7.4 细菌营养
章节大纲
-
What do bacteria need to grow?
::细菌需要生长什么?Like most everything else, they need food . Given the right conditions, can grow from just a few to millions or billions overnight.
::与大多数其它东西一样,他们需要食物。 在合适的条件下,他们可以在一夜之间从几百万或数十亿一夜之间增长到数百万或数十亿。Prokaryote Metabolism
::新陈代谢Like all living things, need energy and carbon. They meet these needs in a variety of ways. In fact, prokaryotes have just about every possible type of metabolism . They may get energy from light (photo) or chemical compounds (chemo). They may get carbon from carbon dioxide ( autotroph ) or other living things ( heterotroph ). Most prokaryotes are chemoheterotrophs . They depend on other organisms for both energy and carbon. Many break down organic wastes and the remains of dead organisms. They play vital roles as decomposers and help recycle carbon and nitrogen. Photoautotrophs are important . They are especially important in .
::和所有生物一样, 需要能量和碳。 它们以各种方式满足这些需求。 事实上, prokaryotes 几乎有每一种可能的新陈代谢。 它们可能从光( 光) 或化学化合物( 化学化合物( 化学) ) 获得能量。 它们可能从二氧化碳( 自动) 或其他生物物质( 湿化) 获得碳 。 大多数 prokaryotes 是化学冷冻剂 。 它们既依靠其他生物来获取能量和碳。 许多将有机废物和死亡生物的残骸分解开来。 它们作为分解者发挥着关键作用, 并且帮助回收碳和氮。 光生养分非常重要 。 它们特别重要 。Classification of Prokaryotes Based on Metabolism
::基于新陈代谢的Prokaryotes分类Two major nutritional needs can be used to group prokaryotes. These are (1) carbon metabolism, their source of carbon for building organic molecules within the cells, and (2) energy metabolism, their source of energy used for growth.
::两种主要的营养需求可以用来组聚原虫。 它们是1) 碳新陈代谢,其碳源用于在细胞内制造有机分子;(2) 能源新陈代谢,其用于增长的能源来源。
In terms of carbon metabolism, prokaryotes are classified as either heterotrophic or autotrophic:
::就碳新陈代谢而言,原虫被归类为异氧营养或自养:-
Heterotrophic organisms use
, usually from other organisms, as carbon sources.
::热营养生物通常从其他生物中作为碳来源使用。 -
Autotrophic organisms use carbon dioxide (CO
2
) as their only source or their main source of carbon. Many autotrophic bacteria are photosynthetic, and get their carbon from the carbon dioxide in the
atmosphere
.
::自养生物将二氧化碳(CO2)作为碳的唯一来源或主要来源,许多自养细菌是光合成细菌,从大气中的二氧化碳中获取碳。
Energy metabolism in prokaryotes is classified as one of the following:
::prokaryotes的能源新陈代谢被归类为以下类别之一:-
Phototrophic organisms capture light energy from the sun and convert it into chemical energy inside their cells.
::光生生物从太阳中捕捉光能,将其转化为细胞内的化学能量。 -
Chemotrophic organisms break down either organic or inorganic molecules to supply energy for the cell. Some chemotrophic organisms can also use their organic energy-supplying molecules as a carbon supply, which would make them chemoheterotrophs.
::化学富营养性生物分解有机分子或无机分子,为细胞提供能量。 一些化学富营养性生物也可以将有机能量供给分子用作碳供应,从而形成化学老化。 -
Photoheterotrophs
are organisms that capture light energy to convert to chemical energy in the cells, but they get carbon from organic sources (other organisms). Examples are purple non-sulfur bacteria, green non-sulfur bacteria and heliobacteria.
::光生养分是捕捉光能以在细胞中转换为化学能源的生物,但它们从有机来源(其他生物)获得碳,例如紫非硫细菌、绿色非硫细菌和白细胞。 -
Chemoheterotrophs are organisms that get their energy source and carbon source from organic sources. Chemoheterotrophs must consume organic building blocks that they are unable to make themselves. Most get their energy from organic molecules such as sugars. This nutritional mode is very common among
eukaryotes
, including humans.
::化学血清营养素是有机来源的能源来源和碳来源的有机体。 化学血清营养素必须消耗他们自己无法制造的有机构件。 大多数人的能量来自糖等有机分子。 这种营养模式在包括人类在内的欧洲人中非常常见。 -
Photoautotrophs are cells that capture light energy, and use carbon dioxide as their carbon source. There are many photoautotrophic prokaryotes, which include
cyanobacteria
. Photoautotrophic prokaryotes use similar compounds to those of plants to trap light energy.
::光亚营养素是捕捉光能、使用二氧化碳作为碳源的细胞。 有很多光亚亚亚营养学先质,包括氰球菌。 光亚营养学先质使用与植物相似的化合物来捕捉光能。 -
Chemoautotrophs
are cells that break down inorganic molecules to supply energy for the cell, and use carbon dioxide as a carbon source. Chemoautotrophs include prokaryotes that break down hydrogen sulfide (H
2
S the “rotten egg” smelling gas), and ammonia (NH
4
).
Nitrosomonas
, a
of
soil
bacterium, oxidizes NH
4
+
to nitrite (NO
2
-
). This reaction releases energy that the bacteria use. Many chemoautotrophs also live in extreme environments such as deep sea vents.
::化学二氧化物是分解无机分子的细胞,为细胞提供能量,并将二氧化碳用作碳源。化学二氧化物包括分解硫化氢(H2S,“红蛋”气味)和氨(NH4)。氮蛋(一种土壤细菌)氧化NH4+至亚硝酸(NO2),这种反应释放出细菌使用的能量。许多化学二氧化物也生活在深海通风口等极端环境中。
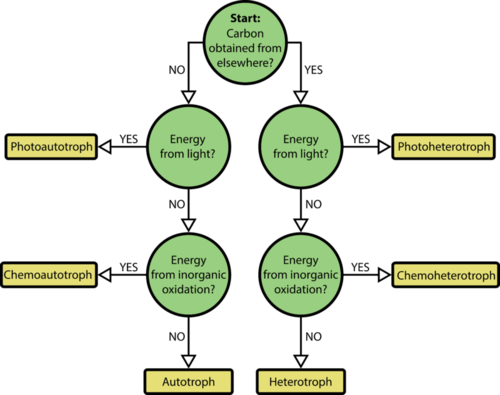
This flowchart helps to determine if a species is an autotroph or a heterotroph, a phototroph or a chemotroph. For example, “Obtain carbon elsewhere?” asks if the source of carbon is another organism. If the answer is “yes”, the organism is heterotrophic. If the answer is “no,” the organisms is autotrophic.
::这个流程图有助于确定一种物种是自发性还是血化、光化或化化。 比如,“其他地方的碳吗? ” 问碳源是否是另一个生物体。 如果答案是“是的 ” , 生物体是血化的。 如果答案是“否 ” , 生物体是自发性的。Summary
::摘要-
Prokaryotes fulfill their carbon and energy needs in various ways. They may be photoautotrophs, chemoautotrophs, photoheterotrophs, or chemoheterotrophs.
::蛋白质以各种方式满足其碳和能量需求。 它们可以是光自养、化学自养、光电富集、或化学再生。
Review
::回顾-
Describe metabolism of most prokaryotes.
::描述大多数原虫的新陈代谢 -
Define phototrophic and chemotrophic organisms.
::定义光营养生物和富营养生物。 -
What are photoautotrophs?
::什么是光力养分? -
What are photoheterotrophs?
::什么是光血化症?
Resources
::资源 -
Heterotrophic organisms use
, usually from other organisms, as carbon sources.