15.3 库伦姆法律
Section outline
-
Electric cars are becoming more popular. One large advantage for electric cars is the low cost of operation, which may become an ever bigger advantage as gas prices climb. costs for electric cars average about one-third of the cost for gasoline engine cars, but they can only travel about 200 miles per charge at this point. These cars run using the science of electrical charges and forces.
::电动汽车越来越受欢迎。 电动汽车的一大优势是操作成本低,随着煤气价格的攀升,这可能会成为更大的优势。 电动汽车的成本平均约为汽油发动机汽车成本的三分之一左右,但目前它们只能每收费200英里。 这些汽车使用电费和电力科学运行。Coulomb’s Law
::库伦姆法The questions regarding the relationship between the electrical force, the size of the charge, and the separation between the charges were solved by Charles Coulomb in 1785. He determined that electrical force between two charges is directly related to the size of the charges and inversely proportional to the between the charges. This is known as Coulomb’s law .
::Charles Coulomb于1785年解决了电力、电量大小和电量分离之间的关系问题。 他确定,两个电量之间的电力与电量有直接关系,与电量的大小成反比。 这被称为Coulomb的法律。
::Fe=Kq1q2d2In this equation, q 1 and q 2 are the two charges, d is the distance between the two charges, and K is a constant of proportionality. F e is the electric force , which occurs as a result of interactions between two charged particles. For the purpose of calculating electric forces, we assume all charge is a point charge , in which the entire charge of the particle is located in a massless point.
::在这个等式中, q1 和 q2 是两个电荷的距离, d 是两个电荷之间的距离, K 是相称性的常数 。 Fe 是电力, 这是两个电荷粒子相互作用的结果 。 为了计算电力, 我们假设所有电荷都是点电荷, 粒子的全部电荷都位于一个无质量点 。The SI unit of charge is the coulomb, C , which is the charge of electrons. The charge on a single electron is . The charge on a single electron is known as the elementary charge . The charge on a proton is the same magnitude but opposite in sign. When the charges are measured in coulombs, the distance in meters, and the force in Newtons, the constant K is .
::单电子电荷为1.60×10-19 C。单电子电荷为1.60×10-19 C。单电子的电荷称为基本电荷。质子的电荷与质子的电量相同,但信号正好相反。当电荷用脉冲、米的距离和牛顿的威力测量时,恒定K是9.0×109 Nm2/C2。The electrical force, like all forces, is a vector quantity. If the two charges being considered are both positive or both negative, the sign of the electrical force is positive and this force is repulsive. If the two charges are opposite in sign, the force will have a negative sign and the force is attractive.
::与所有力量一样,电力是一个矢量。 如果考虑的两个电荷是正或负的,那么电力的信号是正的,这种力量是可憎的。 如果两个电力的信号是相反的,那么电力将有一个负的信号,而力量是吸引人的。Examples
::实例Example 1
::例1Object A has a positive charge of . Object B has a positive charge of . If the distance between A and B is 0.030 m, what is the force on A?
::对象A的正电荷为6.0x10-6C。 对象B的正电荷为3.0x10-6C。 如果A和B之间的距离为0.030米,A的强度是多少?
::Fe=Kq1q2d2=(9.0×109 Nm2/C2)(6.0×10-6 C)(3.0×10-6 C)(0.030 m)2=180 NThe positive sign of the force indicates the force is repulsive. This makes sense, because both objects have a positive charge.
::力量的正征兆表明力量是令人厌恶的。这有道理,因为两个物体都有正面攻击力。Example 2
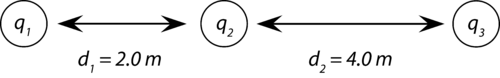
::例2In the sketch below, the charges are , and . Calculate the total force on q 2 .
::在下面的草图中,电荷是 q1=10.0×10-6 C,q2=2.0×10-6 C,和q3=6.0×10-6 C。 计算 q2 的总力。
::Fe=Kq1q2d2=(9.0×109 Nm2/C2)(10.0×10-6 C)(2.0×10-6 C)(2.0m)2=0.045 N(向上Q3)
::Fe=Kq2q3d2=(9.0×109 Nm2/C2)(2.0×10-6 C)(-6.0×10-6 C)(400米)20.007 N(向上Q3)Since the two forces act in the same direction, their absolute values can be added together; the total force on q 2 is 0.052 N towards q 3 .
::由于两支部队朝着同一方向行动,它们的绝对值可以加在一起;在q2上的总兵力为0.052 N对Q3。Launch the Coulomb’s law simulation below. Start with adjusting the Configuration slider to a Hydrogen Atom, the Overlay slider to Electric Field and then Click to Draw the Electric Field. By simply clicking around the simulation screen, you can unveil the electric field vector at every point in space. These vector arrows are used to visualize the magnitude and direction of the electric force a positively charged object would feel if placed at that point. The longer the arrow, the greater the force. Have fun exploring:
::在下面启动库伦姆的法律模拟。 从将配置滑块调整为氢原子开始, 将重叠滑块调整为电场, 然后单击以绘制电场。 只需点击模拟屏幕, 您可以在空间的每个点打开电场矢量 。 这些矢量箭头被用来直观电力的大小和方向。 如果在那个点放置一个正电动对象, 就会感觉到一个正电动物体。 箭头越长, 力就越大。 玩得开心地探索 :Further Reading
::继续阅读Summary
::摘要-
Coulomb determined that electrical force between two charges is directly related to the size of the charges and inversely proportional to the distance between the charges:
::Coulomb公司确定,两项收费之间的电力力量与收费规模直接相关,与收费之间的距离成反比:Fe=Kq1q2d2 -
The SI unit of charge is the coulomb,
C
, which is the charge of
electrons.
::SI的电荷单位是C,C,电荷为6.25×1018电子。 -
The charge on a single electron is
and is known as the elementary charge.
::单一电子的电荷为1.60×10-19C,称为基本电荷。 -
The electrical force is a vector quantity that is positive in repulsion and negative in attraction.
::电力是一种矢量,在回击中呈正数,在吸引中呈负数。
Review
::回顾-
Suppose that two point charges, each with a charge of +1.00 C, are separated by a distance of 1.0 m:
-
Will the charges attract or repel?
::收费会吸引还是击退? -
What is the magnitude of the force between them?
::他们之间的力量有多大? -
If the distance between them is doubled, what does the force become?
::如果它们之间的距离翻了一番,力量会变成什么?
::假设两点收费,每点收费+1.00C, 相距为1.0米:电费会吸引还是击退?它们之间的力有多大?如果两点之间的距离翻了一番,那么电费会变成什么? -
Will the charges attract or repel?
-
What is the electrical force between two balloons, each having 5.00 C of charge, that are 0.300 m apart?
::两个气球之间的电力是多少? 每个气球有5.00C的电荷, 相距0.300米? -
Two spheres are charged with the same charge of -0.0025 C and are separated by a distance of 8.00 m. What is the electrical force between them?
::两个球体的电荷为-0.0025C,距离为8.00米。 它们之间的电力是多少? -
A red foam ball and a blue foam ball are 4.00 m apart. The blue ball has a charge of 0.000337 C and is attracting the red ball with a force of 626 N. What is the charge on the red ball?
::红色泡沫球和蓝色泡沫球相隔4米。 蓝色球充电0.000337C, 吸引红色球626N。 红色球的充电量是多少?
Explore More
::探索更多Use this resource to answer the questions that follow.
::使用此资源回答下面的问题 。-
What happens when like charges are placed near each other?
::当像收费一样 彼此相邻时会怎样呢? -
What happens when opposite charged are placed near each other?
::当相反的电荷相互靠近时会怎么样? -
What happens to the force of attraction if the charges are placed closer together?
::如果电荷更紧密地放在一起 吸引力会怎么样?