10.1 肌肉系统组织
Section outline
-
What exactly are muscles?
::什么是肌肉?Does the word "muscle" make you think of the biceps of a weightlifter like the man pictured above? Muscles that move the body are easy to feel and see, but they aren’t the only muscles in the . Many muscles are deep within the body. They form the walls of internal organs such as the heart and stomach . You can flex your biceps like a body builder, but you cannot control the muscles inside you. It’s a good thing that they work on their own without any conscious effort on your part because movements of these muscles are essential for survival.
::“肌肉”一词是否让你想到像上面所描绘的人那样重量提升器的二头肌?移动身体的肌肉很容易感觉和看到,但并不是身体中唯一的肌肉。许多肌肉在体内深处。它们形成心脏和胃等内脏的墙壁。你可以像身体建筑师一样伸展你的肌肉,但你无法控制你的肌肉。一件好事是,它们自己工作,而你没有做出任何有意识的努力,因为这些肌肉的移动对于生存至关重要。Muscle Tissues
::肌肉组织The muscular system is the biological system that allows humans to move. The muscular system, in vertebrates , is controlled through the . Much of your muscle movement occurs without your conscious control and is necessary for your survival. The contractions of your heart and the intestinal movements, called peristalis, that push food through your are examples of involuntary muscle movements. Involuntary muscle movement is controlled by the autonomic nervous system . Voluntary muscle contractions are used to move the body and can be finely controlled, such as the pincer-type movements of the fingers that are needed to pick up chess pieces or the gross movements of legs, arms, and the torso that are needed in skating, as shown in Figure . Voluntary muscle movement is controlled by the somatic nervous system .
::肌肉系统是允许人类移动的生物系统。在脊椎动物体内,肌肉系统通过它来控制。你的肌肉运动大部分是在没有意识控制的情况下进行的,对于你的生存来说是必要的。你的心脏收缩和肠道运动(称为peristalis,将食物刺穿你的肠道运动)是非自愿肌肉运动的例子。非自愿肌肉运动由自主神经系统控制。自愿肌肉收缩被用来移动身体,并且可以受到精细控制,例如摘取象棋片所需的手指的针形运动,或滑雪所需的腿、手臂和手的毛运动,如图所示。自愿肌肉运动由心神经系统控制。You need muscles to play chess. Playing chess requires fine motor movement, but not a lot of gross muscle movement. Skating, on the other hand, requires a lot of gross muscle movement of the limbs and the entire body.
::玩象棋需要肌肉。 玩象棋需要良好的运动运动,但并不需要大量的肌肉运动。 而滑冰则需要四肢和整个身体的肌肉运动。Each muscle in the body is composed of specialized structures called muscle fibers . Muscle fibers are long, thin that have a special talent that other cells do not have—they are able to contract. Muscles, where attached to or internal organs and , are responsible for movement. Nearly all movement in the body is the result of muscle contractions. Exceptions to this are the actions of cilia , the flagellum on cells, and the amoeboid movements of some white blood cells .
::肌肉纤维长薄,具有其他细胞所不具备的特殊才华——它们能够收缩。肌肉肌肉是附属于或内部器官的,对运动负有责任。身体中几乎所有运动都是肌肉收缩的结果。除了这种作用外,细胞上的、细胞上的和一些白血细胞的分子运动。There are three types of muscle tissue in the body: skeletal, smooth, and cardiac.
::身体有三种肌肉组织:骨骼、光滑和心脏。-
is usually attached to the skeleton. Skeletal muscles are used to move the body. They generally contract voluntarily (controlled by the somatic nervous system), although they can also contract involuntarily through
reflexes
.
::骨骼肌肉通常用来移动身体,一般是自愿结合(由身体神经系统控制),虽然也可以通过反射非自愿结合。 -
Smooth muscle
is found within the walls of organs and structures such as the
esophagus
, stomach, intestines,
bronchi
,
uterus
,
urethra
,
bladder
, and blood vessels. Unlike skeletal muscle, smooth muscle is involuntary muscle, which means it is not under your conscious control.
::在食道、胃、肠、支气管、子宫、尿道、膀胱和血管等器官和结构的墙壁中,可以找到滑动的肌肉。 与骨骼肌肉不同,滑动的肌肉是非自愿的肌肉,这意味着它不在你的自觉控制之下。 -
Cardiac muscle
is also an involuntary muscle, but it is a specialized kind of muscle found only within the heart.
::心肌也是一种非自愿的肌肉, 但它是一种特殊的肌肉 只能在心脏里找到。
Cardiac and skeletal muscles are striated (they have striations ), meaning they contain highly-regular arrangements of bundles of fibers that give them a “striped” appearance. Smooth muscle does not have such bundles of fibers and is non-striated. While skeletal muscles are arranged in regular, parallel bundles, cardiac muscle fibers connect at branching, irregular angles. Skeletal muscle contracts and relaxes in short, intense bursts, whereas cardiac muscle contracts constantly for 70 to 80 years (an average life span) or even longer.
::心肌和骨骼肌肉被撕裂(它们有裂痕),这意味着它们含有高度常规的纤维捆绑安排,使它们具有“撕裂”的外观。光滑肌肉没有这种纤维捆绑,而且没有裂痕。骨骼肌肉安排在正常的、平行的捆绑中,心脏肌肉纤维连接在分枝、非正常角度上。骨骼肌肉在短、密集的连发中进行合同和放松,而心脏肌肉持续约约70至80年(平均寿命)甚至更长。A frontal view of the major skeletal muscles. You would not see smooth and cardiac muscles included in diagrams of the muscular system because such diagrams usually show only the muscles that move the body (skeletal muscles).
::对主要骨骼肌肉的正面视图。 您看不到肌肉系统图中包含的光滑和心脏肌肉, 因为这样的图表通常只显示移动身体的肌肉( 骨骼肌肉 ) 。Skeletal Muscle
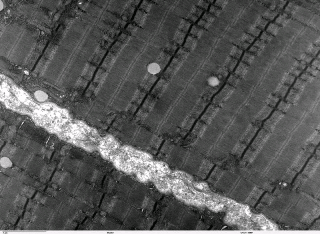
::骨骼肌肉Skeletal muscle, which is attached to bone, is responsible for body movements and body posture. There are approximately 639 skeletal muscles in the human body, all under voluntary control. Some are shown in Figure . The basic units of skeletal muscles are muscle cells that have many . Each cell acts independently of its neighboring muscle cells. These cells also contain light and dark stripes called striations, which are shown in Figure . The striations are a result of the orientation of the contractile proteins inside the cells. On average, adult males are made up of 40 to 50 percent skeletal muscle tissue , and an adult female is made up of 30 to 40 percent skeletal muscle tissue.
::与骨头相连的骨骼肌肉负责身体运动和身体姿势,在人体中约有639个骨骼肌肉,都处于自愿控制之下,图中显示了其中一些。骨骼肌肉的基本单元是肌肉细胞,有许多肌肉细胞。每个细胞与相邻的肌肉细胞不相干。这些细胞还包含光和暗的条纹,如图所示。这些条纹是细胞内肉状蛋白取向的结果。平均而言,成年男性占40%至50%的骨骼肌肉组织,成年女性占30%至40%的骨骼肌肉组织。A micrograph of skeletal muscle. The stripy appearance of skeletal muscle tissue is due to long protein filaments that run the length of the fibers.
::骨骼肌肉的显微镜 骨骼肌肉组织有条纹的外观Smooth Muscle
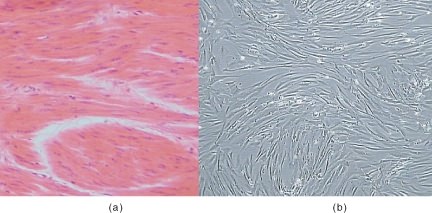
::平滑肌肉Smooth muscle is found in the walls of the hollow internal organs such as blood vessels, the intestinal tract, the urinary bladder , and the uterus. It is under the control of the autonomic nervous system. Unlike skeletal muscle, smooth muscle cells do not have striations (smooth muscle is called non-striated muscle). Smooth muscle cells are spindle-shaped, have one central nucleus, and are generally arranged in sheets or bundles rather than the regular grouping that skeletal muscle cells form. Smooth muscle cells are connected by gap junctions, which are little pores or gaps in the that link adjoining cells, allowing for quick passage of chemical messages between cells. Smooth muscle is very different from skeletal muscle and cardiac muscle in terms of structure and function, as shown in Figure . Smooth muscle contracts slowly and rhythmically.
::滑动肌肉在血管、肠道、尿囊和子宫等空心内器官的墙壁中发现,它受自主神经系统控制。与骨骼肌肉不同,滑动肌肉细胞没有裂痕(肌肉称为非裂纹肌肉)。滑动肌肉细胞是脊椎形,有一个中央核,一般排列在板块或捆包中,而不是骨骼肌肉细胞形成的正常组合中。滑动肌肉细胞通过隔缝连接而连接,这些交叉点是小孔或紧接细胞的缝隙,使得化学信息能够在细胞之间快速传递。如图所示,滑动肌肉在结构和功能方面与骨骼肌肉和心肌肉有很大不同。滑动肌肉缓慢和有节奏。Smooth muscle. The appearance of smooth muscle is very different from skeletal and cardiac muscle. The muscle protein fibers within smooth muscles are arranged very differently than the protein fibers of skeletal or cardiac muscles, shown in (a). The spindly shape of smooth muscle cells can be seen in (b).
::滑动肌肉。光滑肌肉的外观与骨骼和心脏肌肉大不相同。光滑肌肉中的肌肉蛋白纤维与(a)中所示的骨骼或心脏肌肉蛋白纤维的排列非常不同。(b)中可以看到光滑肌肉细胞的圆形形状。Cardiac Muscle
::心脏肌肉Cardiac muscle, which is found in the walls of the heart, is also under the control of the autonomic nervous system. A cardiac muscle cell has characteristics of both a smooth muscle and a skeletal muscle cell. It has one central nucleus, similar to smooth muscle, but is striated like skeletal muscle. The cardiac muscle cell is rectangular in shape, as can been seen in Figure . The contraction of cardiac muscle is involuntary, strong, and rhythmical. Cardiac muscle has many adaptations that makes it highly resistant to fatigue. For example, it has the largest number of per cell of any muscle type. The mitochondria supply the cardiac cells with energy for constant movement. Cardiac cells also contain myoglobins (oxygen-storing pigments) and are provided with a large amount of nutrients and oxygen by a rich supply.
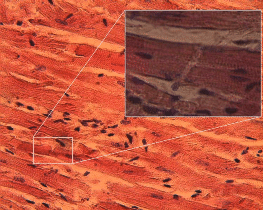
::在心脏壁壁上发现的心肌也处于自主神经系统的控制之下。心脏肌肉细胞具有光滑肌肉和骨骼肌肉细胞的特性。它有一个中核,类似于光滑肌肉,但像骨骼肌肉一样被撕裂。心肌肉细胞的形状是矩形的,如图所示。心肌的收缩是非自愿的、强的和有节奏的。心肌有许多适应性,使其对疲劳有很强的抵抗力。例如,它拥有每个肌肉型细胞中数量最多的细胞。米托孔迪亚为心脏细胞提供恒定运动的能量。心肌细胞还含有蛋白质(氧的发色素),并且由丰富的供应提供大量营养素和氧。Cardiac muscle is similar to skeletal muscle in chemical composition and action. However, the structure of cardiac muscle is different in that the muscle fibers are typically branched, like a tree branch, and connect to other cardiac muscle fibers through intercalated discs, which are a type of gap junction. A close-up of an intercalated disc is shown in Figure .
::心肌在化学成分和作用方面与骨骼肌肉相似,但心脏肌肉的结构则不同,因为肌肉纤维通常像树枝一样被分割开来,通过隔热圆盘与其他心脏肌肉纤维相连,这种圆盘是一种隔热连接。图中显示了隔热圆盘的闭合情况。Cardiac muscle. Cardiac muscle fibers are connected together through intercalated discs.
::心血管肌肉 心血管肌肉纤维通过隔热盘连接在一起Summary
::摘要-
639 muscles are skeletal muscles; these are voluntarily controlled, striated, and attached to bones.
::639个肌肉是骨骼肌肉;这些肌肉是自愿控制、磨碎和附在骨头上。 -
The muscles lining internal organs are composed of non-striated cells and are controlled by the autonomic nervous system.
::内部肌肉内衬器官由非分离细胞组成,由自主神经系统控制。 -
Cardiac muscles are specialized striated muscles that are involuntarily controlled and found only in the heart.
::心肌是专门断裂的肌肉,非自愿控制,只存在于心脏中。
Review
::回顾-
What are the similarities and differences between the three muscle types?
::三种肌肉类型之间有什么相似之处和不同之处? -
What are intercalated discs?
::什么是隔音盘?
-
is usually attached to the skeleton. Skeletal muscles are used to move the body. They generally contract voluntarily (controlled by the somatic nervous system), although they can also contract involuntarily through
reflexes
.