1.1 地理基础(8天)
章节大纲
-
Chapter Challenges
::章次 挑战-
Summarize the focus of geography and the two main branches of the discipline.
::概述地域重点和学科的两个主要分支。 -
Describe the tools geographers use to study the earth’s surface.
::描述用于研究地球表面的工具。 -
Summarize the grid system of latitude and longitude and how it relates to seasons and time zones.
::概述了纬度和经度的网格系统及其与季节和时区的关系。 -
Explain the difference between the different types of regional distinctions recognized in geography.
::解释地理上公认的不同类型区域区别之间的区别。 -
Describe the spatial nature of geography and how each place or region is examined, analyzed, and compared with other places or regions.
::说明地理的空间性质,以及每个地点或区域如何得到检查、分析和与其他地点或区域进行比较。 -
Describe the basic geographic realms and their locations.
::描述基本地理领域及其位置。
Student Learning Objectives
::学生学习目标TEKS Regional Unit 01 Physical Patterns and Processes Chapter 1.1 Geography Basics
::TEKS 地区单位 01 物理模式和过程 第1.1章 地理基础WG.2B Explain how changes in societies such as population shifts, technological advancements, and environmental policies have led to diverse uses of physical features over time such as terrace farming, dams, and polders.
::WG.2B 解释人口变化、技术进步和环境政策等社会变化如何导致随着时间的推移对自然特征的多种利用,如梯田耕种、水坝和耕种者。WG.3A Explain weather conditions and climate in relation to annual changes in Earth-Sun relationships.WG.3B Describe the physical processes that affect the environments of regions, including weather, tectonic forces, erosion and soil-building processes.WG.3C Describe how physical processes such as hurricanes, El Nino, earthquakes, and volcanoes affect the lithosphere, atmosphere, hydrosphere, and biosphereWG.4A Explain how elevation, latitude, wind systems, ocean currents, position on a continent, and mountain barriers influence temperature, precipitation, and distribution of climate regions.WG.4B Describe different landforms, such as plains, mountains, and islands, and the physical processes that cause their development.WG.4C: Explain the influence of climate on the distribution of biomes in different regions.WG.19A Evaluate the significance of major technological innovations in the areas of transportation and energy that have been used to modify the physical environment.WG.20A Describe the impact of new information technologies such as the Internet, Global Positioning System (GPS), or Geographic Information Systems (GIS).WG.21A Analyze and evaluate the validity and utility of multiple sources of geographic information such as primary and and secondary sources, aerial photographs, and maps.WG.21C Create and interpret different types of maps to answer geographic questions, infer relationships, and analyze change.WG.22A Create appropriate graphics such as maps, diagrams, tables, and graphs to communicate geographic features, distributions, and relationships.WG.22C Use social studies terminology correctly.What Is Geography?Geography Basics
::什么是地理? 地理基础Geography is the spatial study of the earth’s surface (from the Greek geo , which means “Earth,” and graphein , which means “to write”). Geographers study the earth’s physical characteristics, its inhabitants and cultures, phenomena such as climate, and the earth’s place within the universe. Geography examines the spatial relationships between all physical and cultural phenomena in the world. Geographers also look at how the earth, its climate, and its landscapes are changing due to cultural intervention.
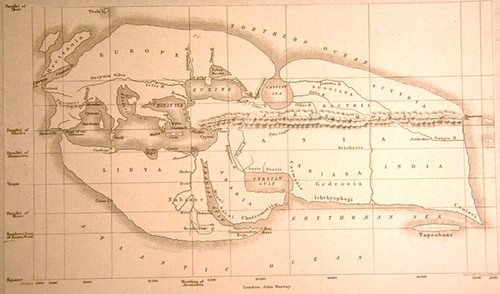
::地理是对地球表面的空间研究(来自希腊地理,即“地球”和石墨,即“写字 ” ) 。 地理学家研究地球的物理特征、居民和文化、气候等现象以及地球在宇宙中的位置。 地理考察了世界上所有物理和文化现象之间的空间关系。 地理学家还考察了地球、气候及其景观如何因文化干预而变化。The first known use of the word geography was by (modern-day Libya in North Africa), an early Greek scholar who lived between 276 and 194 B.C.E. He devised one of the first systems of and and calculated the earth’s circumference. Additionally, he created one of the first maps of the world based on the available knowledge of the time. Around the same time, many ancient cultures in China, southern Asia, Polynesia, and the Arabian Peninsula also developed maps and navigation systems used in geography and cartography.
::第一个已知的地理用法是早期希腊学者(北非的现代利比亚),他生活在公元前276-194年和公元前194年之间。 他设计并计算了最早的地球环绕系统之一。 此外,他根据当时的现有知识绘制了首批世界地图之一。 同时,中国、南亚、波利尼西亚和阿拉伯半岛的许多古代文化也开发了地理和制图中使用的地图和导航系统。
19th-century reconstruction of Eratosthenes map of the known world, circa 194 B.C.E.
::19世纪重建已知世界的埃拉托西恩地图,公元前194年。
The discipline of geography can be broken down into two areas of focus: physical geography and human geography. These two main areas use a spatial perspective, include the study of place, and the comparison of one place with another.
::地理学科可分为两个重点领域:物理地理和人文地理,这两个主要领域采用空间视角,包括地点研究以及一个地方与另一个地方的比较。Physical geography is the spatial study of natural phenomena in the environment, such as rivers, mountains, landforms, weather, climate, soils, plants, and any other physical aspects of the earth’s surface. Physical geography focuses on geography as a form of earth science. It tends to emphasize the main physical parts of the earth—the lithosphere (surface layer), the atmosphere (air), the hydrosphere (water), and the biosphere (living organisms)—and the relationship of these parts.
::物理地理是环境自然现象的空间研究,例如河流、山区、陆地形态、天气、气候、土壤、植物和地球表面的任何其他物理方面。物理地理侧重于地理作为地球科学的一种形式。自然地理往往强调地球的主要物理部分——地圈(地表层)、大气(空气)、水圈(水)和生物圈(生物体)以及这些部分之间的关系。The major forms of study within physical geography include the following:
::在物理地理范围内的主要学习形式包括:-
(the study of the earth’s surface features)
:研究地球表面特征)
-
(the study of glaciers)
:冰川研究)
-
(the study of the coastal regions)
:沿海区研究)
-
(the study of climates and climate change)
:气候和气候变化研究)
-
(the study of the geographic patterns of species distribution)
:研究物种分布的地理格局)
Some physical geographers study the earth’s place in the . Others are environmental geographers, part of an emerging field that studies the spatial aspects and cultural perceptions of the natural environment. Environmental geography requires an understanding of both physical and human geography, as well as an understanding of how humans measure their environment and the physical landscape.
::一些物理地理学家研究地球在地球中的位置。 另一些人则是环境地理学家,这是研究自然环境空间方面和文化观念的新兴领域的一部分。 环境地理学需要了解物理和人文地理,以及人类如何测量其环境和自然景观。Physical landscape is the term used to describe the natural terrain at any one place on the planet. The forces of erosion, weather, tectonic plate action, and water have formed the earth’s physical features. Many and in the United States preserve the land for the public to enjoy.
::自然景观是用来描述地球上任何一个地方自然地形的术语。 侵蚀、天气、构造板块动作和水的力量形成了地球的物理特征。 许多人和美国都保留了供公众享用的土地。
The Grand Canyon is a national park located in Arizona in the United States.
::大峡谷是位于美国亚利桑那州的一个国家公园。
Human geography is the study of human activity and its relationship to the earth’s surface. Human geographers examine the spatial distribution of human populations, religions, languages, ethnicity, political systems, economics, urban dynamics, and other human activity. They study patterns between human cultures and various environments and focus on the causes and consequences of human settlement and distribution over the landscape. While the economic and cultural aspects of humanity are the primary focuses of human geography, these aspects cannot be understood without describing the landscape on which economic and cultural activities take place.
::人类地理是人类活动及其与地球表面关系的研究,人类地理学家研究人类人口、宗教、语言、族裔、政治制度、经济学、城市动态和其他人类活动的空间分布,研究人类文化和各种环境的格局,并侧重于人类定居和分布的原因和后果,人类的经济和文化方面是人类地理的主要焦点,但如果不描述开展经济和文化活动的地貌,这些方面是无法理解的。is the term used to describe the parts of the earth’s surface that have been altered or created by people. For example, the urban cultural landscape of a city includes buildings, streets, signs, parking lots, and vehicles. includes fields, orchards, fences, barns, and farms. Cultural forces unique to a given place—such as religion, language, ethnicity, customs, and heritage—influence the cultural landscape of that place at a given time. The colors, sizes, and shapes of the cultural landscape usually symbolize meaning regarding societal norms. Spatial dynamics help in identifying and evaluating cultural differences.
::例如,一个城市的城市文化景观包括建筑物、街道、标志、停车场和车辆。 包括田地、果园、围栏、谷仓和农场。 特定地方特有的文化力量 — — 如宗教、语言、族裔、习俗和遗产 — — 影响到特定时间当地的文化景观。 文化景观的颜色、大小和形状通常象征着社会规范的意义。 空间动态有助于识别和评估文化差异。The field of cartography is an important discipline for geographers. While cartography continues to be a significant part of geography, geographers also look at spatial (space) and temporal (time) relationships of many types of data, such as physical landscape types, economies, and human activity. Geography also examines the relationships between the processes of humans and their physical and cultural environments.
::制图领域是地理学家的重要学科,虽然制图仍然是地理的一个重要部分,但地理学家也研究许多类型数据的空间(空间)和时间(时间)关系,如物理景观类型、经济和人类活动,地理还研究人类过程及其物理和文化环境之间的关系。Because maps are powerful graphic tools that allow us to illustrate relationships and processes at work in the world, cartography and Geographic Information Systems have become important in modern science. Maps are the most common method of illustrating different spatial qualities, and geographers create and use maps to communicate spatial data about the earth’s surface.
::由于地图是强有力的图形工具,让我们得以说明世界工作中的关系和过程,制图和地理信息系统在现代科学中变得非常重要。 地图是展示不同空间质量的最常用方法,地理学家创造和使用地图来交流地球表面的空间数据。Geospatial techniques are tools used by geographers to illustrate, manage, and manipulate spatial data. Cartography is the art and science of making maps, which illustrate data in a spatial form and are invaluable in understanding what is going on at a given place and time.
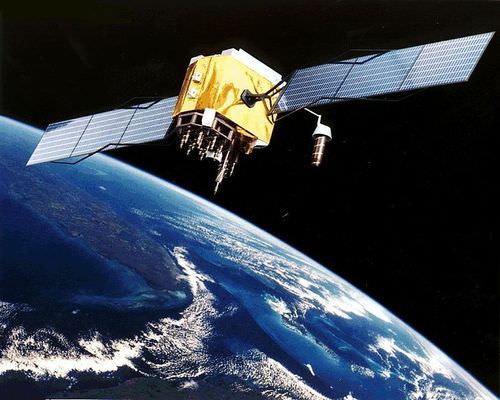
::地理空间技术是地理学家用来说明、管理和操作空间数据的工具,制图是制作地图的艺术和科学,以空间形式展示数据,对于了解特定地点和时间发生的情况非常宝贵。Making maps and verifying a location have become more exact with the development of the Global Positioning System (GPS). A GPS unit can receive signals from orbiting satellites and calculate an exact location in latitude and longitude, which is helpful for determining where one is located on the earth or for verifying a point on a map. GPS units are standard equipment for many transportation systems and have found their way into products such as cell phones, handheld computers, fish finders, and other mobile equipment. GPS technology is widely implemented in the transport of people, goods, and services around the world.
::随着全球定位系统的开发,绘制地图和核实位置的工作变得更加精确,全球定位系统单位可以接收轨道卫星的信号,计算纬度和经度的确切位置,这有助于确定一个人在地球的位置或核实地图上的某一点,全球定位系统单位是许多运输系统的标准设备,已经进入移动电话、手持计算机、渔获器和其他移动设备等产品,全球定位系统技术在全世界人员、货物和服务的运输中广泛应用。
An artist's conception of GPS Block II-F satellite in Earth's orbit by NASA.
::美国航天局对地球轨道GPS Block II-F卫星的艺术家概念。
Remote sensing technology acquires data about the earth’s surface through aerial photographs taken from airplanes or images created from satellites orbiting the earth. Remotely sensed images allow geographers to identify, understand, or explain a landscape and determine the land use of a place. These images can serve as important components in the cartographic process. These technologies provide the means to examine and analyze changes on the earth’s surface caused by natural or human forces.
::遥感技术通过飞机的航空照片或卫星环绕地球的图像获取地球表面数据。遥感图像使地理学家能够识别、理解或解释一个地方的景观和确定一个地方的土地利用情况。这些图像可以作为制图过程中的重要组成部分。 这些技术提供了研究和分析自然或人类力量造成的地球表面变化的手段。Geographic Information Science (GIS), often referred to as , uses a computer program to assimilate and manage many layers of map data, which then provide specific information about a place. GIS data are usually in digital form and arranged in layers. The GIS computer program can sort layers of data to illustrate a specific feature or activity. GIS programs are used in a wide range of applications.
::地理信息科学(GIS)通常称为:利用计算机程序同化和管理许多层次的地图数据,然后提供关于某一地点的具体信息;地理信息系统数据通常以数字形式排列,按层次排列;地理信息系统计算机程序可以对数据层次进行分类,以说明某一具体特征或活动;地理信息系统程序用于广泛的应用。
The forest-cover layer (light green) forms the bottom layer, with the topographic layer (contour lines) over it. Next is a standing water layer (pond, lake) and then a flowing water layer (stream, river), followed by the boundary layer, and finally the road layer on top. The order is important to display the final result.
::森林覆盖层( 浅绿色) 形成底层, 上面有地形层( 轮廓线 ) 。 下一个是立水层( 支架、 湖泊 ) , 然后是流动水层( 河、 河) , 后面是边界层, 最后是顶部的道路层。 此顺序对于显示最终结果很重要 。
GIS specialists often create and analyze geographical information for government agencies or private businesses. They use computer programs to take raw data to develop the information these organizations need for making decisions. For example, in business applications, GIS can be used to find a good location for a retail store based on the analysis of spatial data layers such as population distribution, highway or street arrangements, and the locations of similar stores. GIS can integrate a number of maps into one to help analysts understand a place that best suits their needs.
::地理信息系统专家经常为政府机构或私营企业创建和分析地理信息,他们利用计算机程序收集原始数据,以开发这些组织决策所需的信息,例如,在商业应用中,地理信息系统可以用来根据对人口分布、公路或街道安排等空间数据层以及类似商店的地点的分析,为零售商店找到一个良好的地点。地理信息系统可以将一些地图合并成一个地图,帮助分析人员了解最适合其需要的地方。GIS also focuses on storing information about the earth (both cultural and natural) in computer databases that can be retrieved and displayed in the form of specialized maps for specific purposes. GIS specialists require knowledge about computer and database systems. Over the last ten years, GIS has revolutionized the field of cartography, and nearly all cartography is now done with the assistance of GIS software. GIS software and specialized maps are an important part of urban planning and other social and physical sciences because they help to track patterns in people and the physical world. GIS can also refer to techniques used to represent, analyze, and predict spatial relationships of different phenomena.
::地理信息系统还侧重于将关于地球(文化和自然)的信息储存在计算机数据库中,这些数据库可以为特定目的以专门地图的形式检索和显示。地理信息系统专家需要了解计算机和数据库系统。在过去10年中,地理信息系统使制图领域发生了革命,几乎所有制图工作现在都在地理信息系统软件的协助下完成。地理信息系统软件和专门地图是城市规划和其他社会和物理科学的重要组成部分,因为它们有助于跟踪人文和物理世界的格局。地理信息系统还可以提及用来代表、分析和预测不同现象的空间关系的技术。Geography is a much broader field than many people realize. Geography is the study of the earth, including how human activity has changed it. Geography involves studies that are much broader than simply understanding the shape of the earth’s landforms. Physical geography involves all the planet’s physical systems. Human geography incorporates studies of human culture, spatial relationships, interactions between humans and the environment, and many other areas of research.
::地理领域比许多人所意识到的要广得多。 地理是对地球的研究,包括人类活动如何改变地球。 地理涉及的研究比单纯理解地球地貌形态的形状要广得多。 物理地理涉及地球的所有物理系统。 人类地理包含人类文化、空间关系、人类与环境之间的相互作用以及许多其他研究领域的研究。The Earth and Graticule Location
::地球和地块位置When identifying a region or location on the earth, the first step is to understand its relative and absolute locations. Relative location is the location on the earth’s surface with reference to other places, taking into consideration features such as transportation access or terrain. Relative location helps one compare the advantages of one location with those of another. Absolute location refers to an exact point on the earth’s surface without regard to how that point is related to any other place. Absolute location is vital to the cartographic process and to human activities that require a method of identifying a place.
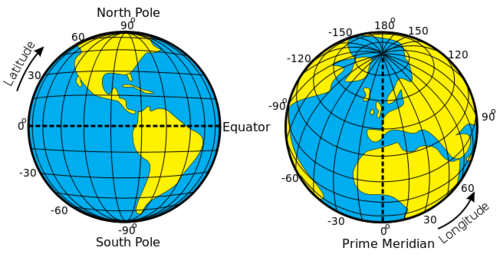
::当确定地球上的区域或位置时,第一步是了解其相对和绝对位置。相对位置是地球表面相对于其他地方的位置,同时考虑到交通通道或地形等特征。相对位置有助于将一个位置的优势与另一个位置的优势进行比较。绝对位置是指地球表面的准确点,而不论该点与任何其他地方的关系。绝对位置对于制图过程和需要确定地点的方法的人类活动至关重要。Just as you were taught in geometry that there are 360 degrees in a circle or a sphere, the earth also has 360 degrees, and they are measured using a grid pattern called the graticule. Lines of latitude and longitude allow any absolute location on the earth to have an identifiable address of degrees north or south and east or west, which allows geographers to accurately locate, measure, and study spatial activity.
::正如您在几何学中学到的,一个圆圈或球体中有360度,地球也有360度,并且用称为可流体的网格模式测量。 纬度和经度线允许地球上任何绝对位置有一个可以识别的北、南、东或西度位置,使地理学家能够准确定位、测量和研究空间活动。Geographers and cartographers organize locations on the earth using a series of imaginary lines that encircle the globe. The two primary lines are the equator and the prime meridian. From these lines, the systems of longitude and latitude are formed, allowing you to locate yourself anywhere on the planet. The line is the longest when you travel along in an east-west direction. At the equator, the sun is directly overhead at noon on the two equinoxes, which occur in March and September.
::地理学家和制图师利用环绕地球的一系列假想线来组织地球上的定位。 两种主要线是赤道和主要近距线。 从这两条线中, 经度和纬度系统形成, 允许您在地球的任何地方定位。 当您沿着东西方向行走时, 这条线是最长的。 在赤道, 太阳在3月和9月发生的两个五分仪的正午直接俯伏在两个五分仪上。
Latitude and Longitude of the Earth
::地球的纬度和经度Parallels or Lines of Latitude
::纬度的平行线或线The equator is the largest circle of latitude on Earth. The equator divides the earth into the Northern and Southern Hemispheres and is called 0 degrees latitude. The other lines of latitude are numbered from 0 to 90 degrees going toward each of the poles. The lines north of the equator toward the North Pole are north latitude, and each of the numbers is followed by the letter “N.” The lines south of the equator toward the South Pole are south latitude, and each of the numbers is followed by the letter “S.” The equator (0 latitude) is the only line of latitude without any letter following the number.
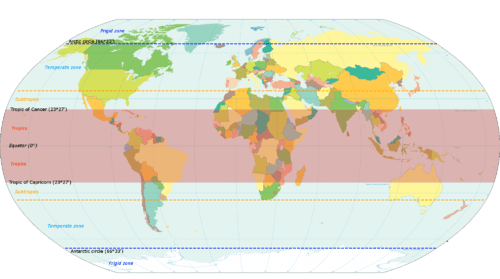
::赤道是地球上最大的纬度圈。赤道将地球分为北半球和南半球,称为0度纬度。其他的纬度线从0度到90度向每一极前进。赤道以北向北极的线线是北纬,每个数字后面的字母是“N”。赤道以南向南向南极的线是南纬,每个数字后面的字母是“S”。赤道(0度)是唯一的纬度线,没有数字的字母。Notice that all lines of latitude are parallel to the equator (they are often called parallels) and that the North Pole equals 90 degrees N and the South Pole equals 90 degrees S. Noted parallels include both the Tropic of Cancer and the Tropic of Capricorn, which are 23.5 degrees from the equator. At 66.5 degrees from the equator are the Arctic Circle and the Antarctic Circle near the North and South Pole, respectively.
::请注意,所有纬度线都与赤道平行(通常称为平行线),北极等于北纬90度,南极等于南纬90度。 注意的平行线既包括癌症热带,也包括上角热带,离赤道为23.5度,赤道为66.5度,北极和南极附近为北极圈和南极圈。Meridians or Lines of Longitude
::中经线或经经线The prime meridian sits at 0 degrees longitude and divides the earth into the Eastern and Western Hemispheres. The prime meridian is defined as an imaginary line that runs through the Royal Observatory in Greenwich, England, a suburb of London. The Eastern Hemisphere includes the continents of Europe, Asia, and Australia, while the Western Hemisphere includes North and South America. All meridians (lines of longitude) east of the prime meridian (0 and 180) are numbered from 1 to 180 degrees east (E); the lines west of the prime meridian (0 and 180) are numbered from 1 to 180 degrees west (W). The 0 and 180 lines do not have a letter attached to them.
::顶端的西经为0度,将地球分为东半球和西半球。顶端的西经被定义为通过伦敦郊区英国格林威治的皇家天文台运行的假想线。东半球包括欧洲、亚洲和澳大利亚大陆,西半球包括南北美洲。主端的东经(0和180)从东经1度到180度(E)不等;顶端的西经(0和180)从西经1度到180度(W)不等。0和180线没有附信。
Royal Observatory, Greenwich. A time ball sits atop the Octagon Room.
::皇家天文台 格林威治 时球在八角厅顶上
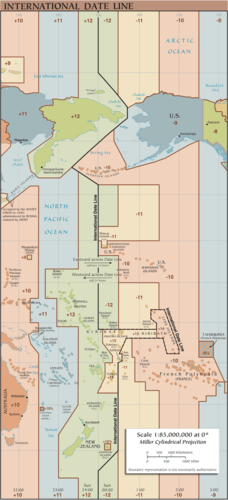
The meridian at 180 degrees is called the International Date Line. (180 degrees longitude) is opposite the prime meridian and indicates the start of each day. Each day officially starts at 12:01 a.m. at the International Date Line. Do not confuse the International Date Line with the prime meridian (0 longitude). The actual International Date Line does not follow the 180-degree meridian exactly. A number of alterations have been made to the International Date Line to accommodate political agreements to include an island or country on one side of the line or another.
::180度的中间线称为国际日期线。 (180度经度) 对准主要度线, 表示每天的开始时间。 每天每天12时01分在国际日期线上正式开始。 不要将国际日期线与主要度( 0度) 混淆起来。 实际的国际日期线并不与180度的中间线完全吻合。 对国际日期线作了一些修改,以适应政治协议, 将一个岛屿或国家包括在线的一边或另一边。
A map illustrating the current (post 2011) International Date Line.
::显示当前(2011年后)国际日期线的地图。Climate and Latitude
::气候和纬度The earth is tilted on its axis 23.5 degrees. As it rotates around the sun, the tilt of the earth’s axis provides different climatic seasons because of the variations in the angle of direct sunlight on the planet. Places receiving more direct sunlight experience a warmer climate. Elsewhere, the increased angle of incoming solar radiation near the earth’s poles results in more reflected sunlight and a cooler climate. The Northern Hemisphere experiences winter when sunlight is reflected off the earth’s surface and less of the sun’s energy is absorbed because of a sharper angle from the sun.
::地球在23.5度的轴上倾斜。 地球轴在太阳周围旋转,地球轴的倾斜提供了不同的气候季节,因为地球直接阳光的角不同。 更直接的阳光照射的地方会经历一种更温暖的气候。 在其他地方,地球极地附近太阳辐射照射增加的角会形成更反映阳光和更凉爽的气候。 当太阳从地球表面反射出来时,北半球会经历冬天,太阳的能量由于太阳的尖锐角度而被吸收的减少。The is the parallel at 23.5 degrees north of the equator, which is the most northerly place on Earth, receiving direct sunlight during the Northern Hemisphere’s summer. Remember that the earth is tilted 23.5 degrees, which accounts for seasonal variations in climate. The is the parallel at 23.5 degrees south of the equator and is the most southerly location on Earth, receiving direct sunlight during the Southern Hemisphere’s summer.
::这是赤道以北23.5度的平行点,赤道是地球上最北端的地方,在北半球夏季直接阳光照射。 记住地球倾斜23.5度,这是气候季节性变化的原因。 赤道以南23.5度的平行点,也是地球上最南端的地方,在南半球夏季直接阳光照射。
A world map illustrating the Tropic of Cancer and the Tropic of Capricorn.
::一张世界地图 描绘了癌症热带 和摩尔山的热带
The tropics (Cancer and Capricorn) are the two imaginary lines directly above in which the sun shines on the two solstices, occurring on or near June 20 or 21 (summer solstice in the Northern Hemisphere) and December 21 or 22 (winter solstice in the Northern Hemisphere). The sun is directly above the Tropic of Cancer at noon on June 20 or 21, marking the beginning of summer in the Northern Hemisphere and the beginning of winter in the Southern Hemisphere. The sun is directly above the Tropic of Capricorn at noon on December 21 or 22, marking the beginning of winter in the Northern Hemisphere and the beginning of summer in the Southern Hemisphere.
::热带(Cancer和Capricorn)是直接上方的两条想象线,在这两条线上,太阳照耀于6月20日或21日(北半球夏季)和12月21日或22日(北半球冬季)及12月21日或22日(北半球冬季);太阳直接在6月20日或21日正值北半球夏季的开始和南半球冬季的开始。太阳直接照耀于6月20日或21日(北半球夏季)或附近(北半球夏季)和12月21日或22日中午(北半球冬季和南半球夏季的开始)两座独角兽的热带之上。太阳直接照耀于12月21日或22日正值北半球冬季的开始和南半球夏季的开始。Solstices are the extreme ends of the seasons, when the line of direct sunlight is either the farthest north or the farthest south that it ever goes. The region between the Tropics of Cancer and Capricorn is known as the tropics. This area does not experience dramatic seasonal changes because the amount of direct sunlight received does not vary widely. The higher latitudes (north of the Tropic of Cancer and south of the Tropic of Capricorn) experience significant seasonal variation in climate.
::太阳是季节的极端终点,当直接阳光线是其去向最远的北方或最远的南方时,太阳是季节的极端终点。癌症热带和摩尔摩尔之间的地区被称为热带地区。由于直接阳光的接收量变化不大,该地区没有发生剧烈的季节性变化。较高纬度(癌症热带以北和摩尔摩尔热带以南)在气候方面经历了重大的季节性变化。
A sign depicting that the Tropic of Cancer passes through Madhya Pradesh in India.
::表示癌症热带穿过印度中央邦。A monument marking the Tropic of Capricorn just north of Antofagasta, Chile
::位于智利安托法加斯塔以北的一座标志摩角热带的纪念碑
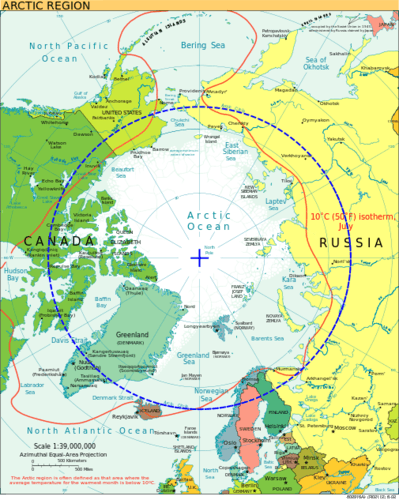
The is a line of latitude at 66.5 degrees north. It is the farthest point north that receives sunlight during its winter season (90 N − 23.5 = 66.5 N). During winter, the North Pole is away from the sun and does not receive much sunlight. At times, it is dark for most of the 24-hour day. During the Northern Hemisphere’s summer, the North Pole faces more toward the sun and may receive sunlight for longer portions of the 24-hour day.
::这是北纬66.5度的一条纬度线。 北纬最远的点是冬季的阳光照射(90N-23.5=66.5N)。 冬季,北极远离太阳,没有多少阳光。 有时,24小时大部分时间的阳光是暗的。 在北半球夏季,北极更多地面对太阳,24小时的阳光可能更长。
A map of the Arctic with the Arctic Circle in blue.
::北极的地图 北极圈是蓝色的A sign along the Dalton Highway marking the location of the Arctic Circle in Alaska.
::沿着道尔顿高速公路的标志 标志着阿拉斯加北极圈的位置
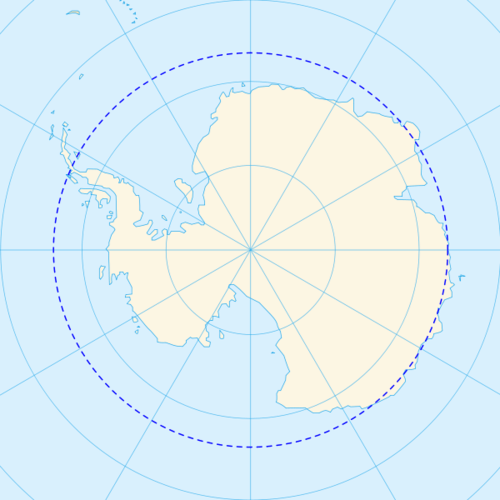
The is the corresponding line of latitude at 66.5 degrees south. It is the farthest location south that receives sunlight during the winter season in the Southern Hemisphere (90 S − 23.5 = 66.5 S). When it is winter in the north, it is summer in the south.
::南纬66.5度为相应的纬度线,南纬最远处是南半球冬季的阳光照射区(90西-23.5=66.5西)。 北纬冬季,南纬夏季。
A map of the Antarctic with the Antarctic Circle in blue.
::南极地图 南极圈是蓝色的
The Arctic and Antarctic Circles mark the extremities (southern and northern, respectively) of the polar day (24-hour sunlit day) and the polar night (24-hour sunless night). North of the Arctic Circle, the sun is above the horizon for 24 continuous hours at least once per year and below the horizon for 24 continuous hours at least once per year. This is true also near the Antarctic Circle, but it occurs south of the Antarctic Circle, toward the South Pole. Equinox, when the line of direct sunlight hits the equator and days and nights are of equal length, occurs in the spring and fall on or around March 20 or 21 and September 22 or 23.
::北极圈和南极圈分别标志着极日(24小时日落日)和极日(24小时或夜间)的极端(南纬和北纬)和极日(24小时或夜间),北极圈北部的太阳在地平线之上至少每年连续24小时,在地平线之下至少连续24小时,每年至少连续24小时,在地平线之下至少连续24小时。南极圈附近也是如此,但南极圈以南的南极圈向南极圈以南飞向南极。埃奎诺,当直接阳光照射赤道时,日日夜相同长时,春季发生,3月20日、21日、9月22日或23日前后或前后坠落。Time Zones
::时区Universal Time (UT), Coordinated Universal Time (UTC), (GMT), or Zulu Time (Z) are defined as the local time at 0 degrees longitude, which is the prime meridian located in . This is the same time under which many military operations, international radio broadcasts, and air traffic control systems operate worldwide. UTC is set in zero- to 24-hour time periods, as opposed to two 12-hour time periods (a.m. and p.m.). The designations of a.m. and p.m. are relative to the central meridian: a.m. refers to ante meridian , or “before noon,” and p.m. refers to post meridian , or “after noon.” UT, UTC, GMT, and Z all refer to the same 24-hour time system that assists in unifying a common time in regard to global operations. For example, all air flights use the 24-hour time system so the pilots can coordinate flights across time zones and around the world.
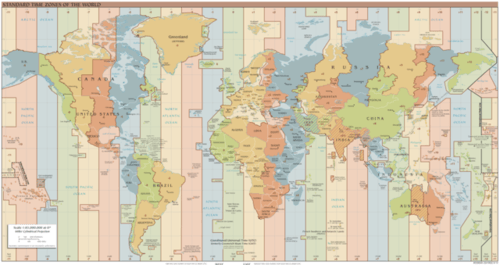
::世界时(UT),协调世界时(UTC),(GMT),或Zulu时(Z),被定义为位于0度的当地时间,即纬度为0度,这是位于......的主要度度。这是许多军事行动、国际无线电广播和空中交通管制系统在全世界运作的时间。世界时(UT)以零至24小时为时段,而不是以2至12小时为时段(上午和下午)。上午和下午的指定与中心度相对:上午是指某中度,或“中午前”,而下午是指后中度,或“中午后”。 UT, UTC, GMT和Z都指同样的24小时系统,它有助于在全球业务中统一一个共同时间段(上午和下午)。例如,所有空中飞行都使用24小时系统,使飞行员能够协调穿越时区和世界各地的飞行。The earth rotates on its axis once every 24 hours at the rate of 15 degrees per hour (15 × 24 = 360). are established roughly every 15 degrees longitude so that local times correspond to similar hours of day and night. With this system, the sun is generally overhead at noon in every time zone that follows the 15-degree-wide system. The continental United States has four main time zones.
::地球在轴上每24小时旋转一次,每小时15度(15×24=360),大约每15度经度确定一次,使当地时间与白天和夜晚的时数相仿,在该系统下,太阳一般在15度全系统后每个时区正午俯冲,美国大陆有四个主要时区。
CIA World Fact Book map of the standard time zones in the world.
::中央情报局《世界实况书》世界标准时区地图
The 24 time zones are based on the prime meridian in regard to Universal Coordinated Time (UTC), Greenwich Mean Time (GMT), or Zulu Time (Z), which all operate on the 24-hour time clock. Local time zones are either plus or minus determined by the distance from the prime meridian.
::24个时区以世界协调时间(UTC)、格林尼治平时(GMT)或祖鲁时间(Z)的主要中间线为基础,这些时区都24小时工作,当地时区由与主要时段的距离决定。The eastern standard time zone is five hours earlier than the time at the prime meridian (UTC) because it is about 75 degrees west of 0 degrees (5 × 15 = 75). For example, if it is noon in London, then it is 7 a.m. in New York. If it is 1 p.m. in New York, it is 10 a.m. in San Francisco, which is three times zones to the west. Since there are 24 hours in a day, there are 24 time zones on Earth. Each time zone is 15 degrees wide.
::东部标准时区比主要中间地带(UTC)时间早5小时,因为它在西纬约75度零度(5×15=75),例如,如果伦敦是中午,则在纽约是上午7时。如果纽约是下午1时,则在旧金山是上午10时,是西经三倍。由于每天24小时,地球上有24个时区。每个时区宽15度。A problem with the 15-degree time zones is that the zones do not necessarily follow state, regional, or local boundaries. The result is that time zones are seldom exactly 15 degrees wide and usually have varied boundary lines. In the United States, the boundaries between the different time zones are inconsistent with the lines of longitude. In some cases, time zones zigzag to follow state lines or to keep cities within a single time zone. Other countries address the problem differently. China, for example, is as large in land area as the United States, yet it operates on only one time zone for the entire country.
::15度时区的问题在于这些时区不一定遵循州、地区或地方边界,结果是时区很少完全宽达15度,而且通常有不同的边界线;在美国,不同时区之间的边界与经度线不一致,在有些情况下,用zigzag时区沿州线或将城市保留在一个时区内,其他国家对这个问题的处理方式不同。例如,中国的陆地面积与美国一样大,但全国只有一个时区。Regions in Geography
::地理区域A region is a basic unit of study in geography—a unit of space characterized by a feature such as a common government, language, political situation, or landform. A region can be a formal country governed by political boundaries, such as France or Canada. A region can also be defined by a landform, such as the drainage basin of all the water that flows into the Mississippi River. Moreover, a region can be defined by the area served by a shopping mall. Cultural regions can be defined by similarities in human activities, traditions, or cultural attributes. Geographers use the regional unit to map features of particular interest, and data can be compared between regions to help understand trends, identify patterns, or assist in explaining a particular phenomenon.
::一个区域是地理——一个具有共同政府、语言、政治形势或地貌特征的空间单位的基本研究单位;一个区域可以是正式的国家,受政治边界管辖,如法国或加拿大;一个区域也可以由陆地形态来界定,例如流入密西西比河的所有水的排水盆地;此外,一个区域可以由购物中心所服务的区域来界定;文化区域可以由人类活动、传统或文化特征的相似性来界定;地理学家利用区域单位来绘制特别感兴趣的特征;数据可以在各区域之间进行比较,以帮助了解趋势、确定模式或协助解释特定现象。Regions are traditionally defined by internal characteristics that provide a sense of place. Their boundaries vary with the type of region, whether it is formal, functional, or vernacular, and each type has its own meaning and defined purpose. A formal region has a governmental, administrative, or political boundary and can have political as well as geographic boundaries that are not open to dispute or debate. Formal boundaries can separate states, provinces, or countries from one another. Physical regions can be included within formal boundaries, such as the Rocky Mountains or New England. An official boundary, such as the boundary of a national park, can be considered a formal boundary. School districts, cities, and county governments have formal boundaries.
::区域传统上由提供地点感的内部特点来界定,其边界因区域类型而异,不论区域是正式的、功能性的还是本地的,每一类型都有其自己的意义和明确的目的;正式区域有政府、行政或政治边界,具有政治或地理边界,不能引起争议或辩论;正式边界可以将各州、省份或国家彼此分开;实际区域可以包括在正式边界内,如落基山脉或新英格兰;正式边界,如国家公园的边界,可以视为正式边界;学校区、城市和县政府有正式边界。Natural physical geographic features have a huge influence on where political boundaries of formal regions are set. If you look at a world map, you will recognize that many political boundaries are natural features, such as rivers, mountain ranges, and large lakes. For example, between the United States and Mexico, the Rio Grande makes up a portion of the border. Between Canada and the United States, a major part of the eastern border is along the Saint Lawrence Seaway and the Great Lakes. Alpine mountain ranges in Europe create borders, such as the boundary between Switzerland and Italy.
::自然自然地理特征对正式区域政治边界的划定具有巨大影响,如果看一看世界地图,你就会认识到许多政治边界是自然特征,例如河流、山脉和大湖,例如美国与墨西哥之间的边界是里奥格兰德河的一部分,加拿大与美国之间的边界是东部边界的主要部分,沿圣劳伦斯海道和大湖。欧洲的阿尔卑斯山脉是边界,例如瑞士与意大利之间的边界。
The Himalayan Mountains form a natural boundary separating India and China.
::喜马拉雅山形成了印度和中国之间的自然边界。
While geographic features can serve as convenient formal borders, political disputes will often flare up in adjacent areas, particularly if valuable natural or cultural resources are found within the geographic features. Oil drilling near the coast of a sovereign country, for example, can cause a dispute between countries about which one has dominion over the oil resources. The exploitation of offshore fisheries can also be disputed. A Neolithic mummy of a man who died in 3300 B.C.E. caused tension between Italy and Switzerland. The body was originally taken to Innsbruck, Switzerland, but when it was determined that the body was found about 90 meters (180 feet) inside the border of Italy, Italian officials laid claim to the body.
::虽然地理特征可以作为方便的正式边界,但政治争端往往会在邻近地区爆发,特别是在地理特征内发现宝贵的自然或文化资源的情况下。例如,一个主权国家海岸附近的石油钻探可能会在对石油资源拥有控制权的国家之间造成争端。对近海渔业的开发也可能引起争议。一个在公元前3300年死亡的男子的尼奥氏木乃伊造成了意大利和瑞士之间的紧张关系。尸体最初被带往瑞士因斯布鲁克,但当确定尸体在意大利边界内发现约90米(180英尺)时,意大利官员向该机构提出了索赔要求。Functional regions have boundaries related to a practical function within a given area. When the function of an area ends, the functional region ends and its boundaries cease to exist. For example, a functional region can be defined by a newspaper service or delivery area. If the newspaper goes bankrupt, the functional region no longer exists. Church parishes, shopping malls, and business service areas are other examples of functional regions. They function to serve a region and may have established boundaries for limits of the area to which they will provide service. An example of a common service area—that is, a functional region—is the region to which a local pizza shop will deliver.
::功能区域有与某一区域内实际功能有关的边界,当某一区域的功能结束时,功能区域结束,其边界不复存在,例如,一个功能区域可以由报纸服务或交付区来界定,如果报纸破产,功能区域就不复存在,教会教区、购物中心和商业服务区是功能区域的其他例子,它们为某一区域服务,并可能为它们提供服务的区域的界限划定了界限,例如,一个共同服务区——即功能区域——就是当地一家比萨店将前往的区域。Vernacular regions have loosely defined boundaries based on people’s perceptions or thoughts. Vernacular regions can be fluid—that is, different people may have different opinions about the limits of the regions. Vernacular regions include concepts such as the region called the “Middle East.” Many people have a rough idea of the Middle East’s location but do not know precisely which countries make up the Middle East. Also, in the United States, the terms Midwest or South have many variations. Each individual might have a different idea about the location of the boundaries of the South or the Midwest.
::高地地区根据人们的观念或想法划定了松散的边界。 高地地区可以是多变的 — — 也就是说,不同的人可能对地区的界限有不同的看法。 高地地区包括了所谓的“中东”等概念。 许多人对中东的地理位置有粗略的了解,但并不确切知道中东的构成国。 另外,在美国,中西部或南方的术语有许多不同之处。 每个人对南部或中西部边界的位置都可能有不同的看法。Whether the state of Kentucky belongs in the Midwest or in the South might be a matter of individual perception. Similarly, various regions of the United States have been referred to as the Rust Belt, Sun Belt, or Bible Belt without a clear definition of their boundaries. The limit of a vernacular area is more a matter of perception than of any formally agreed-upon criteria. Nevertheless, most people would recognize the general area being discussed when using one of the vernacular terms in a conversation.
::肯塔基州是否属于中西部州或南方州,可能是一个个人看法的问题。 同样,美国各地区被称作“鲁斯特带 ” 、 “ 太阳带 ” 、 或“圣经带 ” , 其边界没有明确界定。 本地地区的界限与其说是正式商定的标准,不如说是概念问题。 然而,大多数人在谈话中使用一个方言时会承认所讨论的一般区域。Using a State as a Comparison Guide
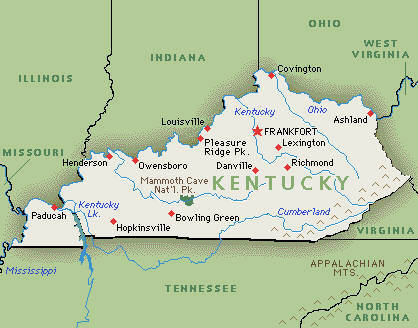
::使用国家作为比较指南In comparing one formal political region with another, it is often helpful to use a familiar country, state, province, or political unit as a reference or guide. Wherever you are located, you can research the statistical data for a formal region familiar to you to provide a common reference. The US state of Kentucky is one example that can be used to compare formal political regions. Kentucky ranks close to the middle range of the 50 US states in terms of its population of approximately 4.5 million people. Kentucky is also within the median range of the 50 states in the overall physical area. The state’s 40,409-square-mile physical area ranks it thirty-seventh in size in the United States.
::在比较一个正式政治区域与另一个正式政治区域时,使用一个熟悉的国家、州、省或政治单位作为参考或指南往往是有益的。无论你身处何处,你都可以研究一个你熟悉的正式区域的统计数据,以提供一个共同的参考。美国肯塔基州是一个可以用来比较正式政治区域的例子。 肯塔基州人口约为450万,接近美国50个州的中位数。 肯塔基州也位于整个物理区内50个州的中位数范围内。 州面积为40409平方英里,其面积在美国排在第37位。Kentucky is not as large in physical area as the western states, but it is larger in physical area than many of the eastern states. Kentucky includes part of the rural peripheral region of Appalachia. However, the state also has cosmopolitan core urban centers such as Lexington and Louisville. Kentucky also borders the metropolitan city of Cincinnati. The rural peripheral regions of the state are home to agriculture and mining. The urban core areas are home to industry and service centers. Other US states could also be used as examples. Identifying a state’s geographical attributes provides readers both in and outside the United States with a comparison indicator for geographic purposes.
::肯塔基州的实际面积不如西部州大,但实际面积大于东部州。肯塔基州包括阿帕拉契亚农村周边地区的一部分。然而,该州也拥有列克星顿和路易斯维尔等世界性核心城市中心。肯塔基州也与辛辛那提市接壤。该州农村外围地区是农业和采矿的家园。城市核心地区是工业和服务中心的家园。其他美国州也可以作为例子。确定美国的地理特征为美国国内外读者提供了地理比较指标。
Use the state of Kentucky to compare world regions. Kentucky ranks in the middle range of the 50 US states.
::利用肯塔基州的状况来比较世界各区域。 肯塔基州在50个美国州中位居中位。World Regional Geography
::世界区域地理World regional geography studies various world regions as they compare with the rest of the world. Factors for comparison include both the physical and the cultural landscape. The main questions are: Who lives there? What are their lives like? What do they do for a living? Physical factors of significance can include location, climate type, and terrain. Human factors include cultural traditions, ethnicity, language, religion, economics, and politics.
::世界地理与世界其他地方相比,对世界各区域进行了不同的区域地理研究,比较因素包括物理和文化景观。主要问题是:谁住在那里?他们的生活是怎样?他们为生活做什么?具有重大意义的物理因素包括地点、气候类型和地形。人类因素包括文化传统、族裔、语言、宗教、经济和政治。World regional geography focuses on regions of various sizes across the earth’s landscape and aspires to understand the unique character of regions in terms of their natural and cultural attributes. Spatial studies can play an important role in regional geography. The scientific approach can focus on the distribution of cultural and natural phenomena within regions as determined by many natural and cultural factors. The focus is on the spatial relationships within any field of study, such as regional economics, resource management, regional planning, and landscape ecology.
::世界区域地理侧重于地球地貌不同大小的区域,希望从自然和文化属性的角度了解各区域的独特性。空间研究可以在区域地理中发挥重要作用。科学方法可以侧重于许多自然和文化因素决定的区域内文化和自然现象的分布。重点是任何研究领域的空间关系,如区域经济学、资源管理、区域规划和地貌生态。Once again, this textbook takes a regional approach focusing on the globalization process, which in turn helps us to better understand our world. The regions studied in world regional geography can be combined into larger areas called realms. Realms are large areas on our planet, usually with multiple regions, that share the same general geographic location. Regions outlined are cohesive areas within each realm. You will explore the following realms in the upcoming chapters:
::这本教科书再次采取了侧重于全球化进程的区域方法,这反过来又有助于我们更好地了解我们的世界。在世界区域地理中研究的区域可以合并为更大的领域,称为领域。地盘是地球上的大片地区,通常有多个区域,具有相同的一般地理位置。概述的区域是每个领域内具有凝聚力的区域。您将在即将到来的章节中探讨以下领域:-
Europe
::欧洲 欧洲 -
Russia
::俄罗斯 俄罗斯 -
North America
::北美北美 -
Middle America
::中东 中东 -
South America
::南美洲南美洲 -
North Africa, Middle East, and Central Asia
::北非、中东和中亚 -
Sub-Saharan Africa
::撒哈拉以南非洲 -
Southern Asia
::南亚 -
Eastern Asia
::东亚东亚 -
Southeast Asia
::东南亚东南亚 -
Australia
::澳大利亚 澳大利亚 -
Pacific
::太平洋
Key Takeaways
::密钥外出-
Geography is the spatial study of the earth’s surface.
::地理是地球表面的空间研究。 -
The discipline of geography bridges the social sciences with the physical sciences.
::地理学科将社会科学与物理科学联系起来。 -
The two main branches of geography include physical geography and human geography.
::地理的两个主要分支包括地理物理和人文地理。 -
GIS, GPS, and remote sensing are tools that geographers use to study the spatial nature of physical and human landscapes.
::地理信息系统、全球定位系统和遥感是地理学家用来研究物理和人类景观空间性质的工具。 -
A grid system called the graticule divides the earth by lines of latitude and longitude that allow for the identification of absolute location on the earth’s surface through geometric coordinates measured in degrees.
::一个称为 " 流星体 " 的网格系统将地球按纬度和经度线分隔,以便通过按度测量的几何坐标确定地球表面的绝对位置。 -
There are 24 time zones that are set at 15-degree intervals each and organize time intervals around the world.
::全世界有24个时区,每个时区15度间隔,并组织时间间隔。 -
The tilt of the earth’s axis at 23.5 degrees helps create the earth’s seasonal transitions by either absorbing or reflecting the sun’s energy. The line of direct sunlight always hits the earth between 23.5 degrees north (Tropic of Cancer) and 23.5 degrees south (Tropic of Capricorn), depending on the time of year.
::地球轴在23.5度的倾斜有助于通过吸收或反映太阳的能量来创造地球的季节性转变。 直接阳光直射地球的线总是在北纬23.5度(癌症热带)至南纬23.5度(摩尔克热带)之间,这取决于每年的时间。 -
A region is the basic unit of study in geography.
::区域是地理研究的基本单位。 -
Three main types of boundaries define a region: formal, functional, and vernacular.
::三种主要的边界类型界定一个区域:正式的、功能性的和本地的。 -
World regional geography is the study of a particular group of world regions or realms as each compares with the rest of the world.
::世界区域地理是研究某一组世界区域或地区的研究,每个区域或地区与世界其他地区相比都是如此。
Vocabulary Terms
::词汇术语术语Vocabulary Quizlet: Chapter 1
::词汇表Quizlet:第一章-
atmosphere:
the gaseous area of air surrounding Earth
::大气:地球周围空气的气体面积 -
biomes:
large ecosystems characterized by common climate, common vegetation, and common animal life
::生物群:以共同气候、共同植被和共同动物生命为特征的大型生态系统 -
biosphere:
the areas of Earth that support plant and animal life
::生物圈:支持动植物生命的地球区域 -
climate:
a pattern of the combination of precipitation and temperature over time
::气候:长期降水和温度相结合的模式 -
erosion:
the wearing away of the Earth's surface caused by the movement of water, ice, or wind
::水、冰或风的移动导致地球表面消失 -
geographic factors:
physical and human conditions that impact the environments of places and regions.
::地理因素:影响地点和区域环境的物质条件和人的条件。 -
geography:
the study of the Earth's people, places, features, and environment from a spatial perspective
::地理地理:从空间角度研究地球人、地点、特征和环境 -
human geography:
the study of human activities related to interaction with the environment and control of the Earth's surface
::人类地理:研究与环境相互作用有关的人类活动和控制地球表面 -
hydrosphere:
the water areas of Earth, including oceans, lakes, rivers, groundwater, glaciers, and water vapor
::水圈:地球的水区,包括海洋、湖泊、河流、地下水、冰川和水蒸气 -
landforms:
a specific physical feature of the Earth's surface
::地面形态:地球表面的具体物理特征 -
lithosphere:
the solid surface of Earth, including the soil and landforms
::地圈:地球的固体表面,包括土壤和地面形态 -
patterns:
an observable model, style or trend, generally observed on maps in geography
::在地理地图上普遍观察到的可观测模型、风格或趋势 -
physical geography:
physical and human conditions that impact the environments of places and regions
::物理地理地理:影响地点和区域环境的物质条件和人的条件 -
processes:
a particular method that brings changes to the physical or human geography
::进程:使物理或人文地理变化的特定方法 -
soil building process:
the creation of organic matter formed from weathered rock, air, and water
::土壤建设过程:产生由气候岩石、空气和水形成的有机物 -
tectonic forces:
a physical process involving the movement of the Earth's crust
::构造力:涉及地球地壳移动的物理过程
Applying Knowledge
::应用知识Interactive Notebook Activities
::互动笔记活动-
Summarize the focus of geography and the two main branches of the discipline.
::概述地域重点和学科的两个主要分支。 -
List the tools geographers use to study the earth’s surface.
::列出用于研究地球表面的工具。 -
Summarize how the grid system of latitude and longitude relates to seasons and time zones.
::总结纬度和经度网格系统与季节和时区的关系。 -
Describe the difference between the different types of regional distinctions recognized in geography.
::说明地理上公认的不同类型区域区别之间的区别。 -
Explain the spatial nature of geography and how each place or region is examined, analyzed, and compared with other places or regions.
::解释地理的空间性质,以及如何考察、分析和比较每个地点或区域,并与其他地点或区域进行比较。 -
List the basic geographic realms and their locations.
::列出基本地理领域及其位置。
Discussion and Study Questions
::讨论和研究问题-
How does the discipline of geography provide a bridge between the social sciences and the physical sciences?
::地理学科如何在社会科学和物理科学之间提供桥梁? -
How does the cultural landscape assist in indicating the differences between a wealthy neighborhood and a poverty-stricken neighborhood?
::文化景观如何帮助显示富裕邻里与贫困邻里之间的差异? -
How can remote sensing technology assist in determining what people do for a living?
::遥感技术如何协助确定人们为谋生而做什么? -
What is the significance of the Tropic of Cancer and the Tropic of Capricorn?
::癌症热带和摩尔摩托热带的意义何在? -
What occupations depend on knowledge of the seasons for their success?
::哪些职业的成功取决于对季节的知识? -
If it is 4 p.m. in San Francisco, what time is it in London, England?
::如果现在是旧金山下午4点 英国伦敦几点了? -
How would GIS, GPS, or remote sensing technology be used to evaluate the destruction caused by a tornado in Oklahoma?
::如何利用地理信息系统、全球定位系统或遥感技术来评价俄克拉荷马州龙卷风造成的破坏? -
How is the cultural landscape influenced by the physical landscape?
::文化景观如何受到自然景观的影响? -
Can you list a formal region, a functional region, and a vernacular region that would include where you live?
::您能否列出一个正式区域、功能区域和包括您居住地在内的本地区域? -
What methods, topics, or procedures would be helpful to include in the study of world geography?
::哪些方法、专题或程序有助于列入世界地理学研究?
Real-World Geography Exercise
::现实世界地理演习Using , locate the places on the list below. Next, using , determine the latitude and longitude for each location. Be prepared to share your answers.
::使用 , 定位下面列表中的位置 。 接下来, 使用 , 确定每个位置的纬度和经度 。 准备分享您的答案 。-
-
Arctic Circle
::北极圈 -
Antarctic Circle
::南极圈 -
Equator
::赤道 -
International Date Line
::国际日期线 -
North Pole
::北极 -
Prime meridian
::初中度 -
Tropic of Cancer
::癌症热带 -
Tropic of Capricorn
::摩角热带 -
South Pole
::南极
::北极圈 南极圈 赤道国际日期线 北极极北极 南极 摩角南极 -
Arctic Circle
Tech Activities
::技术合作活动-
Use
to locate your current school or residence.
::学校、学校、学校、学校、学校、学校、学校、学校、学校、学校、学校、学校、学校、学校、学校、学校、学校、学校、学校、学校、学校、学校、学校、学校、学校、学校、学校、学校、学校、学校、学校、学校、学校、学校、学校、学校、学校、学校、学校、学校、学校、学校、学校、学校、学校、学校、学校、学校、学校、学校、学校、学校、学校、学校、学校、学校、学校、学校、学校、学校、学校、学校、学校、学校、学校、学校、学校、学校、学校、学校、学校、学校、学校、学校、学校、学校、学校、学校、学校、学校、学校、学校、学校、学校等。 -
Draw a map of your home state or province and include lines of latitude and longitude.
::绘制您所在的州或省份的地图, 并包含纬度和经度的线条 。 -
Compile the statistical data on your home state, province, or territory to use in comparing formal political regions.
::• 汇编关于贵国、省份或领土的统计数据,用于比较正式的政治区域。
Mapping Exercise
::绘图绘制作业Mapping Our World ESRI- ARGIS Online Module 1 Lesson 1
::绘制我们世界的ESRI-ARGIS在线单元1: This computer activity will show students how to start the ArcGIS Online program. Students will be guided through the basics of using the ArcGIS Online map viewer to explore maps. After students do this activity, they will be prepared to complete other GIS activities.
::: 计算机活动将展示学生如何启动ArcGIS在线方案。学生将通过使用ArcGIS在线地图查看器来探索地图的基本知识来指导学生。学生在开展这项活动后,将准备完成其他地理信息系统活动。Videos for Geography Enrichment
::地理丰富视频Helpful Websites for the Study of Geography
::地理研究有用网站is an encyclopedia funded by the Canadian government covering all branches of knowledge. Their scholarly collection includes interactive materials.
::该百科全书由加拿大政府资助,涵盖所有知识分支,其学术收藏包括交互式材料。provides information on the people, history, government, economy, energy, geography, communications, transportation, military, and transnational issues for the world's entities.
::向世界各实体提供关于人民、历史、政府、经济、能源、地理、通信、运输、军事和跨国问题的资料。is a US government website where you can find federal legislation, past and present, as well as information about the US legal system.
::是一个美国政府的网站,您可以在此找到过去和现在的联邦立法以及关于美国法律制度的信息。is a government agency website that provides current news, resources, topics of interest, information about drugs, careers in the DEA, and a tip hotline.
::是一个政府机构网站,提供最新消息、资源、感兴趣的话题、毒品信息、在缉毒局的职业以及一条小费热线。Online mapping software and activities for the classroom
::课堂在线绘图软件和活动ESRI The Science of Where
::ESRI " 哪里科学科学 "is the largest library in the world and provides manuscripts, files, information, pictures, and videos.
::图书馆是世界上最大的图书馆,提供手稿、文件、信息、图片和录像。is a US government agency website that allows users to search for and retrieve satellite images of Earth.
::这是一个美国政府机构的网站,用户可以搜索和检索地球的卫星图像。is a US government website that provides historical documents, photos, records, publications, and educator resources.
::这是一个美国政府网站,提供历史文件、照片、记录、出版物和教育资源。is a US government agency website that provides weather-related information and ocean research.
::是一个提供气象信息和海洋研究的美国政府机构网站。is a website by the United States Geological Survey and other federal, state, and local agencies that delivers topographic information for the United States.
::这是美国地质调查局和其他联邦、州和地方机构为美国提供地形信息的网站。is a massive central data source and a handy way to graphically compare nations.
::是一个庞大的中央数据源,是用图形比较国家的一种方便方式。is a website that measures most locations in the world for air pollution in real time.
::是一个实时测量世界上大多数空气污染地点的网站。is a unique statistical database, which allows you to research and compare a multitude of different data on US states.
::这是一个独特的统计数据库, 使你能够研究和比较关于美国各州的多种不同数据。is an international organization founded in 1945 and made up of 193 member states. The UN maintains international peace and security, protects human rights, delivers humanitarian aid, promotes sustainable development, and upholds international law.
::联合国是一个国际组织,成立于1945年,由193个成员国组成。 联合国维护国际和平与安全,保护人权,提供人道主义援助,促进可持续发展,维护国际法。is a US government agency that provides a population clock, data, surveys, statistics, a library with information and infographics, news about the economy, and much more.
::这是一个美国政府机构,它提供人口钟、数据、调查、统计、一个拥有信息和信息资料的图书馆、关于经济的新闻,以及更多。is a US government agency website that provides scientific information about the natural hazards that threaten lives, the natural resources we rely on, the health of our ecosystems and environment, and the impacts of climate and land-use change.
::这是一个美国政府机构的网站,提供科学信息,说明威胁生命的自然危害、我们赖以生存的自然资源、生态系统和环境的健康以及气候和土地使用变化的影响。is a US government website that provides the latest presidential news, information about the budget, policy, defense, and many more topics.
::提供最新总统新闻、预算、政策、国防等资讯, 以及更多议题。is under the United Nations and provides leadership on matters critical to health; shapes the research agenda on health; and monitors the health situation and assessing health trends around the world. Their website provides information on the state of health around the world, outbreaks, current health news, and more.
::他们的网站提供世界各地卫生状况、疫情爆发、最新卫生新闻等信息。is an intergovernmental organization that regulates international trade. The website provides information on the history of the multilateral trading system, featured videos, news and events, trade topics, and more.
::该网站提供关于多边贸易体系历史的信息、视频、新闻和事件、贸易专题等等。 -
Summarize the focus of geography and the two main branches of the discipline.