4.3 牢房的变异
Section outline
-
Bacteria Attack!
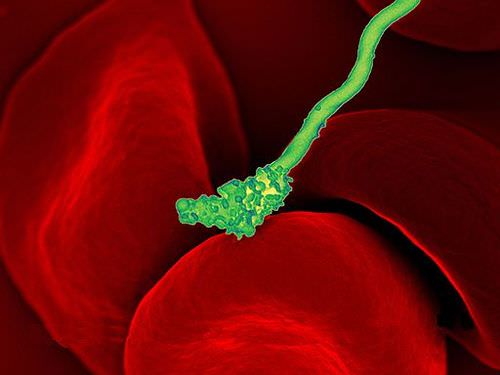
::细菌攻击!This colorful image shows a bacterial ( in green) attacking human red blood cells . The causes a disease called relapsing fever. The bacterial and human cells look very different in size and shape. Although all living cells have certain things in common — such as a plasma membrane and cytoplasm — different types of cells, even within the same organism , may have their own unique structures and functions. Cells with different functions generally have different shapes that suit them for their particular job. Cells vary not only in shape, but also in size, as this example shows. In most organisms, however, even the largest cells are no bigger than the period at the end of this sentence. Why are cells so small?
::这种多彩的图像显示了一种细菌(绿色)攻击人类红细胞,造成一种称为复发热的疾病。细菌和人类细胞在大小和形状上看起来大不相同。虽然所有活细胞都有某些共同之处,例如等离子膜和细胞图象,但不同种类的细胞,即使在同一个生物体中,可能都有它们自己的独特的结构和功能。具有不同功能的细胞一般有不同的形状,适合它们的特殊工作。细胞不仅形状不同,大小也不同,如本例所示。在大多数生物体中,甚至最大的细胞也不比本句结尾的时期大。为什么细胞这么小?Explaining Cell Size
::解释单元格大小Most organisms, even very large ones, have microscopic cells. Why don' t cells get bigger instead of remaining tiny and multiplying? What limits cell size?
::大部分生物,甚至非常大的生物,都有显微镜细胞。为什么细胞不会变得更大,而不是保持微小和倍增?什么限制细胞大小?Once you know how a cell functions, the answers to these questions are clear. To carry out life processes, a cell must be able to quickly pass substances in and out of the cell. For example, it must be able to pass nutrients and oxygen into the cell and waste products out of the cell. Anything that enters or leaves a cell must cross its outer surface. The size of a cell is limited by its need to pass substances across that surface.
::一旦知道一个细胞的功能,这些问题的答案是明确的。为了进行生命过程,一个细胞必须能够迅速将物质从细胞中传入和传出。例如,它必须能够将养分和氧气传递到细胞中,从细胞中排出废物产品。进入或离开细胞的任何物质都必须穿过其外表面。细胞的大小因需要通过物质而受到限制。Look at the two cubes in the figure . As this figure shows, a larger cube has less surface area relative to its volume than a smaller cube. This relationship also applies to cells — a larger cell has less surface area relative to its volume than a smaller cell. A cell with a larger volume also needs more nutrients and oxygen, and produces more wastes. Because all of these substances must pass through the surface of the cell, a cell with a large volume will not have enough surface area to allow it to meet its needs. The larger the cell is, the smaller its ratio of surface area to volume, and the more difficult it will be for the cell to get rid of its wastes and take in necessary substances. This is what limits the size of the cell.
::查看图中的两个立方体 。 如图所示, 一个较大的立方体的表面积比一个较小的立方体的面积小。 这个关系也适用于细胞—— 一个较大的细胞比一个较小的细胞的面积小,一个更大的细胞比其体积小。一个体积大的细胞也需要更多的养分和氧气,并产生更多的废物。由于所有这些物质都必须穿过细胞的表面,一个体积大的细胞将没有足够的表面面积来满足其需要。细胞的面积越大,其表面积与体积的比例越小,细胞摆脱其废物和吸收必要物质的难度就越大。这就是限制细胞大小的原因。
Surface Area to Volume Comparison. A larger cube has a smaller surface area (SA) to volume (V) ratio than a smaller cube. This also holds true for cells, which limits how large they can be.
::面积与体积比较。更大的立方体的表面积(SA)与体积(V)之比小于一个立方体。对于细胞来说也是如此,这限制了它们的体积。Cell Form and Function
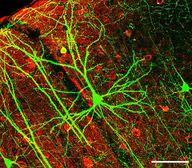
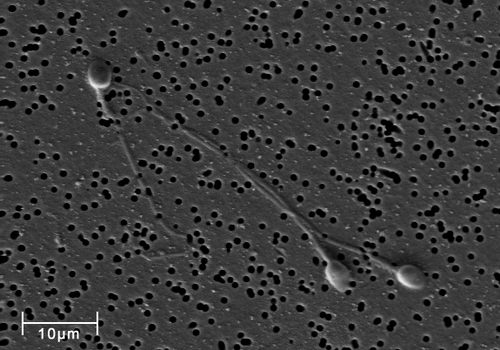
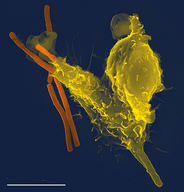
::单元格窗和函数Cells with different functions often have varying shapes. The cells pictured are just a few examples of the many different shapes that human cells may have. Each type of cell in the figure has characteristics that help it do its job. T he job of the nerve cell, for example, is to carry messages to other cells. The nerve cell has many long extensions that reach out in all directions, allowing it to pass messages to many other cells at once. Do you see the tail of each tiny cell? Its tail helps a sperm cell "swim" through fluids in the female reproductive tract in order to reach an egg cell. The white blood cell has the job of destroying bacteria and other . It is a large cell that can engulf foreign invaders.
::具有不同功能的单元格往往有不同的形状。 所绘制的单元格只是人类细胞可能具有的多种不同形状的几个例子。 图表中的每类细胞都有有助于它开展工作的特性。 例如, 神经细胞的工作是将信息传送到其他细胞。 神经细胞有许多长长长的伸展, 能够从各个方向向外传递信息。 您看到每个小细胞的尾巴吗? 它的尾巴通过雌性生殖器官的液体帮助精子细胞“ 跳动” 进入卵细胞。 白血细胞的工作是摧毁细菌和其他细胞。 它是一个大细胞, 能够吞噬外来入侵者 。Human nerve cell
::人类神经神经细胞Human sperm cell
::人类精子细胞Human white blood cell engulfing and destroying bacteria (orange)
::吞并和摧毁细菌(橙色)的人类白血细胞Cells With and Without a Nucleus
::有和没有核心细胞的细胞The is a basic present in many — but not all — living cells. The nucleus of a cell is a structure in the cytoplasm that is surrounded by a membrane (the nuclear membrane) and contains . Based on whether or not they have a nucleus, there are two basic types of cells: prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic cells .
::这是许多(但不是全部)活细胞的基本存在,细胞的核心是细胞顶板结构,环绕在膜(核膜)和内含。根据它们是否有核核,细胞有两种基本类型:手表细胞和表情细胞。Prokaryotic Cells
::蛋白细胞Prokaryotic cells are cells without a nucleus. The DNA in prokaryotic cells is in the cytoplasm, rather than enclosed within a nuclear membrane. Prokaryotic cells are found in single-celled organisms, such as the bacterium represented by the model . Organisms with prokaryotic cells are called . They were the first type of organisms to evolve, and they are still the most common organisms today.
::蛋白质细胞是没有核的细胞。在蛋白质细胞中的DNA在细胞上,而不是被封闭在核膜内。在单细胞生物中,比如模型所代表的细菌中,可以找到蛋白质细胞。有蛋白质细胞的有机体被称为。它们是第一种进化的有机体,它们仍然是当今最常见的有机体。
Model of a prokaryotic cell: bacterium
::蛋白细胞模型:细菌Eukaryotic Cells
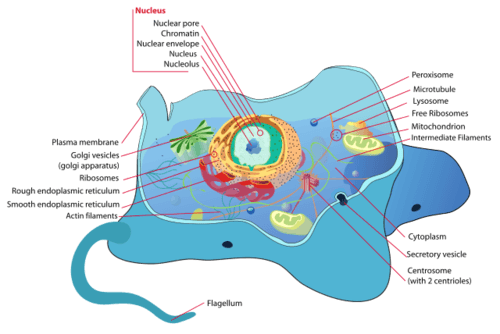
::Eukaryod 细胞Eukaryotic cells are cells that contain a nucleus. A typical eukaryotic cell is represented by the model . Eukaryotic cells are usually larger than prokaryotic cells. They are found in some single-celled and all . Organisms with eukaryotic cells are called eukaryotes , and they range from to humans .
::Eukaryatic细胞是含有核的细胞。典型的eukaryatic细胞由模型代表 。 Eukaryatic细胞通常大于 prokary 细胞。 它们在某些单细胞和所有细胞中找到。 带有eukaryotes 的eukaryotes 生物体被称为 eukaryotes, 它们从人类到人类都有。Besides a nucleus, eukaryotic cells also contain other . An organelle is a structure within the cytoplasm that performs a specific job in the cell. Organelles called , for example, provide energy to the cell, and organelles called vacuoles store substances in the cell. Organelles allow eukaryotic cells to carry out more functions than prokaryotic cells can.
::除核外, eukaryaty cells 也包含其他 。 有机体是在细胞内进行特定工作的细胞托盘结构。 例如, 有机体为细胞提供能量, 而有机体则在细胞内储存真空物质。 Organelles 允许 eukary cells 发挥比 prokary cells 所能发挥的更多功能。Interestingly, scientists think that mitochondria were once free-living prokaryot es that infected (or were engulfed by) larger cells. The two organisms developed a symbiotic relationship that was beneficial to both of them , resulting in the smaller prokaryote becoming an organelle within the larger cell. This is called endosymbiotic theory , and it is supported by a lot of evidence , including the fact that mitochondria have their own DNA separate from the DNA in the nucleus of the eukaryotic cell. Endosymbiotic theory will be described in more detail in later concepts, and it's also discussed in the video below.
::有趣的是,科学家们认为米托乔因德里亚曾经是自由生存的先兆,曾感染(或被大细胞吞噬 ) 。 这两个生物体形成了一种共生关系,对两者都有利,导致较小的先质在更大的细胞中成为有机体。这被称为内生理论,并得到了许多证据的支持,包括米托乔因德里亚在自生细胞的核心中拥有与DNA分离的DNA。 内生生物理论将在以后的概念中更详细地描述,并在下面的视频中加以讨论。Eukaryotic Cell. Compare and contrast the eukaryotic cell shown here with the prokaryotic cell. What similarities and differences do you see?
::Eukaryatic 单元格。 比较和对比此处显示的 eukaryatic 单元格与 prokarycoy 单元格。 您看到什么相似之处和不同之处 ?Summary
::摘要-
Cells must be very small so they have a large enough surface area-to-volume ratio to maintain normal cell processes.
::电池必须非常小,以便有足够的表面积与体积比例维持正常的细胞过程。 -
Cells with different functions often have different shapes.
::功能不同的单元格往往有不同的形状。 -
Prokaryotic cells do not have a nucleus. Eukaryotic cells
do
have a nucleus, along with other organelles.
::蛋白质细胞没有核。 蛋白质细胞与其他器官细胞一样,也有一个核。
Review
::回顾1. Explain why most cells are very small.
::1. 解释为什么大多数细胞非常小。2. Discuss variations in the form and function of cells.
::2. 讨论细胞形式和功能的变化。3. Compare and contrast prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.
::3. 比较和对比质子细胞和表情细胞。4. True or False: Prokaryotic cells do not have mitochondria.
::4. 真实或假的:prokaryaty细胞没有米托孔德里亚。5. True or False: Prokaryotic cells do not have DNA.
::5. 真实或假:蛋白质细胞没有DNA。6. True or False: All single-celled organisms are prokaryotes.
::6. 真实或假生物:所有单细胞生物都是prokaryotes。7. Which was the first type of organisms to evolve – eukaryotes or prokaryotes? Based on their structures, does this make sense to you? Explain your answer.
::7. 哪种生物是第一种进化的生物—— eukaryotes或prokaryotes?根据它们的结构,这对你们有意义吗?解释一下你的答案。8. Do human cells have organelles? Explain your answer.
::8. 人体细胞是否有风琴?9. Which are usually larger – prokaryotic or eukaryotic cells? What do you think this means for their relative ability to take in needed substances and release wastes? Discuss your answer.
::9. 哪些通常是较大的—— 蛋白质细胞或尿道细胞? 你认为这对其吸收所需物质和释放废物的相对能力意味着什么? 讨论你的答案。10. DNA in eukaryotes is enclosed within the _______ ________.
::10. eukaryotes中的脱氧核糖核酸DNA附在内。11. Name three different types of cells in humans.
::11. 列出人类的三种不同类型的细胞。12. Which organelle provides energy in eukaryotic cells?
::12. 哪一种风琴能为表情细胞提供能量?13. What is a function of a vacuole in a cell?
::13. 牢房中空置的功能是什么?Explore More
::探索更多The video below explains why scientists believe endosymbiosis is the basis for complex cells.
::下面的录像解释了为什么科学家认为内生生物是复杂细胞的基础。There are many different types of cells, with different structures and functions. In this video, a specific type of immune cell (the natural killer cell) is discussed.
::各种细胞种类繁多,结构和功能各有不同,在这一视频中,讨论了一种特定类型的免疫细胞(自然杀手细胞)。 -
Cells must be very small so they have a large enough surface area-to-volume ratio to maintain normal cell processes.