4.6 使用第一次和第二次衍生物试验
章节大纲
-
When defined at a point, the first derivative and the second derivative each provide one of three results: + (value > 0), - (value < 0) or 0. What are all of the result possibilities for and , and which give definitive information on the extrema of ?
::当在某个点上定义时,第一个衍生物和第二个衍生物各提供三种结果之一:+(价值 > 0)、-(价值 < 0)或0。 F`和f ' 的全部结果可能性是什么?Applying the Derivative Tests
::应用衍生测试Now we will apply all that we have learned from the First and Second Derivative Tests to sketch graphs of functions. The following table provides a summary of the tests and can be a useful guide in sketching graphs.
::现在我们将把我们从第一次和第二次衍生试验中学到的所有东西应用到功能的草图图中。下表提供了这些试验的摘要,可以作为草图图的有用指南。Signs of 1 st and 2 nd
::1号和2号的标志Conclusion
::结论 结论 结论 结论 结论Shape of the graphs
::图表形状
::f_(xx) >0+
::f*(x) >0+is increasing
::f 正在增加is concave upward
::f 是向上连接的 f 。
::f_(xx) >0+
::*(x) <0 -is increasing
::f 正在增加is concave downward
::f 是向下连接的 f 。
::========================================================================================
::f*(x) >0+is decreasing
::f 正在下降is concave upward
::f 是向上连接的 f 。
::========================================================================================
::*(x) <0 -is decreasing
::f 正在下降is concave downward
::f 是向下连接的 f 。Take a look at an example where we can use both the First and Second Derivative Tests to find out information that will enable us to sketch the graph.
::举个例子,我们可以使用第一和第二次衍生试验 来找出信息 来绘制图表。Let’s examine the function
::让我们检查 F( x) =x5 - 5x+2 的函数 。-
Find the critical values for which
::查找 f_(c) =0 的关键值。
, which means at
::f_(x)=5x4- 5=0, 表示 x4- 1=0 at x% 1 。-
Apply the First and Second Derivative Tests to determine extrema and points of inflection.
::应用第一次和第二次衍生试验来确定外形和反射点。
We note the signs of and in the intervals partitioned by
::我们注意到在x++1,0的间隔间隔间隔内有F+++和f++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++Key intervals
::键间距Shape of graph
::图形形状形状Increasing, concave down
::不断增长, 凝固下来Decreasing, concave down
::衰落,凝固下来Decreasing, concave up
::腐烂,凝固起来Increasing, concave up
::不断增长,凝固起来At the critical points:
::在关键时刻:-
. By the
we have a relative maximum at
, or the point (-1, 6).
::f*(- 1) % 20 < 0. 。 以 x 1 或点 (-1, 6) 的相对最大值为准 。 -
. By the Second Derivative Test we must have a point of inflection due to the transition from concave down to concave up between the key intervals.
::f*(0)=0。在第二次衍生试验中,我们必须有一个切入点,因为从连接层向下过渡到在键盘间隔之间向上过渡。 -
. By the Second Derivative Test we have a relative minimum at
, or the point (1, -2).
::f(1)=20>0. 根据第二次衍生试验,我们有一个相对最低值 x=1, 或点(1, 2) 。
Now we can sketch the graph.
::现在我们可以画出图表了Now, look at a simple rational function.
::现在,看看一个简单的理性功能。Consider the function .
::考虑函数 f( x) =x+2x- 3 。-
Find the critical values for which
.
::查找 f_(c) =0 的关键值。
which means there are no values that make .
::f*(x) = 1x-3+(x+2) - 1(x-3)2 =5(x-3)2 表示没有值 c 使 f*(c) =0 。Since is not defined at , this is the one critical point .
::由于未在 x=3 上定义 f}(x) , 这是关键点 。-
We note the signs of
and
in the intervals partitioned by
.
::我们注意到在x=3的间隔间隔间隔内有 f 和 f 的标记。
Key intervals
::键间距Shape of graph
::图形形状形状Decreasing, concave down
::衰落,凝固下来Decreasing, concave up
::腐烂,凝固起来At the critical point, there is a vertical asymptote and the function and derivatives are undefined; there are no minima or maxima.
::关键点是,存在垂直零星现象,函数和衍生物没有定义;没有迷你或格言。Now we can sketch the graph.
::现在我们可以画出图表了Examples
::实例Example 1
::例1Earlier, you were asked to chart all of the sign/zero possibilities for and , and identify which give definitive information on the extrema of .
::早些时候,有人要求你绘制所有F-和F-的标志/零可能性图,并指明哪些标志/零可能性能提供f-秒的准确信息。There are nine possibilities as follows:
::有以下九种可能性:Definitive Extrema Info?
::确定性快感信息吗?No
::否 无No
::否 无0 No
::否 无No
::否 无No
::否 无0 No
::否 无0 Yes
::是 是0 Yes
::是 是0 0 No
::否 无Only when there is a critical point with can we use the information on to tell whether we have a minimum or a maximum of .
::只有在f*0有关键点时,我们才能使用f* 上的信息来判断我们是否拥有最低或最高f。Example 2
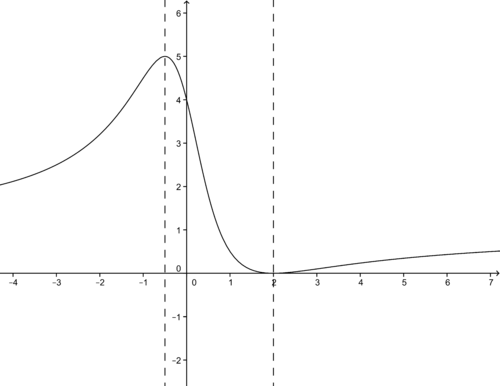
::例2For the function , find all critical values, the corresponding values for each critical value, and classify each point as a relative maximum or a relative minimum
::函数 f( x) =x2 - 4x+4x4x2+1, 查找所有关键值, 每个关键值的相应 Y 值, 并将每个点分类为相对最大值或相对最小值The derivative is:
::衍生物为: f(x)=2( 2x2- 3x-2)( x2+1)2Which gives critical values: and
::它给出了关键值: x* 12 和 x=2This means that: and
::这意味着:f(- 12)=5和f(2)=0The second derivative is:
::第二个衍生物是:f(x)2(4x3+9x2+4x5)(x2+1)3Evaluation at the critical points determines that , which means concave down (a maximum), and means concave up (a minimum).
::关键点的评价确定 f(- 12) < 0, 意思是向下( 最大) , f(2) > 0 表示向上( 最低) 。The function graph is plotted below:
::函数图绘制如下 :Example 3
::例3For the function , find all critical values, classify each point as a relative maximum or a relative minimum, and identify any inflection points
::函数 f( x) = 2x4 - 3x2+2 的函数 f( x) = 2x4 - 3x2+2, 查找所有关键值, 将每个点分类为相对最大值或相对最小值, 并识别任何折点The derivative is:
::衍生物为: f(x)=8x3-6xWhich gives critical values: and
::这给出了关键值: x=0 和 x @ @% 32The second derivative is:
::第二个衍生物是:f(x)=24x2-6Evaluation at the critical points determines that , which means concave down (a maximum), and means concave up (two minima).
::关键点的评价确定,f(0) < 0,这意味着收缩(最大),f()(32)>0意味着收缩(两个小型)。The second derivative is 0 when .
::第二个衍生物在24x2-6=6(2x-1)(2x+1)=0时为0。and are inflection points.
::x=0 和 x* 12 是穿孔点 。Review
::回顾For the #1-8, find the critical points, determine if each is a local minimum or maximum, and determine any points of inflection.
::对于 # 1-8, 找到关键点, 确定每个点是本地最低点还是最大点, 并确定任何偏移点 。-
:xx) =x3 - 3x2+1
-
:xx) =x4-2x3-x2
-
on the interval
.
::f(x) = sin2x 间隔 [0] 。 -
:xx) = 1x2 - x+2
-
:x)=2x3-3x2+6x
-
in the interval [-5, 3]
::f(x) =x3 - 12x+5 间隔 [-5, 3] -
::f(x)=x5+20x+5 -
, (-1, 3]
::f(x) =x2-5x+6, (-1, 3) -
Find the absolute maximum and absolute minimum of
on the interval [0, 4].
::在间隔 [0, 4] 中查找 f(x) =x3-3x2+2 的绝对最大和绝对最小值。
For #10-15, find the critical points and local minima and maxima.
::找到关键点、当地迷你和格朗塔。-
:xx)=x2e-x)
-
:xx) =x2x-1
-
:xx)=5e-x+x3
-
:xx) =e-2x+ex
-
:xx)=3xe-x)
-
on the interval
.
::f(x) =xtanx 间隔 [,] 。
Review (Answers)
::回顾(答复)Click to see the answer key or go to the Table of Contents and click on the Answer Key under the 'Other Versions' option.
::单击可查看答题键, 或转到目录中, 单击“ 其他版本” 选项下的答题键 。 -
Find the critical values for which