1.2 人类活动与环境(7天)
章节大纲
-
Human Activity and the Environment
::人类活动与环境Chapter Challenges
::章次 挑战-
Explain how climate and human habitation are related and distinguish between the main climate types.
::解释气候和人类居住如何相互关联,并区分主要气候类型。 -
Explain the dynamics of tectonic plates and their relationship to earthquakes and volcanic activity.
::解释构造板块的动态及其与地震和火山活动的关系。 -
Outline the main causes of and problems with deforestation. Explain the relationship between deforestation and climate change.
::概述毁林的主要原因和问题,解释毁林与气候变化之间的关系。 -
Describe where the rain shadow effect takes place and explain why it occurs in those places and how it may influence human activity.
::描述雨影效应发生在哪里,并解释为什么在这些地方发生,以及它如何影响人类活动。 -
Summarize how climate change occurs and the relationship between greenhouse gasses such as carbon dioxide and the planet’s temperature regulation.
::总结气候变化是如何发生的,以及二氧化碳等温室气体与地球温度调节之间的关系。
Student Learning Objectives
::学生学习目标TEKS Regional Unit 01 Physical Patterns and Processes; Chapter 1.2 Human Activity and the Environment
::TEKS 区域单位 01 物理模式和过程;第1.2章人的活动和环境WG.2B Explain how changes in societies led to the diverse use of resources
::WG.2B 解释社会变化如何导致资源使用多样化WG.3A Explain weather conditions and climate in relation to annual changes in Earth-Sun relationships
::WG.3A 结合地球-太阳关系的年度变化解释天气条件和气候WG.3C Examine the physical processes that affect the lithosphere, atmosphere, hydrosphere, and biosphere.
::WG.3C 审查影响地圈、大气、水圈和生物圈的物理过程。WG.4B Describe different landforms and the physical processes that cause their development
::WG.4B 描述导致其发展的不同土地形态和物理过程WG.4C Explain the influence of climate on the distribution of biomes in different regions
::WG.4C 解释气候对不同区域生物群落分布的影响WG.8A Compare ways that humans depend on, adapt to, and modify the physical environment, including the influences of culture and technology.
::WG.8A 比较人类依赖、适应和改变自然环境的方式,包括文化和技术的影响。WG.8B Describe the interaction between humans and the physical environment and analyze the consequences of extreme weather and other natural disasters such as El Niño, floods, tsunamis, and volcanoes.
::WG.8B 描述人类与自然环境之间的相互作用,分析极端天气和厄尔尼诺、洪水、海啸和火山等其他自然灾害的后果。WG.8C Evaluate the economic and political relationships between settlements and the environment, including sustainable development and renewable/non-renewable resources. sustainable development and renewable/non-renewable resources
::WG.8C 评价住区与环境之间的经济和政治关系,包括可持续发展和可再生/不可再生资源。WG.11C Assess how changes in climate, resources, and infrastructure (technology, transportation, and communication) affect the location and patterns of economic activities.
::WG.11C 评估气候、资源和基础设施(技术、运输和通信)的变化如何影响经济活动的地点和模式。WG.19A Evaluate the significance of major technological innovations in the areas of transportation and energy that have been used to modify the physical environment
::WG.19A 评价用于改变自然环境的运输和能源领域重大技术革新的重要性WG.19C Evaluate the significance of major technological innovations in the areas of transportation and energy that have been used to modify the physical environment.
::WG.19C 评价用于改变自然环境的运输和能源领域重大技术革新的重要性。Climate and Human Habitation
::气候与人类生境The earth's ability to receive and absorb sunlight is a primary factor in the earth's environment, and it also has a big impact on human populations. There are no large cities or human communities in Antarctica because it is so cold. Most of the sunlight filtering down to Antarctica is reflected off the earth at that latitude because of the tilt of the earth's axis and the resulting angle of incoming solar radiation. Answering the basic questions of where most humans live on Earth and why they live there depends on understanding climate.
::地球接收和吸收阳光的能力是地球环境的一个主要因素,它也对人类人口产生巨大影响。南极洲没有大城市或人类社区,因为它如此寒冷。由于地球轴的倾斜和由此而来的太阳辐射角度,从南极洲渗透到南极的大部分阳光在地球的纬度上被从地球反射出来。回答大多数人类在地球上生活的地方和为什么他们在那里生活的基本问题取决于对气候的理解。Since the region between the Tropic of Cancer and the Tropic of Capricorn receives the most direct sunlight throughout the year, it is favorable to plant and animal life, provided there is adequate moisture or precipitation. Humans have been living in the tropics for a long time, even when the ice sheets were covering parts of the mid-latitudes. The problem with the tropics is that the soils are usually of poor quality and the nutrients have been leached out. Today, when we look at the earth and the distribution of human population, the two main factors that attract human habitation are moderate climates and access to water.
::由于癌症热带和摩角热带之间的地区全年都得到最直接的阳光,只要有足够的水分或降水,植物和动物的生命就比较好;人类长期生活在热带,即使冰盖覆盖中纬度的部分地区;热带的问题是土壤通常质量差,养分被浸出;今天,当我们观察地球和人类人口分布时,吸引人类居住的两个主要因素是温和的气候和水的获取。More than 70 percent of the earth's surface is covered with water. The only problem is that less than three percent of the water is fresh, and most of that fresh water is stored in ice caps at the North or South Pole. This leaves less than one percent of the world's fresh water for human use, usually in lakes, rivers, streams, or groundwater and underground aquifers. Climate plays an important role in where humans live because precipitation is necessary for growing crops, raising livestock, and supplying fresh water to urban communities.
::地球上70%以上的地表被水覆盖,唯一的问题是不到3%的水是淡水,而大部分淡水储存在北极或南极的冰盖中。 这使得世界上供人类使用的淡水不到百分之一,通常在湖泊、河流、溪流或地下水和地下蓄水层中。 气候在人类生活的地方起着重要作用,因为种植作物、饲养牲畜和向城市社区提供淡水需要降水。
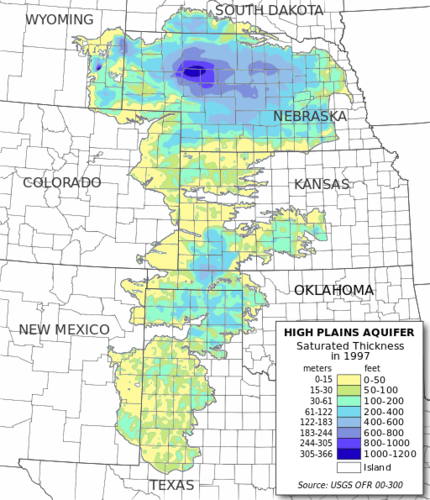
Digital map of the saturated thickness of the High Plains aquifer in parts of Kansas, Nebraska, New Mexico, Oklahoma, South Dakota, Texas, and Wyoming
::堪萨斯、内布拉斯加州、新墨西哥州、俄克拉何马州、南达科塔州、得克萨斯州和怀俄明州部分地区高平原含水层饱和厚度数字地图
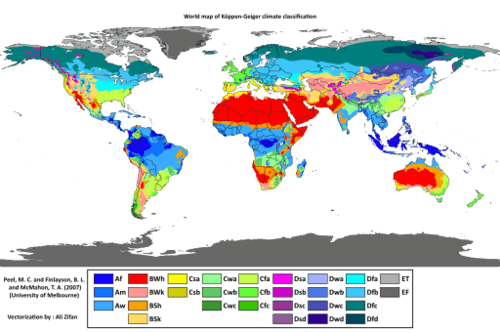
Several geographers have developed categories to identify climate types. Climate can be defined as a long-term average weather pattern evident in a particular region of the world. Weather is a term usually used to define conditions on a short-term or even daily basis. The two main elements in climate conditions are temperature and precipitation. For the purposes of this overview of world geography, the various climate types have been broken down into six basic types—A, B, C, D, E, and H—after the Köppen-Geiger classification system. Type H climates are actually a subset of the type E climate category.
::若干地理学家制定了确定气候类型的类别,可将气候界定为在世界某个特定区域明显可见的长期平均天气模式。天气通常是用来确定短期甚至每日条件的一个术语。气候条件的两个主要要素是温度和降水。为本世界地理概览的目的,各种气候类型分为六类基本类型:A、B、C、D、E和H,继Köppen-Geger分类系统之后。H型气候实际上是E类气候的子类。-
Type A: Tropical or equatorial climates
::A类:热带或赤道气候 -
Type B: Dry or arid climates
::B类:干旱或干旱气候 -
Type C: Moderate or temperate climates
::C类:中温或温带气候 -
Type D: Cold or continental climates
::D类:冷气候或大陆气候 -
Type E: Polar or extreme climates
::E类:极地或极端气候 -
Type H: (Unclassified) highland climates
::H型未分类)高地气候
Köppen-Geiger climate classification is one of the most widely used climate classification systems. It was first published by Russian German climatologist Wladimir Köppen in 1884.
::Köppen-Geiger气候分类是使用最广泛的气候分类系统之一,首次由俄罗斯德国气候学家Wladimir Köppen于1884年出版。
Type A: Tropical or Equatorial Climates
::A类:热带或赤道气候The humid tropical type A climate, usually found in the tropics, has warm temperatures year round with a high level of precipitation, typically in the form of rain. Type A climates have various subgroups that indicate how variably the rainfall is distributed throughout the year. Some type A climates produce a dry season and a wet season (monsoon), while others receive consistent rainfall throughout the year.
::潮湿热带A型气候通常出现在热带地区,每年温温高,降水量高,通常以降雨形式出现,A型气候有不同的分组,表明全年降雨量的分布情况,A型气候产生旱季和湿季(季风),而其他气候则全年连续降雨。
Costa Rica, a country located in Central America, is a type A climate.
::哥斯达黎加是中美洲国家,属于A型气候。
Type B: Dry or Arid Climates
::B类:干或干旱气候The dry type B climate is exemplified by the earth's desert regions. Temperatures can be extreme, with little precipitation. Type B climate regions experience low rainfall and high temperatures during the day and cooler temperatures at night or during the winter season. Terrain in type B climates can range from sand deserts to prairie grasslands or steppes. Type B climates have fewer trees than most other climate areas.
::B类气候地区在白天降雨量低、气温高、夜间或冬季温度更低。B类气候地区从沙滩沙漠到草原草原或草原或草原,其树木比其他大多数气候地区少。
Threemile and Fivemile Mountains near Van Horn, Texas, are in the Chihuahuan Desert. The Chihuahuan Desert is a type B climate.
::德克萨斯州Van Horn附近的三英里和五英里山脉位于奇瓦瓦沙漠。奇瓦瓦沙漠是一种B型气候。
There is a direct relationship between highlands and type B climates in various places in the world. This climate condition, known as the rain shadow effect, or more accurately, the precipitation shadow effect, occurs when one side of a mountain range receives abundant rainfall while the region on the other side of the mountain range has a more arid climate. This phenomenon is evident wherever there is terrain with enough elevation to restrict the movement of precipitation bearing clouds.
::高地与世界不同地方的B型气候有直接关系,这种气候条件被称为雨影效应,更准确地说,降水影子效应,当山脉的一方降雨量充沛,而山脉另一侧的区域气候更干旱时,就会出现这种气候条件,只要地形高得足以限制带云的降水量流动,这种现象就很明显。Rain Shadow Effect
::雨影效应Rain shadows are created when prevailing winds carrying moisture rise quickly in elevation up a mountainside, where the air cools and condenses to precipitate out its moisture in the form of rain or snow. By the time the air mass hits the top of the mountain, its moisture is reduced. The dried air rushes down the other side of the mountain range, where it increases in temperature. The warm, dry air coming off the mountains continues to pull moisture out of the land, resulting in arid climate conditions.
::当潮风湿度迅速上升,升到山顶,空气冷却,凝结,以雨水或雪的形式蒸发水分时,就会形成雨影。当空气质量到达山顶时,水分就会减少。干燥的空气从山脉另一侧冲下,温度会升高。山上的温暖干燥空气继续将水分从陆地拉出,导致干旱的气候条件。The Hawaiian island of Kauai is an example of the rain shadow effect. The island's windward side receives more rain than almost any other place on Earth: as much as 460 inches (almost 40 feet) a year. Only a part of the island, however, receives that amount of rain. The height of the mountains causes a rain shadow on the dry leeward side, creating semi-desert conditions and type B climates.
::夏威夷的考艾岛就是雨影效应的一个例子。岛屿的风向方面降雨量比地球上几乎所有其他地方都要大:每年高达460英寸(近40英尺),但只有一部分岛屿得到如此大雨。山高在干燥的向下方面造成雨影,造成半沙漠条件和B型气候。
Kauai's origins are volcanic, the island having been formed by the passage of the Pacific Plate over the Hawaii hotspot. At approximately six million years old, it is the oldest of the Hawaiian islands. The highest peak on this mountainous island is Kawaikini at 5,243 feet (1,598 m).
::Kauai的起源是火山,该岛是太平洋板块通过夏威夷热点而形成的,大约600万年前是夏威夷群岛中最古老的岛屿,山地岛屿的最高峰值是卡瓦基尼(Kawaikini)5,243英尺(1,598米)。
Death Valley in California is also a result of the rain shadow effect. Little rain falls on Death Valley because any moisture in the prevailing winds falls on the western side of the bordering mountain ranges. The whole state of Nevada is dry because of the rain shadow effect. All the rain coming off of the Pacific Ocean falls on the coastal mountains and the Sierra Nevada in California. The mountains are high enough to shadow that region of Nevada, and the basin and ranges further the rain shadow effect on a local basis.
::加利福尼亚州死亡谷也是雨影效应的结果。 死亡谷降下小雨, 因为大风中的任何水分都落在邻近山脉的西侧。 整个内华达州由于雨影效应而干涸。 太平洋的所有降雨都落在加利福尼亚州的沿海山区和山地内华达山脉上。 山地高得足以让内华达地区蒙上阴影, 盆地和远处的雨影效应也更远。
Death Valley is a desert valley located in Eastern California, in the northern Mojave Desert bordering the Great Basin Desert. It is one of the hottest places in the world at the height of summertime.
::死亡谷是位于东加利福尼亚州、与大盆地沙漠相邻的莫哈韦沙漠北部的一个沙漠谷地,是世界上夏季高峰时期最热闹的地方之一。
On the other side of the earth, the Himalayas are an excellent example of mountains that create the rain shadow effect. Most of western China has a type B climate because of the rain shadow effect caused by high mountains that stop precipitation-bearing clouds from ever reaching the region. The southern side of the Himalayas receives extensive rainfall because of monsoon rains arriving from the Indian Ocean, but western China is essentially a desert. It is sparsely inhabited compared with the high-density regions in China Proper to the east, where rainfall is plentiful.
::在地球的另一面,喜马拉雅山脉是山岳中产生雨影效应的极好例子。中国西部大部分地区都存在B型气候,因为高山带来的雨影效应阻止了降水云一直延伸到该地区。喜马拉雅山脉南部由于季风降雨从印度洋来袭而降雨量大,但中国西部基本上是一片沙漠。与中国东部高密度地区相比,那里居住人口稀少,东部降雨量充足。Type C: Moderate or Temperate Climates
::C型:中度或温热气候Often described as moderate in temperature and precipitation, type C climates are the most favorable to human habitation in that they host the largest human population densities on the planet. Type C climates are found mostly in the mid-latitudes bordering the tropics. Seasonal changes are pronounced, with distinct winters and summers. Winters are cool to cold and summers are usually warm. Precipitation varies from low to high, depending on location. In the United States, C climates dominate the southeast and the West Coast.
::C型气候通常被描述为温和降水温和降水温温和温和,是人类居住最有利的气候,因为它们拥有地球上最大的人口密度。C型气候大多在毗邻热带的中纬度地区。季节性变化显著,冬季和夏季不同。冬季冷却,夏季通常温暖。降水量因地点而异,从低降到高降。在美国,C型气候主宰着东南和西岸。Type C climates are not the most widespread on the planet, but they have attracted the largest human populations. One reason for the attraction has been the abundance of forests, farmland, and fresh water found in type C regions. The main population centers of the planet are in type C climates. With over seven billion people on the planet and growing, humans have populated most of the regions with type C climates and are now filling up the other areas that have A, B, or D climate types.
::C型气候并非地球上最普遍的气候,但它们吸引了最多的人口。 吸引的原因之一是C型地区森林、农田和淡水丰富。 地球上的主要人口中心位于C型气候中。 地球上有70多亿人在不断增长,人类在大多数C型气候地区居住,现在正在填充其他A型、B型或D型气候地区。
Los Angeles, California, in the United States, is a type C climate.
::美国加利福尼亚州洛杉矶 是一种C型气候
Type D: Cold or Continental Climates
::D类型:冷气候或大陆气候Type D climate regions are often found in the interiors of continents away from the moderating influence of large bodies of water. They are often farther north than type C regions, resulting in colder winters. Seasonal variations exist, with cool to hot summers and cold winters. Precipitation is usually in the form of rain in summer and snow in winter. Regions with type D climates can be found in the Great Lakes region of the United States, much of Canada, and a large portion of Russia.
::D型气候区域往往出现在远离大水体调节影响的大陆内地,往往比C型区域更北,导致冬季寒冷,季节性变化,夏季冷到热,冬季冷,夏季通常降雨,冬季下雪,美国大湖地区、加拿大大部分地区和俄罗斯大部分地区都有D型气候。
Minneapolis, Minnesota, in the United States, is a type D climate.
::美国明尼苏达明尼苏达州明尼阿波利斯的气候是D型气候。
Type E: Polar or Extreme Climates
::E类:极地或极端气候Type E is an extreme climate type found in the Polar Regions near or to the north of the Arctic Circle and near or to the south of the Antarctic Circle. Regions with type E climates are cold with permanent ice or permafrost year round. Vegetation is minimal, and there are no trees. Temperatures may warm slightly during the short summer months; however, they rarely rise above 50 degrees.
::E型是北极圈附近或北面极地区域以及南极圈附近或南面的极端气候类型,E型气候寒冷,冰或永久冻土年复一年。植被极少,没有树木。在短短的夏季月中,温度可能稍温,但很少上升到50度以上。
Antarctica is a type E climate.
::南极洲是一种E型气候。
Type H: Highland Climates
::H型:高地气候Type H highland climates are usually listed as a subcategory of type E climates. Mountain ranges can create a variety of climate types because of the change in elevation from the base of the range to the summit. Different climate types can be found on the same mountain at different elevations. Type H climates designate highlands or mountain terrain, although variations in climate exist on most mountain ranges. Climates at the base of mountains will vary depending on whether the mountains are found in the tropics or in the higher latitudes.
::高地气候通常被列为E类气候的一个亚类。山区山脉由于从山脉底部到峰顶的海拔变化,可以产生各种气候类型。在同一座山上的不同海拔上可以发现不同的气候类型。H类气候指高地或山地,尽管大多数山区都存在气候变化。山基的气候将因山脉是在热带还是高纬度而不同。High mountains near the equator may have a type A climate at their base and a type E climate at their summit with various type C and type D climates between them. Type H climates are found where elevation differences are profound enough to provide different climate zones. Higher elevation relief can reach above the tree line and have permanent snow cover at the summit. The term relief is used in geography to indicate elevations of a land surface. Elevation zones with permanent ice or snow can resemble a type E polar climate.
::赤道附近的高山基地可能有A型气候,顶峰上可能有E型气候,有各种C型气候和D型气候。发现H型气候,高海拔差异很深,足以提供不同的气候区。高海拔的降水可达树线以上,在峰顶有永久的雪覆盖。在地理上,降水一词用于标明陆地表面的高地。永久冰雪高地区可以类似于E型极地气候。
The Andes Mountains are located in South America and are a type H climate.
::安第斯山脉位于南美洲,是H型气候。
El Nino
::厄尔尼诺is the warm phase of the El Niño Southern Oscillation (ENSO). This happens when a band of warm ocean water develops in the central and east-central equatorial Pacific, including off the Pacific coast of South America. El Niño refers to the cycle of warm and cold temperatures, as measured by (SST) of the tropical central and eastern Pacific Ocean. The characteristics of El Niño are high air pressure in the western Pacific and low air pressure in the eastern Pacific.
::厄尔尼诺现象是指厄尔尼诺/南方涛动的温暖阶段,在中赤道太平洋中部和中赤道东太平洋,包括南美洲太平洋海岸外,出现一系列温暖的海水,厄尔尼诺现象是指热带中太平洋和东太平洋(SST)所测量的温暖和寒冷的气候循环,厄尔尼诺现象的特点是西太平洋的空气压力高,东太平洋的空气压力低。The cool phase of ENSO, called La Niña, happens when SST in the eastern Pacific is below average. Moreover, air pressure is high in the eastern Pacific and low in the western Pacific. The ENSO cycle of El Niño and La Niña causes global changes in both temperatures and rainfall.
::厄尔尼诺和拉尼娜的周期性厄尔尼诺和拉尼娜造成了全球气温和降雨的变化。Economies that engage in farming and fishing in the regions impacted by El Niño are especially at risk. However, no matter where you are in the world, El Niño has the potential to affect you, from fires, drought, and flooding, to crop failures, insect explosions, plague and higher prices on goods and services.
::在受厄尔尼诺影响地区从事农业和渔业的经济体尤其面临风险,然而,无论你身处何地,厄尔尼诺现象都有可能影响你,从火灾、干旱和洪水到作物歉收、昆虫爆炸、瘟疫和货物和服务价格上涨。Deforestation
::毁林The planet's growing population has increased demands on natural resources, including forest products. Humans have been using trees for firewood, building homes, and making tools for millennia. Trees are a renewable resource, but deforestation occurs when they are removed faster than they can be replenished. Most people in rural areas in developing countries rely on firewood to cook their food. Many of these areas are experiencing a fast decline in the number of trees available. People living in mainly type B climates may not have access to a lot of trees to start with; therefore, when trees are cut down for firewood or for building materials, deforestation occurs.
::地球不断增长的人口增加了对自然资源(包括森林产品)的需求。人类一直在利用树木作为木柴、建造房屋和制造千年的工具。树木是一种可再生资源,但砍伐森林的速度超过补充的速度,就会发生毁林。发展中国家农村地区的大多数人依靠木柴做饭。许多这些地区的树木数量正在迅速下降。主要生活在B型气候条件下的人可能无法从许多树木开始生长;因此,当树木被砍下来作为木柴或建筑材料时,就会产生毁林现象。In the tropical areas, it is common for hardwood trees to be cut down for lumber to gain income or to clear the land for other agricultural purposes, such as cattle ranching. Countries that lack opportunities and advantages look to exploit their natural resources—in this case, trees—for either subsistence agriculture or economic gain. Deforestation has increased across the globe with the rapid rise in the worldwide population.
::在热带地区,通常会砍掉硬木树,以便木材赚取收入,或为其他农业目的,如牧牛等清除土地;缺乏机会和优势的国家希望开发其自然资源,例如树木,以维持生计或取得经济收益;世界各地毁林现象增加,世界人口迅速增加。During the Industrial Revolution, European countries chopped down their forests at a rapid rate. Much of the British Isles was forested at one point, but today few forests remain on the British Isles, and they are typically protected. Colonialism brought the Europeans to the Americas. The United States, in its early development, pushed west from the original thirteen colonies, and many old growth forests were cut down in the process. As railroad tracks were laid down and pioneer development pushed west into the Great Plains, where there were few trees, the great cutover occurred in the eastern and central forests.
::在工业革命期间,欧洲国家迅速砍伐森林。 大部分不列颠岛曾经一度被砍伐过森林,但今天,不列颠岛的森林仍然很少,而且通常受到保护。 殖民主义将欧洲人带到美洲。 美国在早期发展过程中被从最初的十三个殖民地推向西方,许多旧的生长森林在此过程中被砍伐。 随着铁路的铺设和开拓性发展被推向大平原,那里几乎没有树木,东部和中部森林被大砍。Cutover is a term indicating the systematic deforestation of the eastern and central forests. Michigan and Wisconsin saw their trees removed in systematic deforestation. Some areas were allowed to grow back, but many other areas were turned into farmland. Few old-growth forests remain in the United States. Today there are conflicts over how the timber industry is handling the forests in places such as the Pacific Northwest region of the United States.
::密歇根州和威斯康星州看到他们的树木被系统砍伐,有些地区被允许重新种植,但其他许多地区被转化为农田,美国保留了很少的旧林。 今天,在木材工业如何在美国西北太平洋等地处理森林问题上出现了冲突。Countries that are better off economically no longer have to cut down their own trees and can afford to substitute other resources or import lumber from other places. Developing regions of the world in Latin America, Africa, and parts of Asia, are experiencing serious problems with deforestation. Deforestation is widespread; for example, citizens of Haiti have cut down about 99 percent of the country's forests and most of the wood has been used as fuel to cook food. People in Afghanistan have cut down about 70 percent of their forests. Nigeria has lost about 80 percent of its old-growth forests since 1990. Ethiopia has lost up to 98 percent of its forested acreage, and the Philippines has lost about 80 percent of its forests.
::经济上较富裕的国家不再需要砍掉自己的树木,也不必再用其它资源来替代其他资源或从其他地方进口木材。 拉丁美洲、非洲和亚洲部分地区的世界发展中地区正在经历严重的毁林问题。 森林砍伐现象十分普遍;例如,海地公民砍伐了大约99%的本国森林,大部分木材被用作烧饭的燃料。 阿富汗人民砍伐了大约70%的森林。 自1990年以来,尼日利亚损失了大约80%的旧森林。 埃塞俄比亚损失了高达98%的森林面积,菲律宾则损失了大约80%的森林面积。
Illegal slash and burn practice in the region west of Manantenina, Madagascar.
::马达加斯加马南特尼纳以西地区非法砍伐和焚烧。
Brazil's Amazon basin has undergone many projects that have driven deforestation. For example, about half the state of Rondônia in western Brazil has been deforested since 1990. The countries of Central America have lost about half their original forests, and deforestation continues on a systematic basis. Tropical regions of Southeast Asia and Africa are being exploited for their timber at unsustainable rates. This will have consequences that the next generation will have to resolve.
::巴西的亚马逊流域经历了许多导致毁林的项目。 比如,自1990年以来,巴西西部约一半的龙多尼亚州被砍伐森林。 中美洲国家已经失去了一半的原始森林,森林砍伐仍在继续系统地进行。 东南亚和非洲热带地区正在以不可持续的速度被开采木材。 这将产生下一代必须解决的后果。India, with more than one billion people, has a high demand for firewood and building materials. Their forests are declining faster than they can be replanted. China has been attempting to address its deforestation problems by implementing a massive replanting program and conservation measures. Other countries are starting to adopt similar measures.
::印度人口超过10亿,对木柴和建筑材料的需求很高,森林的减少速度快于重新种植的速度。 中国一直试图通过实施大规模重新种植方案和保护措施来解决毁林问题。 其他国家也开始采取类似措施。Tropical rain forests only make up about five percent of the earth's surface, but contain up to 50 percent of the earth's biodiversity. These forests are cut down for a variety of reasons. Norman Meyers, a British environmentalist, estimated that about five percent of deforestation in tropical regions is caused by the push for cattle production. Nineteen percent of these forests are cut down by the timber industry, 22 percent are cut down for the expansion of plantation agriculture, and 54 percent are removed due to slash-and-burn farming. Most tropical rain forests are located in the Amazon basin of South America, in central Africa, and in Southeast Asia. All these areas are looking for advantages and opportunities to boost their economies. Unfortunately, they often target their tropical rain forests as a way to make money.
::热带雨林只占地球表面的5%左右,但占地球生物多样性的50%。这些雨林被砍伐的原因多种多样。诺曼·迈耶斯(Norman Meyers)是英国环保主义者,他估计热带地区大约5%的森林砍伐是由牲畜生产的推动造成的。其中19%的森林被木材工业砍伐,22%的森林被砍掉以扩大种植园农业,54%的雨林由于刀耕火种而消失。大部分热带雨林位于南美洲亚马逊流域、中部非洲和东南亚。所有这些地区都寻求优势和机会来刺激其经济。 不幸的是,它们往往以热带雨林为目标赚钱。What Are the Problems with Deforestation?
::砍伐森林的问题是什么?Deforestation causes more than the loss of trees for fuel, building materials, paper products, or manufacturing. Another related issue with deforestation is soil erosion. Without the trees to hold the soil during heavy rains, soils are eroded away. In tropical areas, soils are often degraded and lack nutrients. Most of the nutrients in the tropical areas rest in decaying material at the base of the trees that supply energy back into the ecosystem. Once the trees are removed, there is little replenishing of this energy supply. Soil erosion in tropical areas makes it hard for forests to grow back once they have been removed.
::在热带地区,土壤往往退化,缺乏养分; 热带地区的大部分养分都是在向生态系统提供能源的树木底部的腐烂物质; 树木被清除后,这种能源供应就很少得到补充; 热带地区的土壤侵蚀使森林在被清除后很难再生长。Landslides can be a more severe component of the soil erosion problem. After heavy rainfall, entire hillsides saturated with water can slide downward, causing serious structural damage to buildings, homes, and agricultural plots. Tree roots help hold hillsides together and therefore help prevent landslides.
::滑坡可能是土壤侵蚀问题中更为严重的部分。 暴雨过后,整个充满水的山坡会滑坡,对建筑物、房屋和农田造成严重的结构破坏。 树根有助于将山坡凝聚在一起,从而帮助防止山崩。Forests play an important role in the water cycle. Trees pull up moisture with their roots from the soil and transpire it through their leaves back into the atmosphere. Moisture in the atmosphere collects into clouds, condenses, and falls back to Earth. Not only do trees store water, but organic matter at the base of the trees also stores water and makes it available to the larger ecosystem, which may slow down water runoff. Forest canopies disperse water during rainfall and create another layer of moisture in their leaves and branches, which either is used by other organisms or evaporates back into the atmosphere.
::森林在水循环中起着重要作用:树木从土壤中根植而来,从树叶中渗入大气;大气中的水分聚集到云层、凝结和回落到地球;树木中不仅储存水,树木底部的有机物也储存水,使更大的生态系统能够获得水,这可能会减缓水的径流;森林树冠在降雨期间散布水,并在树叶和树枝中产生另一层水分,供其他生物使用或蒸发回大气层。Deforestation eliminates the role that forests play in the water cycle. Forest ecosystems provide for a diverse community of organisms. Tropical rain forests are one of the most vibrant ecosystems on the planet. Their abundant biodiversity can provide insight into solutions for the future. Plants and organisms in these habitats may hold the key to medical or biological breakthroughs. Sadly, wildlife and vegetation will be lost as deforestation eliminates their habitat and speeds up the extinction of endangered species.
::森林砍伐消除了森林在水循环中的作用,森林生态系统提供了多样化的生物群落,热带雨林是地球上最具活力的生态系统之一,其丰富的生物多样性可以为未来找到解决办法。 这些生境中的植物和生物可能掌握着医学或生物突破的关键。 可悲的是,由于森林砍伐消除了它们的栖息地并加速濒危物种的灭绝,野生动物和植被将丧失。Trees and plants remove carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and store it in the plant structure through the process of photosynthesis. Carbon dioxide is a major greenhouse gas that is a part of the climate change process. Carbon dioxide and other similar gases reduce the amount of heat that escapes from the earth's atmosphere, resulting in increased temperatures on the planet. As more carbon dioxide is emitted into the atmosphere, climate change occurs. The removal of trees through deforestation results in less carbon dioxide being removed from the atmosphere, which contributes to climate change.
::树木和植物从大气中去除二氧化碳,并通过光合作用过程将其储存在植物结构中; 二氧化碳是气候变化进程的一部分,是主要的温室气体; 二氧化碳和其他类似气体减少了从地球大气中释放出的热量,导致地球温度升高; 随着更多的二氧化碳排放到大气中,气候变化随之发生; 通过砍伐森林清除树木,导致大气中二氧化碳减少,从而导致气候变化。Climate Change
::气候变化气候变化Climate change has been a constant activity in Earth's evolution. The increase in temperature in our environment is the activity that has gained the most attention in recent years. Questions have been raised about the rate and extent of climate change around the world. Understanding the dynamics of the temperature increase can help us to understand how it is related to human activity.
::气候变化是地球演化中不断发生的一项活动。我们环境中的温度升高是近年来引起最多关注的活动。人们提出了关于世界各地气候变化的速度和程度的问题。了解温度升高的动态可以帮助我们了解它与人类活动的关系。The atmosphere is the gaseous layer that surrounds the earth and marks the transition between its surface and space. The atmosphere consists of a mixture of gases, composed of nitrogen (77 percent), oxygen (21 percent), and minor elements (1 percent) including argon, helium, carbon dioxide, and water vapor. The small amount of carbon dioxide is a critical component in the control of the earth's temperature. The atmosphere extends over three hundred miles above the earth's surface, and the lower level makes up the earth's climatic system. This lowest level is called the troposphere and is responsible for the conditions that allow life to exist on the planet's surface.
::大气是环绕地球的气体层,标志着地球表面与空间之间的转变。大气由各种气体组成,由氮(77%)、氧(21%)和微小元素(1%)组成,这些元素包括、、二氧化碳和水蒸气。少量二氧化碳是控制地球温度的关键组成部分。大气在地球表面上方三百多英里,低层构成地球的气候系统。这一最低水平被称为对流层,是地球表面生存的条件。Since the 1960s, scientists have been concerned about the concentrations of carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, and chlorofluorocarbons in the atmosphere. These so-called greenhouse gases can trap heat energy emitted from the earth's surface and may increase global temperatures and cause climate change. Since the Industrial Revolution, human activity—the burning of fossil fuels and large-scale deforestation—has increased the amount of heat-trapping greenhouse gases in the atmosphere. Carbon dioxide and similar gases act like the glass panels of a greenhouse that allow shortwave radiation from the sun to enter but do not allow the long-wave radiation of heat to escape into space.
::自1960年代以来,科学家们一直关注大气中二氧化碳、甲烷、一氧化二氮和氯氟化碳的浓度问题,这些所谓的温室气体可能困住地球表面排放的热能,并可能增加全球温度和造成气候变化,自工业革命以来,人类活动——燃烧化石燃料和大规模砍伐森林——增加了大气中热源温室气体的含量,二氧化碳和类似气体的行为就像一个温室的玻璃板,它允许太阳短波辐射进入,但不允许长波热辐射进入太空。An increase in carbon dioxide and greenhouse gases in the atmosphere will normally cause an increase in the temperature of the planet's climate, which in turn may cause changes in weather conditions on Earth. Temperature changes may affect precipitation patterns and alter weather patterns. This may affect agricultural outputs and influence energy needs that can create increasing economic instability. Changes in climate also impact environmental conditions for organisms adapted to specific habitat ranges. When climates change, an organism's habitable zone may also change, which in turn can impact entire ecosystems.
::大气中二氧化碳和温室气体的增加通常会导致地球气候温度的上升,这反过来又可能导致地球气候条件的变化。温度变化可能会影响降水模式和天气模式的改变。这可能会影响农业产出,影响能源需求,从而造成日益严重的经济不稳定。气候变化还会影响适合特定生境范围的生物的环境条件。当气候变化发生时,有机体的可居住区也会发生变化,而这反过来又会影响整个生态系统。Burning of fossil fuels can also contribute to climate change. Fossil fuels such as coal, oil, and natural gas are created when dead plant and animal life are under pressure, decay for long periods, and retain their carbon component. Burning fossil fuels releases the carbon back into the atmosphere. The increasing need for energy by human activity will continue to contribute to climate change unless alternatives can be found. The increase in temperatures may result in the melting of the ice caps, which in turn may raise sea levels, impacting human activity around the world.
::化石燃料的燃烧也可能助长气候变化。 煤炭、石油和天然气等化石燃料是在植物和动物死亡生命受到压力、长期腐烂并保留碳成分时产生的。 燃烧化石燃料将碳释放回大气层。 人类活动对能源的需求增加将继续助长气候变化,除非找到替代物。 温度的上升可能导致冰盖融化,这反过来会提高海平面,影响世界各地的人类活动。Tectonic Plates
::构造平板The movement of tectonic plates is another aspect of the earth's dynamics that affects human activity. The earth's crust, which is between 10 and 125 miles thick, is a series of plates that cover a molten iron core at the center of the planet. The plates that cover the earth's surface slowly shift and move. Plates can slide away from each other or they can collide, and they can slide parallel to each other in opposite directions. When two plates collide and one plate slides under an adjacent plate, the process is called subduction. Movement or shift where two plates meet can cause earthquakes and is usually associated with volcanic activity.
::构造板块的移动是地球动态中影响人类活动的另一个方面。 地壳厚度在10到125英里之间, 是覆盖行星中心熔化铁岩芯的一系列板块。 覆盖地球表面的板块会慢慢地变化和移动。 板块可以相互滑动或相撞, 并且可以向相反的方向平行滑动。 当两个板块相撞, 一个板块在相邻的板块下滑动时, 这一过程被称为潜移。 两个板块相交的移动或移动会引发地震, 通常与火山活动相关。Mountain chains, such as the Himalayas, are a result of two plates colliding. The collision pushes up the earth into a mountain chain, either by direct pressure or by volcanic activity. Plates can move up to an inch a year in active regions. Driven by the earth's internal heat, these plates have created the planet's mountain landscapes. Earthquakes and volcanic action along plate boundaries (called faults) continue to affect human activity and can cause serious economic damage to a community. Plate boundaries can be found near many natural edges of continents.
::山链,如喜马拉雅山,是两个板块碰撞的结果。碰撞通过直接压力或火山活动,将地球推向一个山链。在活跃地区,板块可移动到一年一英寸。在地球内部热力的驱动下,这些板块创造了地球的山地景观。板块边界(所谓的断层)上的地震和火山行动继续影响人类活动,并可能对一个社区造成严重的经济损害。在大陆的许多自然边缘可以找到板块边界。The continuous action of the plates causes serious earthquakes and volcanic eruptions that can devastate the daily activities of people. Earthquakes near the sea often trigger tsunamis, waves that bring destruction to coastal regions in their path. The earthquake off the east coast of Japan in 2011 created a tsunami that brought additional destruction to nuclear energy facilities, exposing parts of Japan and the rest of the world to radiation.
::板块的连续行动造成了严重的地震和火山爆发,这些地震和火山爆发可能破坏人们的日常活动。 海附近的地震常常引发海啸和波浪,给沿途的沿海地区带来破坏。 2011年日本东海岸的地震造成了一场海啸,给核能设施带来更多的破坏,使日本和世界其他地区暴露在辐射之下。Key Takeaways
::密钥外出-
Human activity on the planet correlates with the type of climate and terrain that presents itself to humans in the form of natural resources or habitability.
::地球上的人类活动与以自然资源或可居住性的形式呈现给人类的气候和地形类型相关。 -
Six basic climate zones (A, B, C, D, E, and H) describe the earth's climate types.
::六个基本气候区(A、B、C、D、E和H)描述地球的气候类型。 -
Temperature and precipitation are the two main variables that create a climate zone and its corresponding environmental attributes.
::温度和降水是造成气候区及其相应的环境属性的两个主要变量。 -
The earth's crust consists of a number of separate plates that move, creating earthquakes and volcanic activity.
::地壳由一些不同的板块组成 形成地震和火山活动 -
Most mountain ranges on Earth are a product of tectonic plate activity.
::地球上大多数山脉都是地质板块活动的结果。 -
Removing trees faster than they can grow back is called deforestation.
::清除树木的速度快于它们能长回来的速度,这叫森林砍伐。 -
Humans are cutting down the forests in many areas at an unsustainable rate.
::人类正在以不可持续的速度砍伐许多地区的森林。 -
Deforestation can result in soil erosion, changes in weather patterns, and the loss of habitats.
::毁林可导致土壤侵蚀、天气模式变化和生境丧失。 -
Trees are being cut down for firewood, building materials, or profit.
::正在砍伐树木,以获取木柴、建筑材料或利润。 -
Mountains or high elevation relief can restrict the passage of rain clouds and cause the clouds to lose their precipitation as the air mass increases in elevation creating a rain shadow effect.
::山地或高海拔降水会限制雨云的通过,并随着高海拔空气量的增加造成雨影效应,使云层丧失降水量。 -
The other side of the mountain or range does not receive any precipitation and is reduced to a more arid or drier region, creating desert conditions.
::山区或山脉另一侧没有任何降水,降水范围缩小到干旱或干燥地区,造成荒漠条件。 -
Climate change is a phenomenon whereby gases such as carbon dioxide and methane increase in the troposphere and restrict long-wave radiation from escaping the planet, which can result in warmer temperatures on Earth.
::气候变化是一种现象,即对流层的二氧化碳和甲烷等气体增加,并限制长波辐射离开地球,这可能导致地球温度升高。 -
Trees remove carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, which may reduce climate change.
::树木将二氧化碳从大气中去除,这可能会减少气候变化。
Vocabulary Terms
::词汇术语术语Chapter 1.2 Human Activity and the Environment
::第1.2章 人类活动与环境b iome
::生物生物A l arge ecosystem characterized by common climate, common vegetation , and common animal life
::以共同气候、共同植被和共同动物生物为特点的大生态系统El Ni n o
::厄尔尼诺A warm ocean current the flows off the west coast of South America every few years. An El Nino event changes weather patterns around the world and may cause extreme weather in some regions
::南美洲西海岸的潮流每隔几年就有一个温暖的海洋潮流。 厄尔尼诺事件改变了全世界的天气模式,并可能在一些地区引起极端天气。crop rotation
::作物轮作The practice of rotating use of different fields from crop to crop each year to avoid exhausting the soil
::每年轮流使用不同田地的做法,从作物到作物,以避免耗尽土壤deforestation
::毁林Removing of or clearing away the trees from a forest often done to clear land for farming and ranching
::清除或清除树木,使树木脱离森林,森林往往是为了清除耕地和牧场f ault
::过错A line on Earth’s surface the results from a deep crack in the crust
::地壳深度裂缝在地表的一条线上产生的结果fossil water
::水、化石水、化石水Water that has been contained in some undisturbed space, in an aquifer, for millennia
::数千年来某些未扰动的空间、含水层和含水层中含有的水global warming
::全球变暖全球升温G radual warming of Earth's surface caused by the accumulation of green house gasses in the atmosphere
::温室气体在大气中积累引起的地球表面逐渐变暖groundwater
::地下水地下水Water lying deep under the ground that supplies wells and springs
::深埋在地下的水 提供水井和泉水irrigation
::灌溉灌溉The supply of water to land or crops to help growth, typically by means of channels. This allows dry areas to support crops
::通常通过渠道向土地或作物供水,以帮助增长,使干旱地区能够支持作物种植La Nina
::丽妮娜A cooling of the water in the equatorial Pacific that occurs at irregular intervals and is associated with widespread changes in weather patterns complementary to those of El Niño, but less extensive and damaging in their effects
::赤道太平洋水的冷却,这种冷却不定期发生,与与补充厄尔尼诺现象的气候模式的广泛变化相关联,但其影响不那么广泛,损害较小o ver - farming
::过度耕作P lanting the same crops every year causing the degradation of nutrients in the soil and yie lding fewer crops
::每年种植同样的作物,造成土壤养分退化,作物产量减少p late-tectonics
::板板构造A large piece of Earths crusts that floats on the liquid mantle
::一块大块的地球结壳 浮在液体地壳上permafrost
::永久冻冻土A layer of soil beneath the earth's surface that is always frozen
::地表下一层土壤 一直被冰冻着r ain shadow effect
::雨的阴影效果T he land on the leeward side of hills or mountains that gets little rain from the descending dry air
::山丘或山丘的向外倾斜的地带,因降下干燥的空气而降下很少的雨水,renewable energy
::可再生能源可再生能源Energy from a source that is not depleted when used, such as wind or solar power
::来自风能或太阳能等使用时未耗竭的能源源的能源smog
::烟雾烟雾A haze in the air caused by air pollution, especially the exhaust from cars and other vehicles
::空气污染造成空气中的烟雾,特别是汽车和其他车辆的废气s ubduction
::下下调The sideways and downward movement of the edge of a plate of the earth's crust into the mantle beneath another plate
::地壳板块边缘向另一板块下方地壳的侧面和向下移动t sunami
::海啸海啸海啸海啸A huge, de structive wave caused by the displacement of a large volume of a body of water, typically by an earthquake or volcanic eruption
::通常由地震或火山爆发引起的大量水体流离失所造成的巨大破坏性浪潮watershed
::分水岭An area of land that is drained by a river and its tributaries
::一片被河流及其支流排干的土地,zones of l atitude
::纬度区域The three main latitude regions of the Earth's surface comprise geographical zones , divided by the major circles of latitude. The differences between them relate to climate. Low latitudes, tropical; middle latitudes, temperate; high latitudes, polar
::地球表面的三个主要纬度区域由地理区域组成,除以主要的纬度圈,它们之间的差异与气候有关,低纬度、热带、中纬度、温带、高纬度、极地。Applying Knowledge
::应用知识Interactive Notebook Activities
::互动笔记活动-
Explain
how climate and human habitation are related and distinguish the main climate types.
::解释气候和人类居住如何相互关联,并区分主要气候类型。 -
Describe
the dynamics of tectonic plates and their relationship to earthquakes and volcanic activity.
::描述构造板块的动态及其与地震和火山活动的关系。 -
Outline
the main causes of deforestation. Explain the relationship between deforestation and climate change.
::概述毁林的主要原因,解释毁林与气候变化之间的关系。 -
Describe
where the rain shadow effect takes place. Explain why it occurs in those places and how it may influence human activity.
::描述雨影效应的发生地点,解释为什么在这些地方发生,以及它如何影响人类活动。 -
Summarize
how climate change occurs and the relationship between greenhouse gases such as carbon dioxide and the planet's temperature regulation.
::概述气候变化是如何发生的,以及二氧化碳等温室气体与地球温度调节之间的关系。
Discussion and Study Questions
::讨论和研究问题-
What climate type do you live in?
::你住哪一种气候? -
What are the main attributes of each climate type?
::每个气候类型的主要属性是什么? -
What two main climatic qualities do humans gravitate toward?
::人类向哪两种主要气候特性倾斜? -
What is the difference between weather and climate?
::天气和气候有什么区别? -
How can the main causes of deforestation be alleviated or diminished?
::如何减轻或减少毁林的主要原因? -
What are tectonic plates, and how do they help shape the planet?
::构造板块是什么? 它们如何帮助塑造这个星球? -
How does tectonic plate movement affect human activities?
::构造板块移动如何影响人类活动? -
Who is responsible for addressing the problems caused by climate change? What can you do about it?
::谁负责解决气候变化造成的问题?你能做些什么呢? -
What causes a rain shadow effect? Name some examples of this phenomenon.
::是什么导致了雨影效应? 请举一些例子说明这一现象。 -
Which regions of the planet are being affected the most by deforestation?
::森林砍伐对地球上哪些区域的影响最大?
Tech Activities
::技术合作活动-
Research and determine when the last three earthquakes nearest where you live occurred. What damage did they cause?
::研究并确定您住址最近的最后三次地震何时发生。这些地震造成了什么损害? -
Chart the annual average temperature for where you live for the past one hundred years to illustrate any trend in climate change.
::图表显示您过去一百年居住地点的年平均温度,以说明气候变化的任何趋势。 -
Using the Internet, determine the nearest location to where you live that is impacted by a rain shadow effect.
::使用 Internet 确定最接近您居住地点的雨影效应。 雨影效应会影响您居住地点 。
Mapping Exercise
::绘图绘制作业: In this activity, students will observe worldwide patterns of seismic activity (earthquakes) and volcanic activity (volcanoes). Students will analyze the relationships of those patterns to tectonic plate boundaries and major physical features of the earth’s surface. Then students will identify cities at risk.
:::在这一活动中,学生将观察全世界地震活动(地震)和火山活动(火山)的模式。 学生将分析这些模式与构造板块边界和地球表面主要物理特征的关系。 然后学生将确定面临风险的城市。Videos for Geography Enrichment
::地理丰富视频Helpful Websites for the Study of Geography
::地理研究有用网站is an encyclopedia funded by the Canadian government covering all branches of knowledge. Their scholarly collection includes interactive materials.
::该百科全书由加拿大政府资助,涵盖所有知识分支,其学术收藏包括交互式材料。provides information on the people, history, government, economy, energy, geography, communications, transportation, military, and transnational issues for the world's entities.
::向世界各实体提供关于人民、历史、政府、经济、能源、地理、通信、运输、军事和跨国问题的资料。is a US government website where you can find federal legislation, past and present, as well as information about the US legal system.
::是一个美国政府的网站,您可以在此找到过去和现在的联邦立法以及关于美国法律制度的信息。is a government agency website that provides current news, resources, topics of interest, information about drugs, careers in the DEA, and a tip hotline.
::是一个政府机构网站,提供最新消息、资源、感兴趣的话题、毒品信息、在缉毒局的职业以及一条小费热线。is the largest library in the world and provides manuscripts, files, information, pictures, and videos.
::图书馆是世界上最大的图书馆,提供手稿、文件、信息、图片和录像。is a US government agency website that allows users to search for and retrieve satellite images of Earth.
::这是一个美国政府机构的网站,用户可以搜索和检索地球的卫星图像。is a US government website that provides historical documents, photos, records, publications, and educator resources.
::这是一个美国政府网站,提供历史文件、照片、记录、出版物和教育资源。is a US government agency website that provides weather-related information and ocean research.
::是一个提供气象信息和海洋研究的美国政府机构网站。is a website by the United States Geological Survey and other federal, state, and local agencies that deliver topographic information for the United States.
::这是美国地质调查局和其他联邦、州和地方机构为美国提供地形信息的网站。is a massive central data source and a handy way to graphically compare nations.
::是一个庞大的中央数据源,是用图形比较国家的一种方便方式。is a website that measures most locations in the world for air pollution in real time.
::是一个实时测量世界上大多数空气污染地点的网站。is a unique statistical database, which allows you to research and compare a multitude of different data on US states.
::这是一个独特的统计数据库, 使你能够研究和比较关于美国各州的多种不同数据。is an international organization founded in 1945 and made up of 193 member states. The UN maintains international peace and security, protects human rights, delivers humanitarian aid, promotes sustainable development, and upholds international law.
::联合国是一个国际组织,成立于1945年,由193个成员国组成。 联合国维护国际和平与安全,保护人权,提供人道主义援助,促进可持续发展,维护国际法。is a US government agency that provides a population clock, data, surveys, statistics, a library with information and infographics, news about the economy, and much more.
::这是一个美国政府机构,它提供人口钟、数据、调查、统计、一个拥有信息和信息资料的图书馆、关于经济的新闻,以及更多。is a US government agency website that provides scientific information about the natural hazards that threaten lives, the natural resources we rely on, the health of our ecosystems and environment, and the impacts of climate and land-use change.
::这是一个美国政府机构的网站,提供科学信息,说明威胁生命的自然危害、我们赖以生存的自然资源、生态系统和环境的健康以及气候和土地使用变化的影响。is a US government website that provides the latest presidential news, information about the budget, policy, defense, and many more topics.
::提供最新总统新闻、预算、政策、国防等资讯, 以及更多议题。is under the United Nations and provides leadership on matters critical to health, shapes the research agenda on health, and monitors the health situation and assessing health trends around the world. Their website provides information on the state of health around the world, outbreaks, current health news, and more.
::网站提供世界各地卫生状况、疫情爆发、最新卫生新闻等信息。is an intergovernmental organization that regulates international trade. The website provides information on the history of the multilateral trading system, featured videos, news and events, trade topics, and more.
::该网站提供关于多边贸易体系历史的信息、视频、新闻和事件、贸易专题等等。 -
Explain how climate and human habitation are related and distinguish between the main climate types.