9.1 南亚:介绍王国(2天)
章节大纲
-
Chapter Challenges
::章次 挑战-
Summarize the realm’s physical geography. Identify each country’s main features and physical attributes and locate the realm’s main river systems.
::概括了王国的地理地理特征,确定了每个国家的主要特征和自然特征,并确定了王国的主要河流系统。 -
Understand the dynamics of the monsoon and how it affects human activities.
::了解季风的动态以及它如何影响人类活动。 -
Outline the early civilizations of South Asia and learn how they gave rise to the early human development patterns that have shaped the realm.
::概述南亚早期文明,并了解这些文明如何产生塑造这个王国的早期人类发展模式。 -
Describe how European colonialism impacted the realm.
::描述欧洲殖民主义是如何影响整个王国的。 -
Learn about the basic demographic trends the realm is experiencing. Understand how rapid population growth is a primary concern for the countries of South Asia.
::了解该地区正在经历的基本人口趋势,了解人口快速增长是南亚国家的首要关切。
Student Learning Objectives
::学生学习目标TEKS Regional Unit 09 South Asia: Chapter 9.1 Introducing the Realm
::TEKS 区域股 09 南亚:第9.1章 介绍王国WG.1A Analyze the effects of physical and human geographic patterns and processes on the past and describe their impact on the present, including significant physical features and environmental conditions that influenced migration patterns and shaped the distribution of culture groups today.
::WG.1A 分析物理和人类地理模式和过程对过去的影响,并描述其对目前的影响,包括影响移徙模式并影响当今文化群体分布的重要物理特征和环境条件。WG.2A Describe the human and physical characteristics of the same regions at different periods of time to evaluate relationships between past events and current conditions.
::WG.2A 描述不同时期同一区域的人的和自然的特征,以评估过去事件与当前状况之间的关系。WG.1B Trace the spatial diffusion of phenomena such as the Colombian Exchange or the diffusion of American popular culture and describe the effects on regions of contact.
::WG.1B 追踪哥伦比亚交流或美国大众文化传播等现象的空间扩散,并描述对接触区域的影响。WG.3B Describe the physical processes that affect the environments of regions, including weather, tectonic forces, erosion, and soil-building processes.
::WG.3B 描述影响区域环境的物理过程,包括天气、构造力、侵蚀和土壤建设过程。WG.4A Explain how elevation, latitude, wind systems, ocean currents, position on a continent, and mountain barriers influence temperature, precipitation, and distribution of climate regions.
::WG.4A 解释高海拔、纬度、风力系统、洋流、大陆位置、山地屏障如何影响气候区域的温度、降水量和分布。WG.4B Explain the influence of climate on the distribution of biomes in different regions.
::WG.4B 解释气候对不同区域生物群落分布的影响。WG.5A Analyze how the character of a place is related to its political, economic, social, and cultural elements.
::WG.5A 分析一个地方的特性如何与其政治、经济、社会和文化因素相关。WG.7A Construct and Analyze population pyramids and use other data, graphics, and maps to describe the population characteristics of different societies and to predict future population trends.
::WG.7A 建立并分析人口金字塔,使用其他数据、图形和地图描述不同社会的人口特征,并预测未来人口趋势。WG.7C Describe trends in world population growth and distribution.
::WG.7C 描述世界人口增长和分布的趋势。WG.21A Analyze and evaluate the validity and utility of multiple sources of geographic information such as primary and secondary sources, aerial photographs, and maps.
::WG.21A 分析和评价多种地理资料来源,例如主要和次要资料来源、航空照片和地图的有效性和效用。WG.22A Design and draw appropriate graphics such as maps, diagrams, tables, and graphs to communicate geographic features, distributions, and relationships.
::WG.22A 设计和绘制适当的图形,如地图、图表、表格和图表,以交流地理特征、分布和关系。WG.22C Use geographic terminology correctly.
::WG.22C 正确使用地理术语。WG.22D Use standard grammar, spelling, sentence structure, and punctuation.
::WG.22D 使用标准语法、拼写、句子结构和标点。South Asia: Introducing the Realm
::南亚:介绍王国The Physical Geography
::自然地理The landmass of South Asia was formed by the Indian Plate colliding with the Eurasian Plate. This action started about 70 million years ago and gave rise to the highest mountain ranges in the world. Most of the South Asian landmass is formed from the land in the original Indian Plate. Pressure from tectonic action against the plates causes the Himalayas to rise in elevation by as much as one to five millimeters per year. Destructive earthquakes and tremors are frequent in this seismically active realm. The great size of the Himalayas has intensely influenced the beliefs and traditions of the people in the realm. Some of the mountains are considered sacred to certain religions that exist here.
::南亚的陆地由印地安板块与欧亚板块的碰撞形成。 这一行动始于大约7000万年前,并产生了世界上最高的山脉。 南亚大部分陆地是由原印度板块中的陆地形成。 对板块的构造行动的压力导致喜马拉雅山每年上升一至五毫米。 地震和震颤在这个地震活跃的领域频繁发生。 喜马拉雅山脉的面积之大,对本王国人民的信仰和传统产生了强烈的影响。 一些山区被认为是这里存在的某些宗教的圣地。
Mount Everest is the world’s highest peak at 29,035 feet.
::珠穆朗玛峰是世界上最高峰值29 035英尺。
The Himalayan Mountains dominate the physical landscape in the northern region of South Asia. Mount Everest is the tallest peak in the world at 29,035 feet. Three key rivers cross South Asia, all originating from the Himalayas. The Indus River, which has been a center of human civilization for thousands of years, starts in Tibet and flows through the center of Pakistan. The Ganges River flows through northern India, creating a core region of the country. The Brahmaputra River flows through Tibet and then enters India from the east, where it meets up with the Ganges in Bangladesh to flow into the Bay of Bengal.
::喜马拉雅山占南亚北部地区自然景观的主导地位。珠穆朗玛峰是世界上最高的高峰,为29 035英尺。南亚有三条主要河流,全部来自喜马拉雅山脉。印度河是人类文明的中心,数千年来一直以西藏为起点,在巴基斯坦中部流动。恒河穿过印度北部,形成了印度的一个核心地区。布拉马普拉河通过西藏,然后从东部进入印度,在那里与孟加拉国的恒河汇合,然后流入孟加拉湾。While the northern part of this region includes some of the highest elevations in the world, the Maldives in the south has some of the lowest elevations, some barely above sea level. The coastal regions in southern Bangladesh also have low elevations. When the seasonal reversal of winds called the monsoon arrives every year, there is heavy flooding and its effect on the infrastructure of the region is disastrous. The extensive Thar Desert in western India and parts of Pakistan, on the other hand, does not receive monsoon rains. In fact, much of southwest Pakistan—a region called Baluchistan—is dry, with desert conditions.
::虽然该区域北部包括世界上一些最高海拔,但南部的马尔代夫有一些最低海拔,有些海拔略高于海平面,孟加拉国南部的沿海区域也有低海拔,当季节性风的季节性逆转,称为季风的季风每年到来时,就会发生严重水灾,对该区域基础设施的影响是灾难性的,而印度西部和巴基斯坦部分地区的大面积的塔尔沙漠却得不到季风雨,事实上,巴基斯坦西南部的很多地区,一个称为俾路支的干旱地区,沙漠条件恶劣。This region is home to Jaipur, Jodhpur and many culturally important cities.
::该地区是斋浦尔、约德普尔和许多重要文化城市的所在地。
The mountains on the border between Pakistan and Afghanistan extend through Kashmir and then meet up with the high ranges of the Himalayas. The Himalayas create a natural barrier between India and China, with the kingdoms of Nepal and Bhutan acting as buffer states with Tibet. Farther south along the east and west coasts of India are shorter mountain ranges called ghats.
::巴基斯坦和阿富汗边界上的山脉穿过克什米尔,然后迎来喜马拉雅山脉的高射程。 喜马拉雅山脉在印度和中国之间建立了天然屏障,尼泊尔和不丹王国与西藏一起充当缓冲国。 印度东岸和西海岸以南较远的山脉被称为青蛙。The Western Ghats reach as high as 8,000 feet, but average around 3,000 feet. These ghats are home to an extensive range of biodiversity. The Eastern Ghats are not as high as the Western Ghats but have similar physical qualities. The ghats provide a habitat for a wide range of animals and are also home to large coffee and tea estates. The Deccan Plateau lies between the Eastern and Western Ghats. The Central Indian Plateau and the Chota-Nagpur Plateau are located in the central parts of India, north of the two Ghat ranges. The monsoon rains ensure that an average of about 52 inches of rain per year falls on the Chota-Nagpur Plateau, which has a tiger reserve and is also a refuge for Asian elephants.
::西加特海拔高达8 000英尺,但平均约为3 000英尺。这些海藻拥有广泛的生物多样性。东加特海拔不及西加特海拔高,但具有类似的体质。这些海拔为各种动物提供了栖息地,同时也拥有大量的咖啡和茶叶。Deccan海台位于东加特和西加特之间。中印度海台和Chota-Nagpur海台位于印度中部,位于两加特山脉以北。季风雨确保每年平均约52英寸的雨水落在Chota-Nagpur海台,该海台有老虎储备,也是亚洲大象的避难所。The Chota Nagpur Plateau is a plateau in eastern India.
::Chota Nagpur高原是印度东部的一个高原。The Monsoon
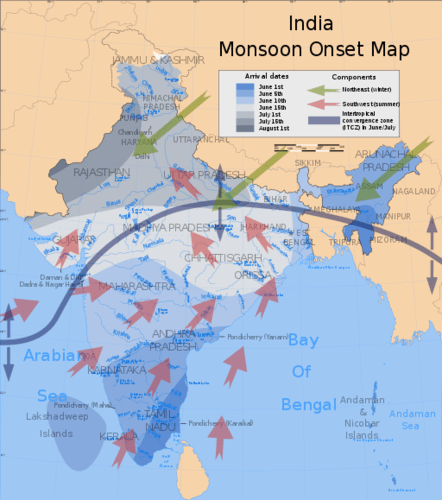
::季风A monsoon is a seasonal reversal of winds that is associated with heavy rains. The summer monsoon rains—usually falling between June and September—feed the rivers and streams of South Asia and provide the water needed for agricultural production. In the summer, the continent heats up, with the Thar Desert fueling the system. The rising hot air creates a vacuum that pulls in warm moist air from the Bay of Bengal and the Indian Ocean. This action shifts moisture-laden clouds over the land, where the water is precipitated out in the form of rain.
::季风是季风的季节性逆转,与暴雨有关,夏季季风雨——通常在6月至9月之间降下——淹没南亚河流和溪流,提供农业生产所需的水,夏季,非洲大陆升温,塔尔沙漠为系统提供燃料,不断上升的热空气造成真空,从孟加拉湾和印度洋的温暖潮湿空气中拉出,使潮湿的云层在陆地上移动,雨水以雨水的形式涌出。This map shows the average onset (monsoon arrival) dates and wind directions prevalent during India's southwest summer monsoon.
::该地图显示印度西南夏季季风中流行的平均开始日期(季节到来)和风向。
The monsoon rains bring moisture to South Asia right up to the Himalayas. As moisture-laden clouds rise in elevation in the mountains, the water vapor condenses in the form of rain or snow and feeds the streams and basins that flow into the major rivers, such as the Brahmaputra, Ganges, and Indus. The Western Ghats creates a similar system in the south along the west coast of India.
::季风雨为南亚带来水分,直达喜马拉雅山。 随着高山高地的潮湿云层上升,水蒸气以雨或雪的形式凝结,为流入主要河流的溪流和流域如布拉马普特拉河、恒河和印度河提供食物。 西加茨河在印度西海岸南部建立了类似的系统。Western Ghats, Maharashtra, India, in May during the dry season.
::印度马哈拉施特拉省西加茨(Western Ghats),
Western Ghats, Maharashtra, India, in August, during Monsoon season.
::8月,在季风季节,印度马哈拉施特拉省西加茨。
Parts of Bangladesh and eastern India receive as much as six feet of rain during the monsoon season, and some areas experience severe flooding. The worst-hit places are along the coast of the Bay of Bengal, such as in Bangladesh. There is less danger of flooding in western India and Pakistan because by the time the rain clouds have moved across India they have lost their moisture.
::孟加拉和印度东部部分地区在季风季节得到多达6英尺的雨水,一些地区遭受严重洪灾。 孟加拉湾沿岸地区,如孟加拉国,受灾最严重的地方是孟加拉湾沿岸。 印度和巴基斯坦西部的洪水风险较低,因为印度西部和巴基斯坦的雨水云已经飘至印度各地,它们已经失去了水分。Desert conditions are evident in the west, near the Pakistan border in the great Thar Desert. On average, fewer than ten inches of rainfall per year in this massive desert. On the northern rim of the region, the height of the Himalayas restricts the warm moist monsoon air from moving across the mountain range. The Himalayas act as a precipitation barrier and create a strong rain shadow effect for Tibet and Western China. The monsoon is responsible for much of the rainfall in South Asia.
::西部,靠近巴基斯坦边界的大塔尔沙漠的沙漠条件显而易见,在这一巨大的沙漠中,平均每年降雨不到10英寸。在该地区的北部边缘,喜马拉雅山的高度限制了温暖的潮湿季风空气跨山移动。喜马拉雅山起到降水屏障的作用,为西藏和中国西部造成了强烈的雨影效应。季风是南亚大部分降雨的原因。A "monsoon burst" over Mumbai.
::孟买上空的"季风暴"
By October, the system has run its course and the monsoon season is generally over. In the winter, the cold, dry air above the Asian continent blows to the south, and the winter monsoon is characterized by cool, dry winds coming from the north. South Asia experiences a dry season during the winter months. Small sections of South Asia, such as Sri Lanka and southeastern India, experience a rainy winter monsoon as well as a rainy summer monsoon. In their case, the winter monsoon winds that come down from the north have a chance to pick up moisture from the Bay of Bengal before depositing it on their shores.
::到10月,这个系统已经运行,季风季节一般结束。在冬天,亚洲大陆上空的寒冷干燥的空气吹向南方,冬季季风的特点是来自北方的寒冷干燥的风。南亚在冬季几个月里经历了一个旱季。南亚的小规模地区,如斯里兰卡和印度东南部,经历了雨季季风和雨季。在它们的情况中,来自北方的冬季季风在将潮湿从孟加拉湾沉入其海岸之前,有机会从孟加拉湾汲取水分。Early Civilizations
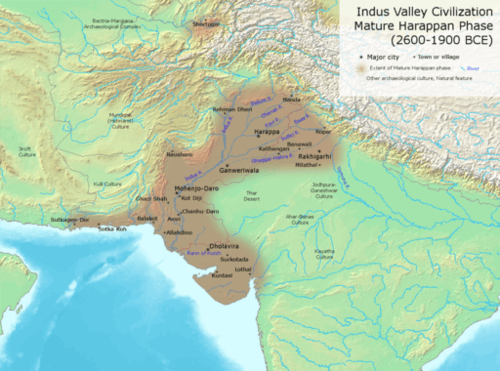
::早期文明The Indian subcontinent has a long history of human occupation and is an area where cities independently developed and civilization emerged. The earliest civilization on the subcontinent was the Indus Valley Civilization, in existence from about 3300 B.C.E. to 1500 B.C.E. This Bronze Age civilization started as a series of small villages that became linked in a wider regional network.
::印度次大陆有着悠久的人类占领历史,是城市独立发展和文明出现的地方,次大陆上最早的文明是印度河谷文明,从公元前3300年到公元前1500年。 青铜时代文明始于一系列小村庄,在更广泛的区域网络中联结起来。The Indus Valley Civilization, or Harappan Civilization, was a Bronze Age civilization (3300–1300 B.C.E.; mature period 2600–1900 B.C.E.) mainly in the northwestern regions of South Asia, extending from what today is northeast Afghanistan to Pakistan and northwest India.
::印度河谷文明化,即哈拉潘文明化,是一个青铜时代文明(公元前3300-1300年-1300年;成熟时期为公元前2600年-19000年),主要在南亚西北地区,从今天的阿富汗东北部延伸到巴基斯坦和印度西北部。
Urban centers developed into various religious and trade networks that spanned as far as Central Asia, Southwest Asia, and perhaps Egypt. The civilization is known for its planned structures. The cities and villages of the urban phases were planned with major streets going north/south and east/west. It had a system of drains that channeled waste water outside the city. The artifacts of pottery and metallurgy all had a similar style that was spread over a vast land area, a fact that aided in the recognition of the expanse of the culture.
::城市中心发展成各种宗教和贸易网络,分布到中亚、西南亚,或许还有埃及,文明以其规划结构著称,城市阶段的城市和村庄计划主要街道向北/南和东/西行进,城市有排水系统,向城市外输送废水,陶器和冶金的工艺品都有类似的风格,遍及广大土地,这一事实有助于承认文化的扩展。Excavated ruins of Mohenjo-Daro, Sindh province, Pakistan, showing the Great Bath in the foreground.
::巴基斯坦信德省Mohenjo-Daro挖掘的废墟,
Invasions by outsiders have the potential effect of bringing with them an influx of new ideas, concepts, and technology. Likewise, the Indus Valley Civilization had an impact on the region that it encompassed. Little is known of the historical events of earlier times. Some of the evidence we rely on today to discern historical events is gleaned from language, religion, and ethnicity.
::外来者的入侵有可能带来新的思想、概念和技术的流入。 同样,印度河谷文明也影响到它所覆盖的区域。对早期的历史事件知之甚少。 我们今天赖以辨别历史事件的一些证据来自语言、宗教和种族。Significant to South Asia is the presence of Indo-European languages. It is presumed that these languages were brought to the region by immigrants from the west, where these languages were dominant. Aryans from Persia and other cultures might have diffused languages such as Hindi to South Asia, which later may have led to Hindi, for example, becoming the lingua franca of the region.
::对南亚具有重要意义的是印欧语言的存在,据推测,这些语言是来自西方的移民带到该地区的,这些语言在西方占主导地位,来自波斯和其他文化的雅利安人可能传播了印地语到南亚等语言,而后者后来又可能导致印地语,例如,成为该地区的通语。The northern plains of South Asia, which extend through the Ganges River valley over to the Indus River valley of present-day Pakistan, were fertile grounds for a number of empires that controlled the region throughout history. After the decline of the Indus Valley Civilization, various phases of Iron Age traditions emerged. Most of this Iron Age culture is defined by the presence of iron metallurgy and distinctive characteristics of ceramics.
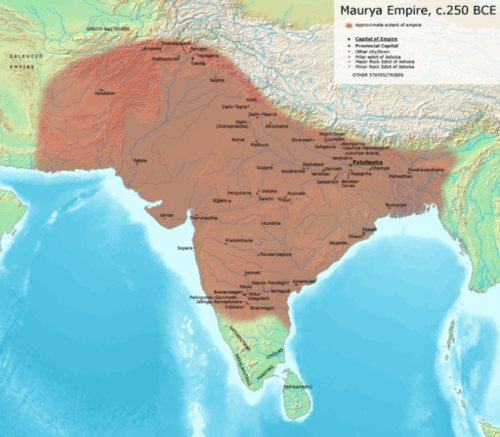
::南亚北部平原穿过恒河河谷延伸到巴基斯坦现今的印度河谷,是历史上控制该地区的一些帝国的肥沃土壤,在印河河谷文明化衰退之后,出现了不同阶段的铁时代传统,这种铁时代文化的大部分由铁冶金和陶瓷的独特特性所界定。The Mauryan Empire existed between 322 and 185 B.C.E. and was one of the most extensive and powerful political and military empires in ancient India. This empire was founded by Chandragupta Maurya in 322 B.C.E., who began to extend his regime westward, easily conquering areas that had been disrupted by the expansion of Alexander the Great’s armies. The Mauryan Empire was prosperous and greatly expanded the region’s trade, agriculture, and economic activities.
::莫里安帝国在公元前322年到公元前185年之间存在,是古印度最广泛和最强大的政治和军事帝国之一。 摩里雅帝国由公元前322年的钱德拉古普塔·毛里拉(Chandragupta Maurya)创立,他开始向西扩张政权,很容易征服因亚历山大大帝军队扩张而中断的地区。 莫里安帝国繁荣,大大扩展了该地区的贸易、农业和经济活动。The Maurya Empire was a geographically extensive Iron Age historical power founded by Chandragupta Maurya which dominated ancient India between 322 B.C.E. and 187 B.C.E.
::Maurya帝国是Chandragupta Maurya创立的具有广泛地理分布的铁时代历史力量,在公元前322年和公元前187年之间统治着古印度。
This empire created a single and efficient system of finance, administration, and security. One of the greatest emperors in the Mauryan dynasty was Ashoka the Great, who ruled over a long period of peace and prosperity. Ashoka embraced Buddhism and focused on peace for much of his rule. He created hospitals and schools and renovated major road systems throughout the empire. His advancement of Buddhist ideals is credited with being the reason why most of the population on the island of Sri Lanka is Buddhist to this day.
::这个帝国创造了一个单一而有效的财政、行政和安全体系,莫里扬王朝中最伟大的皇帝之一是大阿索卡,他统治了很长一段和平与繁荣时期;阿索卡信奉佛教,他的大部分统治都以和平为重心;他在整个帝国中建立了医院和学校,并翻新了主要的道路系统;他的佛教理想的进步是斯里兰卡岛大多数人口至今都信奉佛教的原因之一。Ashoka the Great, was an Indian emperor of the Maurya Dynasty, who ruled almost all of the Indian subcontinent from c. 268 to 232 B.C.E.
::Ashoka大帝是莫律雅王朝的印度皇帝,从公元前268年到公元前232年,他几乎统治了整个印度次大陆。
Islam became a powerful force in South Asia upon its diffusion to the subcontinent. Muslim dynasties or kingdoms that ruled India between 1206 and 1526 are referred to as the Delhi Sultanate. The Delhi Sultanate ended in 1526 when it was absorbed into the expanding Mughal Empire. The Islamic Mughal Empire ruled over much of northern and central India from the 1500s to about the middle of the 19th century.
::伊斯兰教在向次大陆扩散后成为南亚的强大力量。 在1206至1526年间统治印度的穆斯林王朝或王国被称为德里苏丹国。 德里苏丹国在1526年被吸收进扩张的莫卧儿帝国后结束。 伊斯兰穆卧儿帝国从1500年代到19世纪中叶统治了印度北部和中部的大部分地区。After 1725, the Mughal Empire began to decline because of many factors, one of those factors being European colonialism. The Mughal Empire had been religiously tolerant but Muslim oriented. The classic period of this empire began in 1556 and ended in 1707. Many of the monuments we associate with India, including the Taj Mahal, the Red Fort in Lahore, and the Agra Fort, were built during the classical period.
::1725年之后,莫卧儿帝国开始衰落,原因很多,其中之一是欧洲殖民主义。 莫卧儿帝国在宗教上是宽容的,但以穆斯林为导向。 这个帝国的经典时期始于1556年,于1707年结束。 我们与印度结盟的许多纪念碑,包括泰姬马哈勒、拉合尔的红堡和阿格拉堡,都是在古典时期建造的。The largest manufacturing industry in the Mughal Empire was textile manufacturing.
::莫卧儿帝国最大的制造业是纺织制造业。Colonialism in South Asia
::南亚的殖民主义The force of colonialism was felt around the world, including in South Asia. South Asia provides an excellent example of colonialism’s role in establishing most of the current political borders in the world. From the 16th century onward, ships from colonial Europe began to arrive in South Asia to conduct trade. The British East India Company was chartered in 1600 to trade in Asia and India. They traded in spices, silk, cotton, and other goods. Later, to take advantage of conflicts and bitter rivalries between kingdoms, European powers began to establish colonies. Britain controlled South Asia from 1857 to 1947 .
::殖民主义的力量在全世界,包括南亚,都有所感受到。 南亚是殖民主义在建立目前世界大部分政治边界方面所起作用的极好例子。 从16世纪开始,来自殖民地欧洲的船只开始来到南亚进行贸易。 英国东印度公司于1600年被包租到亚洲和印度进行贸易。 它们以香料、丝绸、棉花和其他商品进行交易。 后来,为了利用各王国之间的冲突和激烈竞争,欧洲大国开始建立殖民地。 从1857年到1947年,英国控制了南亚。Goa is the smallest state in modern-day India. In the 16th century, it was first encountered by Portuguese traders, who annexed it shortly after arriving. Goa was a colony of Portugal for the next 450 years. By the mid-1800s, most of the population of the tiny area had been forcibly converted to Christianity. Many of the Hindu traditions, however, survived in the region.
::果阿是现代印度最小的邦。 在16世纪,葡萄牙贸易商首次遇到果阿,他们抵达后不久就吞并了果阿。果阿是葡萄牙今后450年的殖民地。到1800年代中期,该地区大部分人口被迫皈依基督教。然而,印度教的许多传统在该地区生存下来。Hindu holidays are celebrated amongst the expatriate community in India. Christian holidays are also celebrated, especially Christmas and Easter. The cathedrals and secular architecture in many of the historic buildings of Goa are European in style, reflecting its Portuguese origins. This architecture is locally termed “Indo-Portuguese.” Goa was one of the longest-held colonial possessions in the world. It was finally annexed to India in 1961.
::印度海外侨民庆祝印度教节日,基督教节日也庆祝,特别是圣诞节和复活节,许多古迹古迹建筑中的大教堂和世俗建筑是欧洲风格,反映了其葡萄牙血统。 这个建筑在当地被称为“印度葡萄牙人 ” 。 果阿是世界上最古老的殖民财产之一,1961年最终被印度吞并。The Basilica of Bom Jesus is located in Goa, India, and is a UNESCO World Heritage Site.
::Bom Jesus的Basilica位于印度果阿,是教科文组织的世界遗产。
The British no longer controlled South Asia after 1947. Local resistance and the devastating effects of World War II meant the British Empire could not be controlled as it once was. Great Britain pulled away from empire building to focus on its own redevelopment. Upon the British withdrawal from India, Britain realized the immense cultural differences between the Muslims and Hindus and created political boundaries based on those differences.
::1947年后,英国不再控制南亚。 当地抵抗和二战的毁灭性后果意味着英国帝国不可能像过去那样被控制。 英国从帝国建设中撤出,专注于自身的再发展。 在英国从印度撤出后,英国认识到穆斯林和印度教徒之间的巨大文化差异,并基于这些差异建立了政治边界。West Pakistan was carved out of western India, and East Pakistan was carved from eastern India. However, the new borders separating Hindu and Muslim majorities ran through population groups, and some of the population now found itself to be on the wrong side of the border. The West Pakistan-India partition grew into a civil war, as Hindus and Muslims struggled to migrate to their country of choice.
::巴基斯坦西部被从印度西部分割出来,而巴基斯坦东部则被从印度东部分割出来。 然而,印度教和穆斯林多数群体之间的新边界穿过人口群体,部分人口现在发现自己在边界的错误一边。 巴基斯坦和印度之间的西分治发展成内战,印度教和穆斯林为迁移到他们选择的国家而斗争。More than one million people died in the civil war, a war that is still referred to in today’s political dialogue between Pakistan and India. The Sikhs, who are indigenous to the Punjab region in the middle, also suffered greatly. Some people decided not to migrate, which explains why India has the largest Muslim population of any non-Muslim state.
::在内战中,有一百多万人丧生。 这场战争在今天的巴基斯坦和印度政治对话中仍然被提及。 中间旁遮普地区的土生土长的锡克教徒也深受其苦。 有些人决定不移民,这解释了为什么印度是非穆斯林国家中穆斯林人口最多的原因。Another civil war erupted in 1973 between West Pakistan and East Pakistan. When the states were first created in 1947, they operated under the same government despite having no common border and being over 900 miles apart and populated by people with no ethnic similarities. The civil war lasted about three months and resulted in the creation of the sovereign countries of Pakistan and Bangladesh. The name Bangladesh is based on the Bengali ethnicity of most of the people who live there. Both Pakistan and Bangladesh are among the top ten most populous countries in the world.
::1973年西巴基斯坦和东巴基斯坦之间爆发了另一场内战。当各州于1947年首次成立时,它们是在同一个政府下运作的,尽管没有共同的边界,它们相隔900多英里,人口居住着没有种族相似性的人。内战持续了大约三个月,并导致巴基斯坦和孟加拉国等主权国家的建立。孟加拉国的名称是以居住在那里的大多数人的孟加拉族裔命名的。巴基斯坦和孟加拉国都是世界上人口最多的十大国家之一。Language is probably one of the more pervasive ways that Europeans impacted South Asia. In modern-day India and Pakistan, English is the language of choice in secondary education. It is often the language used by the government and military. Unlike many other Asian countries, much of the signage and advertising in Pakistan and India is in English, even in rural areas. Educated people switch back and forth, using English words or entire English sentences during conversation in their native tongue. Some scholars have termed this Hinglish or Urglish as the base languages of northern India and Pakistan are Hindi and Urdu, respectively.
::语言可能是欧洲人影响南亚的更为普遍的方式之一。 在现代印度和巴基斯坦,英语是中等教育的首选语言。它经常是政府和军方使用的语言。与其他许多亚洲国家不同,巴基斯坦和印度的许多标志和广告都是英语,甚至在农村地区也是如此。受过教育的人在用母语交谈时,用英语或整个英语句调换或调换。一些学者称这支Hinglish或Urglish语为印度北部和巴基斯坦的基础语言,分别是印地语和乌尔都语。The British game of cricket is an important cultural and national sport in South Asia. The constant conflict between the nations of India and Pakistan is reflected in the intense rivalry between their national cricket teams. The Cricket World Cup is held every four years and is awarded by the International Cricket Council. South Asian countries have won the Cricket World Cup three times: India (1983), Pakistan (1992), and Sri Lanka (1996).
::英国板球比赛是南亚重要的文化和民族体育。 印度和巴基斯坦两国间的持续冲突反映在两国板球队之间的激烈竞争中。板球世界杯每四年举行一次,并由国际板球理事会颁奖。 南亚国家赢得板球世界杯三次:印度(1983年)、巴基斯坦(1992年)和斯里兰卡(1996年)。Cricket is the most popular sport in India.
::板球是印度最受欢迎的运动Population in South Asia
::南亚人口South Asia is one of the most populous realms in the world. Large populations are a product of large family sizes and a high fertility rate. The rural population of South Asia has traditionally had large families, and religious traditions generally support this. However, the least densely populated country in South Asia is the Kingdom of Bhutan. Bhutan has a population density of approximately 50 people per square mile. Bhutan is mountainous with little arable land. More than one-third of the people in Bhutan live in an urban setting. Population overgrowth for the realm is a serious concern. An increase in population requires additional natural resources, energy, and food production, all of which are in short supply in many areas.
::南亚是世界上人口最多的地区之一,人口众多是家庭规模大、生育率高的产物,南亚农村人口历来拥有大家庭,而宗教传统则普遍支持这一传统,但南亚人口最稠密的国家是不丹王国,不丹的人口密度约为每平方英里50人,不丹是山区,耕地很少,不丹三分之一以上的人口生活在城市环境中,人口过度增长是一个严重关切的问题,人口的增加需要增加自然资源、能源和粮食生产,而许多地区都缺乏这些资源、能源和粮食生产。South Asia’s growing population has placed exceedingly high demands on agricultural production. The amount of area available for food production divided by the population may be a more helpful indicator of population distribution than total population density. For example, large portions of Pakistan are deserts and mountains that do not provide arable land for food production.
::南亚不断增长的人口对农业生产的需求非常高,粮食生产可用面积除以人口,可能比人口总密度更有助于衡量人口分布。 比如,巴基斯坦大部分地区是沙漠和山地,不能提供可耕地用于粮食生产。India has the Thar Desert and the northern mountains. Nepal has the Himalayas. The small country of the Maldives, with its many islands, has almost no arable land. The number of people per square mile of arable land, which is called the physiologic density, can be an important indicator of a country’s status. Total population densities are high in South Asia, but the physiologic densities are even more surprising.
::印度有塔尔沙漠和北部山区。 尼泊尔有喜马拉雅山。 马尔代夫这个拥有许多岛屿的小国几乎没有可耕地。 每平方英里可耕地(即被称为生理密度)的人数可以作为一个国家状况的重要指标。 南亚总人口密度很高,但生理密度甚至更令人吃惊。In Bangladesh, for example, more than 5,000 people depend on every square mile of arable land. In Sri Lanka, the physiologic density reaches to more than 6,000 people per square mile, and in Pakistan, it is more than 2,400. The data are averages, which indicate that the population density in the fertile river valleys and the agricultural lowlands might be even higher. Urban areas of South Asia are expanding rapidly.
::例如,在孟加拉国,5 000多人依赖每平方英里的可耕地;在斯里兰卡,每平方英里的生理密度达到6 000多人;在巴基斯坦,每平方英里超过2 400人;数据为平均数,表明肥沃河谷和农业低地的人口密度可能更高;南亚城市地区正在迅速扩大。Thyagaraya Nagar is a neighborhood in the city of Chennai, India. It is a popular shopping district.
::在印度钦奈市,Thyagaraya Nagar是一个街区,是一个受欢迎的购物区。
The population of South Asia is relatively young. In Pakistan, about 35 percent of the population is under the age of 15, while about 30 percent of India’s almost 1.3 billion people are under the age of 15. Many of these young people live in rural areas, as most of the people of South Asia work in agriculture and live a subsistence lifestyle. As the population increases, the cities reflect the growth in the urban population and the large influx of migrants arriving from rural areas.
::南亚的人口相对年轻。 在巴基斯坦,大约35%的人口年龄在15岁以下,而印度近13亿人口中约有30%的人口年龄在15岁以下。 其中许多年轻人生活在农村地区,因为南亚大部分人务农,过着自给生活方式。 随着人口增长,城市反映了城市人口增长和来自农村地区的移民大量涌入。Rural-to-urban shift is extremely high in South Asia and will continue to fuel the expansion of the urban centers into some of the largest cities on the planet. The rural-to-urban shift that is occurring in South Asia also coincides with an increase in the region’s interaction with the global economy.
::南亚的农村向城市的转变非常高,并将继续推动城市中心扩展到地球上一些最大的城市。 南亚正在发生的农村向城市的转变也与该地区与全球经济互动的增加相吻合。The South Asian countries are transitioning through the five stages of the index of economic development. The more rural agricultural regions are in the lower stages of the index. The realm experienced rapid population growth during the latter half of the 20th century. As death rates declined and family size remained high, the population swiftly increased. India, for example, grew from fewer than 400 million in 1950 to more than one billion at the turn of the century.
::南亚国家正在经历经济发展指数五个阶段的转型,农村农业地区处于较低阶段,20世纪后半叶,该地区人口迅速增长,死亡率下降,家庭人口居高不下,人口迅速增加,例如印度从1950年的不到4亿增加到本世纪初的10亿多。The more urbanized areas are transitioning into stage 3 of the index and experiencing a significant rural-to-urban shift. Large cities such as Mumbai have sectors that are in the latter stages of the index because of their urbanized workforce and higher incomes. Family size is decreasing in the more urbanized areas and in the realm as a whole. Demographers predict that eventually the population will stabilize.
::城市化程度较高的地区正在向该指数的第三阶段过渡,并经历了从农村向城市的重大转变,如孟买等大城市由于劳动力城市化和收入较高而处于该指数的后阶段,家庭规模在城市化程度较高的地区和整个地区正在缩小,人口统计学家预测,最终人口将稳定下来。India is the second-most populated country in the world with nearly a fifth of the world's population. This map reflects the 2001 census.
::印度是世界上人口第二多的国家,占世界人口的近五分之一,这幅地图反映了2001年的人口普查。
At the current rates of population growth, the population of South Asia will double in about 50 years. Without continued attention to how the societies address family planning and birth control, South Asia will likely face serious resource shortages in the future.
::按照目前的人口增长率,南亚人口在大约50年内将翻一番,如果不继续注意各国社会如何处理计划生育和节育问题,南亚今后很可能面临严重的资源短缺问题。Key Takeaways
::密钥外出-
All of the South Asian countries border India by either a physical or a marine boundary. The Himalayas form a natural boundary between South Asia and East Asia (China). The realm is surrounded by deserts, the Indian Ocean, and the high Himalayan ranges.
::所有南亚国家都通过有形边界或海洋边界与印度接壤,喜马拉雅山脉是南亚和东亚(中国)之间的自然边界,周围是沙漠、印度洋和喜马拉雅山脉。 -
The summer monsoon arrives in South Asia in late May or early June and subsides by early October. The rains that accompany the monsoon account for most of the rainfall for South Asia. Water is a primary resource, and the larger river systems are home to large populations.
::夏季季风于5月底或6月初抵达南亚,到10月初就会平息下来。 伴随季风的降雨量占南亚降雨量的大部分。 水是首要资源,而更大的河流系统是人口众多的家园。 -
The Indus River Valley was a location of early human civilization. The large empires of the realm gave way to European colonialism. The British dominated the realm for 90 years from 1857 to 1947 and established the main boundaries of the realm.
::印度河谷是早期人类文明的发源地,大帝国让位于欧洲殖民主义。 从1857年到1947年,英国统治印度河谷已有90年之久,并划定了王国的主要疆界。 -
Population growth is a major concern for South Asia. The already enormous populations of South Asia continue to increase, challenging the economic systems and depleting natural resources at an unsustainable rate.
::人口增长是南亚的一个主要关切,南亚本已庞大的人口继续增加,对经济体系构成挑战,以不可持续的速度消耗自然资源。
Vocabulary Terms
::词汇术语术语Chapter 9.1 Introducing the Realm
::第9.1章 介绍王国Bay of Bengal
::孟加拉湾A Bay that the Ganges River flows into, North of the Indian Ocean, On the eastern side of India, South of Tibet, West of China
::恒河流入印度洋以北、印度东岸、西藏南南、中国西部的一条湾Brahmaputra River
::布拉马普特拉河River that begins in Tibet, flows through northeast India and Bangladesh, joining with the Ganges to empty into the Bay of Bengal
::从西藏开始的河水 穿过印度和孟加拉国东北部 与恒河联手空空进入孟加拉湾Deccan Plateau
::Deccan 高原A high area of land at the center of the Indian subcontinent., it lies between the Adrian Sea and the Bay of Bengal and it is made of lava, which produces a rich black soil; it's bordered on the west and east by the Eastern Ghats and the Western Ghats
::印度次大陆中心高地面积,位于阿德里安海与孟加拉湾之间,由熔岩组成,形成丰富的黑土,西面与东面毗邻东加茨和西加茨。Eastern Ghats
::东加eroded coastal mountains east of the Deccan Plateau in Southern India
::印度南部Deccan高原以东被侵蚀的沿海山区Ganges River
::恒河河A river of South Asia that flows southeast from the Himalayas to the Bay of Bengal., India's most important river, flows across northern India into Bangladesh, Hindus sacred river, they believe it is the "liquid form of God"
::印度最重要的河流, 穿过印度北部, 流到孟加拉国, 印度教徒神圣的河流, 他们相信这是“神的液态形式 ” 。Himalaya Mountains
::喜马拉山A range of mountains with the highest peaks in the world including Mt. Everest. The Himalayas stretch from Pakistan to Bhutan
::喜马拉雅山脉从巴基斯坦延伸到不丹Hindu Kush Mountains
::兴都库什山large mountain range located in northern Pakistan and that provide a barrier between Pakistan and Afghanistan. The Khyber Pass is used to travel between the two countries
::开伯尔山口用于在巴基斯坦和阿富汗之间旅行。Indus River
::印地河A river in South Asia that flows from the Himalayas to the Arabian Sea, the earliest Indian civilization began in the valley of this river
::南亚的一条河流从喜马拉雅山流向阿拉伯海,最早的印度文明起源于这条河谷lagoon
::环环礁湖a shallow body of water in the center of an atoll
::环礁中心浅水体monsoon
::季风regional winds that predictably change direction with the passing of the seasons. These winds blow from land to sea in the winter, and from sea to land in the summer. In summer they are often accompanied by precipitation.
::随着季节的流逝,区域风可以预测地改变方向。 这些风在冬季从陆地吹到海洋,在夏季从海洋吹到陆地。 在夏季,它们常常伴有降水。Mount Everest
::珠珠峰Highest peak in the world, located in the Himalayas
::位于喜马拉雅山的世界最高峰峰subcontinent
::次大陆A large landmass that is part of a continent
::大陆的一块大陆地Western Ghats
::西加兹A chain of eroded mountains in India that forms a triangle of rugged hills with the Eastern Ghats. It prevents yearly rainy winds from reaching the Deccan Plateau
::印度被侵蚀的山脉链条,与东加茨形成坚固的山峰三角地带,使每年的雨季无法到达Deccan高原。Applying Knowledge
::应用知识Discussion and Study Questions
::讨论和研究问题-
Why are the Himalayan Mountains continuing to increase in elevation? Which of the countries of South Asia border the Himalayas?
::喜马拉雅山脉的海拔为何继续上升? 南亚哪个国家与喜马拉雅山接壤? -
What are the three major rivers of South Asia? Where do they start and into what bodies of water do they flow? Why have these river basins been such an important part of the early civilizations of the realm and why are they core population areas today?
::南亚的三条主要河流是什么?它们从何而来,流到何方?这些河流流域为什么是该地区早期文明的重要部分,为什么它们今天是核心人口区? -
Why does the monsoon usually arrive in late May or early June? What is the main precipitation pattern that accompanies the monsoon? Why is the monsoon a major source of support for South Asia’s large population?
::为什么季风通常在5月底或6月初到达? 季风伴有的主要降水模式是什么? 季风为什么是南亚人口众多的主要支助来源? -
What changes did British colonialism bring to South Asia? When did the British control South Asia? Why do you think the British lost control when they did?
::英国殖民主义给南亚带来了什么变化? 英国何时控制南亚? 你认为英国为何失去控制? -
Why is the high population growth rate a serious concern for South Asian countries? What can these countries do to address the high population growth rate?
::为什么高人口增长率是南亚国家严重关切的一个问题?这些国家可以做些什么来解决高人口增长率问题? -
How can Pakistan have a higher fertility rate than Bangladesh but still have the same growth rate and doubling time?
::巴基斯坦的生育率怎么会高于孟加拉国,却仍然保持同样的增长率和翻一番的时间? -
Why would the country of the Maldives be concerned about climate change?
::马尔代夫国家为什么对气候变化感到关切? -
How would you assess the status of each country with regard to the index of economic development?
::你们将如何评估每个国家在经济发展指数方面的现状? -
What are the three dominant religions of the realm? How did religion play a role in establishing the realms’ borders? What happened to East Pakistan?
::三大主要宗教是什么? 宗教如何在建立疆界方面发挥作用? 东巴基斯坦发生了什么事?
Real-World Geography Exercise
::现实世界地理演习-
Using
, complete the following activities:
-
Locate each place on the bulleted list below.
::在下面的子弹名单上 找到每个地方 -
Find the nearest city with an international airport in proximity to each location on the bulleted list below.
::找到最近的城市,在下面子弹清单上每个地点附近有一个国际机场。 -
Calculate the distance and travel time by plane to each city from the
in Charlotte, North Carolina.
::计算从北卡罗来纳州夏洛特飞往每个城市的飞机距离和旅行时间。
::使用,完成以下活动: 定位以下子弹子弹清单上的每个地点; 找到最近的城市, 在下面子弹清单上的每个地点附近有一个国际机场。 计算从北卡罗来纳州夏洛特飞往每个城市的飞机距离和飞行时间。 -
Locate each place on the bulleted list below.
-
Using
, determine the latitude and longitude for each location on the bulleted list below.
::使用,确定以下子弹列表中每个位置的纬度和经度。 -
Be prepared to share and discuss your answers.
::准备分享和讨论你的答案
-
Arabian Sea
::阿拉伯海 -
Baluchistan
::俾路支 -
Bay of Bengal
::孟加拉湾 -
Brahmaputra River
::布拉马普特拉河 -
Central Indian Plateau
::中印度中印度高原 -
Chota-Nagpur Plateau
::Chota-Nagpur高原 -
Deccan Plateau
::Deccan 高原 -
Eastern Ghats
::东加 -
Ganges River
::恒河河 -
Himalayas
::喜马拉雅山 -
Indian Ocean
::印度洋印度洋 -
Indus River
::印地河 -
Kashmir
::克什米尔 -
Mt. Everest
::珠穆峰 -
Punjab
::旁遮普 -
Thar Desert
::塔尔沙漠 -
Western Ghats
::西加兹
Current Events
::当前事件Geography Videos for Enrichment
::用于浓缩的地理录像Helpful Websites for the Study of Geography
::地理研究有用网站is an encyclopedia funded by the Canadian government covering all branches of knowledge. Their scholarly collection includes interactive materials.
::该百科全书由加拿大政府资助,涵盖所有知识分支,其学术收藏包括交互式材料。provides information on the people, history, government, economy, energy, geography, communications, transportation, military, and transnational issues for the world's entities.
::向世界各实体提供关于人民、历史、政府、经济、能源、地理、通信、运输、军事和跨国问题的资料。is a US government website where you can find federal legislation, past and present, as well as information about the US legal system.
::是一个美国政府的网站,您可以在此找到过去和现在的联邦立法以及关于美国法律制度的信息。is a government agency website that provides current news, resources, topics of interest, information about drugs, careers in the DEA, and a tip hotline.
::是一个政府机构网站,提供最新消息、资源、感兴趣的话题、毒品信息、在缉毒局的职业以及一条小费热线。is the largest library in the world and provides manuscripts, files, information, pictures, and videos.
::图书馆是世界上最大的图书馆,提供手稿、文件、信息、图片和录像。is a US government agency website that allows users to search for and retrieve satellite images of Earth.
::这是一个美国政府机构的网站,用户可以搜索和检索地球的卫星图像。is a US government website that provides historical documents, photos, records, publications, and educator resources.
::这是一个美国政府网站,提供历史文件、照片、记录、出版物和教育资源。is a US government agency website that provides weather-related information and ocean research.
::是一个提供气象信息和海洋研究的美国政府机构网站。is a website by the United States Geological Survey and other federal, state, and local agencies that delivers topographic information for the United States.
::这是美国地质调查局和其他联邦、州和地方机构为美国提供地形信息的网站。is a massive central data source and a handy way to graphically compare nations.
::是一个庞大的中央数据源,是用图形比较国家的一种方便方式。is a website that measures most locations in the world for air pollution in real time.
::是一个实时测量世界上大多数空气污染地点的网站。is a unique statistical database, which allows you to research and compare a multitude of different data on US states.
::这是一个独特的统计数据库, 使你能够研究和比较关于美国各州的多种不同数据。is an international organization founded in 1945 and made up of 193 member states. The UN maintains international peace and security, protects human rights, delivers humanitarian aid, promotes sustainable development, and upholds international law.
::联合国是一个国际组织,成立于1945年,由193个成员国组成。 联合国维护国际和平与安全,保护人权,提供人道主义援助,促进可持续发展,维护国际法。is a US government agency that provides a population clock, data, surveys, statistics, a library with information and infographics, news about the economy, and much more.
::这是一个美国政府机构,它提供人口钟、数据、调查、统计、一个拥有信息和信息资料的图书馆、关于经济的新闻,以及更多。is a US government agency website that provides scientific information about the natural hazards that threaten lives, the natural resources we rely on, the health of our ecosystems and environment, and the impacts of climate and land-use change.
::这是一个美国政府机构的网站,提供科学信息,说明威胁生命的自然危害、我们赖以生存的自然资源、生态系统和环境的健康以及气候和土地使用变化的影响。is a US government website that provides the latest presidential news, information about the budget, policy, defense, and many more topics.
::提供最新总统新闻、预算、政策、国防等资讯, 以及更多议题。is under the United Nations and provides leadership on matters critical to health, shapes the research agenda on health, and monitors the health situation and assessing health trends around the world. Their website provides information on the state of health around the world, outbreaks, current health news, and more.
::网站提供世界各地卫生状况、疫情爆发、最新卫生新闻等信息。is an intergovernmental organization that regulates international trade. The website provides information on the history of the multilateral trading system, featured videos, news and events, trade topics, and more.
::该网站提供关于多边贸易体系历史的信息、视频、新闻和事件、贸易专题等等。WG.4B Describe different landforms and the physical processes that cause their development.
::WG.4B 描述不同的土地形态和导致其发展的物理过程。WG.5A Analyze how the character of a place is related to its political, economic, social, and cultural elements.
::WG.5A 分析一个地方的特性如何与其政治、经济、社会和文化因素相关。WG.6A Locate and describe human and physical features that influence the size and distribution of settlements.
::WG.6A 确定并描述影响定居点规模和分布的人文和物理特征。WG.6B Explain the processes that have caused changes in settlement patterns, including urbanization, transportation, access to and availability of resources, and economic activities.
::WG.6B 解释导致住区模式变化的进程,包括城市化、运输、获得和获得资源以及经济活动。WB.12A Analyze how the creation, distribution, and management of key natural resources affects the location and patterns of movement of products, money, and people.
::WB.12A分析关键自然资源的创造、分配和管理如何影响产品、货币和人员流动的地点和模式。WG.13A Interpret maps to explain the division of land, including man-made and natural borders, into separate political units such as cities, states, or countries.
::WG.13A 解释地图,解释土地划分,包括人造边界和自然边界,分为不同的政治单位,如城市、州或国家。WG.14A Analyze current events to infer the physical and human processes that lead to the formation of boundaries and other political divisions.
::WG.14A 分析当前事件,以推断导致形成边界和其他政治分裂的物质和人类过程。WG.15A Identify and give examples of different points of view that influence the development of public policies and decision-making processes on local, state, national, and international levels.
::WG.15A 查明并举例说明影响地方、州、国家和国际各级公共政策和决策进程发展的不同观点。WG.15B Explain how citizenship practices, public policies, and decision making may be influenced by cultural beliefs, including nationalism and patriotism.
::WG.15B 解释公民身份做法、公共政策和决策如何受文化信仰,包括民族主义和爱国主义的影响。WG.16C Explain ways various groups of people perceive the characteristics of their own and other cultures, places, and regions differently.
::WG.16C 解释不同群体对自身和其他文化、地方和区域特征的不同看法。WG.17A Describe and compare patterns of culture such as language, religion, land use, education, and customs that make specific regions of the world distinctive.
::WG.17A 描述和比较使世界特定区域具有独特性的语言、宗教、土地使用、教育和习俗等文化模式。WG.22A Design and draw appropriate graphics such as maps, diagrams, tables, and graphs to communicate geographic features, distributions, and relationships.
::WG.22A 设计和绘制适当的图形,如地图、图表、表格和图表,以交流地理特征、分布和关系。WG.22C Use geographic terminology correctly.
::WG.22C 正确使用地理术语。WG.22D Use standard grammar, spelling, sentence structure, and punctuation.
::WG.22D 使用标准语法、拼写、句子结构和标点。 -
Summarize the realm’s physical geography. Identify each country’s main features and physical attributes and locate the realm’s main river systems.