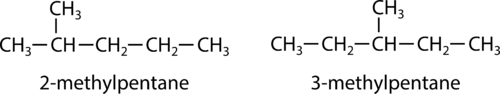25.6 结构异构体和立体异构体
Section outline
-
What difference does the isomer make?
::异构物有什么区别?As we get more into the complexities of organic chemistry , we will see how molecular shape affects reactions. One common reaction for alkenes is the addition of hydrogen across the double bond to form the corresponding alkane . Because of the geometry of the reaction, the different 2-butene shapes have different heats of reaction. These differences are important both from a theoretical standpoint as well as from the point of view of industrial applications. Greater energy requirements mean a higher cost and a more expensive product.
::随着我们更深入地了解有机化学的复杂性,我们将看到分子形状是如何影响反应的。对于代谢者来说,一种常见的反应是双环氢添加形成相应的烷。由于反应的几何结构,不同的二丁烷形状有不同的反应热。从理论角度和从工业应用的角度来看,这些差异都很重要。更高的能源要求意味着更高的成本和更高的产品成本。Isomers
::异构人One of the interesting aspects of organic chemistry is that it is three-dimensional. A molecule can have a shape in space that may contribute to its properties. Molecules can differ in the way the atoms are arranged – the same combination of atoms can be assembled in more than one way. These compounds are known as isomers. Isomers are molecules with the same , but different arrangements of atoms. We will look at some possibilities for alkanes and alkenes.
::有机化学的一个有趣的方面是它是三维的。分子在空间中可以有一个形状,可以促进其特性。分子在空间中可以有不同的形状。分子在原子的排列方式上可以有所不同 — — 原子的组合可以不只一种方式组合。这些化合物被称为异构体。 异构体是同一种分子,但原子的安排不同。我们将研究对 alkanes 和 alkenes 的一些可能性。Structural Isomers
::结构异体A structural isomer is one in which two or more or organic compounds have the same molecular formulas but different structures. The two pentane molecules below differ only in the location of the methyl group.
::结构异构体是一种结构异构体,其中两个或两个以上或有机化合物具有相同的分子式,但结构不同。Alkenes can also demonstrate structural isomerism. In alkenes, there are multiple structural isomers based on where in the chain the double bond occurs. The condensed structural formulas of 1-butene and 2-butene show this.
::Alkenes也能够证明结构性异构主义。在alkees,基于链条中发生双重结合的地点存在多种结构性异构体。一丁烯和二丁烯的压缩结构公式证明了这一点。The number in the name of the alkene refers to the lowest numbered carbon in the chain that is part of the double bond.
::平方体名称中的数字指作为双重保证书一部分的链条中最低编号的碳。Geometric Isomers
::几几何数With a molecule such as 2-butene, a different type of isomerism called geometric isomerism can be observed. Geometric isomers are isomers in which the order of bonding is the same but the arrangement of atoms in space is different. Geometric isomers are also referred to as stereoisomers . The double bond in an alkene is not free to rotate because of the nature of the pi bond . Therefore, there are two different ways to construct the 2-butene molecule. The image below shows the two geometric isomers, called cis -2-butene and trans -2-butene.
::用二丁烷这样的分子,可以观察到一种叫几何异构体的不同类型的异构体,即几何异构体。几何异构体是各种异构体,其结合的顺序相同,但空间原子的排列则不同。几何异构体也称为立体异构体。单极异构体的双倍结合不能自由旋转,因为pi联结的性质。因此,建造二丁分子有两种不同的方式。下面的图像显示两种几何异构体,即cis-2丁烷和trans-2丁烷。The cis isomer has the two single hydrogen atoms on the same side of the molecule, while the trans isomer has them on opposite sides of the molecule. In both molecules, the bonding order of the atoms is the same. In order for geometric isomers to exist, there must be a rigid structure in the molecule to prevent free rotation around a bond. If the double bond in an alkene was capable of rotating, the two geometric isomers above would not exist. In addition, the two carbon atoms must each have two different groups attached in order for there to be geometric isomers. Propene has no geometric isomers because one of the carbon atoms has two single hydrogens bonded to it.
::晶体异构体在分子的同一侧有两个单一氢原子,而反向异构体则在分子的对面有这两个氢原子。在这两个分子中,原子的联结顺序相同。为了使几何异构体存在,分子必须有一个僵硬的结构,以防止在联结上自由旋转。如果一个烷的双倍结合能够旋转,上面的两个几何异构体将不存在。此外,两个碳原子必须各有两个不同的组,才能有几何异构体。Propene没有几何异构体,因为其中一个碳原子有两种单独的氢。Physical and chemical properties of geometric isomers are generally different. While cis -2-butene is a polar molecule , trans -2-butene is nonpolar. or irradiation with light can be used to bring about the conversion of one geometric isomer to another. The input of energy must be large enough to break the pi bond between the two carbon atoms, which is weaker than the sigma bond . At that point, the now single bond is free to rotate and the isomers can interconvert.
::几何异构体的物理和化学特性一般不同,虽然cis-2-丁烷是一种极分子,但转二-丁烷是非极分子。 或光线辐照可用于将一个几何异构体转换成另一个几何异构体。 能量的输入量必须足够大,足以打破两个碳原子之间的pi联系,这两个原子比西格玛联系弱。 在这一点上,现在的单个连接可以自由旋转,而异构体可以相互转换。As with alkenes, alkynes display structural isomerism beginning with 1-butyne and 2-butyne. However, there are no geometric isomers with alkynes because there is only one other group bonded to the carbon atoms that are involved in the triple bond.
::和 alkenes一样, alkynes也表现出结构性的异构主义,从1-丁和2-丁开始。 但是,没有以 alkynes 进行几何异构体,因为与碳原子捆绑在一起的碳原子中,只有另一个组与三重结合有关。Review
::回顾-
What is a structural isomer?
::什么是结构性异构体? -
What is a geometric isomer?
::什么是几何异构体? -
What is another name for a geometric isomer?
::几何异构体的另一个名称是什么? -
Could 1-butene have geometric isomers?
::一丁二烯能有几何异构体吗?
Explore More
::探索更多Use the resource below to answer the questions that follow.
::利用以下资源回答以下问题。-
What does the molecular formula tell us?
::分子公式告诉我们什么? -
What does the structural formula tell us?
::结构公式告诉我们什么? -
What do you add to the name if two double bonds are present in the molecule?
::如果分子中存在两个双倍债券, 你会给名称添加什么?
-
What is a structural isomer?