25.8 芳烃
章节大纲
-
Can a dream affect reality?
::梦想能影响现实吗?Friedrich Kekulé was a German chemist in the 1800s. He supposedly was thinking about the structure of the benzene ring as he fell asleep. While asleep, he dreamed of a snake eating the ring's tail. He used this idea to propose the cyclic structure for benzene. Whether or not he actually had this dream has been debated ever since. Whatever really happened, the tale has persisted until today.
::Friedrich Kekulé在1800年代曾是德国化学家。 他应该是在睡着的时候想到苯环的结构。 当他睡着了的时候,他梦见一只蛇吃着戒指的尾巴。 他用这个想法来提议苯环结构。 他是否真的有这个梦想,从那时起就一直在争论。不管到底发生了什么,故事一直持续到今天。Aromatic Hydrocarbons
::芳芳烃烃Benzene is the parent of the large family of organic compounds known as aromatic compounds. Unlike cyclohexane, benzene only contains six hydrogen atoms, giving the impression that the ring is unsaturated and each carbon participates in one double bond. Two different structures with alternating single and double bonds around the ring can be written for benzene.
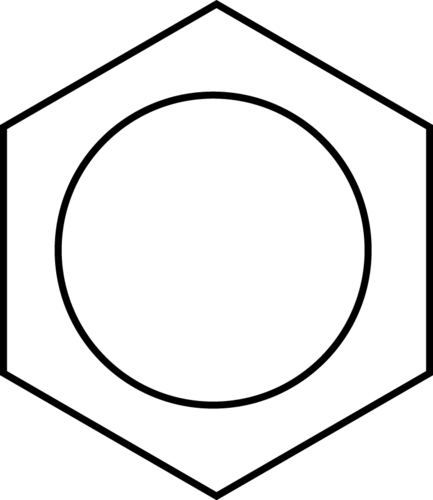
::苯是被称为芳香化合物的有机化合物大家族的母体。 与六氯环己烷不同的是,苯仅含有六个氢原子,给人的印象是,环是不饱和的,每个碳都参与一个双联体。 环周围有交替单和双联体的两种不同的结构可以写成苯。In benzene, the true bonding between carbon atoms is neither a single nor a double bond. Rather, all of the bonds are a hybrid of a single and double bond. In benzene, the pi bonding electrons are free to move completely around the ring. Delocalized electrons are electrons that are not confined to the bond between two atoms, but are instead allowed to move between three or more. The delocalization of the electrons in benzene can best be shown by showing benzene with a ring inside the hexagon, with the hydrogen atoms understood.
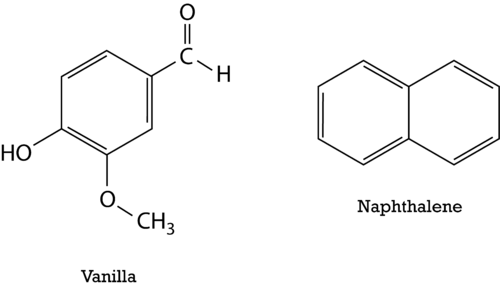
::在苯,碳原子之间的真正联系既不是单一的,也不是双重的。相反,所有债券都是单一的和双重的结合体。在苯,pi的连接电子可以完全在环周围移动。已迁移的电子不局限于两个原子之间的连接,而是允许在三个或三个以上之间移动。在苯中,电子的迁移最好通过在六边形内显示苯和环来显示,而氢原子能理解。Delocalization of the electrons makes for a more stable molecule than a similar molecule that does not have delocalized electrons. Benzene is a more stable and less reactive compound than straight-chain hexenes. The sp 2 hybridization of the carbon atoms results in a planar molecule as opposed to the puckered structure of cyclohexane. Benzene rings are common in a great number of natural substances and biomolecules. The figure below shows the structural formulas for vanilla and naphthalene. Naphthalene is a chemical which is commonly used in mothballs.
::电子离地化使分子比类似分子更稳定,而类似的分子没有去地化电子。苯比直链六氯苯更稳定,反应性更小。碳原子的Sp2混合化形成一个平面分子,而不是环氧环已烷结构。苯环在大量自然物质和生物分子中很常见。下图显示了香草和氯化萘的结构公式。甲苯是一种常见于摩尔球的化学物质。Nomenclature of Aromatic Compounds
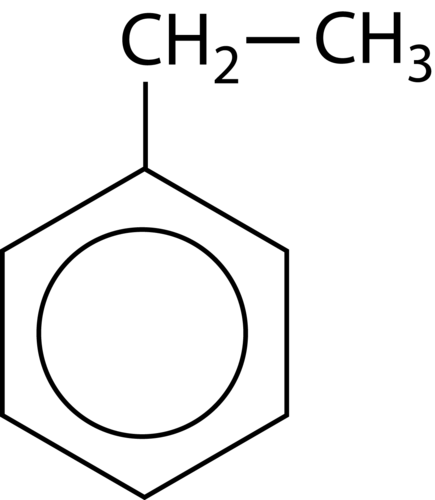
::芳香化合物的命名The simplest aromatic compounds are benzene rings with one substituent replacing one of the hydrogen atoms. If this substituent is an alkyl group , it is named first, followed in one word with “benzene”. The molecule shown below is therefore called ethylbenzene.
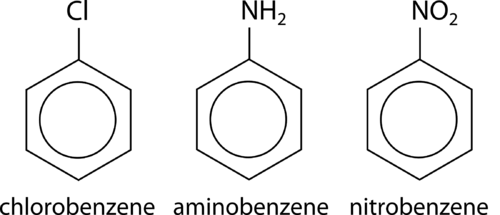
::最简单的芳香化合物是苯环,用一种替代物替代氢原子。如果替代物是一个烷基组,则首先命名,然后用“苯”一词,下面显示的分子称为乙基苯。Substituents can be groups other than alky groups. If a chlorine atom were substituted for a hydrogen, the name becomes chlorobenzene. An –NH 2 group is called an amino group, so the corresponding molecule is called aminobenzene, often referred to as aniline. An –NO 2 group is called a nitro group and so the third example below is nitrobenzene.
::替代分子可以是除藻类以外的组。 如果用氯原子代替氢,则代之以氯原子。 氯原子就变成了氯代谢物。 一种 -NH2 组被称为氨基氨基亚基苯组,因此相应的分子被称为氨基苯,通常称为厌食物。 一种 -NO2 组被称为硝基苯组,下面第三个例子是硝基苯。
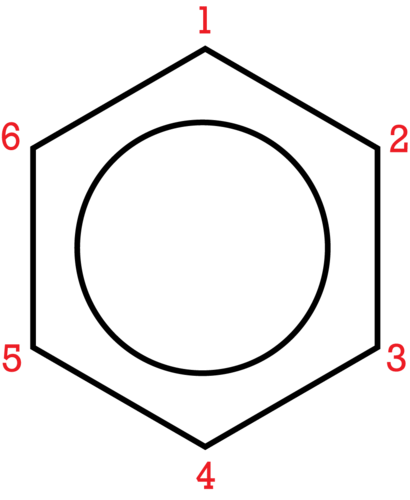
If more than one substituent is present, their location relative to each other can be indicated by numbering the positions on the benzene ring.
::如果存在不止一个替代物,其相对位置可通过对苯环上的位置编号来标明。The number of the carbon location then precedes the name of the substituent in the overall name, with the numbers separated by a comma. As with branched alkanes , the system requires that the numbers be the lowest possible and that prefixes be used for more than one of the same substituent. If there are different substituents, the first in alphabetical order is given the lower number and listed first. The structures below are called 1,2-dimethylbenzene and 1-ethyl-4-methylbenzene.
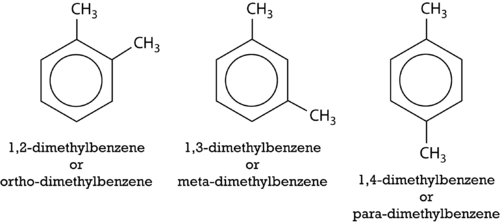
::然后,碳位置的编号先于总名称中的替代体的名称,数字用逗号分开。与分支藻类的情况一样,该系统要求数字尽可能低,而且前缀用于同一个替代体中的多个替代体。如果有不同的替代体,则第一个按字母顺序排列,先给出较低的数字,然后列出。以下结构称为1,2-二甲基苯和1-乙基-4-甲基苯。An alternate system for naming di-substituted benzene rings uses three different prefixes: ortho , meta , and para . If two groups are in the ortho position, they are on adjacent carbon atoms. The meta positioning refers to being in a 1, 3 arrangement. The para positioning refers to being in a 1, 4 arrangement. Shown below are the three possibilities for dimethylbenzene, also called xylene.
::用于命名二代苯环的替代系统使用三种不同的前缀:正弦、元和第2款。如果两个组处于正弦位置,它们就位于相邻的碳原子上。代位定位是指在1,3项安排中。代位定位是指在1,4项安排中。以下显示二甲基苯的三种可能性,也称为二苯。Lastly, a benzene ring missing one hydrogen atom (−C 6 H 5 ) can itself be considered the substituent on a longer chain of carbon atoms. That group is called a phenyl group and so the molecule below is called 2-phenylbutane.
::最后,一个缺少一个氢原子(-C6H5)的苯环本身可被视为碳原子较长链条上的替代物,该组称为苯基组,下面的分子称为2-苯丁烷。Review
::回顾-
Describe the pi bonding electrons in aromatic compounds.
::描述芳香化合物中的 pi 连接电子。 -
What is the rule for numbering substituents on the ring?
::戒指上的替代人编号规则是什么? -
How is numbering affected if there is more than one type of substituent group?
::如果有不止一种替代群体,编号会如何受到影响?
-
Describe the pi bonding electrons in aromatic compounds.