6.13 过渡金属
Section outline
-
What are the similarities and differences between these two cars?
::这两辆车之间有什么相似之处和不同之处?From the outside, the two cars above look the same (except for the flashy paint job on the racing model). They are the same model of the car, but one is a stock edition for regular driving while the other one is built for high-speed racing. We really can’t tell much from the external view. To see the differences, we need to go under the hood, take the engines apart, and look at the braking and suspension systems in order to see how the two cars differ.
::从外部看,上面的两辆汽车看起来都是一样的(除了赛车模型上的闪光油漆工作 ) 。 它们与车型相同,但其中一辆是定期驾驶的库存版,另一辆则是高速赛车的库存版。 从外部看,我们真的看不出什么不同之处。 要看到差异,我们需要从引擎盖下走,把引擎拆开,看看制动和悬浮系统,看看两辆汽车有何不同。Many configurations of are simple and straightforward. We can look at the outer shell and easily understand how that set of elements will react in terms of electron gain or loss. However, there are sets of elements that are more complex in their behavior. One such group is called the transition elements .
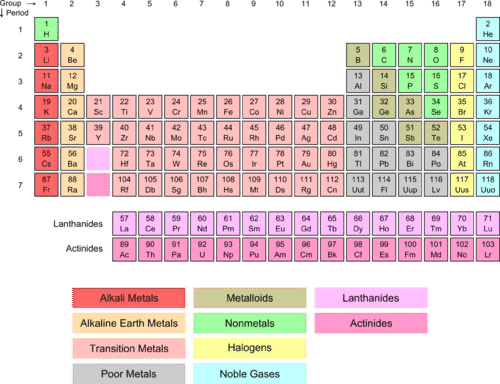
::许多配置简单而直截了当。 我们可以查看外壳, 很容易理解这组元素在电子损益方面的反应方式。 但是, 有一组元素在行为上更为复杂。 其中一组被称为过渡元素 。Transition elements are the elements that are found in Groups 3-12 (old groups IIA-IIB) on the periodic table (salmon-colored block in the middle of the table). The term refers to the fact that the d sublevel , which is in the process of being filled, is in a lower principal energy level than the sublevel filled before it. For example, the electron configuration of scandium, the first transition element, is [Ar]3 d 1 4 s 2 . Remember that the configuration is reversed from the fill order – the 4 s filled before the 3 d begins. Because they are all , the transition elements are often called the transition metals. As a group, they display typical metallic properties and are less reactive than the metals in Groups 1 and 2. Some of the more familiar ones are so unreactive that they can be found in nature in their free, or uncombined state. These include platinum, gold, and silver. Because of this unique filling order, the transition elements are often referred to as “ d -block” elements.
::过渡元素是周期表中的第3-12组(旧的IIA-IIB组)中发现的元素。该词指的是以下事实,即正在填充的D子级在主要能源水平上比之前填充的子级低。例如,第一层过渡元素即扫瞄机的电子配置是[Ar]3d14s2. 记住,配置是从填充顺序中倒转的,即在3D开始之前填充的4个元素。由于它们都是,过渡元素通常被称为过渡金属。作为一个组,它们显示典型的金属特性,与第1组和第2组中的金属相比反应较少。一些熟悉的元素非常不活跃,在自然中可以发现它们的自由状态或不组合状态。这些元素包括白金、银。由于这种独特的填充顺序,过渡元素通常被称为“d-block”元素。Piece of silver.
::银块Compounds of many transition elements are distinctive for being widely and vividly colored. As visible light passes through a transition metal dissolved in water, the d- absorb light of various energies. The visible light of a given energy level which is not absorbed produces a distinctly colored solution.
::许多过渡性元素的化合物具有独特性,具有广泛和生动的颜色。随着可见的光穿过水溶解的过渡金属,各种能量的D吸收光线。未吸收的某一能量水平的可见光产生一种明显有色的溶液。Transition metal compounds dissolved in water exhibit a wide variety of bright colors. From left to right are shown solutions of cobalt(II) nitrate, potassium dichromate, potassium chromate, nickel(II) chloride, copper(II) sulfate, and potassium permanganate.
::在水中溶解的过渡性金属化合物呈现出各种明亮的颜色,从左到右展示了钴(II)硝酸盐、铬酸钾、铬酸钾、氯化镍、硫酸铜(II)硫酸盐和高锰酸钾的溶液。Summary
::摘要-
The transition elements are found in groups IIIA-IIB (new groups 3-12).
::过渡要素见IIIA-IIB组(新的3-12组)。 -
These elements are characterized by having unfilled
d
sublevels.
::这些要素的特点是具有未填充的分层。 -
In general, the next higher
s
sublevel is already filled or has one electron missing.
::一般说来,下一个更高的子层已经填满或缺少一个电子。 -
Many transition element compounds are brightly colored due to the inner-level
d
electron transitions.
::由于内层电子转换,许多过渡元素化合物的颜色亮亮。
Review
::回顾-
List five different transition elements, giving their name, chemical symbol, and atomic number.
::列出五个不同的过渡要素,列出名称、化学符号和原子编号。 -
What is unique about the transition elements in terms of electron configurations?
::电子配置的过渡要素有什么独特之处? -
Why are these elements often referred to as “
d
-block” elements?
::为什么这些要素常常被称为“D-区块”要素? -
Why do many transition element compounds have bright colors?
::为什么许多过渡元素化合物的颜色很亮?
-
The transition elements are found in groups IIIA-IIB (new groups 3-12).