25.9 酒精
Section outline
-
How cold can it get?
::它会有多冷?Water freezes at 0°C which creates problems for cars in the winter. The water in the engine would freeze and crack the engine block. To prevent this, antifreeze is added to lower the point of the . The most common antifreeze is an alcohol known as propylene glycol. It has largely replaced the much more toxic ethylene glycol. Methanol can also be used as an antifreeze, mainly in windshield wiper fluid .
::0°C的水冻结在零°C,这给冬季的汽车造成问题。发动机中的水会冻结和破碎发动机块。为了防止这种情况,将防冻剂添加到较低的点。最常见的防冻剂是被称为丙烯甘醇的酒精。它在很大程度上取代了毒性更大的乙烯甘醇。甲醇也可以用作抗冻剂,主要用于挡风玻璃擦拭液。Alcohols
::酒精酒精An alcohol is an organic compound that contains one or more hydroxyl (−OH) groups. The general formula for alcohols is R−OH. Do not confuse alcohols with inorganic bases that contain the hydroxide (OH − ). The –OH group in an alcohol is covalently bonded to a carbon and does not ionize in solution. The steps for naming alcohols are listed below.
::酒精是一种有机化合物,含有一种或多种氢氧基(-OH)组。酒精的一般配方是R-OH。不要将酒精与含有氢氧化物(OH)的无机基混为一谈。酒精中的-OH组与碳交织在一起,不离子溶解。命名酒精的步骤列于下文。-
Name the parent compound by finding the longest continuous carbon atom chain that also contains the hydroxyl group. If there is one hydroxyl group in the molecule, change the final –
e
in the name of the
alkane
to –
ol
. If there is more than one hydroxyl group, use the full name of the alkane and add a suffix to indicate the number of hydroxyl groups. For example, two hydroxyl groups is –
diol
, three is –
triol
, etc.
::找到含有氢氧基组的最长连续碳原子链,从而给母体化合物命名。 如果分子中有一个氢氧基组,则将最终的-e-e 以烷的名称改为-ol。 如果有一个以上的氢氧基组,则使用烷的全名,并添加一个后缀来表示氢氧基组的数目。 例如,两个氢氧基组为-二醇,三个为-三醇等。 -
Number the carbon chain in a way that makes the sum of hydroxyl numbers as low as possible.
::将碳链编号为尽可能低的 氢氧基数总和。 -
Add the numerical prefix into the name before the name of the alcohol.
::将数字前缀添加到酒精名称之前的名称中。 -
Separate numbers with commas and separate numbers from names or prefixes with a hyphen. There are no spaces in the name.
::带有逗号的单独数字和带有连字符的名称或前缀的单独数字。名称中没有空格。
Following are three examples of alcohols and their IUPAC names.
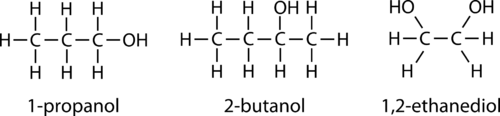
::以下是酒精及其国际化联名称的三个例子。Aliphatic alcohols can be classified according to the number of R groups attached to the carbon with the hydroxyl group. If one R group is attached to that carbon, the alcohol is a primary alcohol. If two R groups are attached, the alcohol is a secondary alcohol. If three R groups are attached, the alcohol is a tertiary alcohol. Shown below is an example of each. The primary alcohol is 1-propanol, the secondary alcohol is 2-butanol, and the tertiary alcohol is 2-methy-2-propanol.
::脂类酒精可按照与氢氧基组碳相连的R组数量进行分类,如果一个R组与碳相连,则酒精为主要酒精;如果两个R组与碳相连,则酒精为次要酒精;如果三个R组相连,则酒精为第三级酒精;以下所示为每种酒精的一个例子,主要酒精为1-丙醇,次要酒精为2-丁醇,第三级酒精为2-methy-2-丙醇。Properties of Alcohols
::酒精成分属性The smallest and lightest alcohols (methanol, ethanol, propanol) are completely soluble in water in all proportions. In a solution, the hydroxyl groups of alcohol molecules and the water molecules form with each other, resulting in complete miscibility. However, as the length of the carbon chain increases, the decreases. The solubility of 1-butanol is 7.4 g per 100 g of water, while that of 1-pentanol is 2.7 g per 100 g water, and 1-octanol is 0.06 g per 100 g water. The carbon chain portion of the larger alcohol molecule is non-polar and leads to the decreased solubility of the overall compound.
::最小和最轻的酒精(甲醇、乙醇、丙醇)在水中可以完全溶解,在溶液中,酒精分子的氢氧基组和水分子形成,导致完全不易腐化,然而,随着碳链长度的增加,1-丁醇的溶解率为每100克水7.4克,1-苯甲醇的溶解度为每100克水2.7克,1-辛醇为每100克水0.06克,更大的酒精分子的碳链部分为非极化,导致整个化合物的溶解性下降。The presence of hydrogen bonds in alcohols also explains the relatively high boiling points of alcohols compared to alkanes of similar (see Table ).
::酒精中存在氢联结也解释了酒精沸点相对较高的原因(见表)。Boiling Point Comparison of Alkanes and Alcohols Compound
::化合物化合物Formula
::公式公式公式Molar Mass (g/mol)
::Molar质量(克/摩尔)Boiling Point (°C)
::沸点(°C)ethane
::乙烷CH 3 CH 3
::CH3CH3 CH3 CH3 CH3 CH3 CH3 CH3 CH3 CH3 CH3 CH3 CH3 CH3 CH3 CH3 CH3 CH3 CH3 CH3 CH3 CH3 CH3 CH3 CH332
-88
methanol
::甲醇CH 3 OH
::CH3O CH3O CH3O CH3O CH3O CH3O CH3O CH3O CH3O CH3O CH3O CH CH3O CH3O CH CH3O CH CH3O CH CH3O CH CH3O CH CH3O CH CH3O CH CH3O CH CH3O CH CH CH3O CH CH CH CH3O CH CH CH CH CH3O CH CH CH CH CH CH CH CH CH CH CH CH CH CH CH CH CH CH CH CH CH CH CH CH CH CH CH CH CH CH CH CH CH CH CH CH CH CH CH CH CH CH CH CH CH CH CH CH CH CH CH CH CH CH CH CH CH CH CH CH CH CH CH CH CH CH CH CH CH CH CH CH CH CH CH CH CH CH CH CH CH CH CH CH CH CH CH CH CH CH CH CH CH CH CH CH CH CH CH CH CH CH CH CH CH CH CH CH CH CH CH CH CH CH CH CH CH CH CH CH CH CH CH CH CH CH CH CH CH30
64.7
propane
::丙烷CH 3 CH 2 CH 3
::CH3CH2CH3 CH3 CH3 CH3 CH3 CH2CH3 CH3 CH3 CH3 CH3 CH3 CH3 CH2CH3 CH3 CH3 CH3 CH3 CH3 CH3 CH3 CH2CH3 CH3 CH3 CH3 CH3 CH3 CH2CH3 CH3 CH3 CH3 CH3 CH3 CH3 CH3 CH2CH3 CH3 CH3 CH3 CH3 CH3 CH3 CH3 CH3 CH3 CH2CH3 CH3 CH3 CH3 CH3 CH3 CH3 CH3 CH3 CH3 CH3 CH3 CH3 CH3 CH3 CH3 CH2CH3 CH3 CH3 CH3 CH3 CH3 CH3 CH3 CH3 CH3 CH3 CH3 CH3 CH3 CH3 CH3 CH3 CH3 CH3 CH3 CH3 CH3 CH3 CH3 CH3 CH3 CH3 CH3 CH3 CH3 CH3 CH3 CH3 CH3 CH344
-42.1
ethanol
::乙醇CH 3 CH 2 OH
::CH3CH2OH(CH3CH2OH)46
78.3
Only weak London dispersion forces hold molecules of non-polar alkanes together in the liquid phase . Consequently, less energy is required to break these molecules away from the surface of the liquid and turn them into a vapor . The stronger between alcohol molecules means that more energy is required to convert the liquid to vapor, and boiling points are therefore high.
::只有弱的伦敦分散力量在液相中将非极alalkanes分子聚集在一起。 因此,将这些分子从液体表面分裂出来,将其变成蒸发器需要更少的能量。 酒精分子之间的强度越强意味着将液体转化为蒸发器需要更多能量,因此沸点也非常高。Review
::回顾-
What is the general formula for an alcohol?
::酒精的一般配方是什么? -
Why are alcohols soluble in water?
::为什么酒精可以在水中溶解? -
What is the boiling point of ethanol?
::乙醇的沸点是什么?
-
Name the parent compound by finding the longest continuous carbon atom chain that also contains the hydroxyl group. If there is one hydroxyl group in the molecule, change the final –
e
in the name of the
alkane
to –
ol
. If there is more than one hydroxyl group, use the full name of the alkane and add a suffix to indicate the number of hydroxyl groups. For example, two hydroxyl groups is –
diol
, three is –
triol
, etc.