4.1 科前和科后中美洲(1天)
Section outline
-
Chapter Challenges
::章次 挑战-
Define the differences between the rimland and the mainland.
::界定林地与大陆之间的差异。 -
Summarize the impact of European colonialism on Middle America.
::概述欧洲殖民主义对中东的影响。 -
Explain the differences between the Mayan and Aztec Empires and identify which the Spanish defeated.
::解释Mayan和Aztec帝国之间的差异,并找出西班牙击败谁。 -
Describe how the Spanish influenced urban development in Middle America.
::描述西班牙人如何影响中美城市发展。
Student Learning Objectives
::学生学习目标TEKS Regional Unit 04; Latin America: Chapter 4.1 Pre-Colonial and Post-Colonial Middle America
::TEKS 区域股04;拉丁美洲:第4.1章WG.1B Trace the spatial diffusion of phenomena such as the Columbian Exchange or the diffusion of American popular culture and describe the effects on regions of contact
::WG.1B 追踪哥伦比亚交流会等现象的空间扩散或美国流行文化的传播,并描述对接触区域的影响WG/2A Describe the human and physical characteristics of the same regions at different periods of time to evaluate relationships between past events and current conditions
::WG/2A 描述同一区域在不同时期的人类和物理特征,以评估过去事件与当前状况之间的关系WG.4C Explain the influence of climate on the distribution of biomes in different regions .
::WG.4C 解释气候对不同区域生物群落分布的影响。WG.6A Locate and describe human and physical features that influence the size and distribution of settlements
::WG.6A 确定并描述影响定居点规模和分布的人类和自然特征WG.6B Explain the processes that have caused changes in settlement patterns, including urbanization, transportation, access to and availability of resources, and economic activities
::WG.6B 解释导致住区模式变化的进程,包括城市化、运输、获得和获得资源以及经济活动WG.7B Examine the benefits and challenges of globalization, including connectivity, the standard of living, pandemics, and loss of local culture
::WG.7B 审查全球化的惠益和挑战,包括连通性、生活水平、流行病和当地文化的丧失WG.8A Compare ways that humans depend on, adapt to, and modify the physical environment, including the influences of culture and technology
::WG.8A 比较人类依赖、适应和改变自然环境的方式,包括文化和技术的影响Pre-Colonial and Post-Colonial Middle America
::科前和科后中美Physical Geography
::物理地理Middle America has various types of physical landscapes, including volcanic islands and mountain ranges. Tectonic action at the edge of the has brought about volcanic activity. This activity has created many of the islands of the region as volcanoes rose above the ocean surface. The island of is one such example. The volcano on this island has continued to erupt in recent years, showering the island with dust and ash and making habitation difficult.
::中美有各种各样的自然景观,包括火山岛和山脉,在火山边缘的构造活动导致了火山活动,随着火山升至海洋表面上空,这一活动创造了该区域许多岛屿,其中一个例子是这个岛屿,近年来,这个岛屿的火山继续喷发,灰尘和灰尘冲洗了该岛,使居住变得困难。Many of the other low-lying islands, such as the , were formed by coral reefs rising above the ocean surface. Tectonic plate activity not only has created volcanic islands but also is a constant source of earthquakes that continue to be a problem for the Caribbean community.
::其他许多低地岛屿,如海底等,都是由海面上方的珊瑚礁形成的,构造板块活动不仅创造了火山岛,而且也是地震的源源不断,对加勒比共同体来说,地震依然是一个问题。The republics of Central America extend from to and form the final connection between North America and South America. The , the narrowest point between the Caribbean Sea and the Pacific Ocean, serves as a land bridge between the continents. The backbone of Central America is mountainous, with many volcanoes located within its ranges. Much of the Caribbean and all of Central America are located south of the and are dominated by tropical type A climates.
::中美洲各共和国从北美洲和南美洲之间的最后联系延伸到并形成它们之间的最后联系,这是加勒比海和太平洋之间的最狭窄点,是各大陆之间的陆地桥梁,中美洲的骨干是山区,许多火山分布在其范围内,大部分加勒比和整个中美洲位于热带A型气候以南,以热带A型气候为主。The mountainous areas have varied climates, with cooler climates located at higher elevations. Mexico has extensive mountainous areas with two main ranges in the north and highlands in the south. There are no landlocked countries in this realm. The coastal areas are rich in natural resources and have been exploited for fishing and tourism.
::山区气候各异,高海拔地区气候较冷,墨西哥山区广泛,北部有两个主要山脉,南部有高原,没有内陆国,沿海地区自然资源丰富,被开发用于捕鱼和旅游。Rimland and Mainland
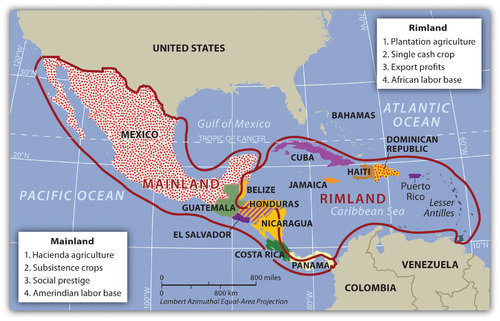
::里姆兰和内大陆Using a regional approach to the geography of a realm helps us compare and contrast a place’s features and characteristics. Location and the physical differences explain the division of Middle America into two geographic areas according to occupational activities and colonial dynamics. The rimland, which includes the Caribbean islands and the Caribbean coastal areas of Central America, and the mainland, which includes the interior of Mexico and Central America, are the two geographical areas.
::利用地区地理方法来比较和对比一个地方的特征和特征。 地点和物理差异解释根据职业活动和殖民动态将中美地区划分为两个地理区域的原因。 包括加勒比岛屿和中美洲加勒比沿海地区以及包括墨西哥和中美洲内陆在内的大陆是这两个地理区域。Colonialism thrived in the rimland because it consists mainly of islands and coastal areas that were accessible to European ships. Ships could easily sail into a cove or a bay to make port and claim the island for their home country. After an island or coastal area was claimed, there was a transformation of the area through plantation agriculture. On a plantation, local individuals were subjugated as servants or slaves.
::殖民主义在林区蓬勃发展,因为它主要由欧洲船只可以进入的岛屿和沿海地区组成,船只可以轻而易举地驶入海湾或海湾,以港口或海湾为母国拥有岛屿,在声称拥有一个岛屿或沿海地区后,通过种植园农业对该地区进行了改造,在种植园中,当地人被征服为仆人或奴隶。The land was planted with a single crop—usually sugarcane, tobacco, cotton, or fruit—grown for export profits. Most of these crops were not native to the Americas but were brought in during colonial times. European diseases killed vast numbers of local Amerindian laborers, so slaves were brought from Africa to do the work. Plantation agriculture in the rimland was successful because of the import of technology, slave labor, and raw materials, as well as the export of the harvest to Europe for profit.
::这块土地种植了单一的作物——通常是甘蔗、烟草、棉花或水果,以赚取出口利润,其中多数作物不是美洲本土作物,而是殖民时期引进的,欧洲的疾病夺去了大批当地美洲印第安人劳工的生命,因此从非洲带来奴隶从事这项工作,林地的种植农业由于技术、奴隶劳动和原材料的进口以及收获出口到欧洲以牟利而取得成功。Plantation agriculture changed the rimland. The local groups were almost eliminated because of disease and colonial subjugation, and by the 1800s most of the population was of African descent. Native food crops gave way to cash crops for export. Marginal lands were plowed up and placed into the plantation system. The labor was usually seasonal because there was a high demand for labor at peak planting and harvest times. Plantations were generally owned by wealthy Europeans who may or may not have lived there.
::种植园农业改变了林地。 当地群体由于疾病和殖民征服而几乎被消灭,到1800年代,大部分人口是非洲裔。 土著粮食作物让位于经济作物供出口。 边远土地被耕种并置于种植园体系中。 劳动力通常是季节性的,因为种植高峰期和收获季节对劳动力的需求很大。 种植园通常为可能或可能没有在那里生活的富有的欧洲人所拥有。The mainland, consisting of Mexico and the interior of Central America, diverged from the rimland in both colonial dynamics and agricultural production. The interior lacked easy access to the sea that the rimland enjoyed. As a result, the hacienda style of land use developed. This Spanish innovation was aimed at land acquisition for social prestige and a comfortable lifestyle. Export profits were not the driving force behind the operation, though they may have existed. The Amerindians, who were poorly paid, if at all, were allowed to live on the haciendas, working their own plots for subsistence. African slaves were not prominent on the mainland.
::大陆由墨西哥和中美洲内地组成,在殖民动态和农业生产两方面都与大陆不同,内地缺乏通向滨海的便捷通道,因此开发了土地利用的庄稼风格,西班牙的这一创新旨在为了社会威望和舒适生活方式而获取土地,出口利润虽然可能存在,但并不是行动背后的驱动力,美洲印第安人即使收入很低,也获准在庄园生活,为维持生计而耕种自己的土地,非洲奴隶在大陆并不突出。On the mainland, European colonialists would enter an area and stake claims to large portions of the land, often as much as millions of acres. Haciendas would eventually become the main landholding structure on the mainland of Mexico and many other regions of Middle America. In the hacienda system, the Amerindian people lost ownership of the land to the European colonial masters. Land ownership or the control of land has been a common point of conflict throughout the Americas where land transferred from local Amerindian ownership to colonial European ownership.
::在大陆上,欧洲殖民主义者将进入对大片土地(往往高达数百万英亩)的面积和股权主张,Haciendas最终将成为墨西哥大陆和中美洲其他许多区域的主要土地拥有结构,在庄园制度下,美洲印第安人将土地的所有权丧失给欧洲殖民主人,土地所有权或土地控制权是整个美洲冲突的一个常见点,在那里,土地从当地的美洲印第安人所有权转移到欧洲殖民所有权。-
The rimland was more accessible to European ships, and the mainland was more isolated from European activity.
::欧洲船舶更容易进入滨海,大陆与欧洲活动更加隔绝。
The plantation and hacienda eras are in the past. The abolition of slavery in the late 1800s as well as the cultural revolutions that occurred on the mainland challenged the plantation and hacienda systems and brought about land reform. Plantations were transformed into either multiple private plots or large corporate farms.
::种植园和庄园时代已经过去,1800年代末废除奴隶制以及大陆发生的文化革命对种植园和庄园制度提出了挑战,并带来了土地改革,种植园转变为多个私人地块或大型企业农场。The hacienda system was broken up, and most of the hacienda land was given back to the people, often in the form of an ejidos system. In an ejidos system, the community owns the land, but individuals can profit from it by sharing its resources. This system has created its own set of problems, and many of the communally owned lands are being transferred to private owners.
::庄园制度被打破,大部分庄园土地被归还给人民,通常是以ejidos制度的形式,在一个ejidos制度中,社区拥有土地,但个人可以通过分享资源从中获利,这个制度造成了自己的一系列问题,许多公有土地正被转让给私人所有者。The agricultural systems changed Middle America by altering both the systems of land use and the ethnicity of the population. The Caribbean Basin changed in ethnicity from being entirely Amerindian to being dominated by European colonizers, to having an African majority population. The mainland experienced the mixing of European culture with the Amerindian culture to form various types of mestizo groups with Hispanic, Latino, or Chicano identities.
::农业体系通过改变土地使用制度和人口种族来改变中美州。 加勒比海盆地从完全由美洲印第安人统治转变为由欧洲殖民者统治、拥有非洲多数人口。 大陆经历了欧洲文化与美洲印第安人文化的混合,形成了有西班牙裔、拉美裔或Chicano身份的多种混血类群体。The European Invasion
::欧洲入侵Though the southern region of the Americas has commonly been referred to as “Latin America,” this is a misnomer because Latin has never been the lingua franca of any of the countries in the Americas. The name of a given country does not always reflect its lingua franca . For example, people in Mexico do not speak a language called “Mexican”; they speak Spanish. Brazilians do not speak “Brazilian”; they speak Portuguese. Latin America is the geopolitical designation for Mexico, Central America, South America, and the Caribbean Islands.
::虽然美洲南部地区通常被称为“拉丁美洲”,但这是一个错误的代号,因为拉丁美洲从来不是美洲任何国家的通用语,某一国家的名称并不总是反映其通用语,例如,墨西哥人不会说一种称为“墨西哥语”的语言;他们讲西班牙语;巴西人不会说“巴西语”;他们讲葡萄牙语;拉丁美洲是墨西哥、中美洲、南美洲和加勒比群岛的地缘政治名称。European colonialism impacted Middle America in more ways than language and religion. Before Christopher Columbus arrived from Europe, the Americas did not have animals such as horses, donkeys, sheep, chickens, and cattle. This meant there were no large animals for plowing fields or carrying heavy burdens. The concept of the wheel, which was so common in Europe, was not found in the Americas.
::欧洲殖民主义对中美的影响比语言和宗教还多。 在克里斯托弗·哥伦布从欧洲来到美洲之前,美洲没有马、驴、羊、鸡和牛等动物。 这意味着没有大型动物耕种田地或承受沉重负担。 轮子的概念在欧洲很常见,在美洲却找不到。Food crops were also different. The potato was an American food crop, as was corn, squash, beans, chili peppers, and tobacco. Europeans brought other food crops—either from Europe itself or from its colonies—such as coffee, wheat, barley, rice, citrus fruits, and sugarcane. Not only food crops were exchanged, but so were building methods, agricultural practices, and diseases.
::土豆是美国的粮食作物,玉米、南瓜、大豆、辣椒、辣椒和烟草也是如此。 欧洲人从欧洲本身或其殖民地带来了其他粮食作物,如咖啡、小麦、大麦、大米、柑橘水果和甘蔗。 不仅粮食作物被交换,建筑方法、农业做法和疾病也是如此。The Spanish invasion of Middle America following Columbus had devastating consequences for the Amerindian populations. It has been estimated that 15 to 20 million people lived in Middle America when the Europeans arrived. However, after a century of European colonialism, only about 2.5 million remained. Few of the Amerindians—such as the Arawak and the Carib on the islands of the Caribbean and the Maya and Aztec on the mainland—had immunity to European diseases such as measles, mumps, smallpox, and influenza.
::西班牙在哥伦布之后对中美洲的入侵给美洲印第安人人口造成了灾难性后果,据估计,当欧洲人抵达时,有1 500万至2 000万人生活在中美洲,然而,经过一个世纪的欧洲殖民主义之后,只剩下大约250万美洲印第安人,例如加勒比岛屿上的阿拉瓦克人和加勒比人以及大陆上的玛雅人和阿兹特克人,很少有人对麻疹、流行性腮腺炎、天花和流感等欧洲疾病享有豁免权。Tlatelolco Marketplace as depicted at Field Museum of Natural History, Chicago. The largest Aztec market was located in Tenochtitlan's neighboring town, Tlatelolco.
::Aztec最大的市场位于Tenochtitlan的邻近城镇特拉特洛尔科。
Through warfare, disease, and enslavement, the local populations were decimated. Only a small number of people still claim Amerindian heritage in the Caribbean Basin, and some argue that these few are not indigenous to the Caribbean, but are descendants of slaves brought from South America by European colonialists.
::通过战争、疾病和奴役,当地人口被毁灭。 只有一小部分人仍然在加勒比海盆地拥有美洲印第安人遗产,有些人认为这些人不是加勒比土著人,而是欧洲殖民主义者从南美带来的奴隶的后裔。Columbus landed with his three ships on the island of Hispaniola in 1492. Hispaniola is now divided into the countries of and the . With the advantage of metal armor, weapons, and other advanced technology, the Spanish invaders quickly dominated the local people. Since Europe was going through a period of competition, warfare, and technological advancements, the same patterns carried forward to the New World.
::1492年,哥伦布与三艘船一起在伊斯帕尼奥拉岛登陆。 伊斯帕尼奥拉号现在被划分为国和国。 在金属盔甲、武器和其他先进技术的优势下,西班牙入侵者迅速控制了当地人民。 自从欧洲经历竞争、战争和技术进步的时期以来,同样的模式也传到了新世界。Amerindians were most often made servants of the Europeans, and resistance resulted in conflict, war, and often death. The Spanish conquistadors were looking for profits and sought gold, silver, and precious gems. This quest for gain pitted the European invaders against the local groups. The Roman Catholic religion was brought over from Europe and at times was imposed on the indigenous people with a “repent or perish” method of conversion.
::美洲印第安人最常成为欧洲人的仆人,抵抗导致冲突、战争和死亡。 西班牙征服者正在寻找利润和金、银和宝石。 这种追求收益的追求让欧洲入侵者与当地群体对立。 罗马天主教从欧洲传来,有时以“悔改或灭亡”的皈依方式强加给土著人民。Many of the Caribbean islands have declared independence, but some remain crown colonies of their European colonizers with varying degrees of autonomy. Mexico achieved independence from Spain by 1821. Central American republics also gained independence in the 1820s. In 1823, the United States implemented the , designed to deter the former European colonial powers from engaging in continued political activity in the Americas.
::1821年,墨西哥从西班牙获得独立,中美洲各共和国在1820年代也获得独立。 1823年,美国实施了旨在阻止前欧洲殖民国家继续参与美洲政治活动的计划。Intervention in the United States has continued in various places in spite of the reduction in European activity in the region. In 1898, the United States engaged Spain in the , in which Spain lost its colonies of , Puerto Rico, and others to the United States. Puerto Rico continues to be under US jurisdiction and is not an independent country.
::尽管欧洲在该区域的活动有所减少,美国在各地继续干预美国。 1898年,美国与西班牙接触,西班牙在西班牙失去其殖民地波多黎各和其他殖民地美国。 波多黎各继续受美国管辖,不是独立国家。The Maya and the Aztec
::玛雅人和阿兹特人The region of Mexico has been inhabited for thousands of years. One of the earliest cultures to develop into a civilization with large cities was the . The Olmec flourished in the south-central regions of Mexico from 1200 B.C.E. to about 400 B.C.E. Anthropologists call this region of Mexico and northern Central America, Mesoamerica. It is considered to be the region’s cultural hearth because it was home to early human civilizations.
::墨西哥地区已居住了数千年,最早发展成大城市文明的文化之一是:奥梅克人从公元前1200年到公元前400年左右在墨西哥中南部地区繁荣发展,人类学家称墨西哥和中美洲北部为中美洲,被认为是该地区文化的耳鸣之一,因为它是早期人类文明的所在地。The established a vast civilization after the Olmec. Mayan stone structures still remain, which attract thousands of tourists every year. The classical era of the Mayan civilization lasted from 300 to 900 C.E. and was centered in the region of Mexico and Central America. Guatemala was once a large part of this vast empire, and Mayan ruins are found as far south as . During the classical era, the Maya built some of the most magnificent cities and stone pyramids in the Western Hemisphere.
::玛雅的古典文明时代从公元前300年延续到900年,以墨西哥和中美洲地区为中心。 危地马拉曾经是这个庞大帝国的一大部分,玛雅的废墟远在南部。 在古典时代,玛雅人建造了一些西半球最辉煌的城市和石头金字塔。The city-states of the empire functioned through a sophisticated religious hierarchy. The Mayan civilization made advancements in mathematics, astronomy, engineering, and architecture. They developed an accurate calendar based on the seasons and the solar system. The extent of their knowledge is still being discovered. The descendants of the Maya people exist today, but their empire does not.
::罗马帝国的城市国家通过复杂的宗教等级体系运作。玛雅文明在数学、天文学、工程学和建筑学领域取得了进步。他们根据季节和太阳系制定了准确的日历。他们的知识范围仍在探索之中。玛雅人的后代今天存在,但他们的帝国却不存在。The classical Mayan era lasted from 300 to 900 C.E. Many magnificent cities were built with stone and remain today as major tourist attractions.
::古典玛雅时代从公元前300年持续到900年。 许多宏伟的城市都是用石头建造的,今天仍然是主要旅游景点。
Model of the Aztec City of Tenochtitlan at the National Museum of Anthropology in Mexico City.
::墨西哥城国家人类学博物馆的阿兹特克城市特诺赫蒂特兰模型。
The Toltec, who briefly controlled central Mexico, came to power after the classical Mayan era. They also took control of portions of the old Mayan Empire from the north. The Aztec federation replaced the Toltec and Maya as the dominant civilization in southern Mexico. The Aztec, who expanded outward from their base in central Mexico, built the largest and greatest city in the Americans of the time known as Tenochtitlán. This city is estimated to have had a population of 100,000 people. Tenochtitlán was located at the present site of Mexico City, and it was from there that the Aztec expanded into the south and east to create an empire.
::短暂控制墨西哥中部的托尔特克人是在古老玛雅时代后上台的,他们也从北方控制了旧玛雅帝国的一部分,阿兹特克人联邦取代托尔特克人和玛雅人作为墨西哥南部的主导文明,阿兹特克人从墨西哥中部的基地向外扩张,在当时称为特诺赫蒂特兰的美国人中建造了最大和最大的城市,估计这座城市的人口为10万人,特诺赫蒂特兰人位于墨西哥城的现址,正是从那里,阿兹特克人向南部和东部扩张,以建立一个帝国。The Aztec federation was a regional power that subjugated other groups and required taxes and tributes from them. Though they borrowed ideas and innovations from earlier groups such as the Maya, they made great strides in agriculture and urban development. The rose to dominance in the 14th century and were still in power when the Europeans arrived.
::阿兹特克联邦是一个征服其他集团并需要从它们那里获得税收和奖励的区域强国。 尽管它们从像玛雅人这样的早期集团中借用了思想和创新,但它们在农业和城市发展方面取得了长足的进步。 14世纪的崛起占据了主导地位,当欧洲人到达时仍然掌权。Spanish Conquest of 1519–21
::1519-21年的西班牙征服After the voyages of Columbus, the Spanish conquistadors came to the New World in search of gold, riches, and profits. They also brought their Roman Catholic religion with them. These Catholic adherents also converted the Amerindians, usually by force. One such conquistador was Hernán Cortés as well as his 508 soldiers, who landed on the shores of the Yucatán in 1519. They made their way west toward the Aztec Empire.
::哥伦布航行后,西班牙征服者来到新世界,寻找黄金、财富和利润,他们也带来了罗马天主教宗教。这些天主教信徒还改变美洲印第安人,通常是用武力。 其中一位征服者是埃尔南·科尔特斯和他的508名士兵,他们于1519年在尤卡坦海岸登陆,向西向阿兹特克帝国前进。The wealth and power of the Aztecs attracted conquistadors such as Cortés, whose goal was to conquer. Even with metal armor, steel swords, sixteen horses, and a few cannons, Cortés and his men did not challenge the Aztecs directly. The Aztec leader Montezuma II originally thought Cortés and his men were legendary “White Gods” returning to recover the empire. Cortés defeated the Aztecs by uniting the people that the Aztecs had subjugated and joining with them to fight the Aztecs. The Spanish conquest of the Aztec federation was complete by 1521.
::阿兹特克人的财富和力量吸引了诸如科特斯这样的征服者,科特斯的目的是征服他们。 即使用金属盔、钢剑、十六匹马和几支大炮,科特斯及其手下也没有直接挑战阿兹特克人。 阿兹特克领导人蒙特祖马二世最初认为科特斯及其手下是传奇的“白神”,他们已经回归帝国。科特斯通过团结阿兹特克人征服并加入他们以对抗阿兹特克人而打败阿兹特克人。 西班牙对阿兹特克联邦的征服在1521年前完成。The Spanish invasion of Middle America had devastating consequences for the Amerindian populations. It is estimated that there were between 15 and 25 million indigenous people in Middle America before the Europeans arrived. After a century of European colonialism, there were only about 2.5 million left. Cortés defeated the Amerindians by killing the learned classes of the religious clergy, priestly orders, and those in authority. The local peasants and workers survived.
::西班牙入侵中美洲对美洲印第安人造成了毁灭性后果,据估计,在欧洲人到达之前,在中美洲有1,500万至2,500万土著人。 经过一个世纪的欧洲殖民主义之后,只剩下大约250万。 科泰斯通过杀害宗教神职人员、神职人员和掌权人员,击败了美洲印第安人。 当地农民和工人幸存下来。The Spanish destroyed the knowledge base of the Maya and Aztec people. Their knowledge of astronomy, their advanced calendar, and their engineering technology were lost. Only through anthropology, archaeology, and the relearning of the culture can we fully understand the expanse of these early empires. The local descendants of the Maya and the Aztec still live in the region, and there are dozens of other indigenous groups in Mexico with their own languages, histories, and cultures.
::西班牙人摧毁了玛雅人和阿兹泰克人的知识基础,他们对天文学的知识、先进的日历和工程技术都丧失了。 只有通过人类学、考古学和对文化的再学习,我们才能充分理解这些早期帝国的广阔范围。 玛雅人和阿兹泰克人的当地后裔仍然生活在这个地区,墨西哥还有数十个拥有自己的语言、历史和文化的其他土著群体。The Spanish Colonial City
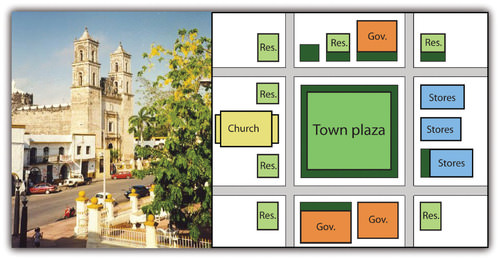
::西班牙殖民城As the Spanish established urban centers in the New World, they structured each town after the Spanish pattern, with a plaza in the center. Around the plaza on one side was the Roman Catholic church. On the other sides of the plaza were government offices and stores. Residential homes filled in around them. This pattern can still be seen in almost all the cities built by the Spanish in Middle and South America. The Catholic Church was a cultural force responsible for shaping and molding the Amerindian societies.
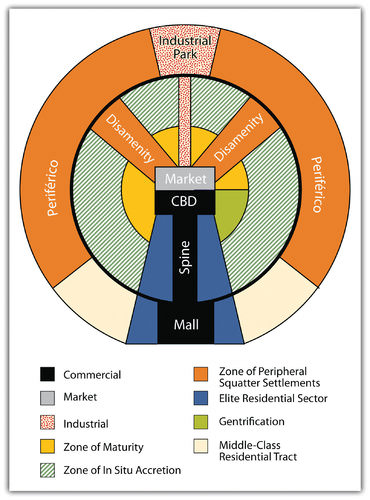
::由于西班牙在新世界建立了城市中心,他们按照西班牙的模式构建了每个城镇,中心有一个广场。广场的一面是罗马天主教教堂。广场的另一面是政府办公室和商店。住宅在广场周围填满。在中美洲和南美洲几乎所有由西班牙人建造的城市中,都可以看到这种模式。天主教会是影响和塑造美洲印第安人社会的文化力量。In Spain, the cultural norm was to develop urban centers wherever administration or military support was needed. Spanish colonizers followed a similar pattern in laying out the new urban centers in their colonies. Extending out from the city center (where the town plaza, government buildings, and church were located) was a commercial district that was the backbone of this model. Expanding out on each side of the spine was a wealthy residential district for the upper social classes, complete with office complexes, shopping districts, and upper-scale markets.
::西班牙的文化规范是,在需要行政或军事支持的地方发展城市中心。 西班牙殖民者在建立其殖民地的新城市中心时也遵循类似模式。 从市中心(城市广场、政府建筑和教堂所在地)延伸为商业区,成为这一模式的支柱。 脊椎两侧的扩张是高社会阶层的富裕住宅区,拥有办公综合体、购物区和上层市场。The Spanish colonial urban pattern had a plaza in the center of the city with government buildings around the square and a Catholic church on one side.
::西班牙殖民城市模式在市中心有一个广场,广场周围有政府建筑,一边有天主教教堂。
Surrounding the central business district (CBD) and the spine of most cities in Middle and South America are concentric zones of residential districts for the lower, working, and middle classes and the poor. The first zone, the zone of maturity, has well-established middle-class residential neighborhoods with city services. The second concentric zone, the zone of transition, has working-class districts mixed with areas with makeshift housing and without city services.
::环绕中央商业区(CBD)和中南美洲大多数城市的脊椎是低层、工作区、中产阶级和穷人居住区的同心地带,第一个地区,即成熟区,拥有有城市服务的中产阶级居住区,第二个同心地带,即过渡区,有工薪阶层地区,有临时住房,没有城市服务。The outer zone, the zone of periphery, is where the expansion of the city occurs, with makeshift housing and squatter settlements. This zone has little or no city services and functions as an informal economy. This outer zone often branches into the city, with slums known as favelas or barrios that provide the working poor access to the city without benefits. Impoverished immigrants that arrive in the city from the rural areas often end up in the city’s outer periphery to eke out a living in some of the worst living conditions in the world.
::外围地带是城市扩张的外围地带,有临时住房和棚户区,城市服务和非正规经济几乎或根本没有城市服务或功能。 这一外围地带往往向城市蔓延,贫民窟被称为贫民窟或小区,无益地为工作穷人提供进入城市的通道。 从农村地区来到城市的贫困移民往往最终来到城市外围地带,在世界上一些最差的生活条件中生活。Cities in this Spanish model grow by having the outer ring progress to the point where eventually solid construction takes hold and city services are extended to accommodate the residents. When this ring reaches maturity, a new ring of squatter settlements emerges to form a new outer ring of the city. This development pattern is repeated, and the city continues to expand outward.
::这一西班牙模式中的城市通过外环发展到最终固态的建筑建成和城市服务扩大以容纳居民。 当这一环成熟时,一个新的棚户区环将形成新的城市外环。 这种发展模式将再次出现,城市将继续向外扩张。Nowadays, the urban centers of Middle and South America are expanding at rapid rates. It is difficult to provide public services to the outer limits of many of the cities. The barrios or favelas become isolated communities, often complete with crime bosses and gang activities that replace municipal security.
::如今,中南美洲和南美洲的城市中心正在迅速扩张,许多城市的外缘很难提供公共服务。 区或棚户区成为孤立的社区,通常由犯罪头目和帮派活动取代城市安全。Spanish-American City Structure According to the Ford-Griffin Model.
::根据福特-格里芬模式,西班牙-美洲城市结构。Key Takeaways
::密钥外出-
Haciendas were located chiefly in the mainland.
::Haciondas主要位于大陆。 -
Plantations were located mainly in the rimland.
::种植园主要位于林地。 -
Both the hacienda and the plantation structures of agriculture altered the ethnic makeup of their respective regions.
::庄园和种植园的农业结构改变了各自地区的民族构成。 -
The rimland had an African labor base.
::林地有非洲劳动力基础。 -
The mainland had an indigenous labor base.
::大陆有一个土著劳工基地。 -
In their quest for wealth, Spanish conquistadors destroyed the Aztec Empire and colonized the Middle American mainland.
::西班牙的征服者为了寻求财富,摧毁了阿兹特克帝国,并殖民了中美大陆。 -
Much historical knowledge was lost with the demise of the learned class of the Aztec Empire.
::阿兹泰克帝国的学识阶级消亡,失去了许多历史知识。 -
Europeans introduced many new food crops and domesticated animals to the Americas and in turn, brought newly discovered agricultural products from America back to Europe.
::欧洲人向美洲引进了许多新的粮食作物和养殖动物,反过来又从美国将新发现的农产品运回欧洲。 -
The Spanish introduced the same style of urban planning to the Americas that was common in Spain.
::西班牙在美洲引入了与西班牙相同的城市规划模式。 -
Many cities in Middle and South America were patterned after Spanish models.
::中南美洲的许多城市都以西班牙模式为模式。
Vocabulary Terms
::词汇术语术语Chapter 4.1 Pre-Colonial and Post-Colonial Middle America
::第4.1章 科前和科后中美colonialism
::殖民主义和殖民主义The policy of maintaining colonies as a source of raw materials and new markets. Practiced during old and new imperialism
::维持殖民地作为原材料和新市场来源的政策。colonization
::殖民化The actions or process of conquering another country or nation of people.
::征服另一个国家或民族的行动或进程。Columbian Exchange
::哥伦比亚交易所The exchange of animals, plants, and diseases between America, Africa, and Europe following the voyage of Christopher Columbus. Trade from the Old World (Europe) to the new World (North and South America) and back.
::在克里斯托弗·哥伦布(Christopher Colombon)的航行之后,美洲、非洲和欧洲之间动物、植物和疾病的交换。 从旧世界(欧洲)到新世界(北美和南美洲)和回转的贸易。Old Imperialism
::旧帝国主义A European policy of conquest that occurs in the 15th through 18th centuries in Africa, India, the Americas, and parts of Asia. The motives were the same for most areas, the establishment of lucrative trade routes. Various European countries dominated these trades routes and one time or another, and some countries, such as Great Britain and Spain, came to dominate entire countries.
::欧洲的征服政策在十五世纪至十八世纪在非洲、印度、美洲和亚洲部分地区发生。 动机对大部分地区来说是一样的,即建立有利可图的贸易路线。 不同的欧洲国家控制着这些贸易路线,有时甚至有,有些国家,如英国和西班牙,控制着整个国家。Latin America
::拉丁美洲 拉丁美洲The Geopolitical designation for Mexico, Central and South America and the Caribbean Islands.
::墨西哥、中美洲和南美洲及加勒比群岛的地缘政治名称。Latin American Revolutions
::拉丁美洲革命Political revolutions in various Latin American countries beginning in the late 18th century. These revolutions were aimed at overthrowing the European powers that controlled these nations. Many were successful, but few achieved the success of the American Revolution.
::拉丁美洲各国的政治革命始于18世纪末。 这些革命旨在推翻控制这些国家的欧洲列强。 许多革命都取得了成功,但很少有国家取得了美国革命的成功。Missionary
::传教士A person who spreads the teachings of a religion.
::传播宗教教义的人。Applying Knowledge
::应用知识Interactive Notebook A ctivities
::互动笔记活动-
Define the differences between the rimland and the mainland.
::界定林地与大陆之间的差异。 -
Summarize the impact of European colonialism on Middle America.
::概述欧洲殖民主义对中东的影响。 -
Explain the differences between the Mayan and Aztec Empires and identify which the Spanish defeated.
::解释Mayan和Aztec帝国之间的差异,并找出西班牙击败谁。 -
Describe how the Spanish influenced urban development in Middle America.
::描述西班牙人如何影响中美城市发展。
Discussion and Study Questions
::讨论和研究问题-
What are the three main regions of Middle America?
::中东三个主要区域是什么? -
What are the main distinctions between the mainland and the rimland?
::大陆和林地的主要区别是什么? -
What are the differences between a hacienda and a plantation?
::庄园和种植园有什么区别? -
What happened to the plantations and haciendas established during the colonial era?
::殖民时代建立的种植园和庄园呢? -
Why is Middle America often referred to as a part of “Latin America”?
::为什么中东经常被称为“拉丁美洲”的一部分? -
Who were the Aztec and the Maya, and when did their empires flourish? What happened to these empires?
::阿兹提克人和玛雅人是谁,他们的帝国何时兴旺?这些帝国怎么了? -
What are some ways that European colonialism affected this realm?
::欧洲殖民主义对这个领域有什么影响? -
What features were found at the center of town in the Spanish urban model?
::在西班牙城市模式的市中心发现了什么特征? -
How did the Spanish organize the structure of their colonial cities?
::西班牙是如何组织殖民城市结构的? -
How does the Ford-Griffin Model illustrate the development of the Spanish-American city?
::Ford-Griffin模型如何说明西班牙-美国城市的发展?
Real-World Geography Exercise
::现实世界地理演习Using , locate the places on the list below. Using scholarly resources on the Internet, research environmental problems happening in each one of the locations. Choose one for which you would like to help, and create a SWAY or PowerPoint presentation to persuade your audience to take action to help. Find facts, maps, photos, videos, and any other material necessary to create a powerful presentation.
::使用以下列表中的位置 。 使用互联网上的学术资源, 研究每个位置发生的环境问题 。 选择您想要帮助的, 并创建一个 SWAY 或 PowerPoint 演示, 以说服您的受众采取行动提供帮助 。 查找事实、 地图、 照片、 视频 以及创建强大演示所需的任何其他材料 。-
Atlantic Ocean
::大西洋大西洋 -
Bahamas
::巴哈马巴哈马巴哈马巴哈马 -
Baja Peninsula
::巴哈半岛 -
Caribbean Sea
::加勒比海加勒比海 -
Central America
::中美洲 中美洲 -
Greater Antilles
::大安的列斯群岛 -
Gulf of Mexico
::墨西哥湾墨西哥湾 -
Isthmus of Panama
::巴拿马地峡 -
Lesser Antilles
::更小的安的列斯群岛 -
Mainland
::大陆大陆 -
Pacific Ocean
::太平洋太平洋 -
Rimland
::里姆兰 -
Yucatán Peninsula
::尤卡坦半岛
Mapping Exercise
::绘图绘制作业Mapping Our World ESRI ARGIS Online Module 6 Lesson 1
::绘制我们世界的ESRI ARGIS在线模块6: In this activity, students will use maps of percentages of GDP in the three sectors to explore patterns of development around the world. Students will also examine two other economic indicators — energy use and GDP per capita — and compare the maps of GDP in economic sectors to the maps of GDP per capita and energy use. Students will evaluate whether or not the economic sector criteria are good indicators of a country’s economic status.
::学生们将研究另外两个经济指标——能源使用和人均国内生产总值,并将经济部门国内生产总值的地图与人均国内生产总值和能源使用图作比较,学生们将评估经济部门标准是否是一国经济状况的良好指标。Videos for Geography Enrichment
::地理丰富视频Helpful Websites for the Study of Geography
::地理研究有用网站is an encyclopedia funded by the Canadian government covering all branches of knowledge. Their scholarly collection includes interactive materials.
::该百科全书由加拿大政府资助,涵盖所有知识分支,其学术收藏包括交互式材料。provides information on the people, history, government, economy, energy, geography, communications, transportation, military, and transnational issues for the world's entities.
::向世界各实体提供关于人民、历史、政府、经济、能源、地理、通信、运输、军事和跨国问题的资料。is a US government website where you can find federal legislation, past and present, as well as information about the US legal system.
::是一个美国政府的网站,您可以在此找到过去和现在的联邦立法以及关于美国法律制度的信息。is a government agency website that provides current news, resources, topics of interest, information about drugs, careers in the DEA, and a tip hotline.
::是一个政府机构网站,提供最新消息、资源、感兴趣的话题、毒品信息、在缉毒局的职业以及一条小费热线。is the largest library in the world and provides manuscripts, files, information, pictures, and videos.
::图书馆是世界上最大的图书馆,提供手稿、文件、信息、图片和录像。is a US government agency website that allows users to search for and retrieve satellite images of Earth.
::这是一个美国政府机构的网站,用户可以搜索和检索地球的卫星图像。is a US government website that provides historical documents, photos, records, publications, and educator resources.
::这是一个美国政府网站,提供历史文件、照片、记录、出版物和教育资源。is a US government agency website that provides weather-related information and ocean research.
::是一个提供气象信息和海洋研究的美国政府机构网站。is a website by the United States Geological Survey and other federal, state, and local agencies that deliver topographic information for the United States.
::这是美国地质调查局和其他联邦、州和地方机构为美国提供地形信息的网站。is a massive central data source and a handy way to graphically compare nations.
::是一个庞大的中央数据源,是用图形比较国家的一种方便方式。is a website that measures most locations in the world for air pollution in real time.
::是一个实时测量世界上大多数空气污染地点的网站。is a unique statistical database, which allows you to research and compare a multitude of different data on US states.
::这是一个独特的统计数据库, 使你能够研究和比较关于美国各州的多种不同数据。is an international organization founded in 1945 and made up of 193 member states. The UN maintains international peace and security, protects human rights, delivers humanitarian aid, promotes sustainable development, and upholds international law.
::联合国是一个国际组织,成立于1945年,由193个成员国组成。 联合国维护国际和平与安全,保护人权,提供人道主义援助,促进可持续发展,维护国际法。is a US government agency that provides a population clock, data, surveys, statistics, a library with information and infographics, news about the economy, and much more.
::这是一个美国政府机构,它提供人口钟、数据、调查、统计、一个拥有信息和信息资料的图书馆、关于经济的新闻,以及更多。is a US government agency website that provides scientific information about the natural hazards that threaten lives, the natural resources we rely on, the health of our ecosystems and environment, and the impacts of climate and land-use change.
::这是一个美国政府机构的网站,提供科学信息,说明威胁生命的自然危害、我们赖以生存的自然资源、生态系统和环境的健康以及气候和土地使用变化的影响。is a US government website that provides the latest presidential news, information about the budget, policy, defense, and many more topics.
::提供最新总统新闻、预算、政策、国防等资讯, 以及更多议题。is under the United Nations and provides leadership on matters critical to health, shapes the research agenda on health, and monitors the health situation and assessing health trends around the world. Their website provides information on the state of health around the world, outbreaks, current health news, and more.
::网站提供世界各地卫生状况、疫情爆发、最新卫生新闻等信息。is an intergovernmental organization that regulates international trade. The website provides information on the history of the multilateral trading system, featured videos, news and events, trade topics, and more.
::该网站提供关于多边贸易体系历史的信息、视频、新闻和事件、贸易专题等等。The Toltec, who briefly controlled central Mexico, came to power after the classical Mayan era. They also took control of portions of the old Mayan Empire from the north. The Aztec federation replaced the Toltec and Maya as the dominant civilization in southern Mexico. The Aztec, who expanded outward from their base in central Mexico, built the largest and greatest city in the Americans of the time known as Tenochtitlán. This city is estimated to have had a population of 100,000 people. Tenochtitlán was located at the present site of Mexico City, and it was from there that the Aztec expanded into the south and east to create an empire. -
Define the differences between the rimland and the mainland.