4.27 呼吸系统疾病 -- -- 高级
章节大纲
-
Saltwater Fish vs. Freshwater Fish?
::盐水鱼类对淡水鱼类?, like all cells, have semi-permeable membranes. Eventually, the concentration of "stuff" on either side of them will even out. A fish that lives in salt will have somewhat salty water inside itself. Put it in the freshwater, and the freshwater will, through osmosis, enter the fish, causing its cells to swell, and the fish will die. What will happen to a freshwater fish in the ocean?
::与所有细胞一样, 都有半渗透膜。 最终, 它们两边的“ 食物” 浓度会平息。 生活在盐中的鱼体内会有一些咸水。 把它放入淡水中, 淡水会通过渗透进入鱼体内, 导致鱼细胞膨胀, 鱼会死。 海洋中的淡水鱼会怎样呢?Osmosis
::骨循环Imagine you have a cup that has 100ml water, and you add 15g of table sugar (sucrose, C 12 H 22 O 11 ) to the water. The sugar dissolves and the mixture that is now in the cup is made up of a solute (the sugar), that is dissolved in the solvent (the water). The mixture of a solute in a solvent is called a solution .
::想象一下您有一个有100毫升水的杯子, 并且您在水中添加了15克的餐桌糖( sucrosse, C12H22O11) 。 糖溶液和现在杯中的混合物是由溶剂( 水) 溶剂( 溶剂) 溶剂( 溶剂) 溶剂中的溶液组成。 溶剂中溶液的混合物被称为溶液 。Imagine now that you have a second cup with 100ml of water, and you add 45 grams of sucrose to the water. Just like the first cup, the sugar is the solute, and the water is the solvent. But now you have two mixtures of different solute concentrations. In comparing two solutions of unequal solute concentration, the solution with the higher solute concentration is hypertonic , and the solution with the lower concentration is hypotonic . Solutions of equal solute concentration are isotonic . The first sugar solution is hypotonic to the second solution. The second sugar solution is hypertonic to the first.
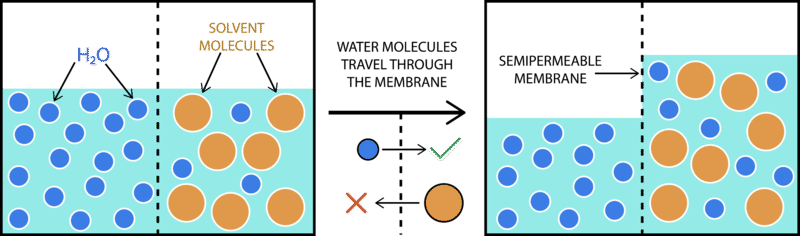
::想象一下,现在你有一个有100毫升水的第二个杯子,你在水中添加了45克苏格鲁斯。就像第一个杯子一样,糖是溶液,水是溶剂。但现在你有两种不同溶液浓度的混合物。比较两种溶液浓度不平等的溶液,溶液浓度高的溶液是高调的,溶液是低浓度的溶液是低调的。溶液是等溶液的溶液是异质的。第一个糖溶液是第二个溶液的低调。第二个糖溶液是第一种高调的溶液。You now add the two solutions to a beaker that has been divided by a selectively permeable membrane. The pores in the membrane are too small for the sugar molecules to pass through, but are big enough for the water molecules to pass through. The hypertonic solution is on one side of the membrane and the hypotonic solution on the other. The hypertonic solution has a lower water concentration than the hypotonic solution, so a concentration gradient of water now exists across the membrane. Water molecules will move from the side of higher water concentration to the side of lower concentration until both solutions are isotonic.
::现在,您将两种解决方法加到用选择性的渗透膜隔开的玻璃瓶中。 薄膜中的孔孔太小, 糖分子无法通过, 但足够大, 水分子可以通过。 超音量溶液在膜的一边, 低音量溶液在另一边。 超音量溶液的水浓度比低温溶液低, 所以现在在膜上方存在水的浓度梯度。 水分子将从水浓度较高的一边移动到浓度较低的一边, 直到两种溶液都分解为止 。What if the two solutions being compared are on either side of a ? A hypertonic solution is one having a larger concentration of a substance on the outside of a cell than is found within the cells themselves. A hypotonic solution contains a lesser concentration of impermeable solutes outside the cell compared to within the cell.
::如果比较的两种溶液位于一个 ? 高音溶液在细胞外部的物质浓度大于在细胞内发现的物质浓度。 与细胞内相比,低音溶液在细胞外部的不可渗透溶液浓度较低。Osmosis is the of water molecules across a selectively permeable membrane from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration. Water moves into and out of cells by osmosis. If a cell is in a hypertonic solution, the solution has a lower water concentration than the cell cytosol does, and water moves out of the cell until both solutions are isotonic. Cells placed in a hypotonic solution will take in water across their membrane until both the external solution and the cytosol are isotonic.
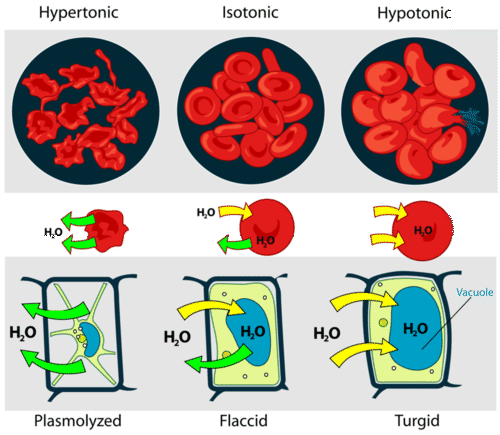
::溶液是指从高浓度地区到低浓度地区的有选择渗透性膜的水分子。水通过渗透进入和流出细胞。如果细胞处于超声解溶液中,溶液的水浓度会低于细胞细胞细胞细胞细胞细胞细胞溶液,水会从细胞细胞中流出,直到两种溶液都具有等离子。放入低温溶液中的细胞会进入细胞膜的水中,直到外部溶液和细胞索都具有等离子。A cell that does not have a rigid cell wall (such as a red cell), will swell and lyse (burst) when placed in a hypotonic solution. Cells with a cell wall will swell when placed in a hypotonic solution, but once the cell is turgid (firm), the tough cell wall prevents any more water from entering the cell. When placed in a hypertonic solution, a cell without a cell wall will lose water to the environment, shrivel, and probably die. In a hypertonic solution, a cell with a cell wall will lose water too. The plasma membrane pulls away from the cell wall as it shrivels, a process called plasmolysis . cells tend to do best in an isotonic environment, plant cells tend to do best in a hypotonic environment. This is demonstrated in Figure .
::没有硬体细胞壁(如红细胞)的细胞在被放入低调溶液中时会膨胀和呼吸。带软体溶液的细胞壁在被放入低压溶液时会膨胀,但一旦细胞变硬(体),硬体细胞壁会阻止更多的水进入细胞。如果被放入高压溶液中,没有细胞壁的细胞会失去环境的水,会窒息,甚至可能死亡。在高压溶液中,带细胞壁的细胞也会失去水。血浆将细胞壁从细胞壁上拉走,因为细胞壁里会颤动,这是一种叫作螺旋体解的过程。细胞在异体环境中往往能做得最好,植物细胞在低温环境中往往会做得最好。这一点在图中可以说明。Unless an animal cell (such as the red blood cell in the top panel) has an adaptation that allows it to alter the osmotic uptake of water, it will lose too much water and shrivel up in a hypertonic environment. If placed in a hypotonic solution, water molecules will enter the cell causing it to swell and burst. Plant cells (bottom panel) become plasmolyzed in a hypertonic solution, but tend to do best in a hypotonic environment. Water is stored in the central vacuole of the plant cell. Osmotic Pressure
::肌肉压力When water moves into a cell by osmosis, osmotic pressure may build up inside the cell. If a cell has a cell wall, the wall helps maintain the cell's water balance . Osmotic pressure is the main cause of support in many plants. When a is in a hypotonic environment, the osmotic entry of water raises the turgor pressure exerted against the cell wall until the pressure prevents more water from coming into the cell. At this point the plant cell is turgid ( Figure ). The effects of osmotic pressures on plant cells are shown in Figure .
::当水由渗透体进入细胞时,表面压力可能会在细胞内积聚。如果细胞有细胞墙,墙会帮助维持细胞的水平衡。在许多植物中,表面压力是主要支撑力的原因。当一个在低温环境中时,水的表面进入会提高细胞墙承受的压强,直到压力阻止更多的水进入细胞。此时,植物细胞是拖动的(图 )。表面压力对植物细胞的影响见图 。These elodea cells are turgid, meaning their vacuoles are storing about as much water as they can. While the vacuole cannot be seen, you can observe it pressing the small, green chloroplasts out to the inner edges of the cell wall. Osmosis can be seen very effectively when potato slices are added to a high concentration of salt solution (hypertonic). The water from inside the potato moves out of the potato cells to the salt solution, which causes the potato cells to lose turgor pressure. The more concentrated the salt solution, the greater the difference in the size and weight of the potato slice after plasmolysis.
::当土豆切片添加高浓度的盐溶液(高压)时,就可以看到非常有效的骨质疾病,土豆内部的水从土豆细胞向盐溶液移动,导致土豆细胞失去高压,盐溶液越集中,土豆切片的大小和重量差异越大,除光解外,土豆切片的大小和重量差异就越大。The action of osmosis can be very harmful to organisms , especially ones without cell walls. For example, if a saltwater fish (whose cells are isotonic with seawater), is placed in fresh water, its cells will take on excess water, lyse, and the fish will die. Another example of a harmful osmotic effect is the use of table salt to kill slugs and snails.
::宇宙体的动作可能对生物非常有害,特别是那些没有细胞壁的生物。 比如,如果咸水鱼类(其细胞与海水的异质细胞)被放在淡水中,其细胞将吸收过多的水,液压,鱼类将死亡。 另一个有害的食腐效应例子是使用食盐杀死鼻涕和蜗牛。Controlling Osmosis
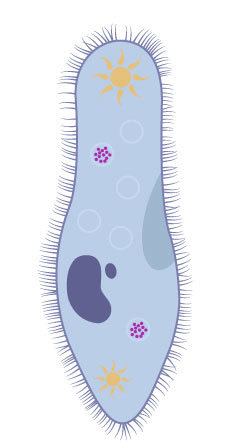
::控制循环Organisms that live in a hypotonic environment such as freshwater, need a way to prevent their cells from taking in too much water by osmosis. A contractile vacuole is a type of vacuole that removes excess water from a cell. Freshwater , such as the paramecia shown in Figure , have a contractile vacuole. The vacuole is surrounded by several canals, which absorb water by osmosis from the cytoplasm . After the canals fill with water, the water is pumped into the vacuole. When the vacuole is full, it pushes the water out of the cell through a pore. Other protists, such as members of the genus Amoeba , have contractile vacuoles that move to the surface of the cell when full and release the water into the environment.
::生活在淡水等低温环境中的生物体需要一种方法来防止细胞被渗透体吸收过多的水。 缩压真空是一种从细胞中清除多余水的真空。 淡水,如图中显示的paramecia,有缩压真空。 真空环绕着几条运河,这些运河吸收了细胞托盘中的渗透体的水。 在运河填满水后,水被抽进真空中。 当真空填满时,它将水从细胞中推出一个孔。 其他原生者,如Amoeba人的成员,在将水全部排入环境中时,会进入细胞表面的缩压真空。The contractile vacuole is the star-like structure within the paramecia. Summary
::摘要-
Osmosis is the diffusion of water molecules across a semipermeable membrane and down a concentration gradient. They can move into or out of a cell, depending on the concentration of the solute.
::骨质疏松是水分子在半透膜和低浓度梯度之间扩散。它们可以移动到或离开细胞,视溶液的浓度而定。
Review
::回顾-
How does osmosis differ from diffusion?
::宇宙与扩散有何不同? -
What would cause the central vacuole of a plant cell to shrink and become smaller than normal? What is the likely solute concentration of the cells' environment which has caused this change?
::是什么导致植物细胞的中央真空缩小并变得小于正常水平? 导致这种变化的细胞环境可能溶液浓度是多少?
-
Osmosis is the diffusion of water molecules across a semipermeable membrane and down a concentration gradient. They can move into or out of a cell, depending on the concentration of the solute.