rhythms.
::每天的行为周期,包括睡眠和觉醒, 被称为Circadian节奏。
Explore More
::探索更多Use the resources below to answer the questions that follow.
::利用以下资源回答以下问题。Explore More I
::探索更多-
Red Knot Migration - Port Royal Sound
at
(2:07)
::Red Knot 移民 - 皇家港口音响(2:07)
-
Thousands of Red Knots migrate through New Jersey
at
(2:55)
::成千上万的红手在2:55时通过新泽西移民
-
How far do Red Knots (
Calidris canutus
) migrate each year?
::红顶(Calidris Canutus)每年移徙多远? -
Are Red Knots the only species of bird to use horseshoe crab (
Limulus polyphemus
) eggs as a resource?
::红球是否是唯一使用马蹄蟹(Limulus polyphemus)蛋作为资源的鸟类物种? -
What information do scientists collect from the red Knots? How do they use this information?
::科学家们从红色的Knts收集到什么信息?他们如何使用这些信息? -
Why do scientists think Red Knot populations are declining? How is this connected to their extremely long migration?
::科学家们为什么认为红顶人口在下降? 这与他们长期移民有何关系?
Explore More II
::探索更多情况二-
Ocean Life - Vertical Migration & Aggregation
at
(7:16)
::海洋生命 -- -- 垂直移徙和汇总(7:16)
-
What is the largest migration of animals on the planet? When does this occur?
::地球上最大的动物迁徙是什么?这是什么时候发生的? -
Why do animals undergo this migration? What types of organisms undergo this migration?
::为什么动物要经历这种移徙?什么样的生物会经历这种移徙? -
How does the timing of this migration vary throughout the year?
::这种移徙的时间安排在全年中如何不同?
Review
::回顾-
What are two examples of yearly cycles of behavior?
::每年行为周期的两个例子是什么? -
What is the difference between a nocturnal and a diurnal animal?
::夜夜动物和阴阳动物有什么区别? -
What is a circadian rhythm?
::什么是Circadian节奏? -
What controls circadian rhythms in humans? Explain how this process works.
::是什么控制了人类的中枢节奏? 解释这个过程是如何运作的 。
-
Yearly cycles of behavior include hibernation and migration.