7.2 Prokaryaty细胞分部 - 高级
Section outline
-
How do bacteria reproduce?
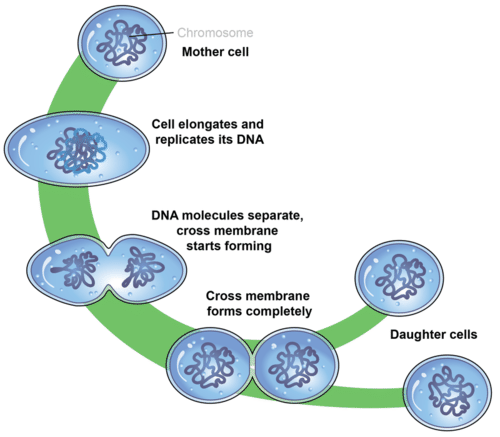
::细菌如何繁殖?Essentially, after replicating their , they just grow and divide. As shown here, they grow larger and then split into two separate but genetically identical .
::基本上,在复制了它们之后,它们只是成长和分裂。正如这里所显示的,它们变大,然后分裂成两个分开但基因相同的部分。Cell Division in Prokaryotes
::Prokaryotes 的单元格分区Prokaryotic organisms reproduce asexually by binary fission , a process that produces identical offspring ( Figure ). In , a single parent produces genetically identical offspring. As do not have a , and have only one circular , they do not need to reproduce by the same mechanism as eukaryotic cells ; does not exist in prokaryotic cells . Prokaryotic is a much simpler process. In prokaryotic cell division, after the single chromosome is copied, the cell grows larger. Eventually the two chromosomes separate and move to opposite ends of the cell. Newly formed then grows into the center of the cell, separating the two chromosomes, and forming two genetically identical daughter cells . Some eukaryotic , such as and , also divide by binary fission.
::蛋白质生物通过二进制裂变性繁殖,这种过程产生相同的后代(图 )。在 中,单亲家庭产生基因相同的后代。由于没有, 并且只有一个循环, 它们不需要用与雌激素细胞相同的机制繁殖; 在蛋白质细胞中并不存在。 Prokary生物体是一个简单得多的过程。 在蛋白质细胞分裂中, 复制单一染色体后, 细胞会变大。 最终, 两个染色体会分离并移动到细胞的对面。 新形成后, 成长到细胞的中心, 将两个染色体分开, 形成两个基因相同的女儿细胞。 某些蛋白质细胞, 例如和二进制裂分。
Binary fission can be described as a series of steps, although it is actually a continuous process. The steps are described below and also illustrated in Figure . They include DNA replication , chromosome segregation, and finally the separation into two daughter cells.
::二进制裂变可以描述为一系列步骤,尽管它实际上是一个持续的过程。下面描述这些步骤,图中也说明了这些步骤。这些步骤包括DNA复制、染色体隔离以及最后将两个女儿细胞分离。-
Step 1: DNA Replication. Just before the cell divides, its DNA is copied in a process called DNA replication. This results in two identical chromosomes instead of just one. This step is necessary so that when the cell divides, each daughter cell will have its own chromosome.
::第一步 : DNA复制。 就在细胞分裂之前, 它的DNA被复制到一个叫做DNA复制的过程。 这导致两个相同的染色体, 而不是一个。 这个步骤是必要的, 这样当细胞分裂的时候, 每个女儿的细胞都会有自己的染色体 。 -
Step 2: Chromosome Segregation. The two chromosomes then attach themselves to different
membrane. Segregation or separation of the chromosomes occurs as they move to opposite ends of the cell during the cell separation process.
::第2步:染色体隔离。两种染色体随后附着在不同的膜上。在细胞隔离过程中,染色体向细胞对面移动时会发生分离或分离。 -
Step 3: Separation. A new cell membrane starts growing into the center of the cell, and the
cytoplasm
splits apart, forming two daughter cells. New
cell wall
must also form around the two cells. This new developing cell walls between the cells is known as a
division
septum
.
As the cell begins to pull apart, the new and the original chromosomes are separated. The two daughter cells that result are genetically identical to each other and to the
parent cell
.
::步骤 3 : 分离。 一个新的细胞膜开始成长到细胞中心, 细胞板块分裂, 形成两个子细胞。 新的细胞墙也必须在两个细胞周围形成。 细胞之间的这个新的发育细胞墙被称为分裂线。 当细胞开始分离时, 新的和原有的染色体被分离。 由此形成的两个子细胞在基因上彼此和母细胞相同 。
In binary fission, the single chromosome is copied and eventually separates into two separate chromosomes, the cell grows larger, and two identical cells form by the formation of new cell membrane (and cell wall) and the division of the cytoplasm. Under ideal conditions, in is extremely efficient, with some bacteria reproducing every 20 minutes. This makes bacteria an extremely effective tool for the molecular biologist. However, bacteria do not usually live in ideal conditions; otherwise, bacteria would grow and divide extremely rapidly, eventually covering the surface of Earth. Bacterial growth is limited by nutrients and , , and by their own wastes.
::在理想条件下,极其高效,有些细菌每20分钟再生一次,这使细菌成为分子生物学家极为有效的工具。 但是,细菌通常不生活在理想条件下;否则细菌会迅速生长和分裂,最终覆盖地球表面。 细菌生长受到养分、养分和废物的限制。Cell division is relatively simple in prokaryotic cells. The two cells divide by binary fission. Green and orange lines indicate old and newly-generated bacterial cell walls, respectively. Eventually the parent cell will pinch apart to form two identical daughter cells. Left, growth at the center of bacterial body, such as in Bacillus subtilis and E. coli. Right, apical growth from the ends of the bacterial body, such as in Corynebacterium diphtheriae. Summary
::摘要-
Binary fission is a form of cell division in prokaryotic organisms that produces identical offspring.
::二进制裂变是一种细胞分裂形式,在蛋白质生物中形成细胞分裂,产生相同的后代。
Review
::回顾-
What is asexual reproduction?
::什么是性生殖? -
What is binary fission?
::二进制裂变是什么? -
Describe the process of prokaryotic cell division.
::描述蛋白质细胞分裂的过程 。 -
What is division septum?
::什么是师腔?
-
Step 1: DNA Replication. Just before the cell divides, its DNA is copied in a process called DNA replication. This results in two identical chromosomes instead of just one. This step is necessary so that when the cell divides, each daughter cell will have its own chromosome.