17.2 消化系统介绍
章节大纲
-
We All Scream for Ice Cream
::我们都为冰淇淋而尖叫If you’re an ice cream lover, then just the sight of this yummy ice cream cone may make your mouth . The “water” in your mouth is actually saliva , a fluid released by glands that are part of the . Saliva contains digestive , among other substances important for digestion . When your mouth waters at the sight of a tasty treat, it’s a sign that your digestive system is preparing to digest food .
::如果你是一个冰淇淋情人,那么只要看到这个美味的冰淇淋甜筒就可以让你的嘴。 你口中的“水”其实是唾液,一种流体,一种来自作为冰激凌一部分的腺体释放出来的液体。 唾液中含有消化剂和其他重要的消化物质。 当你的口水看到美味的甜食时,它是一种迹象,表明你的消化系统正在准备消化食物。What Is the Digestive System?
::什么是消化系统?The digestive system consists of organs that break down food, absorb its nutrients , and expel any remaining waste. Organs of the digestive system are shown in the figure. Most of these organs make up the gastrointestinal (GI) tract, through which food actually passes. The rest of the organs of the digestive system are called accessory organs . These organs secrete enzymes and other substances into the GI tract, but food does not actually pass through them.
::消化系统由分解食物的器官组成,吸收其营养素,并排出任何残留的废物。消化系统的器官见于图中。这些器官大多由胃肠道组成,而食物实际上通过胃肠道。消化系统的其他器官称为辅助器官。这些器官秘密酶和其他物质进入GI道,但食物实际上并没有通过它们。The components of the digestive system include the gastrointestinal tract and accessory organs of digestion. Find the organs of the digestive system in this diagram as you read about them below.
::消化系统的组成部分包括胃肠道和消化的辅助器官。请在此图中查找消化系统的器官,请在下图中读到这些器官。Functions of the Digestive System
::消化系统功能The digestive system has three main functions relating to food: digestion of food, absorption of nutrients from food, and elimination of solid food waste. Digestion is the process of breaking down food into components the body can absorb. It consists of two types of processes: mechanical digestion and chemical digestion . Mechanical digestion is the physical breakdown of chunks of food into smaller pieces, and it takes place mainly in the mouth and stomach . Chemical digestion is the chemical breakdown of large, complex food molecules into smaller, simpler nutrient molecules that can be absorbed by body fluids ( or lymph). This type of digestion begins in the mouth and continues in the stomach, but occurs mainly in the .
::消化系统有与食物有关的三个主要功能:食物消化、食物养分吸收以及消除固体食品废物;消化是将食物分解成身体可以吸收的成分的过程,由两种过程组成:机械消化和化学消化;机械消化是将食物块块分解成小块的物理分解,主要在口中和胃中进行;化学消化是将大型、复杂的食物分子化学分解成较小的、较简单的营养分子,可由体液(或淋巴)吸收;这种消化从口中开始,在胃中继续,但主要是在胃中。After food is digested, the resulting nutrients are absorbed. Absorption is the process in which substances pass into the bloodstream or lymph system to circulate throughout the body. Absorption of nutrients occurs mainly in the small intestine. Any remaining matter from food that is not digested and absorbed passes out of the body through the anus in the process of elimination.
::吸收是物质进入血液或淋巴系统以在整个身体中循环的过程,吸收养分主要发生在小肠中,食物中任何未消化的残留物质通过肛门从体内吸收出来,在消除过程中通过肛门从体内吸收。Gastrointestinal Tract
::肠胃手术The gastrointestinal (GI) tract is basically a long, continuous tube that connects the mouth with the anus. If it were fully extended, it would be about 9 meters (30 feet) long in adults. It includes the mouth, pharynx , esophagus , stomach, and small and large intestines. Food enters the mouth, and then passes through the other organs of the GI tract, where it is digested and/or absorbed. Finally, any remaining food waste leaves the body through the anus at the end of the . It takes up to 50 hours for food or food waste to make the complete trip through the GI tract.
::胃肠道基本上是连接口腔和肛门的长、连续的管,如果完全伸长,成人的胃肠道大约为9米(30英尺),包括口腔、口腔、口腔、食道、胃和大小肠道;食物进入口腔,然后通过口腔的其他器官,在那里消化和(或)吸收;最后,任何剩余的食物废物都会在肛门最后通过肛门离开身体。食物或食物废物需要50小时才能完全通过口腔。Tissues of the GI Tract
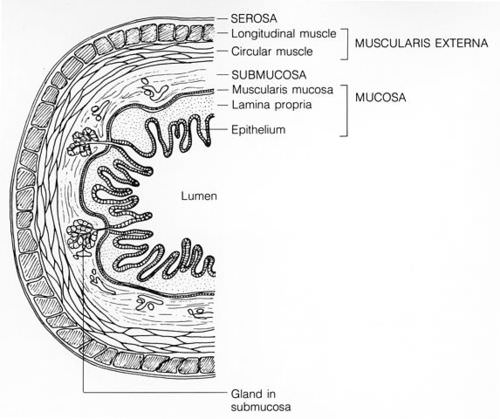
::GITract 组织组织The walls of the organs of the GI tract consist of four different tissue layers, which are illustrated in the figure : mucosa, submucosa, muscularis externa, and serosa.
::GI道器官的墙壁由四个不同的组织层组成,如图所示:肌肉、亚肌肉、肌肉外向和血清。-
The
mucosa
is the innermost layer surrounding the lumen (open space within the organs of the GI tract). This layer consists mainly of epithelium with the capacity to secrete and absorb substances.
T
he epithelium can secret digestive enzymes and
mucus
, and it can absorb nutrients and water.
::粘合物是月球周围最深层的一层(GI草原器官内部的开阔空间),该层主要由具有隐秘和吸收能力的附合物组成,该层可以隐蔽消化酶和粘液,可以吸收养分和水。 -
The
submucosa
layer consists of
connective tissue
that contains blood and
lymph vessels
, as well as
nerves
. The vessels are needed to absorb and carry away nutrients after food is digested, and nerves help control the
of the GI tract organs.
::亚乳胶层由含有血液和淋巴容器以及神经的连接组织组成,在食物消化后,这些容器需要吸收和搬运养分,神经帮助控制GI道器官。 -
The
muscularis externa
layer contains two types of
smooth muscle
: longitudinal muscle and circular muscle. Longitudinal muscle runs the length of the GI tract organs, and circular muscle encircles the organs. Both types of muscles contract to keep food moving through the tract by the process of
peristalsis
, which is described below.
::肌肉外表层包含两种光滑的肌肉:纵向肌肉和圆形肌肉。 纵向肌肉长于GI道器官的长度,循环肌肉环绕器官。 这两种肌肉都与食物通过持久性过程在长片中流动有关,如下文所述。 -
The
serosa
layer is the outermost layer of the walls of GI tract organs. This is a thin layer that consists of connective tissue and separates the organs from surrounding cavities and tissues.
::血清层是GI道器官壁的最外层,是一个薄层,由连接组织组成,将器官与周围的洞穴和组织分开。
This cross-sectional diagram of the wall of a typical GI tract organ shows the layers that comprise it.
::这个横截面图显示一个典型的GI道器官的墙壁,显示其中的层层。Peristalisis in the GI Tract
::GITract 的持久性The muscles in the walls of GI tract organs enable peristalsis, which is illustrated in the figure . Peristalsis is a continuous sequence of involuntary and relaxation that moves rapidly along an organ like a wave, similar to the way a wave moves through a spring toy. Peristalsis in organs of the GI tract propels food through the tract.
::GI道器官墙壁的肌肉使常态化,如图所示。常态性是非自愿和放松的连续序列,它沿着象波浪那样的器官迅速移动,类似于波浪穿过弹簧玩具的方式。GI道器官的常态化将食物推进到长道。Peristalsis pushes food through the GI tract.
::持久性把食物推穿GI道Immune Function of the GI Tract
::GI Trackt 的光功能The GI tract plays an important role in protecting the body from . The surface area of the GI tract is estimated to be about 32 square meters, or about half the area of a badminton court. This is more than three times the area of the exposed skin of the body, and it provides a lot of area for pathogens to invade the tissues of the body. The innermost mucosal layer of the walls of the GI tract provides a barrier to pathogens so they are less likely to enter the blood or lymph circulations. T he mucus produced by the mucosal layer, for example, contains antibodies that mark many pathogenic microorganisms for destruction. Enzymes in some of the secretions of the GI tract also destroy pathogens. In addition, stomach acids have a very low pH that is fatal for many microorganisms that enter the stomach.
::GIPr在保护身体不受干扰方面起着重要作用。GIPr的表面面积估计约为32平方米,大约是羽毛球场面积的一半。这是人体皮肤暴露面积的三倍以上,它为病原体侵入人体组织提供了许多区域。GIpr的墙壁最深层的肌肉层为病原体设置了屏障,因此它们更不可能进入血液或淋巴循环。例如,肌肉层产生的粘结含有许多致病微生物需要销毁的抗体。GIrpr的分泌中含有的酶也摧毁了病原体。此外,胃酸的pH值非常低,对进入腹部的许多微生物来说是致命的。Divisions of the GI Tract
::GI轨道的分区The GI tract is often divided into an upper GI tract and a lower GI tract. For medical purposes, the upper GI tract is typically considered to include all the organs from the mouth through the first part of the small intestine, called the duodenum . For our instructional purposes, it makes more sense to include the mouth through the stomach in the upper GI tract, and all of the small intestine — as well as the large intestine — in the lower GI tract.
::GI道往往分为上GI道和下GI道,为医疗目的,上GI道通常被视为包括口口通过小肠道第一部分的所有器官,称为二二肠道,为了我们的指示目的,将口通过胃通过上GI道,以及所有小肠道(以及大肠道)都包含在下GI道。Upper GI Tract
::GI公司上轨The mouth is the first digestive organ that food enters. The sight, smell , or taste of food stimulates the release of digestive enzymes and other secretions by salivary glands inside the mouth. The major salivary gland enzyme is amylase . It begins the chemical digestion of by breaking down starches into sugar. The mouth also begins the mechanical digestion of food. When you chew, your teeth break, crush, and grind food into increasingly smaller pieces. Your tongue helps mix the food with saliva and also helps you swallow.
::口是食物进入的第一种消化器官。 食物的视觉、嗅觉或味道刺激了消化酶的释放,以及口腔中口腔中口腔中口腔中其他分泌物的释放。 主要的唾液甘蓝酶是氨基酶。 它开始化学消化,把淀粉碎成糖。 口也开始食物的机械消化。 当你嚼, 牙齿破碎, 粉碎, 将食物磨碎成越来越小的碎片时。 你的舌头帮助食物与唾液混合, 也帮助你吞咽。A lump of swallowed food is called a bolus. The bolus passes from the mouth into the pharynx, and from the pharynx into the esophagus. The esophagus is a long, narrow tube that carries food from the pharynx to the stomach. It has no other digestive functions. Peristalsis starts at the top of the esophagus when food is swallowed and continues down the esophagus in a single wave, pushing the bolus of food ahead of it.
::被吞食的食物被称作肉丸。肉丸从嘴口传入法林克斯,从法林克斯传入食道。食道是一条长而狭窄的管子,将食物从法林克斯传至胃部。它没有其他消化功能。食道从食道顶部开始,食物被吞入,继续以一波冲下食道,将食物的肉泡推到胃前。From the esophagus, food passes into the stomach, where both mechanical and chemical digestion continue. The muscular walls of the stomach churn and mix the food, thus completing mechanical digestion, as well as mixing the food with digestive fluids secreted by the stomach. One of these fluids is hydrochloric acid. In addition to killing pathogens in food, it gives the stomach the low pH needed by digestive enzymes that work in the stomach. One of these enzymes is pepsin , which chemically digests . The stomach stores the partially digested food until the small intestine is ready to receive it. Food that enters the small intestine from the stomach is in the form of a thick slurry (semi-liquid) called chyme.
::从食道到胃部,食物进入胃部,有机械和化学的消化持续。胃部的肌肉壁,将食物混合在一起,从而完成机械消化,以及将食物与胃中隐藏的消化液混合在一起。其中一种液体是盐酸。除了在食物中杀死病原体外,它还使胃部的消化酶所需的低pH值为胃部的消化酶所需的低pH值。其中一种酶是pepsin,这种酶是化学消化剂。胃部储存部分消化的食物,直到小肠子准备好接收它。从胃进入小肠的食品是一种叫作chyme的粗螺旋(半液体)形式。Lower GI Tract
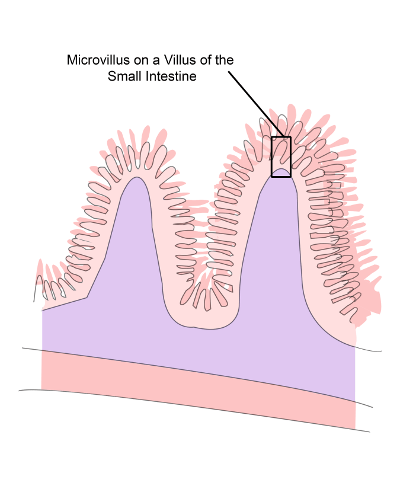
::下GI 轨迹The small intestine is a narrow, but very long tubular organ. It may be almost 7 meters (23 feet) long in adults. It is the site of most chemical digestion and virtually all absorption of nutrients. Many digestive enzymes are active in the small intestine, some of which are produced by the small intestine itself, and some of which are produced by the pancreas , an accessory organ of the digestive system. Much of the inner lining of the small intestine is covered by tiny finger-like projections called villi , each of which is covered by even tinier projections called microvilli. These projections, shown in the drawing , greatly increase the surface area through which nutrients can be absorbed from the small intestine.
::小肠道是一个狭窄但非常长的管状器官,在成人体内可能长近7米(23英尺),是大部分化学消化和吸收养分的场所。许多消化酶都活跃在小肠道中,其中一些由小肠道本身产生,有些由消化系统的一个辅助器官,即胰腺产生。小肠的内衬大部分都由小手指般的微粒投影覆盖,每个微小的投影都覆盖在微小的投影中。图中显示,这些投影大大增加了小肠道吸收养分的表层面积。Each tiny projection (villus) of the lining of the small intestine is also covered with tiny projections (microvilli).
::小肠内衬的每个微小投影(villus)也包含微小投影(Microvilli)。From the small intestine, any remaining nutrients and food waste pass into the large intestine. The large intestine is another tubular organ, but it is wider and shorter than the small intestine. It connects the small intestine and the anus. Waste that enters the large intestine is in a liquid state. As it passes through the large intestine, excess water is absorbed from it. The remaining solid waste — called feces — is eventually eliminated from the body through the anus.
::大型肠道是另一个管状器官,但比小肠道更宽、更短,它连接小肠道和肛门,进入大肠道的废物处于液态,随着大肠道的穿透,多余的水被吸收,剩下的固体废料——称为粪便——最终通过肛门从身体中清除。Accessory Organs of the Digestive System
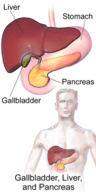
::消化系统附属器官Accessory organs of the digestive system are not part of the GI tract, so they are not sites where digestion or absorption take place. Instead, these organs secrete or store substances needed for the chemical digestion of food. The accessory organs include the liver , gallbladder , and pancreas. They are shown in the figure and described in the text that follows.
::消化系统器官不是GI道的一部分,因此它们不是消化或吸收的场所,而是这些器官的秘质或储存食物化学消化所需的物质,辅助器官包括肝脏、胆囊和胰腺,在下图中列出,并在以下文字中说明。This diagram shows the locations of the accessory organs of digestion: the liver, gallbladder, and pancreas.
::本图显示消化的辅助器官的位置:肝脏、胆囊和胰腺。-
The
liver
is an organ
with
multitude of functions. Its main digestive function is producing and secreting a fluid called
bile
, which reaches the small intestine through a duct. Bile breaks down large globules of
into smaller ones that are easier for enzymes to chemically digest. Bile is also needed to reduce the acidity of food entering the small intestine from the highly acidic stomach, because enzymes in the small intestine require a less acidic environment in order to work.
::肝脏是具有多种功能的器官,其主要消化功能是生产和分解一种液态,叫做胆,通过一条管子进入小肠道,而大球体分解成小球体,较容易酶消化化学。 还需要胆量来减少从高酸胃进入小肠道的食物的酸性,因为小肠胃的酶需要较少的酸环境才能工作。 -
The
gallbladder
is a small sac below the liver that stores some of the bile from the liver. The gallbladder also concentrates the bile by removing some of the water from it. It then secretes the concentrated bile into the small intestine as needed for fat digestion following a meal.
::胆囊是肝脏下面的一个小囊,它从肝脏中储存出一些胆囊。胆囊也通过去除部分水来浓缩胆囊。然后,它将浓缩的胆囊分解到小肠中,作为一顿饭后脂肪消化所需要的。 -
The
pancreas
secretes many digestive enzymes, and releases them into the small intestine for the chemical digestion of carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids. The pancreas also helps lessen the acidity of the small intestine by secreting bicarbonate, a basic substance that neutralizes acid.
::胰腺分泌了许多消化酶,并将它们释放到小肠中,用于碳水化合物、蛋白质和脂类的化学消化。 胰腺还有助于通过分离碳酸(一种能中和酸的基本物质)来降低小肠酸性。
Summary
::摘要-
The digestive system consists of organs that break down food, absorb its nutrients, and expel any remaining food waste.
::消化系统由分解食物、吸收养分和排出任何剩余食物废弃物的器官组成。 -
Digestion is the process of breaking down food into components that the body can absorb. It includes mechanical digestion and chemical digestion. Absorption is the process of taking up nutrients from food by body fluids for circulation to the rest of the body. Elimination is the process of excreting any remaining food waste after digestion and absorption are finished
.
::消化法是将食物分解成身体可以吸收的成分的过程,其中包括机械消化和化学消化;吸收法是将食物中的养分通过体液吸收到身体其余部分的过程;消除法是在消化和吸收完成后排出任何剩余的食物废物的过程。 -
Most digestive organs form a long, continuous tube called the gastrointestinal (GI) tract. It starts at the mouth, which is followed by the pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, and large intestine. The upper GI tract consists of the mouth through the stomach, while the lower GI tract consists of the small and large intestines.
::大部分消化器官形成一个称为胃肠道的长长、连续管,从嘴开始,接着是口腔、食道、胃、小肠和大肠。 上胃由口组成,下胃由大肠组成。 下胃由小肠组成。 -
Digestion and/or absorption take place in most of the organs of the GI tract. Organs of the GI tract have walls that consist of several tissue layers that enable them to carry out these functions.
T
he inner mucosa has cells that secrete digestive enzymes and other digestive substances, as well as cells that absorb nutrients. The muscle layer of the organs enables them to contract and relax in waves of peristalsis to move food through the GI tract.
::GI的器官有墙壁,由若干组织层组成,使其能够发挥这些功能; 内粘膜有细胞,秘密消化酶和其他消化物质,以及吸收养分的细胞; 器官的肌肉层,使他们能够在持久性的波浪中收缩和放松,将食物通过GI的干道。 -
Three digestive organs — the liver, gallbladder, and pancreas — are accessory organs of digestion. They secrete substances needed for chemical digestion into the small intestine.
::三种消化器官——肝脏、胆囊和胰腺——是消化的辅助器官,它们将化学消化所需的物质分泌到小肠中。
Review
::回顾1. What is the digestive system?
::1. 什么是消化系统?2. What are the three main functions of the digestive system? Define each function.
::2. 消化系统的三个主要功能是什么?界定每个功能。3. Describe the GI tract.
::3. 描述GI的传单。4. Distinguish between the upper and lower GI tracts.
::4. 区分GI上部和下部。5. Relate the tissues in the walls of GI tract organs to the functions the organs perform.
::5. 将GI道器官墙上的组织与器官的功能联系起来。6. Identify accessory organs of digestion, as well as their general function in digestion.
::6. 查明消化的附属器官及其消化的一般功能。7. Identify the points in the GI tract where food becomes a bolus, chyme, and feces, respectively.
::7. 查明GI草原中食物分别变成肉、肉和粪的点。8. Does food pass through the pancreas? Why or why not?
::8. 食物是否通过胰腺?为什么或为什么没有?9. True or False: Absorption mainly occurs in the stomach.
::9. 真实或虚假:吸收主要发生在胃部。10. True or False: Some chemical digestion occurs in the mouth.
::10. 真实或假:口中发生某种化学消化。11. Most chemical digestion occurs in the _____________ .
::11. 大多数化学消化过程发生在______________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________a. gall bladder
::a. 胆囊b. stomach
::b. 胃部c. small intestine
::c. 小肠d. large intestine
::d. 大肠12. Describe one way in which proteins and carbohydrates are at least partially chemically digested in the digestive system.
::12. 说明蛋白质和碳水化合物在消化系统中至少部分被化学消化的一种方式。13. If the villi in your small intestine were damaged and could not function normally, how might it affect your body ? Explain your reasoning.
::13. 如果小肠中的葡萄酒受损,不能正常运转,会如何影响你的身体?解释你的推理。14. The esophagus is considered...
::14. 食道被认为是...a. an accessory organ of the digestive system
::a. 消化系统的一个辅助器官b. part of the upper GI tract
::b. 上GI大块面积的一部分c. part of the lower GI tract
::c. 下GI大块的一部分d. the longitudinal muscle
::d. 纵向肌肉Explore More
::探索更多Check out this 3D animation video to see peristalsis in the l arge i ntestine:
::看看这个三维动画视频,Why do we feel hungry? Check out this video to learn more:
::我们为什么感到饥饿? -
The
mucosa
is the innermost layer surrounding the lumen (open space within the organs of the GI tract). This layer consists mainly of epithelium with the capacity to secrete and absorb substances.
T
he epithelium can secret digestive enzymes and
mucus
, and it can absorb nutrients and water.