3.1 心心
章节大纲
-
What's the most active muscle in the body?
::身体中最活跃的肌肉是什么?The heart. An absolutely remarkable organ . Obviously, its main function is to pump throughout the body. And it does this extremely well. On average, this muscular organ will beat about 100,000 times in one day and about 35 million times in a year. During an average lifetime, the human heart will beat more than 2.5 billion times.
::心脏, 绝对非凡的器官。 显然, 它的主要功能是在整个身体中抽动。 它做得很好。 平均而言, 它的肌肉器官在一天中将击打大约10万次, 一年中大约3500万次。 在平均寿命期间, 人类的心脏将击打超过25亿次。The Heart
::心心The , shown in Figure , is an organ system that moves nutrients , , gases, and wastes to and from body and distributes heat to maintain . The main components of the cardiovascular system are the heart, the , and the blood.
::如图所示,这是一种器官系统,将营养物、气体和废物从身体移动到身体,传播热量以维持健康。心血管系统的主要组成部分是心脏、心和血液。The function of the circulatory system is to move materials around the body. The main organs of the circulatory system are the heart, blood vessels, and blood. Blood acts as the transporter in the body, while blood vessels act like little (one way) roads.
::循环系统的作用是将材料绕着身体移动,循环系统的主要器官是心脏、血管和血液。血液是人体的运输工具,血管则像一条小路。The heart is the muscular organ that pumps blood through the blood vessels by repeated, rhythmic contractions. The term cardiac means "related to the heart" and comes from the Greek word kardia, meaning "heart." The heart is made up mostly of cardiac muscle tissue (shown in Figure ), which contracts to pump blood around the body. In adults, the normal mass of the heart is 250-350 grams (9-12 oz), or about three quarters the size of a clenched fist, but badly diseased hearts can be up to 1000 g (2 lb) in mass due to enlargement of the cardiac muscle.
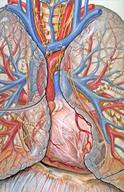
::心脏是用反复的、有节奏的收缩在血管中抽血的肌肉器官。 心脏一词的意思是“ 与心脏有关 ” , 源自希腊语“ kardia ” , 意思是“心脏 ” 。 心脏主要由心脏肌肉组织(图示)组成,组织在身体周围抽血。 在成人中,心脏的正常质量为250-350克(9-12 oz),或大约3/4的握紧拳,但心脏肌肉的扩大导致心脏重度可高达1000克(2磅),但心脏肌肉的扩大,导致心脏疾病严重。External and internal views of the human heart. The aorta in the photo cannot be seen clearly because it is covered by a layer of adipose tissue (fat).
::照片中的动脉无法被清晰看到,因为它被一层脂肪组织(脂肪)覆盖。The heart is usually found in the left to middle of the chest, with the largest part of the heart slightly to the left. The heart is usually felt to be on the left side because the left ventricle is stronger (it pumps to all the body parts). The heart is surrounded by the lungs . The left lung is smaller than the right lung because the heart takes up more room in the left side of the chest. The position of the heart within the chest is shown in Figure .
::心脏通常在左到胸部中间发现,心脏的最大部分在左略微,心脏通常感觉在左侧,因为左心室较强(所有身体部位都有泵)。心脏周围是肺部。左肺小于右肺,因为心脏在胸部左侧占据了更多房间。胸内心脏的位置在图中显示。The position of the heart in relation to the lungs. The heart can be seen in the lower middle area of the figure, behind the lungs.
::心脏与肺的相对位置。心脏在下半部部位,在肺后面可以看到。Blood Flow Through the Heart
::血流满心Blood flows through the heart in two separate loops; you could think of them as a “left side loop” and a “right side loop.” The right side and left side of the heart refer to your heart as it sits within your chest. Its left side is your left side, and its right side is your right side.
::血液在两个不同的循环中流过心脏;你可以把它们视为“左侧循环”和“右侧循环 ” 。 心脏的右侧和左侧指着你的心,当心心坐在你胸中的时候。左侧是你的左侧,右侧是你的右侧。The right side of the heart collects deoxygenated blood from the body and pumps it into the lungs, where it releases carbon dioxide and picks up oxygen. The left-side carries the oxygenated blood back from the lungs and into the left side of the heart, which then pumps the oxygenated blood throughout the rest of the body.
::心脏的右侧从身体中收集脱氧血液并将其泵入肺部,释放二氧化碳并吸收氧气。 左侧携带氧血液,从肺部返回到心脏的左侧,然后将氧血液泵入身体的其余部分。The heart has four chambers: the two upper atria and the two lower ventricles. Atria (singular atrium) are the thin-walled blood collection chambers of the heart. Atria pump the blood into the ventricles. Ventricles are the heart chambers that collect blood from the atria and pump it out of the heart. On the right side of the heart, deoxygenated blood from the body enters the right atrium from the superior vena cava and the inferior vena cava , as shown in Figure . Blood enters the right ventricle, which then pumps the blood through the pulmonary arteries and into the lungs. In the lungs, carbon dioxide is released from the blood, and oxygen is picked up.
::心脏有4个室室: 上方的2个腹部和下方的2个腹部。 Atria( singal atria) 是心脏的薄壁血采集室。 Atria 将血液抽进腹部。 胸室是从腹部收集血液并将血液抽出心脏的心脏室。 在心脏右侧, 身体的脱氧血液从上方进入上方的宫殿右侧, 如图所示。 血液进入右心室, 然后通过肺动脉和肺抽出血液。 在肺部, 二氧化碳从血液中释放出来, 氧被吸收。Pulmonary veins bring the oxygenated blood back toward the heart and into the left atrium. From the left atrium, the blood moves to the left ventricle, which pumps it out to the body through the aorta . On both sides, the lower ventricles are thicker and stronger than the upper atria. The muscle wall surrounding the left ventricle is thicker and stronger than the wall surrounding the right ventricle because the left ventricle needs to exert enough force to pump the blood through the body. The right ventricle only needs to pump the blood as far as the lungs, which does not require as much contractile force.
::肺血管将氧化血液带回心脏和左心室。 左心室, 血液向左心室移动, 通过动脉抽出血流到身体。 在两侧, 下心室的厚度和强度都比上方更强。 左心室周围的肌肉壁比右心室周围的墙壁厚, 更强, 因为左心室需要用足够的力量将血液抽出身体。 右心室只需要将血液抽到肺部, 肺部不需要那么多的压力。Valves in the heart maintain the flow of blood by opening and closing in one direction only. Blood can move only forward through the heart and is prevented from flowing backward by the valves. Such movement of the blood is called unidirectional flow. There are four valves of the heart:
::心脏的阀门只能向一个方向打开和封闭,保持血液流动。血液只能通过心脏向前移动,不能通过阀门向后流。这种血液流动被称为单向流动。心脏有四个阀门:-
The two
atrioventricular (AV) valves
ensure blood flows from the atria to the ventricles and not the other way. The AV valve on the right side of the heart is called the tricuspid valve, and the one on the left side of the heart is called the mitral, or bicuspid, valve.
::两个动静脉阀(AV)确保血液从阿提里亚流到直肠,而不是从另一方向流出。心脏右侧的AV阀被称作三振阀,而心脏左侧的AV阀被称作线性阀,或双振动阀。
-
The two
semilunar (SL)
valves
are present in the
arteries
leaving the heart, and they prevent blood from flowing back from the arteries into the ventricles. The SL valve on the right side of the heart is called the pulmonary valve because it leads to the pulmonary arteries, and the SL valve on the left side of the heart is called the aortic valve because it leads to the aorta. The valves of the heart are shown in
Figure
.
::心脏的动脉中存在两个半卢纳尔(SL)阀门,它们防止血液从动脉流回到心室。心脏右侧的SL阀门被称为肺动脉,因为它导致肺动脉,而心脏左侧的SL阀门则被称为动脉阀门,因为它导致动脉。心脏的阀门在图中显示。
The direction of blood flow through the heart.
::血液流向心脏The Heartbeat
::心跳The heart is a meshwork of cardiac muscle cells that are interconnected by little channels called gap junctions. This interconnection allows the electrical stimulation of one cell to spread quickly to its neighboring cells. Cardiac muscle is self-exciting. This contrasts , which needs nervous stimulation to contract. The heart's rhythmic contractions occur spontaneously, although the frequency of the contractions, called the heart rate, can be changed by nervous or hormonal signals, such as during or when perceiving danger.
::心脏是心脏肌肉细胞的网格,它们通过被称为隔间连接的小渠道连接。这种连结使得一个细胞的电刺激能够迅速扩散到其邻近的细胞。心肌是自我刺激的。这种对比需要神经刺激来收缩。心脏的节奏收缩是自发的,尽管叫作心脏速率的收缩频率可以通过神经或激素信号改变,例如在发现危险期间或时。Control of the Heartbeat
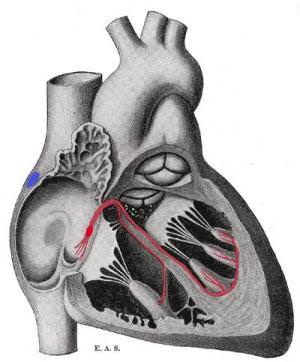
::心脏节跳控制中心The rhythmic sequence of contractions of the heart is coordinated by two small groups of cardiac muscle cells called the sinoatrial (SA) and atrioventricular (AV) nodes. The sinoatrial node (SA node), often known as the "cardiac pacemaker," is found in the upper wall of the right atrium and is responsible for creating an action potential to start the wave of electrical stimulation that starts atrial contraction. The action potential causes the cardiac cells to contract. This wave of contraction then spreads across the cells of the atrium, reaching the atrioventricular node (AV node), which is found in the lower right atrium, as shown in Figure . The AV node conducts the electrical impulses that come from the SA node through the atria to the ventricles. The impulse is delayed there before being conducted through special bundles of heart muscle cells called the bundle of His and the Purkinje fibers, which leads to a contraction of the ventricles. This delay allows for the ventricles to fill with blood before the ventricles contract. Heartbeat is also controlled by nerve messages originating from the autonomic nervous system .
::心脏收缩的节奏序列由两小组心脏肌肉细胞小组(称为神经神经(SA)和动静脉(AV)节点)协调。神经节点(SA节点)通常被称为心心动起搏器,在右庭院的上壁上方发现,它负责创造行动潜力,以启动开始审判收缩的电动刺激波。行动潜力导致心脏细胞萎缩。这种收缩波随后扩散到小庭的细胞中,到达右下方的原子节点(AV节点),如图所示,该节点位于右下方。AV节点是来自SA节点的电动脉冲,通过心脏肌肉细胞的特殊捆绑进行,这导致心血管收缩。这种延缓使得心电动在心血管收缩之前以血液填充,而心跳节点则由神经神经系统控制。There are important physiological differences between cardiac cells found in the nodes and cardiac cells found in the ventricles. Differences in ion channels and mechanisms of polarization give rise to unique properties of SA node cells—the most important being the spontaneous depolarizations necessary for the SA node's pacemaker activity.
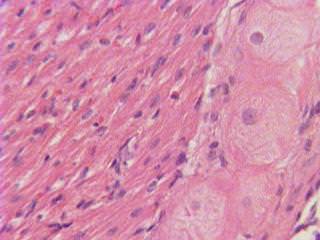
::在节点中发现的心细胞与在心室中发现的心细胞之间存在重要的生理差异,离子渠道和两极分化机制的差异导致SA节点细胞具有独特的特性,最重要的是南澳大利亚节点起搏活动所需的自发去极化。The Bundle of His is a collection of heart muscle cells (fibers) specialized for electrical conduction that transmits the electrical impulses from the AV node. The bundle of His branches into the Purkinje fibers. Purkinje fibers, shown in Figure , are specialized cardiac muscle cells that conduct action potentials into the ventricles, causing the cardiac muscle of the ventricles to contract in a controlled way.
::他的腰包是专门用于导电的心脏肌肉细胞(纤维)的集合,它从AV节点传输电脉冲。他的树枝捆绑到Purkinje纤维中。图中显示,Purkinje纤维是专门的心脏肌肉细胞,可以对腹部进行动作,导致腹部的心脏肌肉以有控制的方式收缩。A schematic representation of the atrioventricular Bundle of His. The SA node is blue, and the AV node is red and visible in the right atrium. The AV node forms the Bundle of His. Sometimes the left and right Bundles of His are called Purkinje fibers.
::以图示显示他的原生骨囊。SA节点是蓝色的,AV节点是红色的,在右端的阁楼中可见。AV节点形成他的捆绑。有时他的左、右两节点被称为Purkinje纤维。The larger round cells on the right are Purkinje fibers. Because of their specializations to rapidly conduct impulses (numerous sodium ion channels and mitochondria and fewer myofibrils than the surrounding muscle tissue), Purkinje fibers take up stain differently than the surrounding muscles cells, and, on a slide, they often appear lighter and larger than their neighbors.
::右侧的较大的圆形细胞是Purkinje纤维。由于它们的专长是快速进行脉冲(无数的离子钠渠道和mitocondria,以及比周围肌肉组织少的近光膜),Purkinje纤维的染色与周围肌肉细胞不同,在幻灯片上,它们看起来往往比周围的肌肉细胞轻和大。The heartbeat is made up of two parts: and relaxation. Systole is the contraction of the heart chambers, which drives blood out of the chambers. Diastole is the period of time when the heart relaxes after contraction. All four chambers of the heart undergo systole and diastole in a timed fashion so that blood is moved forward through the cardiovascular system. For example, ventricular systole is the point at which the ventricles are contracting, and atrial systole is the point at which the atria are contracting. Likewise, ventricular diastole is the period during which the ventricles are relaxing, while atrial diastole is the period during which the atria are relaxing. In general, when referring to systole and diastole, the chambers being referred to are the ventricles, which are shown in Figure .
::心跳由两部分组成: 和放松。 脉搏是心脏室的收缩, 心脏室的收缩导致血液流出室室。 diastole是心脏在收缩后放松的时期。 心脏所有四个室都以一个时钟的方式接受细胞和氨, 血液通过心血管系统向前移动。 例如, 心血管系统是心室收缩的点, 审判系统是手术室收缩的点。 类似地, 心血管异质是心室放松的时期, 而审判性腹膜则是腹部放松的时期。 一般而言, 提到细胞和腹部时, 指的是心室, 图中显示的心室。When the atria contract, the blood gets pushed into the ventricles, which are in diastole. When the ventricles contract (ventricular systole), the blood gets pushed out of the heart.
::当阿提里亚合同签订时,血液被推入直肠中的直肠中,直肠中的直肠中。当直肠中出现直肠(静脉激素),血液就会被挤出心脏。Heart Sounds
::心脏声音In healthy adults, there are two normal heart sounds, often described as a "lub" and a "dub," that occur with each heart beat (lub-dub, lub-dub). In addition to these normal sounds, a variety of other sounds may be heard including heart murmurs or clicks. A medical practitioner uses a stethoscope to listen for these sounds, which gives him or her important information about the condition of the heart.
::在健康成年人中,有两种正常的心声,通常被描述为“阴茎”和“阴茎 ” 。 两种正常的心声出现在每个心跳中(卢布、卢布、卢布、杜巴 ) 。 除了这些正常的心声之外,其他声音也可能被听到,包括心脏杂音或点击。 医生用听诊器来倾听这些声音,这给了他或她关于心脏状况的重要信息。The sound of the heart valves shutting causes the heart sounds, or a heartbeat. The closing of the mitral and tricuspid valves (known together as the atrioventricular valves) at the beginning of ventricular systole causes the first part of the "lub-dub" sound made by the heart as it beats. The second part of the "lub-dub" sound is caused by the closure of the aortic and pulmonic valves at the end of ventricular systole. As the left ventricle empties, its pressure falls below the pressure in the aorta, and the aortic valve closes. Similarly, as the pressure in the right ventricle falls below the pressure in the pulmonary artery, the pulmonic valve closes.
::关闭心脏阀门的声响导致心声或心跳。 关闭在心肺管开始时的线性阀门和三振阀门( 一起被称为动脉阀门) 关闭时, 心肺管的声响的第一部分是心脏在跳动时发出的“ 鲁布- 杜巴” 声的第一部分。 “ 鲁布- 杜布” 声的第二部分是关闭在心血管管尾端的动脉和脉动阀门造成的。 随着左心肺管的气管关闭, 其压力将低于动脉压和动脉阀关闭的压力。 同样, 右心室的压力将低于肺动脉的压力, 肺动脉阀将关闭 。Summary
::摘要-
The heart, blood vessels, and blood are the main components of the cardiovascular system, which moves nutrients, hormones, gases, and wastes to and from body cells and distributes heat to maintain homeostasis.
::心脏、血管和血液是心血管系统的主要组成部分,将营养素、荷尔蒙、气体和废物从身体细胞移动到身体细胞之间,并分配热量以保持全能。 -
Blood flows into the heart through the superior and inferior vena cava, enters the right atrium, and is pumped into the lungs by the right ventricle. Blood returns through the pulmonary vein, flows into the left atrium, and is pumped through the aorta to the rest of the body by the left ventricle.
::血液通过上等和低等的Vena cava进入心脏,进入右中庭,并被右心室抽入肺部。血液通过肺静脉流出,流进左心室,通过左心室从动脉抽入身体其余部分。 -
The rhythmic sequence of contractions of the heart is coordinated by two small groups of cardiac muscle cells called the sinoatrial (SA) and atrioventricular (AV) nodes, although the heart rate can be changed by nervous or hormonal signals, such as during exercise or when perceiving danger.
::心脏收缩的有节奏序列由两组心脏肌肉细胞组成小组协调,称为神经神经细胞(SA)和动静脉结点,尽管心脏速率可以通过神经或荷尔蒙信号改变,例如在锻炼期间或发现危险时。 -
The heartbeat is made up of two parts: muscle contraction (known as systole) and relaxation (known as diastole).
::心跳由两部分组成:肌肉收缩(称为赛斯托尔)和放松(称为赛斯托尔)。
Review
::回顾-
Which ventricle wall is thicker, the left or the right?
::哪个心室壁更厚, 左边还是右边? -
Why are electrical pulses delayed slightly at the AV node before causing a contraction of the ventricles?
::为什么电脉冲在AV节点稍有延迟,然后导致心室收缩? -
What is responsible for the "lub-dub" sound of a normal heartbeat?
::正常心跳的"鲁巴巴巴"声音 是什么责任? -
Why is the heart felt to be usually on the left?
::为什么心通常在左边? -
What affects heart rate?
::什么影响心率?
Explore More
::探索更多 -
The two
atrioventricular (AV) valves
ensure blood flows from the atria to the ventricles and not the other way. The AV valve on the right side of the heart is called the tricuspid valve, and the one on the left side of the heart is called the mitral, or bicuspid, valve.