1.11 生命的特征 -- -- 高级
章节大纲
-
What do a bacterium and a whale have in common?
::细菌和鲸鱼有什么共同点?Do they share characteristics with us? All living organisms , from the smallest to the largest whale, share certain characteristics of life. For example, all living things are made of and they must reproduce to make the next generation. Without these characteristics, there is no life .
::它们是否与我们具有共同的特性?所有生物,从最小的鲸鱼到最大的鲸鱼,都具有生命的某些特性。例如,所有生物都是由它们组成的,它们必须繁殖才能创造下一代。没有这些特性,就没有生命。Characteristics of Life
::生命的特征Biology examines the structure, function, growth, origin, evolution, and distribution of living things. It classifies and describes organisms, their functions, how come into existence, and the interactions they have with each other and with the natural environment. Four unifying principles form the foundation of modern biology: , evolution, genetics and .
::生物学研究生物体的结构、功能、生长、起源、进化和分布。生物体分类和描述生物体、它们的功能、它们是如何存在的、它们彼此之间以及与自然环境的相互作用。四项统一原则构成了现代生物学的基础:进化、遗传学和。Most biological sciences are specialized areas of study. Biology includes biochemistry , cell biology, microbiology, immunology, genetics, physiology , zoology , ecology , evolutionary biology, and botany. Biochemistry is the study of the chemicals that make up life. Cell biology is the study of life at the level of the cell. Microbiology is the study of microscopic organisms. Immunology is the study of an organism's resistance to disease. Genetics is the study of how organisms pass traits to their offspring. The study of how the works is called physiology. Zoology is the study of . The study of how organisms interact with their environment and each other is called ecology. Evolutionary biology is the study of how and species change over time. Botany is the study of plants. The four unifying principles are important foundations for each and every field of biology. Applied fields of biology such as medicine and genetic research involve many specialized areas of study.
::生物学包括生物化学、细胞生物学、微生物学、免疫学、遗传学、生理学、动物学、生态学、进化生物学和植物学;生物化学是对构成生命的化学物的研究;细胞生物学是对细胞一级生命的研究;微生物生物学是对微生物体的研究;免疫学是对生物体对疾病的抗药性的研究;遗传学是对生物体如何将特征传给其后代的研究;对生物体如何被称作生理学的研究;动物学是研究;动物学是研究生物体如何与环境相互作用和相互相互作用的研究;进化生物学是研究物种随时间变化的方式和物种的研究;植物研究是植物研究;四项统一原则是生物学每个领域的重要基础;医学和遗传学等应用生物学领域涉及许多专门研究领域。What Is Life?
::什么是生命?Not all scientists agree exactly about what makes up life. Many characteristics describe most living things. However, with most of the characteristics listed below, we can think of one or more examples that would seem to break the rule, with something non-living being classified as living or something living being classified as non-living.
::并非所有科学家都同意生命的构成。许多特征描述着大多数生物。然而,根据下面列出的大多数特征,我们可以想象出一个或几个似乎打破了规则的例子,一些非生物被归类为生活,或者某些生物被归类为非生活。There is not just one distinguishing feature that separates a living thing from a non-living thing. A cat moves but so does a car. A tree grows bigger, but so does a cloud. A cell has structure, but so does a crystal. Biologists define life by listing characteristics that living things share. Something that has all of the characteristics of life is considered to be alive. The duck decoy in the Figure may look like a duck, act like a duck in that it floats about, but it is not alive. The decoy cannot reproduce, respond to its environment, or breathe.
::不仅有将活物与非活物区分开来的独特特征。 猫动起来, 汽车也动起来。 树越大, 云层越大。 细胞有结构, 水晶也一样。 生物学家通过列出生活物共有的特征来定义生命。 具有生命所有特征的东西被认为是活的。 图中的鸭子诱饵可能看起来像鸭子, 看起来像鸭子, 像鸭子一样漂浮着, 但它不是活的。 诱饵不能繁殖, 反应环境, 呼吸。Is it a duck? Both of these objects move across the water’s surface. But, how can you tell which one is alive and which is not? You can tell by seeing which of them have all of the characteristics of life. An individual living creature is called an organism . There are many characteristics that living organisms share. All living organisms :
::个体生物被称为有机体。生物体有许多共同特征。所有生物体:-
respond to their environment
::适应其环境 -
grow and change
::增长和变化 -
reproduce and have offspring
::生儿育子,生儿育子, -
have
complex chemistry
::化学性质复杂 -
maintain homeostasis
::保持全常状态 -
are built of structures called cells
::是由称为单元格的结构构建的 -
pass their traits onto their offspring
::将自己的性格传递给后代,
Responding to the Environment
::应对环境All living organisms respond to their environment. If you step on a rock, it will just lie there, but if you step on a turtle, it may move or even snap at you. Living things know what is going on around them, and respond to changes in the environment. An adaptation refers to the process of becoming adjusted to an environment. Adaptations may include structural, physiological, or behavioral traits that improve an organism's likelihood of survival, and thus, .
::所有活生物体都对环境作出反应。如果你踩在岩石上,它就会躺在那里,但是如果你踩在海龟上,它可能会移动甚至朝你飞动。生活的东西知道它们周围的情况,并对环境的变化作出反应。适应是指适应环境的过程。适应可能包括结构、生理或行为特征,这些特征可以改善生物体的生存可能性,从而,可以改善生物体的生存可能性。Growth and Change
::增长与变化All living organisms have the ability to grow and change. A seed may look like a pebble, but under the right conditions, it will sprout and form a seedling that will grow into a larger plant. The pebble of course will not grow. Even the smallest bacteria must grow. This bacteria will reproduce by dividing into two separate bacteria. If the parent bacterium does not grow, then each subsequent generation will just be smaller than the previous generation. Eventually, the bacteria will be too small to function properly.
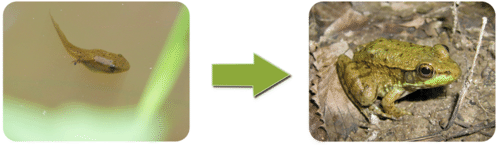
::所有生物都有生长和改变的能力。种子可能看起来像一个卵石,但是在适当的条件下,它会发芽和形成一个苗圃,会长成一个更大的植物。当然,卵石不会生长。即使是最小的细菌也必须生长。这种细菌会通过分裂成两种不同的细菌而繁殖。如果母细菌不生长,那么后代的每代都会比前代小。最终,细菌会太小,无法正常运转。Tadpoles, like those shown here, go through many changes to become adult frogs. Reproduction
::复制复制All living organisms must have the ability to reproduce. Living things make more organisms like themselves. Whether the organism is a rabbit, a tree, or a bacterium, life will create more life. If a species cannot create the next generation, the species will go extinct. Reproduction is the process of making the next generation and may be a sexual or an asexual process. involves two parents and the fusion of gametes , haploid sex cells from each parent. Sexual reproduction produces offspring that are genetically unique and increases within a species. involves only one parent. It occurs without a fusion of gametes and produces offspring that are all genetically identical to the parent.
::所有活生物体必须具有繁殖能力。活生物体使更多的生物象自己一样。无论生物体是兔子、树或细菌,生命都会创造更多的生命。如果物种不能创造下一代,物种就会灭绝。再生是下一代的过程,可能是性或非性过程。它涉及父母双方,以及双胞胎、双胞胎、双胞胎、双胞胎、双胞胎、双胞胎、双胞胎、双胞胎、双胞胎、双胞胎、双胞胎、双胞胎、双胞胎、双胞胎、双胞胎、双胞胎、双胞胎、双胞胎、双胞胎、双胞胎、双胞胎、双胞胎、双胞胎、双胞胎、双胞胎、双胞胎、双胞胎、双胞胎、双胞胎、双胞胎、双胞胎、双胞胎、双胞胎、双胞胎、双胞胎、双胞胎、双胞胎、双胞胎、双胞胎、双胞胎、双胞胎、双胞胎、双胞胎、双胞胎、双胞胎、双胞胎、双胞胎、双胞胎、双胞胎、双胞胎、双胞胎、双胞胎、双胞胎、双胞胎、双胞胎、双胞胎、双胞胎、双胞胎、双胞胎、双胞胎、双胞胎、双胞胎、双胞胎、双胞胎、双胞胎、双胞胎、双胞胎、双胞胎、双胞胎、双胞胎、双胞胎、双胞胎、双胞胎、双胞胎、双胞胎、双胞胎、双胞胎、双胞胎、双胞胎、双胞胎、双胞胎、双胞胎、双胞、双胞胎、双胞胎、双胞、双胞胎、双胞胎、双胞胎、双胞胎、双胞胎、双胞胎、双胞胎、双胞胎、双胞胎、双胞胎、双胞胎、双胞、双胞胎、双胞胎、双胞胎、双胞胎、双胞、双胞胎、双胞胎、双胞胎、双胞胎、双胞胎、双胞胎、双胞、双胞胎、双胞胎、双胞胎Have Complex Chemistry
::拥有复杂的化学All living organisms have a complex chemistry. A flower has a complicated and beautiful structure. So does a crystal. But if you look closely at the crystal, you see no change. The flower, on the other hand, transports through its petals , producing pigment molecules, breaking down sugar for energy , and undergoing a large number of other that are needed for living organisms to stay alive. The sum of all the chemical reactions in a cell is metabolism .
::所有的活生物体都有复杂的化学成分。 花朵有复杂而美丽的结构。 水晶也是一样。 但如果你仔细观察晶体, 你看不到任何变化。 另一方面, 花朵通过花瓣运输, 生产色素分子, 分解糖作为能量, 并经历大量其他生物体生存所需的。 细胞中所有化学反应的总和是新陈代谢。Maintain Homeostasis
::保持原常态A human body has a temperature of 37 degrees Celsius, (about 98.6 degrees Fahrenheit). If you step outside on a cold morning, the temperature might be below freezing. Nevertheless, you do not become an ice cube. You shiver and the movement in your arms and legs allows you to stay warm. Eating food also gives your body the energy it needs to keep warm. Living organisms keep their internal environments within a certain range (they maintain a stable internal condition), despite changes in their external environment. This process is called homeostasis and is an important characteristic of all living organisms.
::人体的温度为37摄氏度(约98.6华氏度)。如果你在寒冷的早晨走出门,温度可能低于冰层。然而,你不会成为冰块。你颤抖,你的胳膊和腿的移动使你保持温暖。吃食物也使你的身体拥有保持温暖所需的能量。活生物体将内部环境保持在一定范围内(它们保持稳定的内部条件),尽管外部环境发生变化。这一过程被称为自足状态,是所有活生物体的一个重要特征。Built of Cells
::建造牢房If you look closely at any organism you can see that it is made of structures called cells . Organisms that are very different such as , , and elephants all look similar at the cellular level. A cell is the basic unit of structure and function of all living organisms. All living organisms are made of one or more cells: a simple bacterium will consist of just one cell, whereas you are made of trillions of cells.
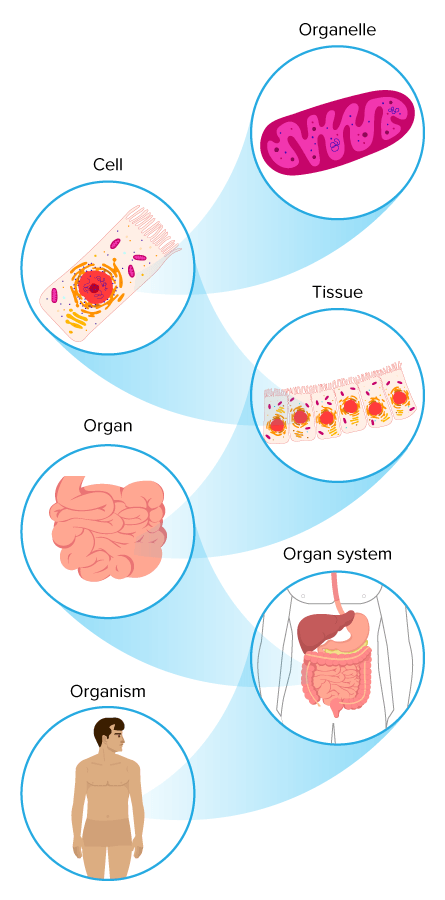
::如果你仔细观察任何有机体,你可以看到它是由叫做细胞的结构构成的。在细胞一级,非常不同的生物体,例如,,和大象,都看起来相似。细胞是所有生物体的结构和功能的基本单位。所有生物体都是由一个或多个细胞构成的:一个简单的细菌将只有一个细胞组成,而你则由数万亿个细胞组成。All living organisms are made of one or more cells. Eg: Frog red blood cells (left); Bacteria (right) Organisms are organized at the microscopic level from atoms up to cells. The matter is structured in an ordered way. Atoms are arranged into molecules, then into macromolecules, which make up , which work together to form cells. Beyond this, cells are organized in higher levels to form entire , as shown in the Figure . Cells together form tissues , which make up organs , which are part of organ systems , which work together to form an entire organism. Of course, beyond this, organisms form populations that make up parts of an . All of Earth's ecosystems together form the diverse environment that is Earth.
::从原子到细胞,生物组织在微显微层次上,从原子到细胞。物质是按顺序排列的。原子被排列成分子,然后被排列成大型分子,这些分子组成,共同组成细胞。除此之外,细胞组织在较高层次上,形成整个细胞,如图所示。细胞形成组织,组成器官,器官是器官系统的一部分,它们共同组成整个有机体。当然,除此之外,有机体构成构成构成构成一个生物体组成部分的种群。地球的所有生态系统共同构成不同的环境,即地球。Organization of living things: Organelles work together to form cells, cells form tissues, which make up organs, which are part of organ systems, which work together to form an entire organism. Summary
::摘要-
The seven characteristics of life include:
-
responsiveness to the environment;
::对环境的反应; -
growth and change;
::增长和变化; -
ability to reproduce;
::复制能力; -
have a metabolism and breathe;
::具有新陈代谢和呼吸; -
maintain homeostasis;
::保持顺势; -
being made of cells; and
::由单元格制成;以及 -
passing traits onto offspring.
::传给后代的传承特征。
::生命的七个特征包括:对环境的反应;成长和变化;繁殖能力;新陈代谢和呼吸;保持顺势;由细胞组成;以及将特性传给后代。 -
responsiveness to the environment;
Review
::回顾-
What are the four unifying principles that form the foundation of modern biology?
::构成现代生物学基础的四项统一原则是什么? -
Identify three of the seven characteristics of living things.
::确定生命的七个特征中的三个。 -
What is adaptation?
::什么是适应? -
Distinguish between metabolism and homeostasis.
::区分新陈代谢和自闭症。 -
What is a cell?
::什么是细胞?
-
respond to their environment