14.8 双卷卷卷
章节大纲
-
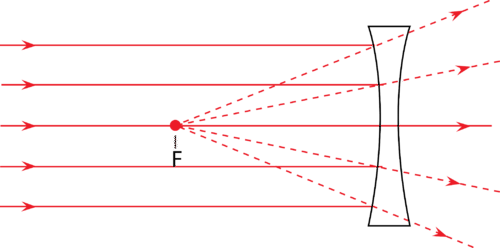
The three light rays traveling into the concave lens shown above travel away from each other. For this reason, concave lens are also called diverging . As a result of this light divergence, concave lenses create only virtual images.
::三个光线穿透上面显示的圆形镜头。 基于这个原因, 圆形镜头也被称为差异。 由于这种光差, 圆形眼镜只产生虚拟图像 。Images in Double Concave Lenses
::双叠加镜头中的图像Every concave lens causes all rays to diverge. Rays that approach the lens parallel to the principal axis refract as if they came from the focal point .
::每一个相形镜片都导致所有射线出现差异。 接近镜头与主轴反折线平行的射线, 仿佛它们来自焦点。As you can see in the figure above, the light rays hit the lens and refract away from each other. Since none of these rays will intersect, a real image cannot exist. Instead, all images created by a double concave lens are virtual images. Like in all ray diagrams, images can be found using two rays.
::正如您在上图中看到的, 光线击中镜头, 并互相折射。 由于这些光线中没有一个会交叉, 真正的图像无法存在。 相反, 所有由双相形镜生成的图像都是虚拟图像。 和所有光图一样, 图像可以用两个光线来找到 。The first ray, shown above, begins from the tip of the image and travels to the lens parallel to the principal axis. Within the lens, this ray is refracted away from the principal axis such that the virtual ray (shown as a dotted line) travels back to the focal point. The second ray also leaves from the tip of the object, and travels straight through the center of the lens. The image will be where these two rays intersect - one real and one virtual. Since one ray is a virtual ray, the image will always be virtual, as well as upright and diminished.
::上面显示的第一道射线从图像的端端端开始,然后到与主轴平行的镜头。 在镜头中, 这个射线与主轴相平行的镜头重新断裂, 使虚拟射线( 以虚线表示) 返回到焦点。 第二个射线也从对象的端端离开, 直穿镜头的中心。 图像将位于这两个射线的交叉点: 一个是真实的, 一个是虚拟的。 由于一个射线是虚拟的射线, 图像将永远是虚拟的, 并且是直直直的, 并降低 。Like for convex lenses, the lens equation and magnification equations can be used to calculate image size and for double concave lenses. When using the lens equation with a concave lens, however, the focal length must be assigned a negative value.
::光镜和放大式方程式可以用来计算图像大小和双凝胶镜。 但是,在使用透镜和凝胶镜的透镜方程式时,对焦距必须设定负值。In the Contact Lens simulation below, the Lens Slider allows you to choose between a converging (convex) contact lens and a diverging (concave) contact lens. Try to view different objects at different distances using these two lenses and determine what is the best shape for the contact lens:
::在下面的“接触镜头”模拟中,“镜头滑动器”允许您在相近(convex)的隐形眼镜和不同的(concave)隐形眼镜之间做出选择。尝试使用这两个隐形眼镜在不同距离查看不同的物体,并确定隐形眼镜的最佳形状:Further Reading
::继续阅读Summary
::摘要-
A concave lens causes all rays to diverge.
::腐烂的透镜导致所有射线出现差异。 -
Concave lenses create only virtual images. After the rays are refracted, they never converge and so there will be no real images.
::凝聚镜片只创造虚拟图像。 在光线重新断裂后, 它们从不聚集, 因此没有真实的图像 。 -
All concave lens images will be upright, virtual, and diminished, and can be found between the
F
and the lens.
::所有隐形透镜图像都将是直立的、虚拟的和缩小的,并且可以在F和镜头之间找到。 -
When using the lens equation with a concave lens, the focal length must be assigned a negative value (
@$\begin{align*}\frac1{d_i}+\frac1{d_o}=\frac{1}{-f}\end{align*}@$
).
::当使用透镜透镜的透镜方程式时, 焦距必须被分配为负值( @ $\ begin{ align}\\ frac1{ d_ ifrac1{ d_ ofrac{ 1\\\\- f{ end{ align} $ ) 。
Review
::回顾-
An object is placed 15.0 cm in front of a concave lens with a focal length of 8.00 cm. Find the image distance. Hint:
@$\begin{align*}\frac1{d_i}+\frac1{d_o}=\frac{1}{-f}\end{align*}@$
::对象被放置在焦距为8:00厘米的圆锥形镜头前15.0厘米。 查找图像距离 。 提示 : @$\ begin{ align} frac1{ d_ i_ i_ frac1{ d_ ofrac{ 1}- f{ end{ align} $ -
An object is placed 3.00 cm in front of a concave lens with a focal length of 5.00 cm. Find the image distance. Hint:
@$\begin{align*}\frac1{d_i}+\frac1{d_o}=\frac{1}{-f}\end{align*}@$
::对象在焦距为 5. 00 厘米的圆锥体前放置 3. 00 厘米。 查找图像距离 。 提示 : @ $\ begin{ align\\ frac1} d_ i\\ frac1{ d_ o\\ frac{ 1}- f{ end{ ALign} $ -
What physical characteristic of a lens distinguishes a converging lens from a diverging lens?
::镜片的物理特征是什么,将相融合的镜片与不同的镜片区别开来? -
An 2.00 cm tall object is placed 20.0 cm in front of a concave lens with a focal length of 5.00 cm. Find the image distance and the height of the image. Hint:
@$\begin{align*}\frac1{d_i}+\frac1{d_o}=\frac{1}{-f}\end{align*}@$
and
@$\begin{align*}\frac{{h}_{i}}{{h}_{o}}= -\frac{{d}_{i}}{{d}_{o}}\end{align*}@$
::2.00厘米高的天体被放置在焦距为5.00厘米的圆锥形镜头前。 查找图像的距离和高度 。 提示 : @ $\ begin{ align_ frac1{ d_ ifrac1{ d_\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\fn\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\
Explore More
::探索更多Use this resource to answer the questions that follow.
::使用此资源回答下面的问题 。-
Concave lenses are _________________ (thicker or thinner) in the middle.
::中间的隐形眼镜(厚或薄)在中间。 -
Concave lenses are also called _________________ lenses.
::隐形透镜也被称为“隐形透镜”。 -
All images from concave lenses are _________________ (real or virtual).
::所有来自凝结镜片的图像均为(真实或虚拟)。